reply to u/iamharunjonuzi at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/12bvcmn/how_do_i_store_when_coming_across_an_actual_fact/
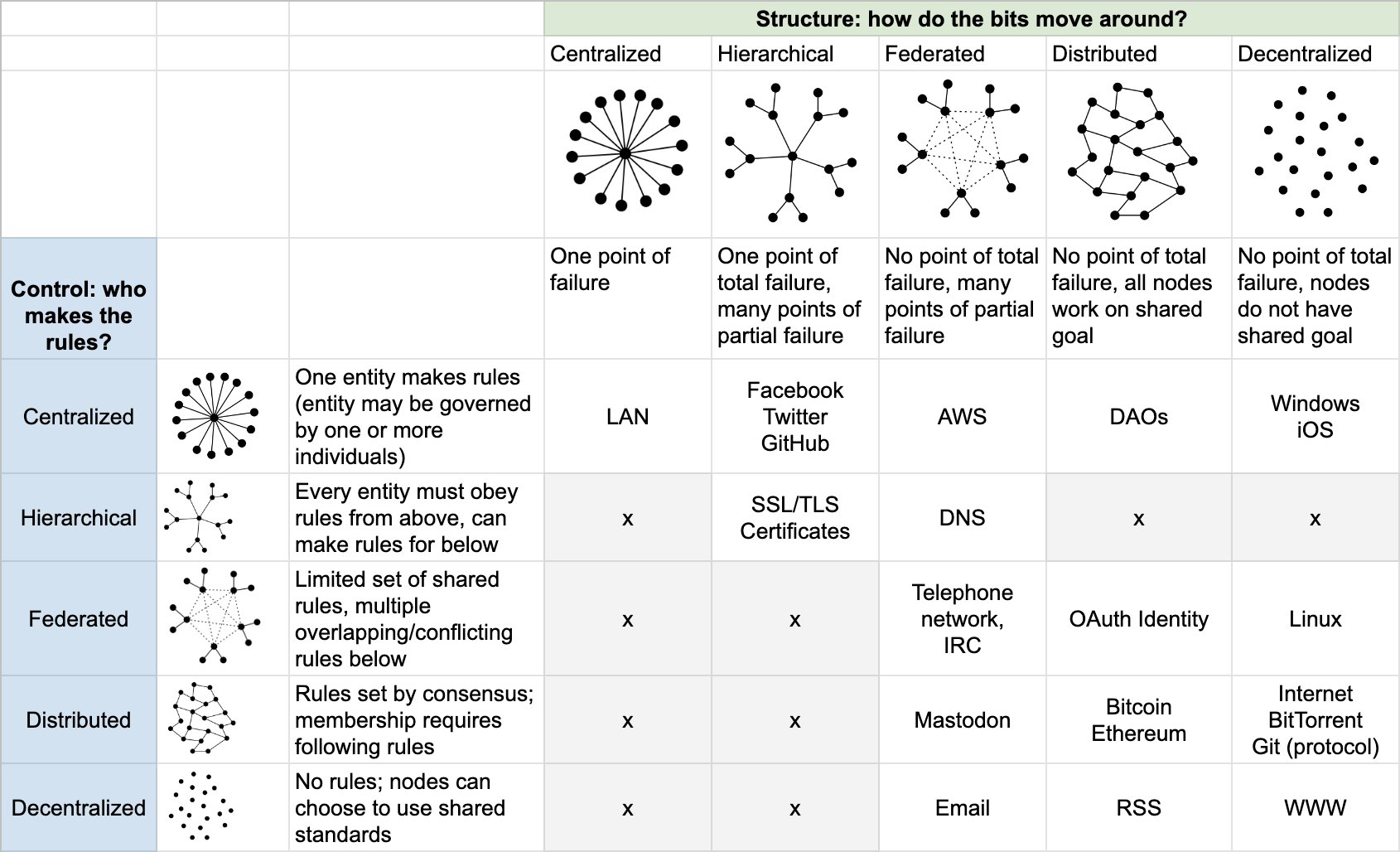
How central is the fact to what you're working at potentially developing? Often for what may seem like basic facts that are broadly useful, but not specific to things I'm actively developing, I'll leave basic facts like that as short notes on the source/reference cards (some may say literature notes) where I found them rather than writing them out in full as their own cards.
If I were a future biologist, as a student I might consider that I would soon know really well what a cell was and not bother to have a primary zettel on something so commonplace unless I was collecting various definitions to compare and contrast for something specific. Alternately as a non-biologist or someone that doesn't use the idea frequently, then perhaps it may merit more space for connecting to others?
Of course you can always have it written along with the original source and "promote" it to its own card later if you feel it's necessary, so you're covered either way. I tend to put the most interesting and surprising ideas into my main box to try to maximize what comes back out of it. If there were 2 more interesting ideas than the definition of cell in that documentary, then I would probably leave the definition with the source and focus on the more important ideas as their own zettels.
As a rule of thumb, for those familiar with Bloom's taxonomy in education, I tend to leave the lower level learning-based notes relating to remembering and understanding as shorter (literature) notes on the source's reference card and use the main cards for the higher levels (apply, analyze, evaluate, create).
Ultimately, time, practice, and experience will help you determine for yourself what is most useful and where. Until you've developed a feel for what works best for you, just write it down somewhere and you can't really go too far wrong.
 Link to tweet:
Link to tweet: