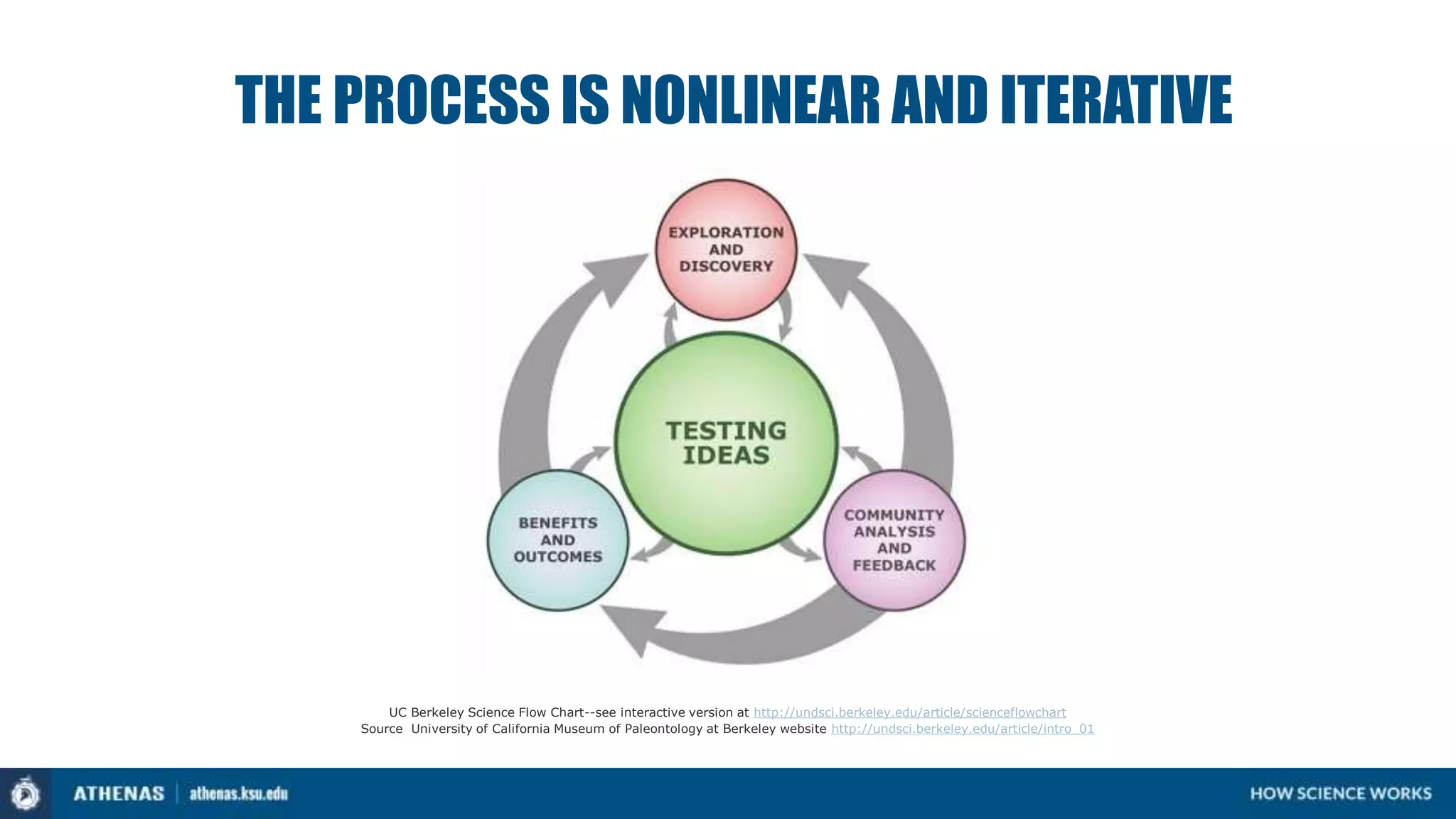
eLife assessment
This valuable study combines prospective cohort, metabolomics, and machine learning to identify a panel of 9 circulating metabolites that improved the ability in risk prediction of progression from prediabetes to diabetes. The findings are solid and the methods, data, and analyses support the claims. However, the interpretation would benefit from a more rigorous description. With revision of these weaknesses, this paper would provide insights into the integration of these metabolites into clinical and public health practice.