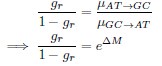Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
In this study, the authors identified and described the transcriptional trajectories leading to CMs during early mouse development, and characterized the epigenetic landscapes that underlie early mesodermal lineage specification.
The authors identified two transcriptomic trajectories from a mesodermal population to cardiomyocytes, the MJH and PSH trajectories. These trajectories are relevant to the current model for the First Heart Field (FHF) and the Second Heart Field (SHF) differentiation. Then, the authors characterized both gene expression and enhancer activity of the MJH and PSH trajectories, using a multiomics analysis. They highlighted the role of Gata4, Hand1, Foxf1, and Tead4 in the specification of the MJH trajectory. Finally, they performed a focused analysis of the role of Hand1 and Foxf1 in the MJH trajectory, showing their mutual regulation and their requirement for cardiac lineage specification.
Strengths:
The authors performed an extensive transcriptional and epigenetic analysis of early cardiac lineage specification and differentiation which will be of interest to investigators in the field of cardiac development and congenital heart disease. The authors considered the impact of the loss of Hand1 and Foxf1 in-vitro and Hand1 in-vivo.
Weaknesses:
The authors used previously published scRNA-seq data to generate two described transcriptomic trajectories.
(1) Details of the re-analysis step should be added, including a careful characterization of the different clusters and maker genes, more details on the WOT analysis, and details on the time stamp distribution along the different pseudotimes. These details would be important to allow readers to gain confidence that the two major trajectories identified are realistic interpretations of the input data.
The authors have also renamed the cardiac trajectories/lineages, departing from the convention applied in hundreds of papers, making the interpretation of their results challenging.
(2) The concept of "reverse reasoning" applied to the Waddington-OT package for directional mass transfer is not adequately explained. While the authors correctly acknowledged Waddington-OT's ability to model cell transitions from ancestors to descendants (using optimal transport theory), the justification for using a "reverse reasoning" approach is missing. Clarifying the rationale behind this strategy would be beneficial.
(3) As the authors used the EEM cell cluster as a starting point to build the MJH trajectory, it's unclear whether this trajectory truly represents the cardiac differentiation trajectory of the FHF progenitors:<br />
- This strategy infers that the FHF progenitors are mixed in the same cluster as the extra-embryonic mesoderm, but no specific characterization of potential different cell populations included in this cluster was performed to confirm this.
- The authors identified the EEM cluster as a Juxta-cardiac field, without showing the expression of the principal marker Mab21l2 per cluster and/or on UMAPs.
- As the FHF progenitors arise earlier than the Juxta-cardiac field cells, it must be possible to identify an early FHF progenitor population (Nkx2-5+; Mab21l2-) using the time stamp. It would be more accurate to use this FHF cluster as a starting point than the EEM cluster to infer the FHF cardiac differentiation trajectory.
These concerns call into question the overall veracity of the trajectory analysis, and in fact, the discrepancies with prior published heart field trajectories are noted but the authors fail to validate their new interpretation. Because their trajectories are followed for the remainder of the paper, many of the interpretations and claims in the paper may be misleading. For example, these trajectories are used subsequently for annotation of the multiomic data, but any errors in the initial trajectories could result in errors in multiomic annotation, etc, etc.
(4) As mentioned in the discussion, the authors identified the MJH and PSH trajectories as non-overlapping. But, the authors did not discuss major previously published data showing that both FHF and SHF arise from a common transcriptomic progenitor state in the primitive streak (DOI: 10.1126/science.aao4174; DOI: 10.1007/s11886-022-01681-w). The authors should consider and discuss the specifics of why they obtained two completely separate trajectories from the beginning, how these observations conflict with prior published work, and what efforts they have made at validation.
(5) Figures 1D and E are confusing, as it's unclear why the authors selected only cells at E7.0. Also, panels 1D 'Trajectory' and 'Pseudotime' suggest that the CM trajectory moves from the PSH cells to the MJH. This result is confusing, and the authors should explain this observation.
(6) Regarding the PSH trajectory, it's unclear how the authors can obtain a full cardiac differentiation trajectory from the SHF progenitors as the SHF-derived cardiomyocytes are just starting to invade the heart tube at E8.5 (DOI: 10.7554/eLife.30668).
The above notes some of the discrepancies between the author's trajectory analysis and the historical cardiac development literature. Overall, the discrepancies between the author's trajectory analysis and the historical cardiac development literature are glossed over and not adequately validated.
(7) The authors mention analyzing "activated/inhibited genes" from Peng et al. 2019 but didn't specify when Peng's data was collected. Is it temporally relevant to the current study? How can "later stage" pathway enrichment be interpreted in the context of early-stage gene expression?
