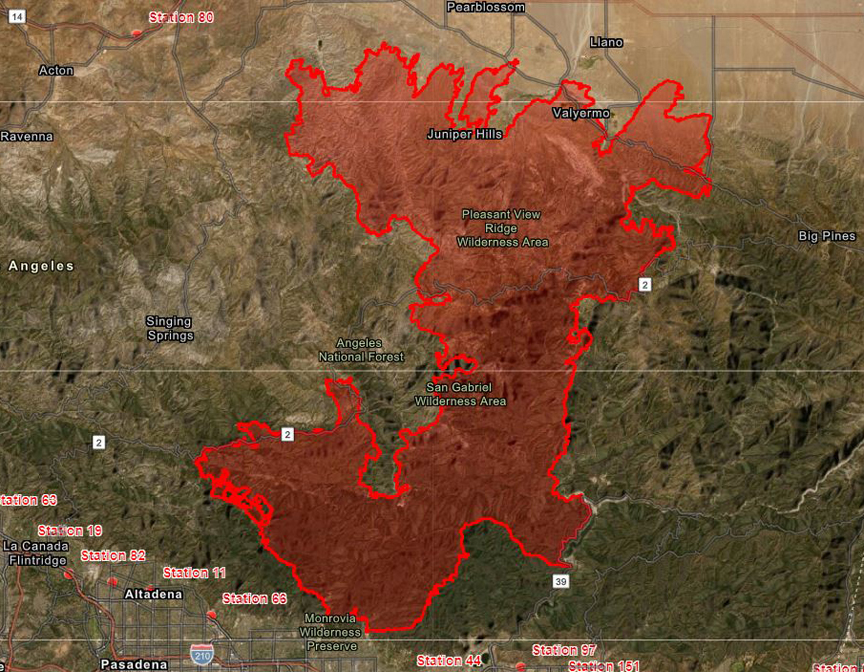
Wildfire Recovery Compensation Program<br /> https://energized.edison.com/wildfire-recovery-compensation-program
- Jan 2026
-
-
Your guide to SoCal Edison's Eaton Fire payout plan<br /> https://laist.com/news/climate-environment/edison-payout-guide
-
-
danallosso.substack.com danallosso.substack.com
-
Ironically, like Roger Taney’s opining in Dred Scott, it first raises its head in a “headnote” to a case not dealing with the issue. In remarks setting the scene for their decision in Santa Clara County v. Southern Pacific Railroad (1886), the court remarked, “The court does not wish to hear argument on the question whether the provision in the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution, which forbids a State to deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws, applies to these corporations. We are all of the opinion that it does.” This statement, that the court were “all of the opinion” that “any person” applied to the fictional entities created by state charters, precluded any formal challenge by telegraphing the outcome. Thus, in a sneaky way, the court avoided having to actually produce a decision of an actual case to establish this principle. Talk about legislating from the bench!
-
- Sep 2025
-
abc7.com abc7.com
-
Eaton Fire updates: New photos appear to show start of deadly Los Angeles fire as DOJ files lawsuits against SoCal Edison - ABC7 Los Angeles<br /> by [[Josh Haskell]]<br /> accessed on 2025-09-05T14:53:04
-
- Aug 2025
- May 2025
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Eine Studie zeigt, dass das Kraftwerk Drax in North Yorkshire trotz Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) bis in die 2050er Jahre die CO₂-Emissionen erhöhen wird. Die intensive Waldnutzung zur Gewinnung von Holzpellets in den USA reduziert die Kohlenstoffspeicher in Wäldern für mindestens 25 Jahre. Selbst mit CCS-Technologie bleiben die Emissionen über Jahrzehnte hoch, was die Klimakrise verschärft. Kritiker bezweifeln Drax' Behauptung, "klimaneutral" zu sein, und fordern eine Neubewertung der staatlichen Unterstützung für Biomasse-Energie. [Zusammenfassung generiert mit Mistral] https://www.theguardian.com/business/2024/nov/04/drax-will-keep-raising-carbon-emission-levels-until-2050s-study-says
-
- Mar 2025
-
www.latimes.com www.latimes.com
-
Palm trees are about as L.A. as it gets. But is it time to bid them a frond farewell? by [[Patt Morrison]] - Los Angeles Times
-
- Feb 2025
-
www.sce.com www.sce.com
-
www.latimes.com www.latimes.com
-
Edison wants to raise rates to pay for wildfires linked to its equipment - Los Angeles Times by [[Melody Petersen]]
-
In 2017, there were 105 ignitions involving Edison’s equipment. That number rose to 173 ignitions in 2021. Last year, there were 90 ignitions — a 14% decline since 2017.
