- Aug 2023
-
americanhistory.si.edu americanhistory.si.edu
-
Although Diller generated a lot of her own material, she elicited some gags from other writers. One of her top contributors was Mary MacBride, a Wisconsin housewife with five children. A joke obtained from another writer includes the contributor’s name on the index card with the gag.
Not all of the jokes in Phyllis Diller's collection were written by her. Many include comic strips she collected as well as jokes written by others and sent in to her.
One of the biggest contributors to her collection of jokes was Wisconsin housewife Mary MacBride, the mother of five children. Jokes contributed by others include their names on the individual cards.
-
-
transcription.si.edu transcription.si.edu
-
Numbers on Cards The curatorial and collections teams are trying to learn more about the appearance of "No. #" on cards. Please transcribe this number on a separate line underneath the Date line, above the Joke line.
Some of the cards in Phyllis Diller's gag file were numbered, but the curatorial and collections team at the Smithsonian didn't have enough data to determine what these were or what they meant at the time of transcription.
-
-
blog.jerrybrito.com blog.jerrybrito.com
-
After all, Luhmann himself didn’t have automatic backlinking. He had to manually add the cross-references to his analog notecards, and yet the system allowed him to write dozens of books and papers. Indeed, as Christian from Zettelkasten.de has said, automation might actually be an impediment to the cogitation and deep understanding the method seeks to engender.
-
-
www.lesswrong.com www.lesswrong.com
-
Indigenous cultures can "see" dark constellations (example: the Australian emu in the sky) which are defined empty spaces which are explicitly visible.
Using this concept, one could think of or use blank index cards in a zettelkasten or even the empty (negative) spaces between cards as "dark ideas" (potential ideas which need to be thought of and filled in).
-
Here’s a child node. It could be a comment on the thought -- an aside, a critique, whatever. It could be something which goes under the heading.
Lone child nodes cry out for siblings.
When I was in middle school a teacher told me only to put a sub-bullet point in an outline only if it wasn't an orphan (if you had one sub-point it should have at least one sibling, otherwise don't include it). This was miserable advice because it ended trains of thought which might otherwise grow into something.
On the other hand it could be better framed that if you have only one child, you should brainstorm to come up with others.
-
I could continue a thread anywhere, rather than always picking it up at the end. I could sketch out where I expected things to go, with an outline, rather than keeping all the points I wanted to hit in my head as I wrote. If I got stuck on something, I could write about how I was stuck nested underneath whatever paragraph I was currently writing, but then collapse the meta-thoughts to be invisible later -- so the overall narrative doesn’t feel interrupted.
Notes about what you don't know (open questions), empty outline slots, red links as [[wikilinks]], and other "holes" in tools for thought provide a bookmark for where one may have quit exploring, but are an explicit breadcrumb for picking up that line of thought and continuing it at a future time.
Linear writing in one's notebooks, books they're reading, and other places doesn't always provide an explicit space which invites the reader or writer to fill them in. One has to train themselves to annotate in the margins to have a conversation with the text. Until one sees these empty spaces as inviting spaces they can be invisible to the eye.
-
I mentioned that I knew I liked Zettelkasten within the first 30 minutes. I think it might be important that when I sat down to try it, I had an idea I was excited to work on. It wasn’t a nice solid mathematical idea -- it was a fuzzy idea, one which had been burning in the back of my brain for a week or so, waiting to be born. It filled the fractal branches of a zettelkasten nicely, expanding in every direction.
abramdemski suggests starting with an idea you're interested in working on and fleshing out when you start your zettelkasten. This harkens back to Montessori teaching philosophies.
-
I use the Staples index-cards-on-a-ring which put all the cards on a single ring, and protect them with plastic covers.
Rather than using card index boxes, abramdemski prefers using book rings to hold his cards together in batches.
-
one early reader of this write-up decided to use half 3x5 cards, so that they’d fit in mtg deck boxes.
First reference I've seen for someone suggesting using half size 3 x 5" index cards so that they could use commercially available Magic: The Gathering (MTG) boxes.
Oxford and possibly other manufacturers already make 1/2 size 3 x 5" index cards.
-
others have reported large productivity boosts from the technique as well.
Which others? where?
To my knowledge there weren't many (any?) examples floating around in 2019.
-
However, I strongly recommend trying out Zettelkasten on actual note-cards, even if you end up implementing it on a computer. There’s something good about the note-card version that I don’t fully understand.
Another advising to use the analog method for learning even if one is going to switch to a digital zettelkasten.
He uses the word "good" here while others may have potentially used the word "magic", but writing in a space that values critical thinking, he would have been taken to task for having done so. In any case he's not able to put his finger on the inherent value of analog over digital.
-
However, I honestly didn’t think Zettelkasten sounded like a good idea before I tried it. It only took me about 30 minutes of working with the cards to decide that it was really good.
I've seen people describing how many cards they think they need before the method is useful, but this is the first time I've seen someone use a timeframe to describe useful effects.
-
Early this year, Conor White-Sullivan introduced me to the Zettelkasten method of note-taking.
This article was likely a big boost to the general idea of zettelkasten in the modern zeitgeist.
Note the use of the phrase "Zettelkasten method of note-taking" which would have helped to distinguish it from other methods and thus helping the phrase Zettelkasten method stick where previously it had a more generic non-name.
-
https://www.lesswrong.com/posts/NfdHG6oHBJ8Qxc26s/the-zettelkasten-method-1
A somewhat early, comprehensive one page description of the zettelkasten method from September 2019.
Tags
- red links
- prompts
- zettelkasten critical mass
- The Great Conversation
- zettelkasten boxes
- 3 x 5" index cards
- tools for thought affordances
- Magic: The Gathering (MTG)
- blank page
- dark constellations
- bullet points
- Montessori philosophy
- writing advice
- zettelkasten
- tree branching
- Workflowy
- margins
- emu in the sky
- card index for productivity
- outlining
- magic of note taking
- negative space
- empty spaces
- 2.5 x 3" index cards
- critical thinking
- invisibility
- book rings
- analog vs. digital
- zettelkasten method
- annotations
- dark ideas
- outliners
- zettelkasten method one pager
- zettelkasten pedagogy
- child nodes
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.amazon.com www.amazon.com
-
Using Magic: The Gathering boxes for younger children and teenagers might be a more palatable way to introduce the zettelkasten method of note taking to them, particularly when it's a game in which they have a pre-existing interest.
-
-
-
www.lesswrong.com www.lesswrong.com
-
https://www.lesswrong.com/posts/T382CLwAjsy3fmecf/how-to-take-smart-notes-ahrens-2017
ᔥ[[abramdemski]] in The Zettelkasten Method (accessed:: 2023-08-25 10:12:42)
-
-
luhmann.surge.sh luhmann.surge.sh
-
The slip box needs a number of years in order to reach critical mass. Until then, it functions as a mere container from which we can retrieve what we put in. This changes with its growth in size and complexity.
Niklas Luhmann indicates that it may take a number of years to reach critical mass. This may be different for everyone based on the number of ideas they place into it and the amount of work they do in creating connections.
Ward Cunningham, the creator of the wiki, has indicated that he thinks it takes roughly 500 pages in a wiki for the value to begin emerging.†
How many notes and what level of links/complexity is a good minimal threshold for one to be able to see interesting and useful results?
† Quote in FedWiki session on 2021-12-29
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
https://www.reddit.com/r/Arno_Schmidt/comments/1267heb/arno_schmidt_compulsively_wrote_and_hoarded/
Lots of great anecdotal mentions here which should be tracked down for more authority.
-
-
www.oliverburkeman.com www.oliverburkeman.com
-
https://www.oliverburkeman.com/onwriting
Oliver Burkerman, of Four Thousand Weeks fame, is testing out zettelkasten based on Ahrens' book.
-
-
-
Zettelkasten in one or several language(s)? .t3_15wo3f2._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
As long as you know and understand what you're writing, use as many languages as you or your zettelkasten wants or needs.
I'm often working with ideas from other languages and cultures which have no direct translations into English, so I use those native words interspersed with English. Sometimes I don't have words in any language and make up a shorthand phrase in English until I can come up with a better word. Often I'll collect examples of the same "foreign" words in multiple contexts to tease out their contextual meanings as was comprehensively done with large group zettelkasten like the Thesaurus Linguae Latinae and the Wörterbuch der ägyptischen Sprache. I also frequently use mathematical symbols, equations, and other scientific notations, graphs, drawings, color, etc. to make my meanings clear.
I've also worked with historical figures who have had names in multiple languages over the centuries and cross index them in a variety of different languages based on context. As an example, I've got at least 11 different variations of names for Ramon Llull in almost as many languages and variations of transliterations. I try to keep each one in its original context, but link them in my index.
There are certainly zettelkasten out there written in four and more languages as suited the needs of their users. S.D. Goitein certainly used Hebrew, English, German, Arabic, Aramaic in his and may have likely had other languages (Yiddish, Coptic, Egyptian?) interspersed to lesser extents. Adolph Erman certainly used Egyptian hieroglyphs along with German in his. It can easily be argued that their zettelkasten and work required multiple languages.
https://web.archive.org/web/20180627163317im_/https://aaew.bbaw.de/wbhome/Broschuere/abb08.jpg A example zettelkasten slip showing a passage of text from the victory stele of Sesostris III at the Nubian fortress of Semna. The handwriting is that of Adolf Erman, who had "already struggled with the text as a high school student".
At the end of the day, they're your notes, so write them as you like.
-
-
-
Thanks Sascha for an excellent primer on the internal machinations of our favorite machines beyond the usual focus on the storage/memory and indexing portions of the process.
Said another way, a zettelkasten is part of a formal logic machine/process. Or alternately, as Markus Krajewski aptly demonstrates in Paper Machines (MIT Press, 2011), they are early analog storage devices in which the thinking and logic operations are done cerebrally (by way of direct analogy to brain and hand:manually) and subsequently noted down which thereby makes them computers.
Just as mathematicians try to break down and define discrete primitives or building blocks upon which they can then perform operations to come up with new results, one tries to find and develop the most interesting "atomic notes" from various sources which they can place into their zettelkasten in hopes of operating on them (usually by juxtaposition, negation, union, etc.) to derive, find, and prove new insights. If done well, these newly discovered ideas can be put back into the machine as inputs to create additional newer and more complex outputs continuously. While the complexity of Lie Algebras is glorious and seems magical, it obviously helps to first understand the base level logic before one builds up to it. The same holds true of zettelkasten.
Now if I could only get the
printfportion to work the way I want... -
category theory + zettelkasten... hmmm... feels a bit like Leibniz chasing a universal language
what is a zettelkasten monad?
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
I want to start studying zettelkasten, advise books, video, courses, articles, web pages, please!
Zettelkasten advice:
- Have a goal in mind
- Really... have a goal. Write it down.
- Practice at it, a lot
- When stuck, read some of the bits below
- Practice, practice, practice.
Here are a list of some of the strongest books which focus on the topic or cover things from various interesting perspectives: - Ahrens, Sönke. How to Take Smart Notes: One Simple Technique to Boost Writing, Learning and Thinking – for Students, Academics and Nonfiction Book Writers. Create Space, 2017. - Allosso, Dan, and S. F. Allosso. How to Make Notes and Write. Minnesota State Pressbooks, 2022. https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/write/. (Specifically the first half of the book.) - Barzun, Jacques, and Henry F. Graff. The Modern Researcher. New York, Harcourt, Brace, 1957. http://archive.org/details/modernreseracher0000unse. - Bernstein, Mark. Tinderbox: The Tinderbox Way. 3rd ed. Watertown, MA: Eastgate Systems, Inc., 2017. http://www.eastgate.com/Tinderbox/TinderboxWay/index.html. - Eco, Umberto. How to Write a Thesis. Translated by Caterina Mongiat Farina and Geoff Farina. 1977. Reprint, Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press, 2015. https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/how-write-thesis. - Goutor, Jacques. The Card-File System of Note-Taking. Approaching Ontario’s Past 3. Toronto: Ontario Historical Society, 1980. http://archive.org/details/cardfilesystemof0000gout. - Mills, C. Wright. “On Intellectual Craftsmanship (1952).” Society 17, no. 2 (January 1, 1980): 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02700062. - Sertillanges, Antonin Gilbert, and Mary Ryan. The Intellectual Life: Its Spirit, Conditions, Methods. First English Edition, Fifth printing. 1921. Reprint, Westminster, MD: The Newman Press, 1960. http://archive.org/details/a.d.sertillangestheintellectuallife. (Especially chapter seven). - Weinberg, Gerald M. Weinberg on Writing: The Fieldstone Method. New York, N.Y: Dorset House, 2005.
Read one (or two) and then dive in and actually practice (and practice and practice some more) things for a while.
For some of the smaller subtleties which aren't covered in books, try one of the two following collections for individual bits of advice and insight: - https://writing.bobdoto.computer/zettelkasten/ - https://zettelkasten.de/posts/ - https://boffosocko.com/research/zettelkasten-commonplace-books-and-note-taking-collection/
-
-
www.printables.com www.printables.com
-
https://www.printables.com/model/558873-zettelkasten-index-boxes-slip-box
Someone has designed a DIY printer project for making your own stackable zettelkasten boxes.
See post at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/15wkuel/zettelkasten_index_boxes_slip_box_make_your_own/
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/13nmcym/i_read_the_top_ten_zettelkasten_articles_on/
A list of some popular one-pagers on the Zettelkasten Method.
Read contemporaneously in May 2023
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
BookmarkZettelkasten for historical research?
@pgrhowarth @MartinBB @tevka and other historians (and sociologists, anthropologists, humanists, etc.) who want to delve into some of the ideas of historical method, zettelkasten, note taking, intellectual craftsmanship outside of Luhmann's version, I've compiled a list of various primary sources who have written on a variety of related methods throughout the past few hundred years: https://www.zotero.org/chrisaldrich/tags/note%20taking%20methods/items/KTZXN3EV/item-list
Historians in particular have used indexing their notes as a means of creating analog databases for individual facts outside of their other writing/compiling practices. Thus a mixture of methods may suit your working needs.
To help frame it one might also consult the following: * Thomas, Keith. “Diary: Working Methods.” London Review of Books, June 10, 2010. https://www.lrb.co.uk/the-paper/v32/n11/keith-thomas/diary. * Blair, Ann M. Too Much to Know: Managing Scholarly Information before the Modern Age. Yale University Press, 2010. https://yalebooks.yale.edu/book/9780300165395/too-much-know.
I've got a relatively short overview of some of these methods and examples of users at https://boffosocko.com/2022/10/22/the-two-definitions-of-zettelkasten/.
-
-
-
75000 Zettel,
Context:
Damit hatte der 84-jährige Mommsen ein Projekt initiiert, an dem Profanwie Kirchenhistoriker in Deutschland auch noch lange nach seinem Tode arbeiteten und das gute Fortschritte machte: Al s Jülicher, der nach dem Tode Seecks 1921 die alleinige Leitung übernahm, auf Grund seines Augenleidens 1929 von seinen Verpflichtungen entbunden wurde, Ubergab er der Kommission etwa 75000 Zettel, deren Systematisierung allerdings nicht zum Abschluß kam74. Von einer Veröffentlichung des Materials sah man ab, da «weder der Zustand des Manuskripts noch die inzwischen völlig veränderte wissenschaftliche Lage es gestatteten, die Prosopographie zum Druck zubringen75».
Nachdem nur einige Zettelkästen im Zweiten Weltkrieg verloren gegangen waren, wurde 1951 ein Teil der Materialien leihweise dem von A.H.M. Jones, John Morris und H.-I. Marrou in Cambridge und Paris begründeten Unternehmen, das sich zum Ziel gesetzt hatte, eine weltliche und eine kirchliche Prosopographie der Spätantike zu erarbeiten, zur Verfügung gestellt76. Während wir heute aus technischen und organisatorischen Gründen mit zweiverschiedenen Prosopographien -einer weltlichen und einer kirchlichen- zu arbeiten haben, die beide noch nicht abgeschlossen sind, hatte Mommsen die Nützlichkeit, ja die Notwendigkeit einer spätantiken Prosopographie erkannt, die weltliche und kirchliche Würdenträger gemeinsam erschließt und aufführt.
- Ibid.: Schreiben H. LlETZMANNs vom 6.10.1936.
- Weder die Prosopography oflhe Later Roman Empire (= PLRE) noch die Prosopographie chretienne du Bas-Empire erwähnen diesen Sachverhalt; während in PLRE I (hrsg. v. A.H.M. JONES, J.R. MARTINDALE, J. MORRIS), Cambridge 1971, V zu lesen ist: «The project of a prosopographical dictionary of the Later Roman Empire was originated by Theodor Mommsen but... it failed of fruition, largely through the Intervention of the two World Wars. The bulky archives representing the work of many German seholars lay in Berlin during the second war when they were damaged and in part destroyed, together with essential records, during an Allied bombing raid. Consequently when the prqject was taken up in England after the war, the work had to be restarted from the very beginning. The present volume therefore represents the first stage of fulfilment of Mommsen's original project», heißt es im ersten Band der Prosopographie chretienne: A. MANDOUZE (Hrsg.), Prosopographie de l'Afrique chretienne (303-533), Paris 1982, 7: «On sait qu'ä la fin du siecle dernier, sur l'initiative de Th. Mommsen et d'Ad. Harnack, l'Academie des Sciences de Berlin avait commence' ä preparer un vaste dictionnaire prosopographique du Bas-Empire. Sans doute concu de facon trop ambitieuse, victime aussi des sequelles de la Premiere Guerre mondiale, ce projet fut definitivement abandonne" en 1933»; cf. hierzu auch H. CHANTRAINE, Ein neues Hilfsmittel zur Erforschung der Spätantike: Die Prosopographie chretienne du Bas-Empire, in: Francia 11, 1984,697ff., v.a. 697f.
Machine translation:
The 84-year-old Mommsen had thus initiated a project on which both profane and church historians in Germany continued to work long after his death and which made good progress: Al s Jülicher, who took over the sole management after Seeck's death in 1921 due to his eye problems in 1929 was relieved of his obligations, he handed over around 75,000 slips of paper to the Commission, the systematisation of which, however, was not completed ^74. The material was not published because "neither the condition of the manuscript nor the scientific situation, which had meanwhile completely changed, allowed the prosopography to be printed^75".
After only a few card boxes had been lost in World War II, some of the materials were loaned to A.H.M. Jones, John Morris and H.-I. Marrou in Cambridge and Paris, which had set itself the goal of developing a secular and an ecclesiastical prosopography of late antiquity. While today, for technical and organizational reasons, we have to work with two different prosopographies - one secular and one ecclesiastical - both of which have not yet been completed, Mommsen recognized the usefulness, indeed the necessity, of a late antique prosopography that explores secular and ecclesiastical dignitaries together and performs.
- Ibid.: Letter from H. LlETZMANN dated October 6, 1936.
- Neither the Prosopography oflhe Later Roman Empire (= PLRE) nor the Prosopographie chretienne du Bas-Empire mention this fact; while in PLRE I (ed. by A.H.M. JONES, J.R. MARTINDALE, J. MORRIS), Cambridge 1971, V one can read: «The project of a prosopographical dictionary of the Later Roman Empire was originated by Theodor Mommsen but... it failed of fruition, largely through the Intervention of the two World Wars. The bulky archives representing the work of many German scholars lay in Berlin during the second war when they were damaged and in part destroyed, together with essential records, during an Allied bombing raid. Consequently when the project was taken up in England after the war, the work had to be restarted from the very beginning. The present volume therefore represents the first stage of fulfillment of Mommsen's original project," says the first volume of the Prosopographie chretienne: A. MANDOUZE (ed.), Prosopographie de l'Afrique chretienne (303-533), Paris 1982, 7: "On said qu'a la fin du siecle dernier, sur l'initiative de Th. Mommsen et d'Ad. Harnack, l'Academie des Sciences de Berlin avait commence' a preparer un vaste dictionnaire prosopographique du Bas-Empire. Sans doute concu de facon trop ambitieuse, victime aussi des sequelles de la Premiere Guerre mondiale, ce projet fut definitivement abandonne" en 1933"; cf. on this also H. CHANTRAINE, A new tool for researching the Late antiquity: The prosopography chretienne du Bas-Empire, in: Francia 11, 1984, 697ff., especially 697f.
This would seem to indicate that Theodor Mommsen potentially had a zettelkasten which he was using to compile his work, but there is some ambiguity here that the slips and boxes may have been those of scholars who came after him and were working on his notes and systematizing them for future publication. Perhaps they were Mommsen's and others were arranging them for potential publication as they only had subject heading orderings, which would have been the most likely mode of the day (versus a more Luhmann-artig ordering.)
syndication link: https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/2649/theodor-mommsens-zettelkasten/
-
Rebenich, Stefan. “Theodor Mommsen and the Relationship of Age History and Patristic (Theodor Mommsen und das Verhältnis von Alter Geschichte und Patristik).” In Patristique et antiquité tardive en Allemagne et en France de 1870 à 1930 : Influences et échanges: Actes du colloque franco-allemand de Chantilly (25-27 octobre 1991), edited by Jacques Fontaine, R. Herzog, and Karla Pollmann, 131–54. Paris: Brepols, 1993. https://archiv.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/propylaeumdok/46/1/Rebenich_Mommsen_1993.pdf.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Zettelkasten for Normies: What Normies Really Need to Know .t3_15sqiq2._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/SunghoYahng at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/15sqiq2/zettelkasten_for_normies_what_normies_really_need/
u/SunghoYahng, some of your article sounds like a pared down digital version of a commonplace book which allows for links, so it fits into the older zettelkasten tradition, just not into the more Luhmann-artig version on which this subreddit is generally more focused. Perhaps yours is closer to a digital version of the analog commonplace using index cards that Billy Oppenheimer describes having learned from Ryan Holiday and Robert Greene?
Often people focus too much on Luhmann's prodigious output and then immediately imply or say you should adopt his very specific system without describing what his system did or why it worked so well for him and his particular needs. Very few focus on what it is that they want to accomplish and how they might use his system or the thousands of variations on it throughout history to come to those goals as quickly and easily as they can.
You commit a version of this sin in your opening lines:
The content about Zettelkasten is mostly too long and practically useless. The purpose of this text is to write only what normies really need to know.
Who are these so-called "normies" and what specifically are they trying to accomplish? You don't define either of them, and possibly worse do it in a negative framing. The system you're describing might be a great one, but for whom? What do you expect them to use it for? What will they get out of it?
Many people talk about the "magic" of a zettelkasten and then wave their hands at some version of a workflow of what they think it is or what they think it should be. Perhaps what we all really need is a list of potential affordances that different methods allow and how one might leverage those affordances. How might they be mixed and matched? Then users can decide what outcomes they wish to have (writing, thinking, aggregation, bookmarking, collecting, creativity, artificial memory, serendipity, productivity, wiki, spaced repetition, learning, time wasting, etc., etc.) and which affordances are necessary within their workflow/system to effectuate those specific goals? Finally they can pick and choose a specific version of a methodology/workflow and either an analog substrate (index cards, notebooks, memory palace, etc.) or digital tool/application (Obsidian, Roam Research, The Archive, etc.) to save it all in. Of course once you've chosen that analog or digital tool, does it actually have the affordances you want or need in actual practice? Are they easy to use? Practical? Do they save you time? Are they simple or over-engineered? What happens when they scale to a year of regular use or even a lifetime?
As a simple example, many writers would love a seriously good outliner functionality in their system to pull out the materials they want to work with and then appropriately order them for a potential final written output. In practice, index cards on a big table are fantastic for this process while most (all?) current digital tools are miserable at it. And of course once you've gotten the outline you like in an analog space you have to type it all out to print/publish in a final form, something which the digital affordance of cut and paste would make much simpler. Who wouldn't love a tool that could give you all of these affordances, presuming you needed them?
While we're on outlining, very few talk about the ease-of-use that some professional outliners like Dave Winer's Drummer or Little Outliner have versus some of the more text-editing focused tools like Obsidian which are generally poor as outliners (if you could even call them that) in comparison.
If you're interested in folgezettel and outlining, you might appreciate some subtleties in Bob's piece: https://writing.bobdoto.computer/folgezettel-is-not-an-outline-luhmanns-playful-appreciation-of-disfunction/
cross reference https://hypothes.is/a/OhcWSjxyEe6V8DP9P6WNQQ
-
-
sunghoyahng.substack.com sunghoyahng.substack.com
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
This method is interesting, I like the aesthetics of such commonplace books. However, in terms of functionality, it is nearly fully replaced with the Antinet Zettelkasten method. Perhaps I could use some of this to improve my journals though? In addition, this does inspire me to create progressive summarization pages of my ideas and concepts, contained in Sage Scientia, in Notion or Obsidian.
A method such as this, or Zettelkasten, can help create theoretical expertship... It might not be the MOST EFFICIENT, but it is highly effective.
-
-
www.nerosnotes.co.uk www.nerosnotes.co.uk
-
https://www.nerosnotes.co.uk/collections/foglietto
Looks sort of similar to Ugmonk's offerings...
-
-
reasonabledeviations.com reasonabledeviations.com
-
https://reasonabledeviations.com/2022/04/18/molecular-notes-part-1/
Maybe come back to read this???
-
-
-
https://zettelkasten.de/posts/textmate-zettelkasten/
TextMate could be used as a Zettelkasten app, but doesn't do active links for files and the search is very basic.
-
-
www.hoppersofficefurniture.com www.hoppersofficefurniture.com
-
Has carried used metal card index files in the past for $295
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Does anyone has it’s Zettelkasten in Google Docs, Microsoft Word or Plain Tex (without a hood app like obsidian or The Archive)? .t3_15fjb97._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/Efficient_Earth_8773 at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/15fjb97/does_anyone_has_its_zettelkasten_in_google_docs/
Experimenting can be interesting. I've tried using spreadsheet software like Google Sheets or Excel which can be simple and useful methods that don't lose significant functionality. I did separate sheets for zettels, sources, and the index. Each zettel had it's own row with with a number, title, contents, and a link to a source as well as the index.
Google Docs might be reasonably doable, but the linking portion may be one of the more difficult affordances to accomplish easily or in a very user-centric fashion. It is doable though: https://support.google.com/docs/answer/45893?hl=en&co=GENIE.Platform%3DDesktop, and one might even mix Google Docs with Google Sheets? I could see Sheets being useful for creating an index and or sources while Docs could be used for individual notes as well. It's all about affordances and ease of use. Text is a major portion of having and maintaining a zettelkasten, so by this logic anything that will allow that could potentially be used as a zettelkasten. However, it helps to think about how one will use it in practice on a day-to-day basis. How hard will it be to create links? Search it? How hard will it be when you've got thousands of "slips"? How much time will these things take as it scales up in size?
A paper-based example: One of the reasons that many pen and paper users only write on one side of their index cards is that it saves the time of needing to take cards out and check if they do or don't have writing on the back or remembering where something is when it was written on the back of a card. It's a lot easier to tip through your collection if they're written only on the front. If you use an alternate application/software what will all these daily functions look like compounded over time? Does the software make things simpler and easier or will it make them be more difficult or take more time? And is that difficulty and time useful or not to your particular practice? Historian and author David McCullough prefers a manual typewriter over computers with keyboards specifically because it forces him to slow down and take his time. Another affordance to consider is how much or little work one may need to put into using it from a linking (or not) perspective. Using paper forces one to create a minimum of at least one link (made by the simple fact of filing it next to another) while other methods like Obsidian allow you to too easily take notes and place them into an infinitely growing pile of orphaned notes. Is it then more work to create discrete links later when you've lost the context and threads of potential arguments you might make? Will your specific method help you to regularly review through old notes? How hard will it be to mix things up for creativity's sake? How easy/difficult will it be to use your notes for writing/creating new material, if you intend to use it for that?
Think about how and why you'd want to use it and which affordances you really want/need. Then the only way to tell is to try it out for a bit and see how one likes/doesn't like a particular method and whether or not it helps to motivate you in your work. If you don't like the look of an application and it makes you not want to use it regularly, that obviously is a deal breaker. One might also think about how difficult/easy import/export might be if they intend to hop from one application to another. Finally, switching applications every few months can be self-defeating, so beware of this potential downfall as you make what will eventually need to be your ultimate choice. Beware of shiny object syndrome or software that ceases updating in just a few years without easy export.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
A Fred-box could be very useful. This contains cards with useful snippets of thought, very small usually, that don't need a particular ordering or connection of thought but are worth it to be reminded of every now and then, a shuffle if it were.
If need be used in connective thought as well, the content could be copied over into an Antinet entry as well.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Jul 2023
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
https://zettelkasten.de/posts/overview/
Good overview of the method and details for how to implement.
Possibly the king of the one page zettelkasten descriptions.
-
-
www.magneticmemorymethod.com www.magneticmemorymethod.com
-
https://www.magneticmemorymethod.com/zettelkasten/
I'd found this page through general search and then a few days later someone from Metivier's "team" (an SEO hire likely) emailed me to link to it from a random zk page on my own site (not a great one).
Metivier seems to have come to ZK from the PKM space (via a podcast I listened to perhaps?). This page isn't horrible, but seems to benefit greatly from details I've added to the Wikipedia page over the past few years.
-
-
-
Isn’t it too much time and energy consuming? I’m not provoking, I’m genuine.
reply to IvanCyb at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/1587onp/comment/jt8zbu4/?utm_source=reddit&utm_medium=web2x&context=3 Asking broadly about indexing methods in zettelkasten
When you begin you'll find yourself creating lots of index entries to start, in part because you have none, but you'll find with time that you need to do less and less because index entries already exist for most of what you would add. More importantly most of the entries you might consider duplicating are likely to be very near cards that already have those index entries.
As an example if you have twenty cards on cultural anthropology, the first one will be indexed with "cultural anthropology" to give you a pointer of where to start. Then when you need to add a new card to that section, you'll look up "cultural anthropology" and skim through what you've got to find the closest related card and place it. You likely won't need to create a new index entry for it at all.
But for argument's sake, let's say you intend to do some work at the intersection of "cultural anthropology" and "writing" and this card is also about "writing". Then you might want to add an index entry for "writing" from which you'll branch off in the future. This will tend to keep your index very sparse. As an example you can look at Niklas Luhmann's digitized collection to notice that he spent his career in the area of "sociology" but there are only just a few pointers from his index into his collection under that keyword. If he had tagged every single card related to "sociology" as "sociology" in his index, the index entry for it would have been wholly unusable in just a few months. Broadly speaking his entire zettelkasten is about sociology, so you need to delve a few layers in and see which subtopics, sub-subtopics, sub-sub-subtopics, etc. exist. As you go deeper into specific topics you'll notice that you branch down and out into more specific subareas as you begin to cover all the bases within that topic. If you like, for fun, you can see this happening in my digital zettelkasten on the topic of "zettelkasten" at https://hypothes.is/users/chrisaldrich?q=tag%3A%22zettelkasten%22. The tool only shows the top 50 tags for that subject in the side bar, but you can slowly dig down into subtopics to see what they look like and a bit of how they begin to overlap.
Incidentally, this is one of the problems with those who tag everything with top level topic headings in digital contexts—you do a search for something important and find so much that it becomes a useless task to try to sift through it all. As a result, users need better tools to give them the ability to do more fine-grained searching, filtering, and methods of discovery.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Hello! I've recently encountered the Zettelkasten system and adore the emphasis on connecting ideas. However, I don't want to use the traditional index card way, seeing as I have a ring binder with 90 empty pages thus I don't want it to go to waste. I've researched a lot of methods using a notebook, where some organize their zettels by page number, while others write as usual and connect and index the ideas for every 30 pages or so. But considering that the loose-leaf paper can be in any order I chose, I think there can be a better workaround there. Any suggestions? Thanks in advance!
reply to u/SnooPandas3432 at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/158tzk7/zettelkasten_on_a_ring_binder_with_looseleaf_paper/
She didn't specify a particular dimension, but I recall that Beatrice Webb used larger sheets of paper than traditional index-card sized slips in her practice and likely filed them into something akin to hanging files in a filing cabinet.
For students, I might suggest using the larger sheets/3-ring binder to make Cornell notes for coursework and then later distilling down one or two of the best ideas from a lecture or related readings into index card form for filing away over time. You could then have a repository of bigger formatted literature notes from books/lectures with more space and still have all the benefits of a more traditional card-based zettelkasten for creativity and writing. You could then have the benefit of questions for spaced repetition for quizzes/tests, while still keeping bigger ideas for writing papers or future research needs.
-
-
blog.ayjay.org blog.ayjay.org
-
https://blog.ayjay.org/unanswered-questions/
The index-card based notes pictured in this post certainly makes me think that Alan Jacobs has the sort of note taking/commonplace book sort of practice I thought he would.
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
Robert Hutchins, former dean of Yale Law School (1927–1929), president (1929–1945) and chancellor (1945–1951) of the University of Chicago, closes his preface to his grand project with Mortimer J. Adler by giving pride of place to Adler's Syntopicon. It touches on the unreasonable value of building and maintaining a zettelkasten:
But I would do less than justice to Mr. Adler's achievement if I left the matter there. The Syntopicon is, in addition to all this, and in addition to being a monument to the industry, devotion, and intelligence of Mr. Adler and his staff, a step forward in the thought of the West. It indicates where we are: where the agreements and disagreements lie; where the problems are; where the work has to be done. It thus helps to keep us from wasting our time through misunderstanding and points to the issues that must be attacked. When the history of the intellectual life of this century is written, the Syntopicon will be regarded as one of the landmarks in it. —Robert M. Hutchins, p xxvi The Great Conversation: The Substance of a Liberal Education. 1952.
Adler's Syntopicon has been briefly discussed in the forum.zettelkasten.de space before. However it isn't just an index compiled into two books which were volumes 2 and 3 of The Great Books of the Western World, it's physically a topically indexed card index or a grand zettelkasten surveying Western culture. Its value to readers and users is immeasurable and it stands as a fascinating example of what a well-constructed card index might allow one to do even when they don't have their own yet. For those who have only seen the Syntopicon in book form, you might better appreciate pictures of it in slipbox form prior to being published as two books covering 2,428 pages:
 Two page spread of Life Magazine article with the title "The 102 Great Ideas" featuring a photo of 26 people behind 102 card index boxes with categorized topical labels from "Angel" to "Will".