(8) Motif enrichment: cluster-specific DAEs were analyzed for motifs, but the authors list specific TFs rather than TF families, which is all that motif enrichment can provide. The authors should either list TF families or state clearly that the specific TFs they list were not validated beyond motifs.
(9) The core regulatory network is purely predictive. The authors again should refrain from language implying that the TFs in the CRN have any validated role.
Regarding the in vivo analysis of Hand1 CKO embryos, Figures 6 and 7:
(10) How can the authors explain the presence of a heart tube in the E9.5 Hand1 CKO embryos (Figure 6B) if, following the authors' model, the FHF/Juxta-cardiac field trajectory is disrupted by Hand1 CKO? A more detailed analysis of the cardiac phenotype of Hand1 CKO embryos would help to assess this question.
(11) The cell proportion differences observed between Ctrl and Hand1 CKO in Figure 6D need to be replicated and an appropriate statistical analysis must be performed to definitely conclude the impact of Hand1 CKO on cell proportions.
(12) The in-vitro cell differentiations are unlikely to recapitulate the complexity of the heart fields in-vivo, but they are analyzed and interpreted as if they do.
(13) The schematic summary of Figure 7F is confusing and should be adjusted based on the following considerations:<br />
(a) the 'Wild-type' side presents 3 main trajectories (SHF, Early HT and JCF), but uses a 2-color code and the authors described only two trajectories everywhere else in the article (aka MJH and PSH). It's unclear how the SHF trajectory (blue line) can contribute to the Early HT, when the Early HT is supposed to be FHF-associated only (DOI: 10.7554/eLife.30668). As mentioned previously in Major comment 3., this model suggests a distinction between FHF and JCF trajectories, which is not investigated in the article.<br />
(b) the color code suggests that the MJH (FHF-related) trajectory will give rise to the right ventricle and outflow tract (green line), which is contrary to current knowledge.
Minor comments:
(1) How genes were selected to generate Figure 1F? Is this a list of top differentially expressed genes over each pseudotime and/or between pseudotimes?
(2) Regarding Figure 1G, it's unclear how inhibited signaling can have an increased expression of underlying genes over pseudotimes. Can the authors give more details about this analysis and results?
(3) How do the authors explain the visible Hand1 expression in Hand1 CKO in Figure S7C 'EEM markers'? Is this an expected expression in terms of RNA which is not converted into proteins?
(4) The authors do not address the potential presence of doublets (merged cells) within their newly generated dataset. While they mention using "SCTransform" for normalization and artifact removal, it's unclear if doublet removal was explicitly performed.
Comments on revised version:
Summary:
The authors have not addressed the major philosophical problems with the initial submission. They interpret their data without care to conform to years of prior publications in the field. This causes the authors to draw fanciful conclusions that are highly likely to be inaccurate (at best).
Q1R1: The authors gave more details about the characterization of cell types and the two identified trajectories.
a) It remains unclear how the authors generated this list. Are they manually selected genes based on relevant literature or an unbiased marker gene identification analysis? Either references should be added, or the bioinformatics explanation should be included in the method section.<br />
b) Revised text satisfies the comment.<br />
c) Revised text satisfies the comment.
Other comments:
Figure 1F: left annotation needs to be corrected (two "JCF specific").
Q2R1: Revised text satisfies the comment.
Q3R1 (1): Revised text satisfies the comment.
Q3R1 (2): a) The explanation of how the authors built the JCF trajectory makes sense and the renaming from "MJH" to "JCF" is correct and better represents the identification that was made using time points from E7.5 to E8.5. However, the explanation given does not answer our original question. Our original comment asked about the FHF differentiation trajectory. The authors built the "MJH" trajectory as the combined "FHF/JCF" trajectory, however, it is not directly established whether the FHF and JCF progenitor differentiation trajectories are the same. The authors did not directly try to identify the FHF and JCF trajectories separately using appropriate real time windows but only assumed that they were the same. Every link between JCF and FHF trajectories assuming that they are shared without prior identification of the FHF progenitor differentiation trajectory should be removed from the manuscript (e.g. page 4: "namely the JCF trajectory (the Hand1-expressing early extraembryonic mesoderm - JCF and FHF - CM)").
b) Adding the Mab21l2 ICA plot satisfies the comment.
c) The explanation given by the authors regarding the FHF trajectory analysis is missing important details. The authors started the reverse trajectory analysis from E7.75 cardiomyocytes as being the FHF.