-
That wildfire mitigation work now makes up about 11% of the average bill for an Edison customer, according to the commission’s public advocates office.
Holy shit!
How much of the average bill is paying for covering past fire payouts?
-
-
www.latimes.com www.latimes.com
-
When the Eaton fire erupted beneath a Southern California Edison transmission tower just after 6 p.m.,
-
- Jan 2025
-
academic.oup.com academic.oup.com
-
Many regions of Asia experienced devastating heatwaves, with approximately 1,500 heat stroke fatalities in Myanmar alone (Pearce and Ware 2024). As part of the longest heat wave ever recorded in India
-
Extensive flooding in southern Brazil devastated 478 cities, killed 173 people, and left 38 people missing, 806 injured, and 423,486 displaced
-
- Dec 2024
-
www.derstandard.de www.derstandard.de
-
Auch in diesem Jahr scheitert das Ausweisen großer Meeresschutzgebiete im antarktischen Ozean am Widerstand Chinas und Russlands. Die Antarctic and Southern Ocean Coalition informiert in einer neuen Publikation über die Notwendigkeit, das Meer um die Antarktis angesichts der globalen Erhitzung zu schützen. https://www.derstandard.at/story/3000000240592/umweltschuetzer-fordern-endlich-neue-schutzgebiete-in-der-antarktis
Bericht zum Schutz des antarktischen Ozeans: https://www.asoc.org/ice-archive/protecting-a-changing-southern-ocean/
-
- Nov 2024
-
iopscience.iop.org iopscience.iop.org
- May 2024
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
In den USA führen wachsende Datencenter, die u.a. durch die Industriepolitik steigende Produktion in Fabriken und immer mehr Elektrofahrzeuge zu einem steilen Anstieg des Bedarfs nach Elektrizität. Der zusätzliche Verbrauch wird in fünf Jahren etwa dem jetzigen Kaliforniens entsprechen. Die bestehenden Klimaziele werden dadurch gefährdet. Viele neue Gaskraftwerke werden bereits projektiert, unter anderem, weil die Regulierungen fossile Energien begünstigen. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2024/03/13/climate/electric-power-climate-change.html
Tags
- institution: Southern Environmental Law Center
- industry: digital
- expert: Daniel Brooks
- expert: Tyler H. Norris
- country: USA
- institution: R Street Institute
- by: Brad Plumer
- 2024-03-14
- expert: Devin Hartman
- Reports/The Era of Flat Power Demand is Over
- institution: Electric Power Research Institute
- variable: electricity demand
- by: Nadja Popovich
- expert: Greg Buppert
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
Schwere Überschwemmungen haben im Süden Brasillens mindestens 13 Todesopfer gefordert. Die Strom- und Trinkwasserversorgung war für Zehntausende unterbrochen. Es wurde der Katastrophenzustand ausgerufen. Präsident Lula führte die Überschwemmungen auf die globale Erhitzung zurück. Sie setzen eine Serie von Extremwetterereignissen in Brasilien fort, die auf das Zusammenwirken von Klimaveränderungen und El Niño zurückgehen. https://taz.de/Unwetter-in-Brasilien/!6008323/
-
- Apr 2024
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Eine extreme Hitzewelle hat in der Sahelzone Hunderte, wahrscheinlich Tausende Menschenleben gefordert. World Weather Attribution zufolge ist die Höhe der Temperaturen eindeutig auf die globale Erhitzung durch Treibhausgase zurückzuführen. https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2024/apr/18/lethal-heatwave-in-sahel-worsened-by-fossil-fuel-burning-study-finds
Tags
- by: Jonathan Watts
- region: Sahel
- process: increasing risk of heatwaves
