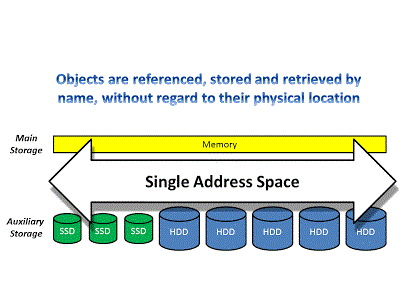
= constructs = Object content addressing =a Web
- significant bandwidth optimization
- untrusted content serving
- permanent links
- ability to make full permanent backups of
- any objects & its references
= comment = for = IndyPLEX
- nodes with all
- outgoing and incoming
- qualified links and target references
Fundamental Unit of coherent local complete structured information pervasive and universal across all computstion and communication and exhange and storage
made permanent via IPFS
permanence ensured by human readable composite naming conventions that the access and qualifying structure of links, forming shapes
slef-organizing, self-revealing, co-evolving conten in contexts exchanged in trust networks with full provenance





.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)