- The authors should be mindful with the distinction between FHF progenitors and FHF-derived cardiomyocytes.<br />
- It is unclear whether cells called after the starting point (E7.75 CMs) in the reverse FHF trajectory, were collected prior E7.75. Can the authors add more details, and a real time point distribution along the FHF pseudotime to their analysis? Also, what cells belong to the FHF trajectory after the E7.75 CMs in the reverse direction? These cells should be shown as in Figure 1A and 1B for the JCF and SHF trajectories.<br />
- As the FHF arises first and differentiates into the cardiac crescent prior to or at the same time the JCF and SHF emerge, it is impossible for late progenitors (JCF and SHF) to contribute to the early FHF progenitor pool. Therefore, the observation that "both JCF and SHF lineages contribute to the early FHF progenitor population" can not be correct. It is also not what Dominguez et al showed. This misinterpretation goes against the current literature (e.g. DOI: 10.1038/ncb3024) and will leads to confusion.
Q4R1: Revised text and figure satisfy the comment.
Q5R1: The answer satisfies the comment.
Q6R1: a) The authors did not address the question and did not change their language in the manuscript. As SHF-derived cardiomyocytes are missing (because they are generated after E8.5), the part of the SHF trajectory going from SHF progenitors to the E8.5 heart tube must be inaccurate.
b) The authors correctly mentioned, both JCF and SHF will contribute to the four-chamber heart. However, as the dataset used by the authors spans only to E8.5 (which is days before the completion of the four-chamber heart), and all SHF and the vast majority of JCF contributions don't reach the heart until after E8.5, any claims about trajectories from JCF/SHF progenitor pools to cardiomyocytes should be removed because they do not correspond to prior published and accepted work.
Q7R1: Especially because gene expression levels change over time, the authors might have considered genes as specific and restricted to a pathway based on their expression at a given time (e.g. later time), but at another time (e.g. earlier time), the same genes could have another expression pattern and not be pathway-specific anymore.
Q8R1: Revised text satisfies the comment.
Q9R1: Revised text satisfies the comment.
Q10R1: Thank you for analyzing deeper the cardiac phenotype of the Hand1 cKO embryos.
Regarding the presence of a heart tube, while, following the authors' model the FHF/JCF trajectory is disrupted:
- Renaming the "MSH" to "JCF" is more accurate to the data shown by the authors as mainly the EEM is altered after Hand1 cKO.<br />
- The presence of the heart tube suggests that even if the JCF is altered, the FHF can still produce a cardiac crescent and a heart tube (as observed in Hand1-null embryos DOI: 10.1038/ng0398-266). The schematic Figure 7F suggests that only the SHF contribution will allow the formation of the heart tube. This unorthodox idea would need to be assessed by an alternate approach. More likely is that the model simply ignores the FHF contribution (the most important up to E8.5). The schematic is therefore incomplete and inaccurate and should be removed or edited to correspond to the prior literature.
Q11R1: It is unclear what "replicates" mean in the authors' answer, as if they have been pooled without replicate-specific barcodes they are no longer replicates and should be considered as a single sample. This should be explicitly written in the method section.<br />
Thank you for your IF staining/quantification. If DAPI was used, it should be written in the figure caption.
Q12R1: Revised text satisfies the comment.
Q13R1: The answer given by the authors did not satisfy the comment because of the following:
- The authors investigated two differentiation trajectories (JCF and SHF) in the article but Figure 7F presents three trajectories (JCF, SHF, and Early HT). The "Early HT" is neither mentioned, nor discussed in the manuscript.<br />
- Figure 7F suggests that the "Early HT" trajectory corresponds to a combination of the SHF and JCF trajectories but does not mention the early FHF trajectory. This is going against the current literature. This relates to the comments of Q10R1.<br />
- As the authors rightly point out, the SHF will be contributing to the heart tube, but through a cell invasion of the already differentiated heart tube (10.1016/j.devcel.2023.01.010). Our prior comments did not question the implication of the SHF to the looping and ballooning process but mentioned that the heart tube arises before the invasion from SHF and is FHF-derived. Figure 7F in the context of Hand1-null suggest that the heart tube will form from the SHF lineage, which is confusing as the SHF is known to contribute by invasion of the (already-formed) FHF-derived heart tube. The FHF lineage is missing from the authors' model.<br />
- In the revised manuscript, the FHF trajectory analysis is still unclear and suggests that the JCF and SHF progenitors contribute to the FHF progenitor which is going against current literature. This relates to the comments of Q3R1 (2).
Overall, the schematic Figure 7F is very confusing as it does not follow already published data without being fully validated and therefore is inaccurate and misleading.
Minor comments:
The answers satisfy the minor comments.