- topic: temperature records
- expert: Kiswendsida Guigma
- event: El Niño 2023/24
- institution: World Weather Attribution
- event: Sahel heat wave April 2024
- 2024-04-18
- institution: Red Cross Red Crescent Climate Centre
- expert: Friederike Otto
- institution: Grantham Institute
- event: humid heat in Southern West Africa March 2024
- topic: attribution
- impact: heat deaths
Annotators
URL
-
-
- Jan 2024
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Zusammenfassender Artikel über Studien zu Klimafolgen in der Antarktis und zu dafür relevanten Ereignissen. 2023 sind Entwicklungen sichtbar geworden, die erst für wesentlich später in diesem Jahrhundert erwartet worden waren. Der enorme und möglicherweise dauerhafte Verlust an Merreis ist dafür genauso relevant wie die zunehmende Instabilität des westantarktischen und möglicherweise inzwischen auch des ostantarktischen Eisschilds. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/dec/31/red-alert-in-antarctica-the-year-rapid-dramatic-change-hit-climate-scientists-like-a-punch-in-the-guts
Tags
- British Antarctic Survey
- Matt King
- Abyssal ocean overturning slowdown and warming driven by Antarctic meltwater
- Bellingshausen Sea
- 2023-12-30
- sea ice loss
- Denman glacier
- Antarctica
- Record low 2022 Antarctic sea ice led to catastrophic breeding failure of emperor penguins
- East antarctic ice sheet
- expert: Lesley Hughes
- The Largest Ever Recorded Heatwave
- Nerilie Abram
- Kaitlin Naughten
- Ice core records suggest that Antarctica is warming faster than the global average
- expert: Matthew England
- Recent reduced abyssal overturning and ventilation in the Australian Antarctic Basin
- Tony Press
- Australian Centre for Excellence in Antarctic Science
- Southern ocean overturning circulation
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Ein Strömungssystem im südlichen Ozean, das man mit dem Golfstrom im nördlichen Atlantik vergleichen kann, hat seit den 90er Jahren um 30% Intensität verloren. Die Folgen dieser Entwicklung können dramatisch sein, unter anderem für die Nahrungsversorgung von Lebewesen im Meer und für die Erhöhung des Meeresspiegels. https://www.theguardian.com/science/2023/may/25/slowing-ocean-current-caused-by-melting-antarctic-ice-could-have-drastic-climate-impact-study-says
-
- Dec 2023
-
climateuncensored.com climateuncensored.com
-
There is now as big a disparity in carbon emissions within countries as there is between them
-
for: carbon emissions - within and between countries, Southern-North, Northern-South, Local North, Local South, Global North - Global South terminology - improving
-
comment
- The wealth and carbon inequality both between and within countries can be better articulated using terminology developed by Stop Reset Go
- Southern-North
- Northern-South
- Local North
- Local South
- The wealth and carbon inequality both between and within countries can be better articulated using terminology developed by Stop Reset Go
-
reference
- Expanding and Improving the Global North / Global South Terminology with Nuances of Post-Colonialism Realities in an Existential Climate Justice Context
-
-
- Nov 2023
-
theconversation.com theconversation.com
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Bei der diesjährigen Konferenz der Kommission zur Erhaltung der lebenden marinen Resourcen der Antarktis verhinderte vor allem die russische Delegation, dass große Gebiete unter Schutz gestellt wurden. Der Guardian berichtet über den Verlauf der Konferenz.
Tags
- NGO: Antarctic and Southern Ocean Coalition
- region: Antarctica
- actor: Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR)
- expert: Emily Grilly
- NGO: Pew Charitable Trusts
- 2023-10-29
- NGO: WWF Antarctic
- country: Russia
- expert: Andrea Kavanagh
- event: CCAMLR Meeting.October 2023
- expert: Claire Christian
Annotators
URL
theguardian.com/world/2023/oct/29/russian-delegation-stymies-creation-of-antarctic-conservation-area -
-
-
Bei der Jahrestagung der Kommission zum Schutz der lebenden Ressourcen der Antarktis ist der Plan, drei große zusammenhängende Gebiete als Schutzzonen auszuweisen, wieder am Widerstand Russlands und Chinas gescheitert. Es kam lediglich zu einer Übereinkunft das Fischen von Krill zu regulieren. https://taz.de/Kaum-Fortschritte-bei-Antarktisschutz/!5969196/
Tags
- NGO: Antarctic and Southern Ocean Coalition
- institution: Pew Bertarelli Ocean Legacy Project
- region: Antarctica
- actor: Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR)
- 2023-10-27
- event: One Planet – Polar Summit
- expert: Andrea Kavanagh
- event: CCAMLR Meeting.October 2023
- expert: Claire Christian
Annotators
URL
-
- Aug 2023
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Phillips also was partly responsible for the design of the Republican "Southern Strategy" of the 1970s and 1980s.
Was there a heavy racist tinge to his version of Southern Strategy? Religious?
-
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
- Jun 2023
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Ausführliche Erklärung des El Nino Phänomens mit einer instruktiven Animation. In diesem und im kommenden Jahr könnte dieses Phänomen in Verbindung mit den Temperaturerhöhungen durch die Treibhausgase zu globalen Temperaturrekorden führen. Mit hoher Wahrscheinlichkeit wird es Extremwetterereignisse verstärken.
-
- Feb 2023
-
-
Going forward, disposal plans including locations and transportation routes for contaminated waste will be subject to EPA review and approval, she said.
Government slows down and impedes everything under the pretense of making it better. This is yet another example of that.
-
-
www.ntsb.gov www.ntsb.gov
-
When train 32N passedthe next HBD, at MP 69.01, the bearing’s recorded temperature was 103°F aboveambient. The third HBD, at MP 49.81, recorded the suspect bearing’s temperature at253°F above ambient.
Though trending up, the bearing temperature was within non-critical limits until shortly before the wreck occurred. It was about 46 miles between the last detector and the one that alerted just before the accident.
-
The train engineer increased the dynamic brake application to further slow andstop the train. During this deceleration, an automatic emergency brake applicationinitiated, and train 32N came to a stop.
After being alerted to the unsafe condition, the crew seemed to respond appropriately by slowing down to stop, but during that process derailment further back in the train must have separated the air hoses causing the emergency braking application.
This suggests that the crew didn't throw the train into emergency as some had suggested.
-
The positive train control system was enabled and operating at thetime of the derailment.
No other trains were involved, but this system is intended to prevent multi-train collisions or crews inattentively passing stopped signals. It indicates that the crew was alert enough to be following inputs within the confines of the system.
-
Train 32N was traveling about 47mph at the time of the derailment, which was less than the maximum authorizedtimetable speed of 50 mph.
So we know it wasn't speeding as some had alleged.
-
-
abc6onyourside.com abc6onyourside.com
-
We ought to know when there is something that is very volatile that is coming into the State of Ohio
A lot of these chemicals are made in Ohio. Seems goofy to be all concerned about stuff coming in that we make right here.
-
- Nov 2022
-
www.npr.org www.npr.org
-
She told WHYY's Fresh Air in 1989 that her husband was a walking contradiction — a wild man on stage, boozing and womanizing, who wouldn't allow a drop of alcohol in his own home.
-
- Sep 2022
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
This year, the University of Southern California pulled its education school out of the rankings because of inaccuracies that went back five years.
