Quando è consigliato postare su linkedin?
- Il consiglio è di postare in questi giorni:
- Martedì;
- Giovedì;
- Sabato;
Gli orari in cui è consigliato pubblicare sono compresi tra le 8 e le 10
Una volta pubblicato il contenuto, linkedin lo mostrerà ad un gruppo di utenti in test
A seconda dell'engagement di questo gruppo di test nel corso delle 2 ore successive alla pubblicazione allora la copertura del post aumenterà o diminuirà.
In termini di metriche è più importante portare le persone a cliccare sul tasto "Visualizza altro" invece che sul "consiglia" o qualche altra reazione.
Per questo è necessario scrivere post della lunghezza di 1200-2000 caratteri.
La metrica più importante è quindi quella del "dwell time", quella che indica quanto tempo le persone passano sul proprio post e che deve essere il più alto possibile (per questo è necessario aumentare questa metrica utilizzando formati adatti come il carosello, i video, i post lunghi ecc)
Altra metrica molto più importante della reazione è il commento.
Il commento è 4 volte più forte di una delle reazioni più semplici ed è 7 volte più potente se tale commento è dato nelle prime due ore.
L'impatto di lasciare un commento di più di 5 parole risulterà in un +8% per chi ha creato il post e del +6% per la persona che ha commentato.
Se la prima persona che lascia il primo commento è quella che ha scritto il post allora la copertura decresce di un ammontare tra il -45% ed il -20%.
Riguardo la modalità creatore, questa aiuta e non aiuta a fare cose:
non aumenta la copertura dei tuoi post;
sposta la copertura dai tuoi collegamenti ai tuoi follower;
aumenta la copertura dei tuoi contenuti se i tuoi contenuti contengono gli hashtag che hai definito nel tuo profilo.
riduce il numero di richieste di collegamento verso di te del triplo
Se contribuisci in maniera coinvolta coi contenuti dei tuoi collegamenti allora anche i tuoi post avranno più engagement.
Il numero ideale di hashtag da utilizzare nei tuoi post è tra i 3 ed i 5
Inoltre è consigliato utilizzare un personal hashtag





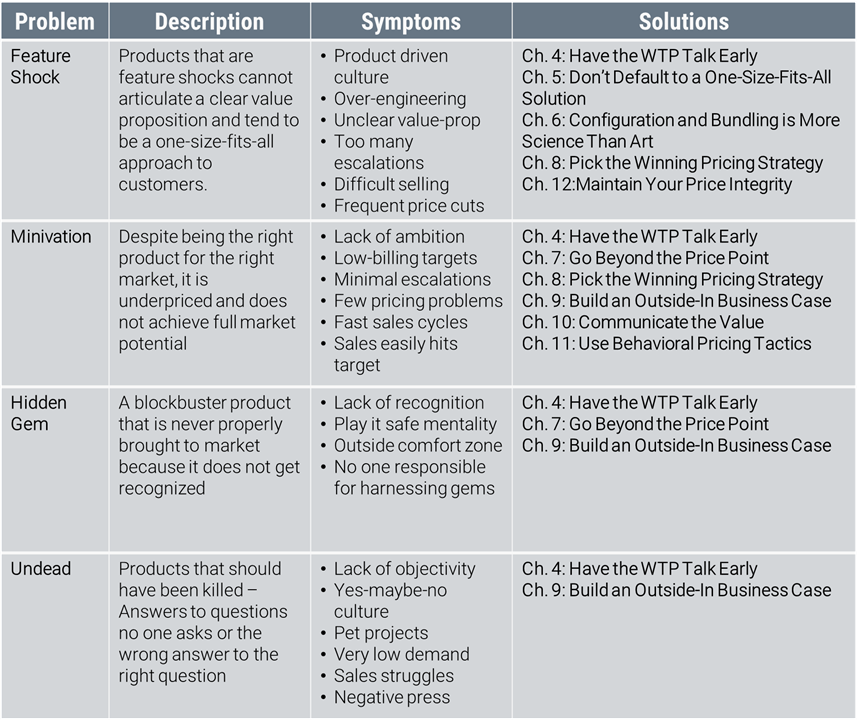 Quelli mostrati nella tabella sono i 4 tipi di problemi in termini di #pricing che si possono incontrare nella creazione di un prodotto.
Quelli mostrati nella tabella sono i 4 tipi di problemi in termini di #pricing che si possono incontrare nella creazione di un prodotto.