Two page spread of Life Magazine article with the title "The 102 Great Ideas" featuring a photo of 26 people behind 102 card index boxes with categorized topical labels from "Angel" to "Will".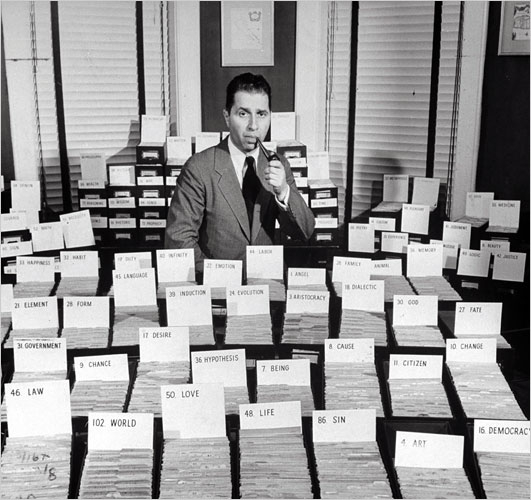 Mortimer J. Adler holding a pipe in his left hand and mouth posing in front of dozens of boxes of index cards with topic headwords including "law", "love", "life", "sin", "art", "democracy", "citizen", "fate", etc.
Mortimer J. Adler holding a pipe in his left hand and mouth posing in front of dozens of boxes of index cards with topic headwords including "law", "love", "life", "sin", "art", "democracy", "citizen", "fate", etc.Adler spoke of practicing syntopical reading, but anyone who compiles their own card index (in either analog or digital form) will realize the ultimate value in creating their own syntopical writing or what Robert Hutchins calls participating in "The Great Conversation" across twenty-five centuries of documented human communication. Adler's version may not have had the internal structure of Luhmann's zettelkasten, but it definitely served similar sorts of purposes for those who worked on it and published from it.
References
- LIFE. “The 102 Great Ideas: Scholars Complete a Monumental Catalog.” January 26, 1948. https://books.google.com/books?id=p0gEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA92&source=gbs_toc_r&cad=2#v=onepage&q&f=false. Google Books.
- Hutchins, Robert M. The Great Conversation: The Substance of a Liberal Education. Edited by Robert M. Hutchins and Mortimer J. Adler. 1st ed. Vol. 1. 54 vols. Great Books of the Western World. Chicago, IL: Encyclopedia Britannica, Inc., 1952.
syndication link: https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/2623/mortimer-j-adlers-syntopicon-a-topically-arranged-collaborative-slipbox/
-
-
-
But I would do less than justice to Mr. Adler's achieve-ment if I left the matter there. The Syntopicon is, in additionto all this, and in addition to being a monument to the indus-try, devotion, and intelligence of Mr. Adler and his staff, astep forward in the thought of the West. It indicates wherewe are: where the agreements and disagreements lie; wherethe problems are; where the work has to be done. It thushelps to keep us from wasting our time through misunder-standing and points to the issues that must be attacked.When the history of the intellectual life of this century iswritten, the Syntopicon will be regarded as one of the land-marks in it.
p xxvi
Hutchins closes his preface to his grand project with Mortimer J. Adler by giving pride of place to Adler's Syntopicon.
Adler's Syntopicon isn't just an index compiled into two books which were volumes 2 and 3 of The Great Books of the Western World, it's physically a topically indexed card index of data (a grand zettelkasten surveying Western culture if you will). It's value to readers and users is immeasurable and it stands as a fascinating example of what a well-constructed card index might allow one to do even when they don't have their own yet.
Adler spoke of practicing syntopical reading, but anyone who compiles their own card index (in either analog or digital form) will realize the ultimate value in creating their own syntopical writing or what Robert Hutchins calls participating in "The Great Conversation" across twenty-five centuries of documented human communication.
See also: https://hypothes.is/a/WF4THtUNEe2dZTdlQCbmXw
The way Hutchins presents the idea of "Adler's achievement" here seems to indicate that Hutchins didn't have a direct hand in compiling or working on it directly.
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/622/syntopicon
Some in the ZK space have looked at the Syntopicon, but they primarily see the finished book product and don't seem to be aware of the slip-based portion of the project.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Is there any app like Obsidian for visual (art) research?
reply to u/gate18 at https://www.reddit.com/r/ObsidianMD/comments/14ve4gi/is_there_any_app_like_obsidian_for_visual_art/
Aby Warburg had a significant physical card-based zettelkasten he used for his visual research in the early 1900s. Perhaps you'd find some interesting inspiration by looking at his methods?
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Converting Commonplace Books? .t3_14v2ohz._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/ihaveascone at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/14v2ohz/converting_commonplace_books/
Don't convert unless you absolutely need to, it will be a lot of soul-crushing make work. Since some of your practice already looks like Ross Ashby's system, why not just continue what you've been doing all along and start a physical index card-based index for your commonplaces? (As opposed to a more classical Lockian index.) As you browse your commonplaces create index cards for topics you find and write down the associated book/page numbers. Over time you'll more quickly make your commonplace books more valuable while still continuing on as you always have without skipping much a beat or attempting to convert over your entire system. Alternately you could do a paper notebook with a digital index too. I came across https://www.indxd.ink, a digital, web-based index tool for your analog notebooks. Ostensibly allows one to digitally index their paper notebooks (page numbers optional). It emails you weekly text updates, so you've got a back up of your data if the site/service disappears. This could potentially be used by those who have analog commonplace/zettelkasten practices, but want the digital search and some back up of their system.
-
-
www.ebay.com www.ebay.com
-
https://www.ebay.com/itm/155257403398
An Underwood & Underwood cabinet for storing stereoview (or stereograph) photos. Could potentially repurposed as a zettelkasten cabinet as the slip sizes should generally be compatible.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
A zettelkasten if used properly by the practitioner, can also have these elements of GRINDE integrated (though it is more textual than visual): - you group knowledge by linking (making a initial connection with folgezettel) - reflective: what you write reflects your own ideas in relation to what you read or are learning (and it is very non-linear) - with a ZK, you can make more distant connections to other notes, and bring them together in hubs - in these hubs, you can create a flow of notes, deciding which are stronger/better, in order (which allows you to emphasise what is better etc.)
note: a ZK is for long term, while a mind map is limited in scope (though probably better for the short term)
-
-
www.amazon.com www.amazon.com
-
www.flickr.com www.flickr.com
-
https://www.flickr.com/photos/hawkexpress/194730263
Hawk Sugano used a Correct Indexcard Dock (C-153DF) box for some of his index card practice.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Inserting a maincards with lack of memory .t3_14ot4na._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } Lihmann's system of inserting a maincard is fundamentally based on a person's ability to remember there are other maincards already inserted that would be related to the card you want to insert.What if you have very poor memory like many people do, what is your process of inserting maincards?In my Antinet I handled it in an enhanced method from what I did in my 27 yrs of research notebooks which is very different then Lihmann's method.
reply to u/drogers8 at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/14ot4na/inserting_a_maincards_with_lack_of_memory/
I would submit that your first sentence is wildly false.
What topic(s) cover your newly made cards? Look those up in your index and find where those potentially related cards are (whether you remember them or not). Go to that top level card listed in your index and see what's there or in the section of cards that come after it. Find the best card in that branch and file your new card(s) as appropriate. If necessary, cross-index them with sub-topics in your index to make them more findable in the future. If you don't find one or more of those topics in your index, then create a new branch and start an index entry for one or more of those terms. (You'll find yourself making lots of index entries to start, but it will eventually slow down—though it shouldn't stop—as your collection grows.)
Ideally, with regular use, you'll likely remember more and more, especially for active areas you're really interested in. However, take comfort that the system is designed to let you forget everything! This forgetting will actually help create future surprise as well as serendipity that will actually be beneficial for potentially generating new ideas as you use (and review) your notes.
And if you don't believe me, consider that Alberto Cevolini edited an entire book, broadly about these techniques—including an entire chapter on Luhmann—, which he aptly named Forgetting Machines!
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
"I keep a dated diary of sorts on index cards, though they rarely go past one card a day."This is something I haven't heard of before. So, you journal/diary on index cards, one per day?
reply to u/taurusnoises (Bob Doto) at tk
Yep, for almost a full year now on 4x6" index cards. (Receipts for the kids: https://boffosocko.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/wp-1688411021709-scaled.jpg)
Previously I'd used a Hobonichi Cousin (page per day) journal for this. (Perhaps I should have stayed with the A6 size instead of the larger A5 for consistency?) Decades ago (around 1988ish?) I had started using a 2 page per day DayTimer pocket planners (essentially pre-printed/timed index cards spiral bound into monthly booklets which they actually shipped in index card-like plastic boxes for storage/archival purposes). Technically I've been doing a version of this for a really long time in one form or another.
It generally includes a schedule, to do lists (bullet journal style), and various fleeting notes/journaling similar to the older Memindex format, just done on larger cards for extra space. I generally either fold them in half for pocket storage for the day or carry about in groups for the coming week(s) when I'm away from my desk for extended periods (also with custom blank index card notebooks/pads).
I won't go into the fact that in the 90's I had a 5,000+ person rolodex... or an index card (in the entertainment they called them buck slips) with the phone numbers and names of \~100 people I dealt with regularly when early brick cell phones didn't have great (or any) storage/functionality.
-
reply to Bob Doto at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/14lcb4z/using_diaries_and_journals_as_source_material_for/
Ross Ashby kept his notes in notebooks/journals but he did cross-index them by topic using index cards. Rather than reference them by notebook (name/title/date) and page number, he kept a set of handwritten running page numbers across the entirety of his notebooks, so instead of Notebook 15 page 55, 1952 he'd simply write "3786" for page 3786. This can be seen on his index card for the indexed word "determinate" as an example.
For other examples, see: http://www.rossashby.info/journal/index/index.html
My own notebooks are usually titled by year and date spans along with page numbers, so I'll use those roughly as Bob describes. This has made it much easier to not need to move all my older notes into a card-based system, but still make them useable and referenceable.
For those with more explicit journaling, diary, or other writing habits, Ralph Waldo Emmerson makes an interesting example of practice as he maintained at least two commonplace books (a poetry-specific one and a general one) as well as a large set of writing journals where he experimented with writing before later publishing his work. Since there are extant (digitized and published copies) and large bodies of scholarship around them, they make an interesting case study of how his process worked and how others might imitate it.
On the diary front, of the historical examples I've seen floating around, only Roland Barthes had a significant practice of keeping his "diary" in index card form, a portion of which was published on October 12, 2010. Mourning Diary is a collection published for the first time from Roland Barthes' 330 index cards focusing on his mourning following the death of his mother in 1977.
Not as extensive, Vladimir Nabokov recorded a "diary" of sixty-four dreams on 118 index cards beginning on October 14, 1964 as an experiment. He was following the instructions of John Dunne, a British philosopher, in An Experiment with Time. The results were published by Princeton University Press in Insomniac Dreams: Experiments with Time by Vladimir Nabokov which was edited by Gennady Barabtarlo.
Presumably if one keeps a diary or journal in index card form in chronological order, they can simply reference it by date and either time or card X of Y, if there are multiple card entries for a single day. I keep a dated diary of sorts on index cards, though they rarely go past one card a day.
-
-
writing.bobdoto.computer writing.bobdoto.computer
-
https://writing.bobdoto.computer/using-diaries-and-journals-as-source-material-for-zettelkasten-notes/
Additional commentary at r/Zettelkasten - Using diaries and journals as source material for zettelkasten notes by Bob Doto
Bob lays out some basic ideas for citing one's personal journal, diaries, notebooks, and other non-published writing for use in a Luhmann-artig zettelkasten. While he focuses on the scale of the mechanics of citation of one's own notes in other forms, what he's really doing is giving people explicit permission to overlap traditions to more easily use their work from other places in their zettelkasten.
Compare this with Scott Scheper's related article on 2023-05-24 at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/13qzgjs/connecting_a_zettelkasten_to_a_commonplace_book/ (and the related YouTube video in which he talks about giving things an "address".
Unmentioned is that in many citation managers, one would likely use a "manuscript" format for citations here. Upon checking it looks like Zotero doesn't have data fields for page number, paragraph, or line numbers for their manuscript type.
-
All source material is handled more or less the same way when working with a Luhmann-style zettelkasten.
I like the fact that Bob Doto is explicitly carving out the space of a Luhmann-style zettelkasten versus all the other flavors.
-
-
item.taobao.com item.taobao.com
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Zk for analyzing components
reply to u/graidan at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/14n5131/zk_for_analyzing_components/
I'm intending to use some of my zk for analysis of components for their uses. Specifically, for looking at materia magica (magical ingredients) across authors / books / systems / etc. For example, all the ways that dandelion is used, looking for consistent commonalities and reasoning.
How would you do this in a ZK system? Create a branch per items under investigation? I feel like a digital solution like notion might work best, but I'd like to incorporate into my analog if I can figure out a good way to do it.
I like u/taurusnoises' description and understand it, but perhaps an alternate perspective and some examples of how others have done these things may be helpful?
One feature/affordance that a Luhmann-esque zettelkasten emphasizes is the ability to build on knowledge from the bottom up while older commonplace book and non-Luhmann zettelkasten traditions have a more top-down and/or categorical-first approach. Either of these methods can be tried in your use case to good benefit, but it helps to think about what is happening over the long run. Bottom up approaches are more useful when you're encountering new material and aren't always sure how to categorize it or know where things may be heading. These also tend to encourage greater admixtures of disparate topics, especially over use with time. Top down approaches are potentially better when you've got a broad idea of fields and sub-fields to begin with and know exactly where new ideas will best fit. Because of this they don't naturally tend to mix disparate fields of knowledge as easily, though this can be done with foresight.
It sounds like you're well-acquainted with your area (of magical ingredients) already, so you're more likely to appreciate a top down approach as a result. A Luhmann-esque zettelkasten is certainly workable here, but you'll be able to scaffold some of your material more easily from the start. You know in advance some of the structure of where you're going and what sorts of questions you'll want to ask of your notes, so you can structure it to be more helpful from the start.
As an example, in your materia magica case (for which I'll make some broad assumptions without any knowledge of the field), you might have a branch for dandelion. Under dandelion you can aggregate notes on what various authors have to say about specific uses and features. Over time you'll have a variety of notes which will allow you to quickly compare and contrast what those authors have to say about the topic. You can repeat this for other herbs, mushrooms, etc. This may make your writing on this particular area much easier.
Of course, potential complications may occur later when you may have different questions about the ideas you've collected. Perhaps you'll ask something like, how did practices differ in different geographical areas? Was practice with dandelions the same across different regions or across time? Did practices for other herbs show similar patterns? This may require additional sets of notes which can cross reference time spans and areas. To better handle this with your initial notes branching according to herbs, you may want to make project notes (maps of content, hub notes, structure notes, or whatever you want to call them) on each of these criteria with links back to the originals for studying and comparing these differences.
To make this easier, you can pull out all the original notes and reorder them accordingly and then make your project notes by noting the original card identifiers/numbers. Or perhaps you just use them to write the particular section directly. Once you're done, you can use the original numbers to file them back into the appropriate places for later use.
The broader ZK community doesn't talk as frequently or as in-depth about adding metadata relating to time, place, etc. for sorting/resorting or searching for material. Having actual index cards may make doing all of this a lot easier.
As illustrative examples, Beatrice Webb talks a bit about her use of collecting notes/data across a variety of dimensions for her sociology work as "scientific notetaking" in Appendix C of her book My Apprenticeship (1926). Broadly speaking, she's using her notes as an early form of searchable database. Similarly, Victor Margolin has a short video about his process for writing about history of design and there he's using his notes along the lines of both location as well as time. In both of these examples, we're looking at non-Luhmann-artig practices (somehow it seems more appropriate to use the German -artig than the French -esque), but I'm sure they would have worked just as well with a Luhmann structured practice as well.
And of course if none of this still makes any sense, I highly recommend you try it anyway. Your experience will assuredly bear out results and you're sure to find the answers you're looking for, and probably a little more to boot. Let us know what you find.
-
- Jun 2023
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
When I create a new note, I write and link it as usual. Then I call up a saved search in The Archive via shortcut. I then go through the notes of my favorites and see if the fresh note is usable for one of my favorites. In doing so, I make an effort to find a connection. This effort trains my divergent thinking. Afterward, I try to understand the nature of the connection from the fresh piece of paper. In this way, I train my convergent thinking.
Sascha's process of incoporating the problems into the ZK workflow
-
This technique is another demonstration of Feynman’s genius. It is simple and efficient: Maintain a collection of 12 favorite problems. Whenever you learn something new, check if it helps you with one of your 12 favorite problems. Richard Feynman was fond of giving the following advice on how to be a genius. You have to keep a dozen of your favorite problems constantly present in your mind, although by and large they will lie in a dormant state. Every time you hear or read a new trick or a new result, test it against each of your twelve problems to see whether it helps. Every once in a while there will be a hit, and people will say, “How did he do it? He must be a genius!”
Effective problem-solving method that can be incorporated with ease in the Zettelkasten technique.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
When it comes to thinking, the Zettelkasten solves an important issue which is the problem of scope, which is impossible at the current moment in mindmapping software such as Concepts.
Mainly, Zettelkasten allows you gain a birds-eye holistic view of a topic, branch, or line of thought, while allowing you to at the same time also gain a microscopic view of an "atomic" idea within that thought-stream, therefore creating virtually infinite zoom-in and zoom-out capability. This is very, very, beneficial to the process of deep thinking and intellectual work.
-
Think of branches not as collections, but rather as conversations
When a branch starts to build, or prove itself, then ask the question (before indexing): "What is the conversation that is building here?"
Also related to Sönke Ahrens' maxim of seeking Disconfirming Information to counter Confirmation Bias. By thinking of branches as conversations instead of collectives, you are also more inclined to put disconfirming information within the branch.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Out of curiosity: anyone here joining Camp NaNo this July? :) .t3_14l2dfo._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/nagytimi85 at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/14l2dfo/out_of_curiosity_anyone_here_joining_camp_nano/
With my ZK I feel like it's NaNoWriMo all the time... Here's some prior conversation about this: https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/xrlnqx/anyone_doing_nanowrimo/
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
The author goes into the correlation between categorization (branching) and the use of the index and the focus on them respectively. He mentions he "learned" that branching would be more beneficial than the using of the index to make finding the cards easier.
I strongly disagree with this focus. I agree with the "relational" principle of put the card between the one that has the closest proximital conceptual relation. The Zettelkasten's power relies in serendipitous creativity (or creativity/insight by chance), this is facilitated highly by the use of connectivity between cards, where each card as you go down the "hierarchy" of "branches" will be more unrelated to the original topic. (See also Luhmann's paper Communication with Zettelkasten, Manfred Kuehn Translation and Johannes F.K. Schmidt's article on Zettelkasten within Forgetting Machines, as well as his video presentation about Zettelkasten). In short, the friction of searching for cards by following trains of thought through connectivity boosters insight by chance and therefore facilitates the power of the system.
This is also, I believe, why Bob Doto argues to let categories emerge after the creation of notes/streams of thought instead of making the names for the "branches" up front.
I believe Luhmann himself also emphasized the use of the index by calling it a system of "query into the database," the index is the main navigational map for the Zettelkasten. If you have a question for your "communication partner" the index is the way to go. For example, if I wanted to know the impact of cognitive load theory within employee management as a CEO, I would go to my index and collect the entrances for both "branches" or terms, and then start reading these thought streams... Afterward, I might synthesize and create a new branch somewhere, in one of the aforementioned categories, or an entire new one, where I put the results of this questioning.
My own system of numbering and branching in this way is the following: A number signifies a note's position within a stream of thought. I branch off if, following the relational principle, a note adds unto a thought on a specific card, but not the stream specifically. This gets signified by a letter.
So, 1a1, 1a2, 1a3, and 1a4 are all part of the same stream while 1a, 1b, and 1c would all be different "branches" stemming from the original card that would be 1 in this case. This can repeat infinitely, therefore facilitating what Luhmann calls "Infinite potential for inward growth" of the system. It's autopoietic and cybernetic. (See also: The Radical Luhmann by Hans-Georg Moeller).
Something that can benefit the finding of notes once the system grows sufficiently large is the use of "structure" or "hub" cards where you put down a few key entrances to concepts related to this stream of thought or "branch" in remote sections of the Zettelkasten.
-
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
I develop ideas, theories on my overview Zettel. Sometimes, like in the book I write after finishing my next one, titled “Modernity as disease”, I develop a theory in a Zettel which serves as an outline and manuscript at the same time. I always state that the method should bend around your thinking and not the other way around. I just can think and write - the Zettelkasten Method does the rest. This is the freedom of the digital version.
-
There is a difference between normal academic reading and reading for the Zettelkasten. It is not about understanding the author but about filling your archive with meaningful thoughts and how to improve its content and connections.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
What I love and appreciate from Metivier, he will cite his sources. He makes it super easy to go back to his sources and mine those materials myself. He gives credit to other memory experts and is transparent throughout his books and course about where he is in his own process of growing and learning. In summary, we don't need originality, we need what works and in the scholarly world- syncretizing multiple sources and distilling them into a process IS original even if every building block is coming from another source. We're all standing on the shoulders of the giants before us.
My note-taking method is informed by the commonplace book and zettelkasten: why reinvent a wheel that needs no reinventing (it is only, really, about translating things from one medium to another)
-
As Chris Aldridge says, for centuries the Zettelkasten approach was the standard and universal method for producing books and articles - until personal computers took over. Nearly every serious work ever published before the 1980s was drafted either with index cards or paper slips, or else with notebooks in a commonplace style. Every writer had their own take on these two options, but that’s what they all used. Then, in a single decade, word processing software took over. These days, most writers use something like Microsoft Word or Google Docs (just try persuading your publisher you’re not giving them a docx file). Scrivener became popular because it critiqued the ‘endless roll of paper’ model and reverted to an index card interface of sorts. But it remained a niche.Today, you either thrive on that word processor model or you don’t. I really don’t, which is why I’ve invested effort, as you have, in researching previous writing workflows, older than the all-conquering PC of the late 1980s and early 90s. At the same time, new writing tools are challenging the established Microsoft way, but in doing so are drawing attention to the fact that each app locks the user into a particular set of assumptions about the drafting and publishing process.The current academic scene is a brutal war to publish or perish. It’s not unusual for a researcher to write or co-write 30-40 peer-reviewed articles per year. General publishing is also frenetic. In the UK, 20 books are published every hour of the day. It all makes Luhmann’s ‘prolific’ output look lazy. Now though, AI is blowing the entire field apart. From now on, prolific writing is what computers do best. There’s no reason not to publish 20,000 books per hour. Soon enough, that will be the output per ‘author’. Where the pieces will eventually land is anyone’s guess. For example, the workflow of the near future might involve one part writing and nineteen parts marketing. Except that AI has got that sewn up too. Meanwhile, until the world ends, I’m just having fun doing my thing.
Before the advent of the computer, the use of a zettelkasten or commonplace book to research was "common place".
What happened with the transition? Perhaps the methodology was lost in the transition, people just dumping things into a word file?
-
-
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x6jyFE9Ps_Q
Possible example for zettelkasten output project
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K3uHeNgy5GM
Possible example for zettelkasten output project.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
A zettelkasten involves a lot of layers in Bloom's taxonomy (see third annotation with context)
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
The command to schools—the invective about education—was, perhaps as ever, Janus-like: the injunction was to teach more and getbetter results, but to get kids to be imaginative and creative at the same time.They had to learn the facts of science, but they shouldn’t have original thinkingsqueezed from them in the process. It was the formal versus progressivecontroversy in a nutshell.
Can the zettelkasten method be a means of fixing/helping with this problem of facts versus creativity in a programmatic way?
-
There are many things that we have to take on trust; everyminute of every day we have to accept the testimony and the guidance of thosewho are in a position to offer an authoritative view.
Perhaps there is a need for balance between the two perspectives of formal and progressive education. While one can teach another the broad strokes of the "rules" of note taking, for example, using the zettelkasten method and even give examples of the good and the bad, the affordances, and tricks, individuals are still going to need to try things out to see what works for them in various situations and for their specific needs. In the end, its nice to have someone hand one the broad "rules" (and importantly the reasons for them), so that one has a set of tools which they can then practice as an art.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
According to Henderson, there are three steps to keeping a commonplace book:
1) Read (Consume)
"Commonplace books begin with observation."
2) Capture (Write) Always also capture the source.
3) Reflect Write own thoughts about the material. Synthesize, think.
I'd personally use a digital commonplace book (hypothes.is), like Chris Aldrich explains, as my capture method and my Antinet Zettelkasten as my reflect methodology. This way the commonplace book fosters what Luhmann would call the thought rumination process.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
(1:21:20-1:39:40) Chris Aldrich describes his hypothes.is to Zettelkasten workflow. Prevents Collector's Fallacy, still allows to collect a lot. Open Bucket vs. Closed Bucket. Aldrich mentions he uses a common place book using hypothes.is which is where all his interesting highlights and annotations go to, unfiltered, but adequately tagged. This allows him to easily find his material whenever necessary in the future. These are digital. Then the best of the best material that he's interested in and works with (in a project or writing sense?) will go into his Zettelkasten and become fully fledged. This allows to maintain a high gold to mud (signal to noise) ratio for the Zettelkasten. In addition, Aldrich mentions that his ZK is more of his own thoughts and reflections whilst the commonplace book is more of other people's thoughts.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Personal Website
reply to u/GlitteringFee1047 at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/147yj2b/personal_website/
I've got a personal site at https://boffosocko.com which I've had for many years and used in part as a digital commonplace book/pseudo-zettelkasten. I've been an active member of the IndieWeb community for many years as well and happy to answer any questions about those experiences. To bring things closer to the overlap of that and this particular community, folks may appreciate the following related material:
-
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
In Carlin’s archives, by contrast, the jokes were “mainly scraps of paper organized into Ziploc baggies then put into a folder by topic.”
quote by Journey Gunderson, the executive director of the National Comedy Center
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
I'm curious if anyone has ever experimented with making an online Luhmann-esque Zettelkasten using WikiMedia as their platform?
What were the pros/cons you found for doing so?
Have you tried other methods (index cards, Obsidian, other(s)?), and if so what affordances did MediaWiki provide or were lacking for what you were attempting to accomplish?
Did you use transclusion functionality?
Did you attempt to build or implement backlink functionality? Use the API or plugins for this?
Did you build some sort of custom index (manually, programatically, other)?
If you used it for writing, what methods did you attempt with respect to taking the smaller pieces/ideas and building them up into longer written pieces?
Links to specific public examples are welcome here. I'll also accept links to public versions of commonplace books or similar forms which also use MediaWiki as their infrastructure.
syndication link: https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/144hzn9/zettelkasten_with_mediawiki/
-
-
www.dsebastien.net www.dsebastien.net
-
The Zettelkasten method aims to help you forget.
I would argue that it is more subtle than this. It allows you to forget, but the aim is to allow you to learn, remember, and slowly build.
-
-
-
These links to these threads are priceless. Two questions: How can I connect with these Reddit users? Never mind, I’m sure I can find the answer myself. Second question - how do you keep these thread references so handy? Is this hypothes.is ? Zotero? Raindrop.io? I have no idea how to capture this kind of info and keep it accessible.
reply to u/coachdan007 at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/13ygoz9/comment/jn80a7z/?utm_source=reddit&utm_medium=web2x&context=3
Mostly these references were using Hypothesis, though I do have some material in Zotero. I don't use Raindrop. IIRC, I knew I'd seen the topics before and did a search for the tag bible and then narrowed it down my adding on zettelkasten and it popped up immediately. A large number of my replies here are just querying my digital ZK and spitting out pre-packaged answers or pointers to relevant material. I also occasionally do the same thing with my analog version, though with those I have to type them out. I follow roughly the same process for doing my own queries and writing. You get surprisingly good at it after a while, particularly when you know it's in there somewhere. Of course r/ has it's own internal search function too, so you could check out: - https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/search/?q=bible&restrict_sr=1 - https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/search/?q=bible&restrict_sr=1
and have a slightly wider net to get the fishes and loaves you're seeking. With the proper notes at hand, perhaps you'll soon be able to turn water into wine? Interestingly, I think you're the first who's ever asked this question here (or other related fora). I hope people don't think I spend all my time writing all these custom answers when I'm just tipping out my zettelkasten. (Though I do always keep my original answers too in the eventuality that I ever want to turn all of these thoughts into an article or book.)
-
-
www.ebay.com www.ebay.com
-
Quarter Sawn Tiger Oak 6 Drawer Card Catalog Vintage American Business Systems
https://www.ebay.com/itm/256099662210
American Business Systems Co. at 212 Summer Street, Boston, MA manufactured six drawer wooden card indexes some time circa early 1900s.
-
-
writingslowly.com writingslowly.com
-
The lost index cards of Harold Innis :: Writing Slowly — by Richard (aka u/atomicnotes)
snippets on my note with some brief extensions...
I'm aware that HI's collection is now missing, but it could be partially recreated from typescript and the numbered notes.
-
Manuscript Collection #845, Innis Papers, Archives of the University of Toronto, Thomas Fisher Library, Box 8
Presumably the archives which contain the papers of Harold Innis.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Zettelkasten Lesson Plan Intro
Not much here beyond his longer article, though it does have a sample format for zettel which can be useful for those starting out.
-
-
www.ebay.com www.ebay.com
-
Wabash NYC Moving Notice, Wabash Cabinet Company, Wabash, IN Indiana 1942
https://www.ebay.com/itm/334894285475
On a postcard dated 1942-07-01, the Wabash Cabinet Company announced the "Removal of its New York Office on July 1st to 60 EAST 42nd STREET, (Lincoln Building)".
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
I have read that a Maincard's Keyword usually is not a word that is used in the thought that you wrote on the card.
reply to u/drogers8 at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/13wlfbs/how_to_select_a_keyword_for_your_main_card/
I'm don't think I've ever seen that advice anywhere in my own reading. I've been doing this for ages and would suggest that it's actively bad advice. Use a keyword that seems useful, beneficial, and which you're likely to have the most interest in in the future. What do you suspect the future you will use to search for that card or a branch on that idea in the future? Use that.
Also, don't overthink this stuff. Just practice. You're going to make some mistakes, but with a small number of cards you'll start to figure it out on your own before things get too large. Your practice today is not going to look like your practice in 6 months and it'll change again 6 months after that.
-
- May 2023
-
random-blather.com random-blather.com
-
https://random-blather.com/2014/04/28/information-isnt-power/
 Illustration by David Somerville based on the original by Hugh McLeod.
Illustration by David Somerville based on the original by Hugh McLeod.Link to: https://hypothes.is/a/ysRBGgACEe6UNPvIvmWBkQ
This diagram is roughly a cartoon of the zettelkasten process, especially if the panels are labeled: reading, excerpting/synopsis, linking, serendipity, writing.
-
-
www.nicksantalucia.com www.nicksantalucia.com
-
Santalucia, Nick. “The Zettelkasten in the Secondary Classroom.” Blog, July 6, 2021. https://www.nicksantalucia.com/blog/the-zettelkasten-in-the-secondary-classroom-k12.
-
Hyper-zettelkastenStudents stick all of their zettels on the walls with sticky tack or tape (be sure students initial or mark their zettels before doing this).Then, students walk around the room and search for connections and create original ideas using those connections.Students physically attach those zettels with string (like a conspiracy theorist would) and stick a zettel on the string explaining the connection.
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
@chrisaldrich, I appreciate your feedback. Indeed there is magic in making notes which comes not only from finding connections in the ZK but also from making connections in mind. Maybe I'm confused. A mindset that makes note-making fun is one way to recruit the body's dopamine mechanism. This creates a positive feedback loop. More mote-making turns to more dopamine which turns to more note-making. Maybe even some notes on dopamine. (I have 11 already!) My sense of Luhmann's phrase "second memory" is a rehashing of an idea—a continued exploration. Using the ZK method is one way of formalizing the continued review of ideas. Without a formal process, it is too easy to fall into old bad habits and not work towards "the serendipity of combinatorial creativity. "
Reply to Will Simpson at https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/comment/17939/#Comment_17939
There should be more conversation about zettelkasten as both a "ratchet" as well as a "flywheeel". Sometimes I feel like it's hard to speak of these things for either lack of appropriate words/naming and/or having a shared vocabulary for them.
Even Luhmann's "second memory" has a mushiness to it, but I certainly see your sense of it as a thing which moves forward. I have the same sort of sense with the Aboriginal cultural idea of a "songline" which acts as both a noun as well as having an internal sense of being a verb to me. The word "google" has physically and specifically undergone the transition from noun to verb in a way which "second memory" and "songline" haven't, though perhaps they should? The difference is that the word google is much more concrete and simple while second memory and songline have a lot more cultural material and meaning sitting with them if you know them and their fuller attendant practices.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/13tv9ls/question_how_fast_did_you_name_your_antinet/
Mine was a bit into the process, but not until I got the filing cabinet where they'll all ultimately live: https://boffosocko.com/2022/08/08/55808119/#Naming
See examples of people naming them here including: - Cvrie (Fallout 4 reference) - torspedia (after username on MediaWiki installation) - Todd (Bad Words reference to study binder) - Plumeria (after 4 months) - Hamilton after video - Epictetus (meaning "to acquire" from stoicism) - Zeke (short for Ezekiel) - Stewie (personal communication, Scheper's nickname, not mentioned on this page)
-
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
I like to imagine that Bob Ross lends his voice to point to the “happy accidents” that happen while working with Zettelkastens.
Bob Ross' "happy accidents" tied to the idea of serendipity or the outcome of combinatorial creativity within a zettelkasten.
Ross's version is related to experimentation and the idea of adjacent possible. Taking a current known and extending it to see what will happening and accepting the general outcome. This was one of the roots of his creative process.
-
communication partners
super interesting that Luhmann referred to his zettelkasten as a communication partner explicitly himself.
also interesting given AI models are easier to train now with several models already open sourced which allows actual interaction with your notes! would love to see where it goes.
-
-
-
of course I had done a lot of thinking even before I ever used a ZK, but now I can record, retrieve, and elaborate these thoughts easily so that they accumulate over time to something bigger. Now, writing a paper or grant proposal often comes down to concatenating a bunch of notes.
-
Wittgenstein, Luhmann, Conrad Gessner, Leibniz, Linnaeus and Walter Benjamin are some I can think of off the top of my head.
reply to u/muhlfriedl by way of reply to u/chounosumuheya at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/13s6dsg/comment/jlpt8ai/?utm_source=reddit&utm_medium=web2x&context=3
Examples of zettelkasten users
S.D. Goitein, Beatrice Webb, Ludwig Wittgenstein, Harold Innis, Victor Margolin, Eminem, Aby Warburg, Antonin Sertillanges, Jacques Barzun, C. Wright Mills, Gotthard Deutsch, Roland Barthes, Umberto Eco, Vladimir Nabokov, Gerald Weinberg, Michael Ende, Twyla Tharp, Hans Blumenberg, Keith Thomas, Arno Schmidt, Mario Bunge, Sönke Ahrens, Dan Allosso for a few more. If you go with those who used commonplace books and waste books, which are notebook-based instead of index card-based, there are thousands upon thousands more.
Historically the easier question might be: what creators didn't use one of these systems and was successful?!? The broad outlines of these methods go back much, much farther than Niklas Luhmann. These patterns are not new...
Personally, I've used my own slip box to write large portions of the articles on my website. I also queried it to compile this reply.
-
-
writing.bobdoto.computer writing.bobdoto.computer
-
The entire point of writing short-ish, single-idea notes—so-called "atomic notes"—is because it’s easier to connect a single idea to many other single-ideas, then it is to connect a complex idea to other complex ideas. We do this, not to gain insight or make meaningful connections, but to write more. Writing is the place where insight is finally crystallized. So, for people who want to write a lot and very often and very regularly, having hundreds of connected ideas to pull from on a weekly basis is a huge win!
Atomic notes are not for making connections, but to facilitate more writing
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
But I wouldn't call them a ZK® (stealing Andy's shorthand!) but they were a box of notes (Zettelkasten?).
-
It is unfortunate that the German word for a box of notes is the same as the methodology surrounding Luhmann.
reply to dandennison84 at https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/comment/17921/#Comment_17921
I've written a bit before on The Two Definitions of Zettelkasten, the latter of which has been emerging since roughly 2013 in English language contexts. Some of it is similar to or extends @dandennison84's framing along with some additional history.
Because of the richness of prior annotation and note taking traditions, for those who might mean what we're jokingly calling ZK®, I typically refer to that practice specifically as a "Luhmann-esque zettelkasten", though it might be far more appropriate to name them a (Melvil) "Dewey Zettelkasten" because the underlying idea which makes Luhmann's specific zettelkasten unique is that he was numbering his ideas and filing them next to similar ideas. Luhmann was treating ideas on cards the way Dewey had treated and classified books about 76 years earlier. Luhmann fortunately didn't need to have a standardized set of numbers the way the Mundaneum had with the Universal Decimal Classification system, because his was personal/private and not shared.
To be clear, I'm presently unaware that Dewey had or kept any specific sort of note taking system, card-based or otherwise. I would suspect, given his context, that if we were to dig into that history, we would find something closer to a Locke-inspired indexed commonplace book, though he may have switched later in life as his Library Bureau came to greater prominence and dominance.
Some of the value of the Dewey-Luhmann note taking system stems from the same sorts of serendipity one discovers while flipping through ideas that one finds in searching for books on library shelves. You may find the specific book you were looking for, but you're also liable to find some interesting things to read on the shelves around that book or even on a shelf you pass on the way to find your book.
Perhaps naming it and referring to it as the Dewey-Luhmann note taking system or the Dewey-Luhmann Zettelkasten may help to better ground and/or demystify the specific practices? Co-crediting them for the root idea and an early actual practice, respectively, provides a better framing and understanding, especially for native English speakers who don't have the linguistic context for understanding Zettelkästen on its own. Such a moniker would help to better delineate the expected practices and shape of a note taking practice which could be differentiated from other very similar ones which provide somewhat different affordances.
Of course, as the history of naming scientific principles and mathematical theorems after people shows us, as soon as such a surname label might catch on, we'll assuredly discover someone earlier in the timeline who had mastered these principles long before (eg: the "Gessner Zettelkasten" anyone?) Caveat emptor.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dU7efgGEOgk
I wish he'd gotten into more of the detail of the research and index card making here as that's where most of the work lies. He does show some of his process of laying out and organizing the cards into some sort of sections using 1/3 cut tabbed cards. This is where his system diverges wildly from Luhmann's. He's now got to go through all the cards and do some additional re-reading and organizational work to put them into some sort of order. Luhmann did this as he went linking ideas and organizing them up front. This upfront work makes the back side of laying things out and writing/editing so much easier. It likely also makes one more creative as one is regularly revisiting ideas, juxtaposing them, and potentially generating new ones along the way rather than waiting until the organization stage to have some of this new material "fall out".
-
-
www.krapp.org www.krapp.org
-
Professor of Film & Media Studies, Informatics, English, and Music - UC Irvine
-
-
www.amazon.com www.amazon.com
-
I am wholly unsurprised that Harold Innis maintained a card index (zettelkasten) through his research life, but I am pleased to have found that his literary estate has done some work on it and published it. The introduction seems to have some fascinating material on the form and structure as well as decisions on how they decided to present and publish it.
https://www.amazon.com/Idea-Harold-Adams-Innis-Heritage/dp/0802063829/
-
-
-
Another important 20th-century thinker to rely on index cards was pioneering media theo-rist Harold Innis.18 The executors of his estate published a tome called The Idea File (1980),composed of 18 inches of index cards, plus five inches of reference cards. Innis had a selection ofhand-written index cards typed up and numbered, 1 through 339. It is unclear if these rumina-tions on television and art, communication and trade, secrecy and money, literature and the oraltradition, archives and history were intended to constitute a book project; the decision to publishthe cards balances the putative will to posterity of an author, and the potential embarrassmentof incomplete work. Clearly Innis intended to work synchronically rather than diachronically,to focus less on logical connections than on analogies, to practice pattern recognition—andthe associative links of a card index lend themselves perfectly to this kind of project.
-
A type-script of 768 pages (labeled simply The Big Typescript) dated from 1933 had been in the estatesince 1951, but only in 1967 were the “Zettel” recognized from which it was compiled.Cut-and-paste was integral: “Usually he continued to work with the typescripts. A methodwhich he often used was to cut up the typed text into fragments (‘Zettel’) and to rearrangethe order of the remarks”.17
via: Georg Henrik von Wright, “The Wittgenstein Papers,” The Philosophical Review 78:4 (1969), 483–563, here: 487.
von Wright seems to indicate that Wittgenstein created typescripts which he cut up into zettel and then was able to rearrange them into final forms.
-
-
www.3x5life.com www.3x5life.com
-
Compare with other products in this category: - Analog (Jeff Sheldon productivity system) - Memindex - Bullet Journal - Frictionless Capture Cards - Pile of Index Cards

-
-
-
Connecting a Zettelkasten to a Commonplace Book
Interesting to see Scott trying this... I'm sure I've seen it before in a setting like this, but its obviously been done in the commonplace space by itself.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Although Niklas Luhmann used zettelkasten on the basis of his academic works, I have seen very few sources on the academic use of zettelkasten, except for a few videos. Is there any source you can recommend on this subject?Another question I have is about the academic reuse of notes. After Luhmann used a note in one academic text, how did he use that note again in another work? Or in general, how can we avoid self-plagiarism in the academic use of zettelkasten?
reply to u/edumanos at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/13p0myn/academic_using_of_zettelkasten/
The Luhmann's method was very specific to him, but the broader slip box method has been in wide use in academic settings for centuries, particularly in the humanities. I most often recommend Umberto Eco's book in conjunction with Adler/Van Doren's How to Read a Book, but below are a small selection of manuals on very closely related note taking methods. These can be found in a handful of languages and some even more specific to particular areas of study, though broadly they're all useful to almost any area. You'll note that some are available for free on archive.org as they're out of copyright, have been scanned, or are open educational resources. I've tried to link most of these for convenience.
If this list isn't enough, or you're looking for something written for a specific subfield (sociology, for example), let me know as I'm sure there are a plethora of others, or even some fun short pieces like: - Thomas, Keith. “Diary: Working Methods.” London Review of Books, June 10, 2010. https://www.lrb.co.uk/the-paper/v32/n11/keith-thomas/diary. - Mills, C. Wright. “On Intellectual Craftsmanship (1952).” Society 17, no. 2 (January 1, 1980): 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02700062.
My favorite short/overview video is that of Victor Margolin's process: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kxyy0THLfuI.
As for self-plagiarism, some have used a red pencil or other means to mark cards (notes) they've used in specific works as they write so that they know they've been used and can then self-cite their prior works to avoid self-plagiarism or to up their citation count.
- Ahrens, Sönke. How to Take Smart Notes: One Simple Technique to Boost Writing, Learning and Thinking – for Students, Academics and Nonfiction Book Writers. Create Space, 2017.
- Allosso, Dan, and S. F. Allosso. How to Make Notes and Write. Minnesota State Pressbooks, 2022. https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/write/.
- Barzun, Jacques. The Modern Researcher. Boston : Houghton Mifflin Co., 1992. http://archive.org/details/modernresearcher00barz_1.
- Bernstein, Mark. Tinderbox: The Tinderbox Way. 3rd ed. Watertown, MA: Eastgate Systems, Inc., 2017. http://www.eastgate.com/Tinderbox/TinderboxWay/index.html.
- Blair, Ann M. “Manuals on Note-Taking (Ars Excerpendi).” In Brill’s Encyclopaedia of the Neo-Latin World. Brill, May 7, 2014. https://referenceworks.brillonline.com/entries/encyclopaedia-of-the-neo-latin-world/manuals-on-note-taking-ars-excerpendi-B9789004271029_0058.
- Chavigny, Paul Marie Victor. Organisation du travail intellectuel, recettes pratiques à l’usage des étudiants de toutes les facultés et de tous les travailleurs. Paris: Delagrave, 1918. https://catalog.hathitrust.org/Record/011209555.
- DeCarlo, Matthew, Cory Cummings, and Kate Agnelli. Graduate Research Methods in Social Work. Open Social Work, 2021. https://doi.org/10.21061/msw-research.
- Dow, Earle Wilbur. Principles of a Note-System for Historical Studies. New York: Century Company, 1924.
- Eco, Umberto. How to Write a Thesis. Translated by Caterina Mongiat Farina and Geoff Farina. 1977. Reprint, Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press, 2015. https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/how-write-thesis.
- Gessner, Konrad. Pandectarum Sive Partitionum Universalium. 1st Edition. Zurich: Christoph Froschauer, 1548.
- Goutor, Jacques. The Card-File System of Note-Taking. Approaching Ontario’s Past 3. Toronto: Ontario Historical Society, 1980. http://archive.org/details/cardfilesystemof0000gout.
- Heyde, Johannes Erich, and Heinz Siegel. Technik des wissenschaftlichen Arbeitens. 10th ed. 1931. Reprint, Berlin: Kiepert, 1970. https://www.worldcat.org/title/TECHNIK-DES-WISSENSCHAFTLICHEN-ARBEITENS.-MIT-E.-ERG.BEITR.-DOKUMENTATION-VON-HEINZ-SIEGEL.-10.DURCHGES.AUFL/oclc/1075391218.
- Kuntze, Friedrich. Die Technik der geistigen Arbeit (The technique of mental work). Carl Winter’s Universitätsbuchhandlung, 1923.
- Langlois, Charles Victor, and Charles Seignobos. Introduction to the Study of History. Translated by George Godfrey Berry. First. New York: Henry Holt and company, 1898. http://archive.org/details/cu31924027810286.
- ———. Introduction to the study of history. London, Cass, 1966. http://archive.org/details/introductiontos00langgoog.
- Leicester, Mal, and Denise Taylor. Take Great Notes. 1st edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications Ltd, 2019.
- Maxfield, Ezra Kempton. “Suggestions for Note Taking.” Delaware College Bulletin 6, no. 4 (December 1910).
- Mei, Jennifer. Refining, Reading, Writing : Includes 2009 Mla Update Card. Nelson Canada, 2007. http://archive.org/details/refiningreadingw0000meij.
- Range, Ellen. Take Note! Taking and Organizing Notes. Ann Arbor, Michigan: Cherry Lake Publishing, 2014.
- Schrag, Zachary M. The Princeton Guide to Historical Research. Princeton University Press, 2021. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctv1pdrrc9.
- Sertillanges, Antonin Gilbert. La vie intellectuelle; son esprit, ses conditions, ses méthodes. Paris, Éditions de la Revue des jeunes, 1921. http://archive.org/details/lavieintellectue00sert.
- Sertillanges, Antonin Gilbert, and Mary Ryan. The Intellectual Life: Its Spirit, Conditions, Methods. First English Edition, Fifth printing. 1921. Reprint, Westminster, MD: The Newman Press, 1960. http://archive.org/details/a.d.sertillangestheintellectuallife.
- Seward, Samuel Swayze. Note-Taking. Boston, Allyn and Bacon, 1910. http://archive.org/details/cu31924012997627.
- Webb, Sidney, and Beatrice Webb. Methods of Social Study. London; New York: Longmans, Green & Co., 1932. http://archive.org/details/b31357891.
- Weinberg, Gerald M. Weinberg on Writing: The Fieldstone Method. New York, N.Y: Dorset House, 2005.
Good luck!
-
-
www.arno-schmidt-stiftung.de www.arno-schmidt-stiftung.de
-
https://www.arno-schmidt-stiftung.de/Archiv/Zettelarchiv.html
The »notes of the day« shown so far from Arno Schmidt's note box for »Zettel's Traum« can be downloaded here:
-
-
-
Oryginalnie na fiszkach Zettelkasten nie ma kolorów, ale postanowiłam to akurat trochę zmienić.
Nie wiem, skąd wzięło się to stwierdzenie. Nawet jeśli zawiesimy kwestię oryginalności Zettelkasten (gdzie jest bowiem oryginał?) i weźmiemy pod uwagę chociążby to, jak notował Luhmann, to zauważymy, że kolorów (przede wszystkim czerwonego) u niego nie brakuje.
-
O ile tagi są podstawą Zettelkasten, o tyle kategorie to już moja interpretacja.
Nie jestem właśnie przekonany. Nie wiem, co tu jest podstawą, a co nie. Według mnie istotą Zettelkasten jest gromadzenie informacji w jednym miejscu, a tym, co pozwala to jedno miejsce określić są kategorie, etykiety z kolei pozwalają nawigować po notatkach, które mogą być rozsiane po różnych kategoriach.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
I went to that website and he mentions the Dewey Decimal Classification System. I have look around and only found examples/files that goes a few levels deep. He gives an example: 516.375 Finsler geometry BUT I can not find any DDC files that goes to that level of classification. The DDC is finer grain than the what the AOoD system goes so for me I am going with the DDC for possible keywords list.Any ideas where I can find a complete DDC listing I can download?
reply to drogers8 at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/13eyg8p/comment/jkaksn4/?utm_source=reddit&utm_medium=web2x&context=3
You can find some basic top level or second level DDC listings online, but to get the full set of listings, you've got to subscribe to the system which is updated every few years, something only library systems and large publishers typically do. To give yourself an idea of how deep this rabbit hole goes the DDC 23 is four volumes long and each volume is in the 1,000 page range. The DDC 23 self-identifies as 0.25.4'31-dc22. For most categories DDC generally only goes as deep as the thousands place (like Finsler geometry) though others will go slightly deeper usually to designate locations/cities. Most libraries only categorize to the tenths place, and sometimes these numbers can be found on the copyright page of books, often with the DDC volume number. I mentioned the UDC in that piece, but didn't give any links, but you could try:<br /> - https://udcsummary.info/php/index.php?lang=en - https://udcc.org/index.php/site/page?view=subject_coverage - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_Decimal_Classification
Honestly, you're wasting time and making way more work for yourself to adopt one of these numbering methods for a Luhmann-esque zettelkasten. Try asking yourself this question: What benefits/affordances will I get in the long run for having my numbering system mirror the DDC or UDC? (Unless you can come up with a really fantastic answer, you're just making more work to look up headings/numbers on a regular basis.)
In practice the numbers are simply addresses so you can quickly find things again using your index. If you're doing threads of cards (folgezettel), you're going to very quickly have tangentially related ideas of things mixed together anyway. (As an example, I've got lots of science and even some anthropology mixed into my math section, so having DDC numbers on those would be generally useless at the end of the day.) If it helps, Nicolas Gatien has a pretty reasonable and short video which makes this apparent: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tdHH3YjOnZE.
-
Extended numbering and why use Outline of Disciplines at all? .t3_13eyg8p._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } Several things:Why are there different listings for the Academic Outline of Disciplines? Some starts the top level with Humanities and other start with Arts which changes the numbering?I am createing an Antinet for all things. Some of the levels of the AOOD has more then 9 items so Scott's 4 digit system would not work. For some levels I would have to use two digits. Thoughts?Why even use said system? Why is it a bad reason to just start with #1 that indicates the first subject sequence, #2 for a different subject etc..?
reply to u/drogers8 at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/13eyg8p/extended_numbering_and_why_use_outline_of/
Based on my research, Scott Scheper was the one of the original source for people adopting the Academic Outline of Disciplines. I've heard him say before that he recommends it only as a potential starting place for people who are new to the space and need it as a crutch to get going. It's an odd suggestion as almost all of the rest of his system is so Luhmann-based. I suspect it's a quirk of how he personally started and once moving it was easier than starting over. He also used his own ZK for showing others, and it's hard to say one thing in a teaching video when showing people something else. Ultimately it's hard to mess up on numbering choices unless you're insistent on using only whole numbers or natural numbers. I generally wouldn't suggest complex numbers either, but you might find some interesting things within your system if you did. More detail: https://boffosocko.com/2022/10/27/thoughts-on-zettelkasten-numbering-systems/ The only reason to have any standardized base or standardized numbers would be if you were attempting to have a large shared ZK with others. If this is your intent, then perhaps look at the Universal Decimal Classification, though a variety of things might also work including Dewey Decimal.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Requesting advice for where to put a related idea to a note I'm currently writing .t3_13gcbj1._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } Hi! I am new to building a physical ZK. Would appreciate some help.Pictures here: https://imgur.com/a/WvyNVXfI have a section in my ZK about the concept of "knowledge transmission" (4170/7). The below notes are within that section.I am currently writing a note about how you have to earn your understanding... when receiving knowledge / learning from others. (Picture #1)Whilst writing this note, I had an idea that I'm not quite sure belongs on that note itself - and I'm not sure where it belongs. About how you also have to "earn" the sharing of knowledge. (Picture #2)Here are what I think my options are for writing about the idea "you have to earn your sharing of knowledge":Write this idea on my current card. 4170/7/1Write this idea on a new note - as a variant idea of my current note. 4170/7/1aWrite this idea on a new note - as a continuation of my current note. 4170/7/1/1Write this idea on a new note - as a new idea within my "knowledge transmission" branch. 4170/7/2What would you do here?
reply to u/throwthis_throwthat at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/13gcbj1/requesting_advice_for_where_to_put_a_related_idea/
I don't accept the premise of your question. This doesn't get said often enough to people new to zettelkasten practice: Trust your gut! What does it say? You'll learn through practice that there are no "right" answers to these. Put a number on it, file it, and move on. Practice, practice, practice. You'll be doing this in your sleep soon enough. As long as it's close enough, you'll find it. Save your mental cycles for deeper thoughts than this.
Asking others for their advice is fine, but it's akin to asking a well-practiced mnemonist what visual image they would use to remember something. Everyone is different and has different experiences and different things that make their memories sticky for them. What works incredibly well for how someone else thinks and the level of importance they give an idea is never as useful or as "true" as how you think about it. Going with your gut is going to help you remember it better and is far likelier to make it easier to find in the future.
-
"So when they continued asking him, he lifted himself up and said to them, he who has not misfiled an idea among you, let him cast the first zettel at her." —Iēsū's zettelkasten, card 8/7,1 #John ⚡🗃️
-
-
-
Figure 2.3 The fi xation of paper slips. (From Wellisch 1981, p. 12.)
This is essentially a version of a modern pinboard with ribbons which are used to hold various pieces onto the board!
Also similar in functionality to Post-it Notes, but with string instead of glue.
-
-
www.ebay.com www.ebay.com
-
4" x 6" Card File Cabinet
Overall measurements for Steelmaster Index Card file for 4 x 6" index cards are 16” deep x 12.25” wide x 5.25” tall.
-
-
www.ebay.com www.ebay.com
-
howaboutthis.substack.com howaboutthis.substack.com
-
I take a lot of notes during my day job. More like a huge amount of notes. On paper. As an experiment I started using several Dingbats* notebooks during the day job to see how they would work4 for me. After about 9 weeks of trials, I learned that I could fill up a 180 page notebook in about 3 weeks, plus or minus a few days. Unfortunately, when you factor in the cost of these notebooks, that’s like spending $1 - $2 per day on notebooks. Dingbats* are lovely, durable notebooks. But my work notes are not going to be enshrined in a museum for the ages5 and until I finally get that sponsorship from Dingbats* or Leuchtuurm19176, I probably need a different solution.
Mark Dykeman indicates that at regular work, he fills up a 180 page notebook and at the relatively steep cost of notebooks, he's paying $1-2 a day for paper.
This naturally brings up the idea of what it might cost per day in index cards for some zettlers' practices. I've already got some notes on price of storage...
As a rough calculation, despite most of my note taking being done digitally, I'm going through a pack of 500 Oxford cards at $12.87 every 5 months at my current pace. This is $0.02574 per card and 5 months is roughly 150 days. My current card cost per day is: $0.02574/card * 500 cards / (150 days) = $12.78/150 days = $0.0858 per day which is far better than $2/day.
Though if I had an all-physical card habit, I would be using quite a bit more.
On July 3, 2022 I was at 10,099 annotations and today May 11, 2023 I'm at 15,259 annotations. At one annotation per card that's 5,160 cards in the span of 312 days giving me a cost of $0.02574/card * 5,160 cards / 312 days = $0.421 per day or an average of $153.75 per year averaging 6,036 cards per year.
(Note that this doesn't also include the average of three physical cards a day I'm using in addition, so the total would be slightly higher.)
Index cards are thus, quite a bit cheaper a habit than fine stationery notebooks.
-
-
howaboutthis.substack.com howaboutthis.substack.com
-
https://howaboutthis.substack.com/p/the-knowledge-that-wont-fit-inside-6d3
Reasonable one page overview of zettelkasten, though it undersells some of they "why."
Has a good list of some of the more popular one-two page articles floating around the blogosphere at the bottom.
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
via https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/comment/17819#Comment_17819
Zettelkasten tutorials for use with Tana: - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PaScw0zHBuE By Kent Langley - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lkYPlN82LRc By Theo Koppen - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FufUz1EWJVA by Andre Foeken - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wvvsTD2RzKE by Cortex Futura - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CzC62nIhq1s by Ev Chapman
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
"[What] I like about the [zettlekasten] system is that it's a constant reminder to to make up your mind and to specify what you what you're thinking."<br /> —Sönke Ahrens, [Tinderbox Meetup - May 7, 2023 00:30:36]
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
I'd been looking at it like a collection of knowledge. A collection that has no purpose apart from... being a collection. But Zettelkasten should be a place for creativity, playing with ideas with output as the goal (at least for me). It should be fun. And managing it definitely shouldn't take more time than using it for your purposes.
u/ittspelledsindi
-
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
How big is your ZettelKasten? .t3_13b0b5c._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/jordynfly at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/13b0b5c/how_big_is_your_zettelkasten/
The idea of notes per day comes up occasionally, here's some discussion on the last go-round: https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/11z08fq/comment/jdbnchv/?utm_source=reddit&utm_medium=web2x&context=3
Many people, especially when getting started, get wrapped up in the idea of doing this for "increased productivity" or the goal of being as prolific as Niklas Luhmann. I would submit (and think others would back me up anecdotally) that there's far more to the practice than raw (or measurable) productivity as the single, driving value. Perhaps approach it as a way to sharpen and improve your thinking instead? If you're seeing life-like behavior already, that's a good sign of appreciating some of the hidden benefits which are difficult to describe and which are likely more valuable than the "productivity" goals many may have.
I've noted before that S.D. Goitein had 1/3 less index cards than Luhmann over an equivalent research lifetime, but produced a 1/3 more written output (in terms of books and journal articles). Others like Aby Warburg and Gotthard Deutsch (70,000 notes) had significant practices, but their writing output was marginal at best, though their impact and influence were outsized, in part, I would suggest as a result of their zettelkasten work.
Others like Roland Barthes (generally low card output of \~12,500) and Deutsch also used their fichier boîte/card index/zettelkasten as teaching tools, so while their written outputs may have varied considerably, their teaching practices were incredibly influential for the students and generations they encountered afterwards.
This being said, I'll share my current easily countable lower bound dating roughly from 2016 as:
- 15,200 notes
- 32,000+ links
- 2.1M words
(Having a zk in digital form makes it reasonably easy to do these sorts of counts versus analog methods of note making.)
Some additional pathways to learning and practicing, including my own, can be found here: https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/11ay28d/how_did_you_teach_yourself_zettelkasten/
-
Why are folks so obsessed with notes per day? Perhaps a proxy for toxic capitalism and productivity issues? Is the number of notes the best measure or the things they allow one to do after having made them? What is the best measure? Especially when there are those who use them for other purposes like lecturing, general growth, knowledge acquisition, or even happiness?
-
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
baronfig.com baronfig.com
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Arno Schmidt compulsively wrote and hoarded scraps of text on index cards, which he cataloged meticulously. 130,000 of these were compiled together to form the basis for his magnum opus "Bottom's Dream". The German word for an index card is "Zettel". .t3_1267heb._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to https://www.reddit.com/r/Arno_Schmidt/comments/1267heb/arno_schmidt_compulsively_wrote_and_hoarded/
Schmidt's zettelkasten (the direct English translation would be slip box thought card index is more appropriate) (or most likely only portions of it) was featured in the 2013 "Zettelkästen. Maschinen der Phantasie" exhibition in Marbach: https://www.dla-marbach.de/presse/presse-details/news/pm-11-2013/. For the interested, the exhibition did publish a book which will likely have more details, but when I looked about a year ago, it was only available in German.
There is a lot of research on zettelkasten methods, which are most often variations of the commonplace book method transferred into the index card or slip form rather than books/notebooks. I've not looked intensively at Schmidt's practice (yet), but it was likely similar to that of Victor Margolin outlined here, though in Margolin's case it was non-fiction: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kxyy0THLfuI. Vladimir Nabokov and Michael Ende are other writers who used similar methods.
There's some more examples/detail about the idea of zettelkasten (aka card indexes) in general on Wikipedia.
-
-
micro.blog micro.blog
-
For $1,900.00 ?
reply to rogerscrafford at tk
Fine furniture comes at a fine price. 🗃️🤩 I suspect that it won't sell for quite a while and one could potentially make an offer at a fraction of that to take it off their hands. It might bear considering that if one had a practice large enough to fill half or more, then that price probably wouldn't seem too steep for the long term security and value of the contents.
On a price per card of storage for some of the cheaper cardboard or metal boxes you're going to pay about $0.02-0.03 per card, but you'd need about 14 of those to equal this and those aren't always easy to stack and access regularly. With this, even at the full $1,900, you're looking at storage costs of $0.10/card, but you've got a lot more ease of use which will save you a lot of time and headache as more than adequate compensation, particularly if you're regularly using the approximately 20,400 index cards it would hold. Not everyone has the same esthetic, but I suspect that most would find that this will look a lot nicer in your office than 14 cheap cardboard boxes. That many index cards even at discount rates are going to cost you about $825 just in cards much less beautiful, convenient, and highly usable storage.
Even for some of the more prolific zettelkasten users, this sort of storage is about 20 years of use and if you compare it with $96/year for Notion or $130/year for Evernote, you're probably on par for cost either way, but at least with the wooden option, you don't have to worry about your note storage provider going out of business a few years down the line. Even if you go the "free" Obsidian route, with computers/storage/backups over time, you're probably not going to come out ahead in the long run. It's not all apples to apples comparison and there are differences in some of the affordances, but on balance and put into some perspective, it's probably not the steep investment it may seem.
And as an added bonus, while you're slowly filling up drawers, as a writer you might appreciate the slowly decreasing wine/whiskey bottle storage over time? A 5 x 8 drawer ought to fit three bottles of wine or as many fifths of Scotch. It'll definitely accommodate a couple of magnums of Jack Daniels. 🥃🍸🍷My experience also tells me that an old fashioned glass can make a convenient following block in card index boxes.

-
-
en.wiktionary.org en.wiktionary.org
-
A repository, especially of knowledge or information.
https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/alveary
This could be a fine English translation of the German word Zettelkasten.
The relationship to bees here is fascinating with respect to the commonplace tradition as well.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Alternative numbering and classifications .t3_132o4w7._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } Although Wikipedia Outline of academic disciplines seems like an ok place to start, it seems not ideal. Are there any guides I could use to develop my own numbering? I'm a historian, so treating it as a subcategory is not ideal, especially given how diverse this field is when it comes to its scope (what I mean by that is that you can divide history into many subcategories by period, field, geography etc.) I've taken a look at Propædia, which provides some interesting categories, but again, some of which are no interest to me (in terms of making notes about them).TLDR; Do you have any times for developing personal numbering system for your notes using decimal system? I'm developing ideas for my thesis and future dissertation, so I could arrange my notes around categories that, but I'd like to still have place for notes outside this spectrum (ideas for future papers etc.).
reply to u/zielkarz at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/132o4w7/alternative_numbering_and_classifications/
Assigning random decimal numbers is more than adequate and is roughly what you'll have in the long term anyway... see https://boffosocko.com/2022/10/27/thoughts-on-zettelkasten-numbering-systems/ for some of what I've written on this before.
Because of the way that the topology of dense sets work in the real (decimal) numbers, any topic you give a number can be made arbitrarily close to any other topic you choose. As a result the numbers you choose are generally inconsequential, so simply choose something that you feel makes sense to you.
-
- Apr 2023
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Each book was assigned a call number which identified the subject and location, with a decimal point dividing different sections of the call number.
Why do people not generally use the name "call number" when referring to the numbers on their Niklas Luhmann-esque zettelkasten cards?
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
💯
Scott Scheper returns to r/zettelkasten...
-
-
micro.blog micro.blog
-
In Australia index cards are often called 'system cards ', but no one says which system is meant.
In Australia index cards are frequently called system cards,
via micro.blog/writingslowly at https://micro.blog/writingslowly/18676734
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Vicky Zhao indirectly frames the answer for "why have a zettelkasten?", especially for learning, as overcoming the "illusion of competence" which is closely related to the mere-exposure effect and the Dunning–Kruger effect.
-
-
-
-
Any good anti-net programs and Android apps out there? .t3_1301mhl._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } I think that I will get an idea of how to go about doing the anti-net note-taking system with an example done by a program. Also with the use of an Android app. Any recommendations for both my phone and my computer? If both of them may be free. Any feedback is welcome.
reply to u/MisterTTS at https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/1301mhl/any_good_antinet_programs_and_android_apps_out/
I've searched for ages, built programs for myself, and come to the conclusion that there is no really good app or workflow that will allow you to do both paper and digital at the same time without a lot of extra unnecessary repetitive work that doesn't provide you with tangible benefit to pay for itself. The best bet currently to save yourself a lot of time and headache is to pick one or the other and just go with it.
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
In case some haven't been watching, I'll mention that Simon Winchester's new book Knowing What We Know on knowledge to transmission was published by Harper on April 25th in North America. For zettelkasten fans, you'll note that it has some familiar references and suggested readings including by our friends Markus Krajewski, Ann Blair, Iaian McGilchrist, Alex Wright, Anthony Grafton, Dennis Duncan, and Mortimer J. Adler to name but a few.
Many are certain to know his award winning 1998 book The Professor and the Madman which was also transformed into the eponymous 2019 film starring Sean Penn. Though he didn't use the German word zettelkasten in the book, he tells the story of philologist James Murray's late 1800s collaborative 6 million+ slip box collection of words and sentences which when edited into a text is better known today as the Oxford English Dictionary.
If you need some additional motivation to check out his book, I'll use the fact that Winchester, as a writer, is one of the most talented non-linear storytellers I've ever come across, something which many who focus on zettelkasten output may have a keen interest in studying.

Syndication Link: https://forum.zettelkasten.de/discussion/2558/knowing-what-we-know-the-transmission-of-knowledge-from-ancient-wisdom-to-modern-magic/p1?new=1
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
Brainstorming: Cover for the Second Edition
Somehow I've always been disappointed with the two dimensional aspects of the pseudo-diagrams on prior books and articles in the space. If you go with something conceptual, perhaps try to capture a multidimensional systems/network feel? It's difficult to capture the ideas of serendipity and combinatorial complexity at play, but I'd love to see those somehow as the "sexier" ideas over the drab ideas people have when they think of their mundane conceptualizations of "just" notes.
Another idea may be to not go in the direction of the dot/line network map or "electronics circuit board route", but go back to the older ideas of clockworks, pneumatics, and steampunk...
By way of analogy, there's something sort of fun and suggestive about a person operating a Jacquard Loom to take threads (ideas) and fashioning something beautiful (https://photos.com/featured/jacquard-loom-with-swags-of-punched-print-collector.html) or maybe think, "How would John Underkoffler imagine such a machine?"
Now that I'm thinking about it I want a bookwheel (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bookwheel) next to my zettelkasten wheel!
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
How I annotate books as a PhD student (simple and efficient)
She's definitely not morally against writing in her books, but there are so many highlights and underlining that it's almost useless.
She read the book four times because she didn't take good enough notes on it the first three times.
Bruno Latour's Down to Earth
Tools: - sticky tags (reusable) - purple for things that draw attention - yellow/green referencing sources, often in bibliography - pink/orange - extremely important - highlighter - Post It notes with longer thoughts she's likely to forget, but also for writing summaries in her own words
Interesting to see another Bruno Latour reference hiding in a note taking context. See https://hypothes.is/a/EbNKbLIaEe27q0dhRVXUGQ
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Tinderbox Meetup April 23, 2023 Video - On Zettelkasten with Sascha Fast from Zettelkasten.de
Attended this live this morning from about 9:20 - 10:34 am.
Notes archived at https://forum.eastgate.com/uploads/short-url/pnp5ngylsg5XNbRicbnD27SwZLa.zip
Original details and other discussion at https://forum.eastgate.com/t/tinderbox-meetup-sunday-april-23-2023-what-does-it-mean-to-use-tinderbox-as-a-zettelkasten-tool-or-tool-for-what-ever-method-we-individually-might-use/6599/32
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Zettelkasten - How Categories Emerge by Nicolas Gatien
Gatien uses Scheper's suggested top level categories, but shows that it doesn't take long for things to end up in dramatically disparate areas. As a result, why bother with a pre-defined set of categories in the first place?
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
I recently watched the documentary Aby Warburg: Metamorphosis and Memory (Wechsler, 2016) via Kanopy (for free using my local library’s gateway) and thought that others here interested in the ideas of memory in culture, history, and art history may appreciate it. While a broad biography of a seminal figure in the development of art history in the early 20th century, there are some interesting bits relating to art and memory as well as a mention of Frances A. Yates whose research on memory was influenced by Warburg’s library.
Of specific "note” is the fact that Aby Warburg (1866-1929) had a significant zettelkasten-based note taking practice and portions of his collection (both written as well as images) are featured within the hour long documentary. You'll see it in the opening scenes in the background during many of the interviews, but there's also a portion featured at the 30 minute mark which looks at a few of his zettels. Like several other zettelkasten practitioners he had a significant zettelkasten practice but did not publish much, but did lecture quite a lot and had outsized influence both during his life as well as posthumously and his zettelkasten and research remain as an archive for scholars who still study and extend his work.
Sadly, I'm unable to catch any screenshots from the film due to technical glitches, but if folks can figure out how to pull some out, I'd appreciate them.
Aby Warburg's extant zettelkasten at the Warburg Institute's Archive consists of ninety-six surviving boxes (of 104 or possibly more) which contain between 200-800 individually numbered index cards. Dividers and envelopes are used within the boxes to separate the cards into thematic sections.
The digitized version is transcribed in the original German and is not available translated into English (at least as of 2023). The digitized version maintains the structure of the dividers and consists of only about 3,200 items. It can be searched at https://wi-calm.sas.ac.uk/CalmView/Aboutcatalogue.aspx. As examples one can find the record for box 4a on "the Renaissance" at https://wi-calm.sas.ac.uk/CalmView/Record.aspx?src=CalmView.Catalog&id=WIA+III.2.1.+ZK%2f4a&pos=1 and the physical divider inside box 4a for "Jakob Burkhardt" with subsections listed at https://wi-calm.sas.ac.uk/CalmView/Record.aspx?src=CalmView.Catalog&id=WIA+III.2.1.+ZK%2f4a%2f2&pos=1
The Warburg Institute archive had this sample photo of some of his decorative/colorful boxes:
Has anyone visited the Warburg archive in London before?
-
-
wi-calm.sas.ac.uk wi-calm.sas.ac.uk
-
The searchable digital archive for Aby Warburg's zettelkasten at The Warburg Institute: https://wi-calm.sas.ac.uk/CalmView/Default.aspx
-
-
wi-calm.sas.ac.uk wi-calm.sas.ac.uk
-
https://wi-calm.sas.ac.uk/CalmView/Record.aspx?src=CalmView.Catalog&id=WIA+III.2.1.+ZK%2f4a&pos=1
Example of record for ZK box 4a on the Renaissance.
-
-
wi-calm.sas.ac.uk wi-calm.sas.ac.uk
-
An example of a digital record of a physical divider in Aby Warburg's zettelkasten for Jakob Burkhardt with subsections listed.
Ref No: WIA III.2.1. ZK/4a/2<br /> Title: Jakob Burkhardt Briefe<br /> Physical Description: Divider<br /> Contents: Subsections: 1rst level: Vorträg Burckhardt 1927 Sommersemester [appr. 56 items, numbered and unnumbered]; 2nd level: Burckhardt an Nietzsche; 3rd level: Brief Nietzsches an Burckhardt 6 Januar 1889. 2nd level: Jakob Burckhardt und die nordische Kunst Conversations Lexikon, Burckhardt Festwesen, zu Rougemont Cicerone, Wanderer in der Schweiz, Hedlinger, Hedlinger.
-
-
wi-calm.sas.ac.uk wi-calm.sas.ac.uk
-
Collection of Index Card Boxes (Zettelkästen) Aby Warburg’s collection of index cards (III.2.1.ZK), containing notes, bibliographical references, printed material and letters, was compiled throughout the scholar’s life. Ninety-six boxes survive, each containing between 200 and 800 individually numbered index cards. Cardboard dividers and envelopes group these index cards into thematic sections. The online catalogue reproduces the structure of the dividers and sub-dividers with their original titles in German and consists of about 3,200 items. Since the titles are transcribed (and not translated into English) you can only search for words in the original German.
Aby Warburg's extant zettelkasten at the Warburg Institute's Archive consists of ninety-six surviving boxes which contain between 200-800 individually numbered index cards. Dividers and envelopes are used within the boxes to separate the cards into thematic sections.
The digitized version is transcribed in the original German and is not available translated into English (at least as of 2023). The digitized version maintains the structure of the dividers and consists of only about 3,200 items.
-
-
warburg.sas.ac.uk warburg.sas.ac.uk
-
A full catalogue of Aby Warburg's correspondence, the Institute's correspondence up to 1933 and Warburg's index card boxes is available online through the Warburg Institute Archive online database.
A full catalog of Aby Warburg's 104 index card boxes (reference: WIA III.2.1.ZK) are available online by way of The Warburg Institute's online database at http://wi-calm.sas.ac.uk/calmview/. They are catalogued at the file level.
via https://warburg.sas.ac.uk/archive/archive-online-catalogues
-
-
www.kanopy.com www.kanopy.com
-
Aby Warburg: Metamorphosis and Memory. Documentary, Biography, 2016. https://www.kanopy.com/en/lapl/video/5913764.
Written, Directed and Produced by Judith Wechsler<br /> Wechsler2016

-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
does my zettelkasten make writing... harder?
Worried about self-plagiarizing in the future? Others like Hans Blumenberg have struck through used cards with red pencil. This could also be done with metadata or other searchable means in the digital realm as well. (See: https://hypothes.is/a/mT8Twk2cEe2bvj8lq2Lgpw)
General problems she faces: 1. Notetaking vs. writing voice (shifting between one and another and not just copy/pasting) 2. discovery during writing (put new ideas into ZK as you go or just keep writing on the page when the muse strikes) 3. Linearity of output: books are linear and ZK is not
Using transclusion may help in the initial draft/zero draft?<br /> ie: ![[example]] (This was mentioned in the comments as well.)
directional vs. indirectional notes - see Sascha Fast's article
Borrowing from the telecom/cable industry, one might call this the zettelkasten "last mile problem". I've also referred to it in the past as the zettelkasten output problem. (See also the description and comments at https://boffosocko.com/2022/07/12/call-for-model-examples-of-zettelkasten-output-processes/ as well as some of the examples linked at https://boffosocko.com/research/zettelkasten-commonplace-books-and-note-taking-collection/)
Many journal articles that review books (written in English) in the last half of the 20th century which include the word zettelkasten have a negative connotation with respect to ZK and frequently mention the problem that researchers/book writers have of "tipping out their ZKs" without the outlining and argument building/editing work to make their texts more comprehensible or understandable.
Ward Cunningham has spoken in the past about the idea of a Markov Monkey who can traverse one's atomic notes in a variety of paths (like a Choose Your Own Adventure, but the monkey knows all the potential paths). The thesis in some sense is the author choosing a potential "best" path (a form of "travelling salesperson problem), for a specific audience, who presumably may have some context of the general area.
Many mention Sonke Ahrens' book, but fail to notice Umberto Eco's How to Write a Thesis (MIT, 2015) and Gerald Weinberg's "The Fieldstone Method (Dorset House, 2005) which touch a bit on these composition problems.
I'm not exactly sure of the particulars and perhaps there isn't enough historical data to prove one direction or another, but Wittgenstein left behind a zettelkasten which his intellectual heirs published as a book. In it they posit (in the introduction) that rather than it being a notetaking store which he used to compose longer works, that the seeming similarities between the ideas in his zettelkasten and some of his typescripts were the result of him taking his typescripts and cutting them up to put into his zettelkasten. It may be difficult to know which direction was which, but my working hypothesis is that the only way it could have been ideas from typescripts into his zettelkasten would have been if he was a "pantser", to use your terminology, and he was chopping up ideas from his discovery writing to place into contexts within his zettelkasten for later use. Perhaps access to the original physical materials may be helpful in determining which way he was moving. Cross reference: https://hypothes.is/a/BptoKsRPEe2zuW8MRUY1hw
Some helpful examples: - academia : Victor Margolin - fiction/screenwriting: - Dustin Lance Black - Vladimir Nabokov - others...
-
Also I really want to see the someone using their zettlekasten for managing knowledge about stuff not zettlekasten related. Mine mainly revolves about artistic appretiation, creativity and art fundamentals. I've been wanting to make a video series about it, just havent find the time. Your videos serve much as inspiration and as example of how may I go about it.
reply to Sara Martínez at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wQPvrcksjUA&lc=UgzbdJ1cdxkjnN0DBOl4AaABAg
Sara, here are some creative/art-related examples that might help:<br /> Dancer/Choreographer Twyla Tharp used a slightly modified slip box method that included much more than notes on cards for her dance-related work. She describes the process well in chapter 6 of her book "The Creative Habit: Learn It and Use It for Life".
If you're into art and image-based work, Aby Warburg had a zettelkasten with images. Search for details on his "Mnemosyne Atlas" at The Warburg Institute at the School of Advanced Study University of London which has some material you may appreciate.
Product designer khimtan has a visual zettelkasten practice you can find examples of on Reddit in the "Antinet" sub.
A variety of comedians like Phyllis Diller, Joan Rivers, Bob Hope, and George Carlin had zettelkasten practices for their comedy work.
Eminem has a fantastic, but tremendously simple zettelkasten for songwriting. Taylor Swift has a somewhat similar digital version which she has talked about using, though she doesn't use the word zettelkasten to describe it.
-
Tara Brabazon
She may have some material on her YouTube channel on the zettelkasten output problem.
-
-
www.ebay.com www.ebay.com
-
Vintage Remington Rand Library Card File Single Half Table Top Index Dovetail - eBay
$16.00 + tax + $15.48 for shipping
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
1. Zettelkasten for INTERMEDIATE users of Obsidian
Buttons for coprolites and oosik... 🤣
His templates look a lot like some of the work and templates I use to import annotations/notes from Hypothes.is into Obsidian.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
Llewelyn, J. E. “Zettel. By Ludwig Wittgenstein. Edited by G. E. M. Anscombe and G. H. von Wright. Translated by G. E. M. Anscombe. (Oxford: Basil Blackwell. 1967. Pp. v + ve + 124 + 124e. Price 37s 6d).” The Philosophical Quarterly 18, no. 71 (April 1968): 176. https://doi.org/10.2307/2217524.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
natural one: we firstmust find something to say, then organize our material, and then put it intowords.
Finding something to say within a zettelkasten-based writing framework is relatively easy. One is regularly writing down their ideas with respect to other authors as part of "the great conversation" and providing at least a preliminary arrangement. As part of their conversation they're putting these ideas into words right from the start.
These all follow the basic pillars of classic rhetoric, though one might profitably take their preliminary written notes and continue refining the arrangement as well as the style of the writing as they proceed to finished product.
-
one must also submit to the discipline provided by imitationand practice.
Too many zettelkasten aspirants only want the presupposed "rules" for keeping one or are interested in imitating one or another examples. Few have interest in the actual day to day practice and these are often the most adept. Of course the downside of learning some of the pieces online leaves the learner with some (often broken) subset of rules and one or two examples (often only theoretical) and then wonder why their actual practice is left so wanting.
-
-
-
A project of the Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media https://rrchnm.org/portfolio-item/tropy/
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Benefits of sharing permanent notes .t3_12gadut._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/bestlunchtoday at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/12gadut/benefits_of_sharing_permanent_notes/
I love the diversity of ideas here! So many different ways to do it all and perspectives on the pros/cons. It's all incredibly idiosyncratic, just like our notes.
I probably default to a far extreme of sharing the vast majority of my notes openly to the public (at least the ones taken digitally which account for probably 95%). You can find them here: https://hypothes.is/users/chrisaldrich.
Not many people notice or care, but I do know that a small handful follow and occasionally reply to them or email me questions. One or two people actually subscribe to them via RSS, and at least one has said that they know more about me, what I'm reading, what I'm interested in, and who I am by reading these over time. (I also personally follow a handful of people and tags there myself.) Some have remarked at how they appreciate watching my notes over time and then seeing the longer writing pieces they were integrated into. Some novice note takers have mentioned how much they appreciate being able to watch such a process of note taking turned into composition as examples which they might follow. Some just like a particular niche topic and follow it as a tag (so if you were interested in zettelkasten perhaps?) Why should I hide my conversation with the authors I read, or with my own zettelkasten unless it really needed to be private? Couldn't/shouldn't it all be part of "The Great Conversation"? The tougher part may be having means of appropriately focusing on and sharing this conversation without some of the ills and attention economy practices which plague the social space presently.
There are a few notes here on this post that talk about social media and how this plays a role in making them public or not. I suppose that if I were putting it all on a popular platform like Twitter or Instagram then the use of the notes would be or could be considered more performative. Since mine are on what I would call a very quiet pseudo-social network, but one specifically intended for note taking, they tend to be far less performative in nature and the majority of the focus is solely on what I want to make and use them for. I have the opportunity and ability to make some private and occasionally do so. Perhaps if the traffic and notice of them became more prominent I would change my habits, but generally it has been a net positive to have put my sensemaking out into the public, though I will admit that I have a lot of privilege to be able to do so.
Of course for those who just want my longer form stuff, there's a website/blog for that, though personally I think all the fun ideas at the bleeding edge are in my notes.
Since some (u/deafpolygon, u/Magnifico99, and u/thiefspy; cc: u/FastSascha, u/A_Dull_Significance) have mentioned social media, Instagram, and journalists, I'll share a relevant old note with an example, which is also simultaneously an example of the benefit of having public notes to be able to point at, which u/PantsMcFail2 also does here with one of Andy Matuschak's public notes:
[Prominent] Journalist John Dickerson indicates that he uses Instagram as a commonplace: https://www.instagram.com/jfdlibrary/ here he keeps a collection of photo "cards" with quotes from famous people rather than photos. He also keeps collections there of photos of notes from scraps of paper as well as photos of annotations he makes in books.
It's reasonably well known that Ronald Reagan shared some of his personal notes and collected quotations with his speechwriting staff while he was President. I would say that this and other similar examples of collaborative zettelkasten or collaborative note taking and their uses would blunt u/deafpolygon's argument that shared notes (online or otherwise) are either just (or only) a wiki. The forms are somewhat similar, but not all exactly the same. I suspect others could add to these examples.
And of course if you've been following along with all of my links, you'll have found yourself reading not only these words here, but also reading some of a directed conversation with entry points into my own personal zettelkasten, which you can also query as you like. I hope it has helped to increase the depth and level of the conversation, should you choose to enter into it. It's an open enough one that folks can pick and choose their own path through it as their interests dictate.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
To buy or not to buy a course? And, if the latter, which one? .t3_12fowjy._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } questionSo, I've been considering buying an online course for Zettelkasten (in Obsidian). Thing is... There are a bunch of them. Two (maybe three) questions:Is it worth it? Has anyone gone down that path and care to share their experience?Any recommendations? I've seen a bunch of options and really don't have any hints on how to evaluate them.
reply to u/Accomplished-Tip-597 at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/12fowjy/to_buy_or_not_to_buy_a_course_and_if_the_latter/
Which "industry", though? Productivity? Personal Knowledge Management? Neither of these are focused on the idea of a Luhmann-esque specific zettelkastenare they?
For the original poster, what is your goal in taking a course? What do you want to get out of it? What are you going to use such a system for? The advice you're looking for will hinge on these.
Everyone's use is going to be reasonably idiosyncratic, so not knowing anything else, my general recommendation (to minimize time, effort, and expense) would be to read one of the following (for free), practice at some of it for a few weeks before you do anything else. Then if you need it, talk u/taurusnoises into a few consultations based on what you'd like to accomplish. He's one of the few who does this who's got experience in the widest variety of traditions in addition to expertise in the platform you want (though I'd still recommend him if you were using something else.)
- https://zettelkasten.de/posts/overview/
- https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/write/ (just 1-7, though the rest is profitable)
- https://www.academia.edu/35101285/Creating_a_Commonplace_Book_CPB_
-
-
books.google.com books.google.comLIFE2
-

-
A staff of at least 26 created the underlying index that would lay at the heart of the Great Books of the Western World which was prepared in a rented old fraternity house on the University of Chicago campus. (p. 93)
-
-
-
TheSyntopicon invites the reader to make on the set whatever demands arisefrom his own problems and interests. It is constructed to enable the reader,nomatter what the stages of his reading in other ways, to find that part of theGreat Conversation in which any topic that interests him is being discussed.
While the Syntopicon ultimately appears in book form, one must recall that it started life as a paper slip-based card index (Life v24, issue 4, 1948). This index can be queried in some of the ways one might have queried a library card catalog or more specifically the way in which Niklas Luhmann indicated that he queried his zettelkasten (Luhmann,1981). Unlike a library card catalog, The Syntopicon would not only provide a variety of entry places within the Western canon to begin their search for answers, but would provide specific page numbers and passages rather than references to entire books.
The Syntopicon invites the reader to make on the set whatever demands arise from his own problems and interests. It is constructed to enable the reader, no matter what the stages of his reading in other ways, to find that part of the Great Conversation in which any topic that interests him is being discussed. (p. 85)
While the search space for the Syntopicon wasn't as large as the corpus covered by larger search engines of the 21st century, the work that went into making it and the depth and focus of the sources make it a much more valuable search tool from a humanistic perspective. This work and value can also be seen in a personal zettelkasten. Some of the value appears in the form of having previously built a store of contextualized knowledge, particularly in cases where some ideas have been forgotten or not easily called to mind, which serves as a context ratchet upon which to continue exploring and building.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
I just finished my Bachelor thesis working with Obsidian! by u/ThiIsAnkou
100 literature- and about 650 permanentnotes. Thanks to Obsidian and Zettelkasten!
-
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
Luhmann, Niklas. “Improved Translation of ‘Communications with Zettelkastens.’” Translated by Sascha Fast. Zettelkasten Method, April 5, 2023. https://zettelkasten.de/communications-with-zettelkastens/.
-
I decided to translate the German “Zettelkasten” as “Zettelkasten” since I consider this an established term.
An example of a bi-lingual German-English speaker/writer specifically translating and using Zettelkasten as an established word in English.
-
Without variation on given ideas, there are no possibilities of scrutiny and selection of innovations. Therefore, the actual challenge becomes generating incidents with sufficiently high chances of selection.
The value of a zettelkasten is as a tool to actively force combinatorial creativity—the goal is to create accidents or collisions of ideas which might have a high chance of being discovered and selected for.
-
Compared to this structure that offers actualizable connection possibilities, the relevance of the actual content of the note subsides. Much of it quickly becomes useless or is unusable for a concrete occasion. That is true for both collected quotes, which are only worth collecting when they are exceptionally concise, and for your own thoughts.
Luhmann felt that quotations aren't worth collecting unless they were "exceptionally concise, and for your own thoughts."
-
The Zettelkasten needs a couple of years to reach critical mass.
I find that this is not the case. Even a few hundred cards is more than enough to create something interesting.
Though what does he mean specifically by "critical mass"?
-
A Zettelkasten that is constructed based on our instructions can achieve high independence. There may be other ways to achieve this goal. The described reduction to a fixed-placement (but merely formal) order, and the corresponding combination of order and disorder, is at least one of them.
The structural components of Luhmann's zettelkasten which allow for "achieving high independence" are also the same structures found in an indexed commonplace book: namely fixed placement (formally by the order in which things are found and collected) as well as combinations of order and disorder (the methods by which they can be retrieved and read).
-
Similarly, you must give up the assumption that there are privileged places, notes of special and knowledge-ensuring quality. Each note is just an element that gets its value from being a part of a network of references and cross-references in the system. A note that is not connected to this network will get lost in the Zettelkasten, and will be forgotten by the Zettelkasten.
This section is almost exactly the same as Umberto Eco's description of a slip box practice:
No piece of information is superior to any other. Power lies in having them all on file and then finding the connections. There are always connections; you have only to want to find them. -- Umberto Eco. Foucault's Pendulum
See: https://hypothes.is/a/jqug2tNlEeyg2JfEczmepw
Interestingly, these structures map reasonably well onto Paul Baran's work from 1964:

The subject heading based filing system looks and functions a lot like a centralized system where the center (on a per topic basis) is the subject heading or topical category and the notes related to that section are filed within it. Luhmann's zettelkasten has the feel of a mixture of the decentralized and distributed graphs, but each sub-portion has its own topology. The index is decentralized in nature, while the bibliographical section/notes are all somewhat centralized in form.
Cross reference:<br /> Baran, Paul. “On Distributed Communications: I. Introduction to Distributed Communications Networks.” Research Memoranda. Santa Monica, California: RAND Corporation, August 1964. https://doi.org/10.7249/RM3420.
-
(Alternating numbers and letters helps the memory and may be an optical aid when searching notes, but is of course not enough).
The alternation of letters and numbers helps to create some visual differentiation of various branches, but how does it help the memory? Help as in it's easier to search for these sorts of combinations versus remembering strings of only numbers?
-
A content-based system (like a book’s table of contents) would mean that you would have to adhere to a single structure forever (decades in advance!).
Starting a zettelkasten practice with a table of contents as the primary organization is difficult due to planning in advance.
-
There are two ways for a communication system to maintain its integrity over long periods of time: you need to decide for either highly technical specialisation, or for a setup that incorporates coincidence and ad hoc generated information. Translated to note collections: you can choose a setup categorized by topics, or an open one. We chose the latter and, after 26 successful years with only occasionally difficult teamwork, we can report that this way is successful – or at least possible.
Luhmann indicates that there are different methods for keeping note collections and specifically mentions categorizing things by topics first. It's only after this that he mentions his own "open" system as being a possible or successful one.
Tags
- references
- distributed
- commonplace tradition
- tables of contents
- commonplace books vs. zettelkasten
- decentralized
- commonplace books
- insight
- indices
- Niklas Luhmann
- serendipity
- zettelkasten numbering
- topical headings
- collector's fallacy
- read
- quotations
- position
- network theory
- privilege
- historical linguistics
- zettelkasten why
- organization
- topology
- Paul Baran
- idea links
- memory
- planning ahead
- topology of zettelkasten
- card index
- zettelkasten
- Niklas Luhmann's zettelkasten
- Umberto Eco
- centralized
- hw-zettelkasten
- creativity catalysts
- combinatorial creativity
- notes per day
Annotators
URL
-
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
Fast, Sascha. “Field Report #5: How I Prepare Reading and Processing Effective Notetaking by Fiona McPherson.” Zettelkasten Method (blog), March 29, 2022. https://zettelkasten.de/posts/field-report-5-reading-processing-effective-notetaking-mcpherson/.
-
Sascha Fast's conceptual diagram of Human and Zettelkasten
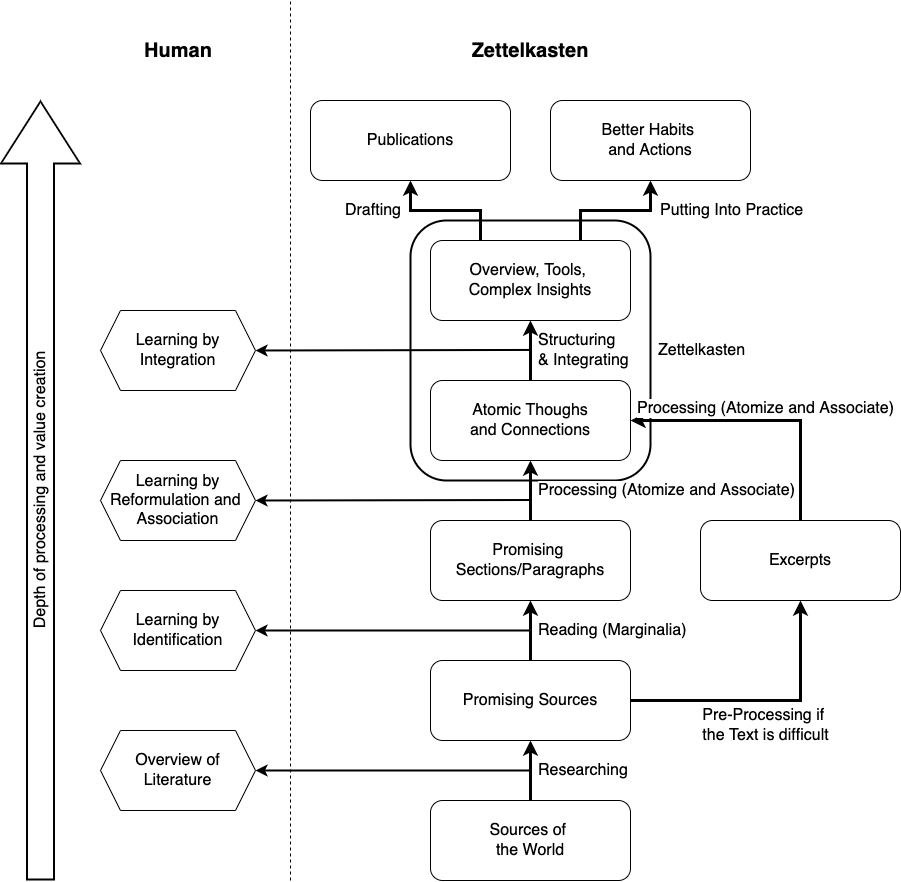
-
-
-
How do I store when coming across an actual FACT? .t3_12bvcmn._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } questionLet's say I am trying to absorb a 30min documentary about the importance of sleep and the term human body cells is being mentioned, I want to remember what a "Cell" is so I make a note "What is a Cell in a Human Body?", search the google, find the definition and paste it into this note, my concern is, what is this note considered, a fleeting, literature, or permanent? how do I tag it...
reply to u/iamharunjonuzi at https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/12bvcmn/how_do_i_store_when_coming_across_an_actual_fact/
How central is the fact to what you're working at potentially developing? Often for what may seem like basic facts that are broadly useful, but not specific to things I'm actively developing, I'll leave basic facts like that as short notes on the source/reference cards (some may say literature notes) where I found them rather than writing them out in full as their own cards.
If I were a future biologist, as a student I might consider that I would soon know really well what a cell was and not bother to have a primary zettel on something so commonplace unless I was collecting various definitions to compare and contrast for something specific. Alternately as a non-biologist or someone that doesn't use the idea frequently, then perhaps it may merit more space for connecting to others?
Of course you can always have it written along with the original source and "promote" it to its own card later if you feel it's necessary, so you're covered either way. I tend to put the most interesting and surprising ideas into my main box to try to maximize what comes back out of it. If there were 2 more interesting ideas than the definition of cell in that documentary, then I would probably leave the definition with the source and focus on the more important ideas as their own zettels.
As a rule of thumb, for those familiar with Bloom's taxonomy in education, I tend to leave the lower level learning-based notes relating to remembering and understanding as shorter (literature) notes on the source's reference card and use the main cards for the higher levels (apply, analyze, evaluate, create).
Ultimately, time, practice, and experience will help you determine for yourself what is most useful and where. Until you've developed a feel for what works best for you, just write it down somewhere and you can't really go too far wrong.
-
- Mar 2023
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
zettelkasten
(free of this context, but I need somewhere just to place this potential title/phrase...)
Purpose Driven Zettelkasten
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.comYouTube1
-
Hypothesis Animated Intro, 2013. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QCkm0lL-6lc.
This was an early animation for Hypothes.is as a tool. It was on one of their early homepages and is (still) a pretty good encapsulation of what they do and who they are as a tool for thought.
-
-
www.insidehighered.com www.insidehighered.com
-
In the fall of 2015, she assigned students to write chapter introductions and translate some texts into modern English.
continuing from https://hypothes.is/a/ddn4qs8mEe2gkq_1T7i3_Q
Potential assignments:
Students could be tasked with finding new material or working off of a pre-existing list.
They could individually be responsible for indexing each individual sub-text within a corpus by: - providing a full bibliography; - identifying free areas of access for various versions (websites, Archive.org, Gutenberg, other OER corpora, etc.); Which is best, why? If not already digitized, then find a copy and create a digital version for inclusion into an appropriate repository. - summarizing the source in general and providing links to how it fits into the broader potential corpus for the class. - tagging it with relevant taxonomies to make it more easily searchable/selectable within its area of study - editing a definitive version of the text or providing better (digital/sharable) versions for archiving into OER repositories, Project Gutenberg, Archive.org, https://standardebooks.org/, etc. - identifying interesting/appropriate tangential texts which either support/refute their current text - annotating their specific text and providing links and cross references to other related texts either within their classes' choices or exterior to them for potential future uses by both students and teachers.
Some of this is already with DeRosa's framework, but emphasis could be on building additional runway and framing for helping professors and students to do this sort of work in the future. How might we create repositories that allow one a smörgåsbord of indexed data to relatively easily/quickly allow a classroom to pick and choose texts to make up their textbook in a first meeting and be able to modify it as they go? Or perhaps a teacher could create an outline of topics to cover along with a handful of required ones and then allow students to pick and choose from options in between along the way. This might also help students have options within a course to make the class more interesting and relevant to their own interests, lives, and futures.
Don't allow students to just "build their own major", but allow them to build their own textbooks and syllabi with some appropriate and reasonable scaffolding.
-
In the fall of 2015, she assigned students to write chapter introductions and translate some texts into modern English.
Perhaps of interest here, would not be a specific OER text, but an OER zettelkasten or card index that indexes a variety of potential public domain or open resources, articles, pieces, primary documents, or other short readings which could then be aggregated and tagged to allow for a teacher or student to create their own personalized OER text for a particular area of work.
If done well, a professor might then pick and choose from a wide variety of resources to build their own reader to highlight or supplement the material they're teaching. This could allow a wider variety of thinking and interlinking of ideas. With such a regiment, teachers are less likely to become bored with their material and might help to actively create new ideas and research lines as they teach.
Students could then be tasked with and guided to creating a level of cohesiveness to their readings as they progress rather than being served up a pre-prepared meal with a layer of preconceived notions and frameworks imposed upon the text by a single voice.
This could encourage students to develop their own voices as well as to look at materials more critically as they proceed rather than being spoon fed calcified ideas.
Tags
- relevance tagging
- build your own textbooks
- knowledge scaffolding
- OER rubric
- build your own major
- annotated syllabus
- pedagogical devices
- OER
- personal interests
- calcified ideas
- serendipity
- OER zettelkasten
- card index for education
- building blocks
- critical thinking
- group serendipity
- smörgåsbord
- combinatorial creativity
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
classicalstudies.org classicalstudies.org
-
Zettel, right

-
-
blog.degruyter.com blog.degruyter.com
-
Smith, Chris. “Thesaurus Linguae Latinae: How the World’s Largest Latin Lexicon Is Brought to Life.” De Gruyter Conversations, July 5, 2021. https://blog.degruyter.com/thesaurus-linguae-latinae-how-the-worlds-largest-latin-lexicon-is-brought-to-life/.
Basic overview article without much direct data/insight
-
Slip box for the word ‘requiro’ © Adam Gitner

-
TLL slip archive © Adam Gitner

-
-
www.npr.org www.npr.org
-
A sample of the note cards the scholars are using to assemble the comprehensive Latin dictionary. Courtesy of Samuel Beckelhymer. hide caption toggle caption Courtesy of Samuel Beckelhymer.

-
The archive contains boxes filled with notes on each Latin word. In most cases, the scholars made the notes more than a century ago. Courtesy of Nigel Holmes hide caption toggle caption Courtesy of Nigel Holmes

-

-
Stefano Rocchi, a researcher on the Thesaurus Linguae Latinae, the comprehensive Latin dictionary that has been in the works since 1894 in Germany. Researchers are currently working on the letters N and R. They don't expect to finish until around 2050. BAdW/Foto Janina Amendt hide caption toggle caption BAdW/Foto Janina Amendt

-
They both talk, though, about going over material again and again. The process of writing an article involves putting words in chronological order, but also creating branching, sub-dividing trees of syntax and semantics.
Interesting to see a reference the branching nature of the meanings of an individual word which has multiple ways of being categorized.
The TLL categorizes words alphabetically first and then by chronologically second. The rest of the structure shakes out from there as editors write articles for each of the words.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
The TLL was moved to a monastery in Bavaria during WWII because they were worried that the building that contained the zettelkasten would be bombed and it actually was.
The slips have been microfilmed and a copy of them is on store at Princeton as a back up just i case.
[01:17:00]
-
Remember the Thesaurus is a work of the human brain and therefore it is fallible. —Kathleen M. Coleman
replace Thesaurus with zettelkasten...
-
Basic statistics regarding the TLL: - ancient Latin vocabulary words: ca. 55,000 words - 10,000,000 slips - ca. 6,500 boxes - ca. 1,500 slips per box - library 32,000 volumes - contributors: 375 scholars from 20 different countries - 12 Indo-European specalists - 8 Romance specialists - 100 proof-readers - ca. 44,000 words published - published content: 70% of the entire vocabulary - print run: 1,350 - Publisher: consortium of 35 academies from 27 countries on 5 continents
Longest remaining words: - non / 37 boxes of ca 55,500 slips - qui, quae, quod / 65 boxes of ca. 96,000 slips - sum, esse, fui / 54.5 boxes of ca. 81,750 slips - ut / 35 boxes of ca 52,500 slips
Note that some of these words have individual zettelkasten for themselves approaching the size of some of the largest personal collections we know about!
[18:51]
-