-
- Jul 2022
-
www.thegreatsimplification.com www.thegreatsimplification.com
-
21:27 - We are just as smart now as we were in the ice age
Our neurophysiology has not changed much since the ice age. In other words, were an ice age descendent were transported by a time machine and were born in our current era, (s)he would have the same cognitive capacity as a modern human.
Peter mentions that we came out of our caves and begun agriculture. There is an interesting research paper that hypothesizes that over a period of the last 1.5 million years, human hunters in the Southern Levant successively extirpated the largest species by overshooting hunting over many generations, until the wild fauna population could no longer support human populations, at which point, humans may have turned to agriculture out of necessity. If true, this would support the idea that nonsustainable practices have been with us for a long time and we were out of balance long before Adam Smith wrote about it.
-
-
www.sciencedaily.com www.sciencedaily.com
-
Prof. Barkai: "In light of previous studies, our team proposed an original hypothesis that links the two questions: We think that large animals went extinct due to overhunting by humans, and that the change in diet and the need to hunt progressively smaller animals may have propelled the changes in humankind. In this study we tested our hypotheses in light of data from excavations in the Southern Levant covering several human species over a period of 1.5 million years." Jacob Dembitzer adds: "We considered the Southern Levant (Israel, the Palestinian Authority, Southwest Syria, Jordan, and Lebanon) to be an 'archaeological laboratory' due to the density and continuity of prehistoric findings covering such a long period of time over a relatively small area -- a unique database unavailable anywhere else in the world. Excavations, which began 150 years ago, have produced evidence for the presence of humans, beginning with Homo erectus who arrived 1.5 million years ago, through the neandertals who lived here from an unknown time until they disappeared about 45,000 years ago, to modern humans (namely, ourselves) who came from Africa in several waves, starting around 180,000 years ago."
The different hominin species studied in this well defined, archeologically rich region were Homo Erectus, Neandertals and Modern Humans..
-
Findings indicate a continual decline in the size of game hunted by humans as their main food source -- from giant elephants 1-1.5 million years ago down to gazelles 10,000 years ago. According to the researchers, these findings paint an illuminating picture of the interaction between humans and the animals around them over the last 1.5 million years.
1.5 million years trend of fauna of decreasing body mass in the Southern Levant - from giant elephants to gazelles.
-
In this way, according to the researchers, early humans repeatedly overhunted large animals to extinction (or until they became so rare that they disappeared from the archaeological record) and then went on to the next in size -- improving their hunting technologies to meet the new challenge. The researchers also claim that about 10,000 years ago, when animals larger than deer became extinct, humans began to domesticate plants and animals to supply their needs, and this may be why the agricultural revolution began in the Levant at precisely that time.
This is an extraordinary claim, that due to extirpation of fauna prey species, we resorted to agriculture. In other words, that we hunted the largest prey, and when they went extinct, went after the next largest species until all the large megafauna became extinct. According to this claim, agriculture became a necessity due to our poor intergenerational resource management skills.
Tags
- extirpate
- early progress trap
- extirpation
- early extinction
- decreasing body mass
- extinction
- gazelle
- Lebanon
- resource management
- early agriculture
- early farming
- Palestian Authority
- Southwest Syria
- giant elephants
- Southern Levant
- resource depletion
- origins of agriculture
- beginning of agriculture
- agriculture
- Jordan
- Israel
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.sciencedirect.com www.sciencedirect.com
-
Multiple large-bodied species went extinct during the Pleistocene. Changing climates and/or human hunting are the main hypotheses used to explain these extinctions. We studied the causes of Pleistocene extinctions in the Southern Levant, and their subsequent effect on local hominin food spectra, by examining faunal remains in archaeological sites across the last 1.5 million years. We examined whether climate and climate changes, and/or human cultures, are associated with these declines. We recorded animal abundances published in the literature from 133 stratigraphic layers, across 58 Pleistocene and Early Holocene archaeological sites, in the Southern Levant. We used linear regressions and mixed models to assess the weighted mean mass of faunal assemblages through time and whether it was associated with temperature, paleorainfall, or paleoenvironment (C3 vs. C4 vegetation). We found that weighted mean body mass declined log-linearly through time. Mean hunted animal masses 10,500 years ago, were only 1.7% of those 1.5 million years ago. Neither body size at any period, nor size change from one layer to the next, were related to global temperature or to temperature changes. Throughout the Pleistocene, new human lineages hunted significantly smaller prey than the preceding ones. This suggests that humans extirpated megafauna throughout the Pleistocene, and when the largest species were depleted the next-largest were targeted. Technological advancements likely enabled subsequent human lineages to effectively hunt smaller prey replacing larger species that were hunted to extinction or until they became exceedingly rare.
We must be careful of overgeneralizing sustainable practices to our early ancestors as the evidence from this research shows that we were not always sustainability-minded. In fact, the evidence suggests that when we find the biggest edible prey fauna species, we hunt them to extinction (extirpate) and when they are no longer able to reproduce in sustainable numbers, we move on to the next largest species. In this way, our early ancestors were the first progenitors of progress traps.
-
The Southern Levant, situated between modern day southern Syria via Israel to Sinai, has a spatiotemporally dense and continuous Paleolithic archaeological record offering a unique opportunity to detect faunal changes, including those predating the appearance of Homo sapiens (Bar-Yosef, 1980; Stutz, 2014). It is thus a suitable model to test long-term changes in the body mass of mammalian assemblages, in view of paleoclimates and changing human lineages, to decipher whether climate and/or humans are responsible for animal body size declines. The excellent archaeological record can further illuminate whether size declines are observed since hominins first colonized the region, or whether they start with the emergence of Homo sapiens (Louys et al., 2021), or are concentrated in the last glacial and its aftermath. We tested whether the size, and size changes, in hominin prey through the Pleistocene and early Holocene were related to time, the prevailing human lineages and cultures, paleoenvironment, and temperatures.
Southern Levant is unique for providing records for this study.
-
- Jun 2022
-
threadreaderapp.com threadreaderapp.com
- Jan 2022
-
www.medrxiv.org www.medrxiv.org
-
Colson, P., Delerce, J., Burel, E., Dahan, J., Jouffret, A., Fenollar, F., Yahi, N., Fantini, J., La Scola, B., & Raoult, D. (2021). Emergence in Southern France of a new SARS-CoV-2 variant of probably Cameroonian origin harbouring both substitutions N501Y and E484K in the spike protein [Preprint]. Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS). https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.24.21268174
-
- Jun 2021
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
-
One pastor, who requested anonymity in order to speak openly, put it to me this way:Having grown up in the South, [I think] Southern Baptist culture is probably uniquely this way, but working in a church that isn’t in the South, this stuff still rears its head. Not as much the same presenting issues, but you still fundamentally get people who are in love with power and will take any means necessary to beat you down so they have power and you are subservient to them, not the Gospel.
A searing indictment of power within religion...
-
- Oct 2020
-
www.scientificamerican.com www.scientificamerican.com
-
Peek, K. (n.d.). Flu Season Never Came to the Southern Hemisphere. Scientific American. Retrieved October 5, 2020, from https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/flu-season-never-came-to-the-southern-hemisphere/
-
- May 2020
-
www.economist.com www.economist.com
-
How deep will downturns in rich countries be? (n.d.). The Economist. Retrieved April 22, 2020, from https://www.economist.com/finance-and-economics/2020/04/16/how-deep-will-downturns-in-rich-countries-be?fsrc=scn/tw/te/bl/ed/pickingofftheweakhowdeepwilldownturnsinrichcountriesbefinanceandeconomics
-
- Aug 2018
-
cstroop.com cstroop.com
-
bars women from teaching men or holding any leadership position over them.
and potentially one of the major reasons people were against Hilary Clinton.
-
- May 2017
-
www.sourcewatch.org www.sourcewatch.org
-
Coalition for Southern Africa
This may be a front group. Investigate, find additional sources, and leave research notes in the comments.
-