- Jan 2023
-
www.riteintherain.com www.riteintherain.com
-
-
-
-
Local file Local file
-
About twenty thousand of those cards are 3 × 5 inches and seven thousand 5 × 8 inches.
Goitein's zettelkasten is comprised of about 20,000 3 x 5" index cards and 7,000 5 x 8" index cards.
Link to: https://hypothes.is/a/TEiQ5H1rEe2_Amfzi4XXmg
While not directly confirmed (yet), due to the seeming correspondence of the number of cards and their corpus descriptions, it's likely that the 20,000 3 x 5" cards were his notes covering individual topics while the 7,000 5 x 8" cards were his notes and descriptions of a single fragment from the Cairo Geniza.
-
In some cases, not unlike his Geniza subjects, Goitein wrotehis notes on pieces of paper that were lying around. To give but one example, a small noterecords the location of the index cards for “India Book: Names of Persons” from ‘ayn to tav:“in red \\ or Gray \\ box of geographical names etc. second (from above) drawer to the left ofmy desk 1980 in the left right steelcabinet in the small room 1972” is written on the back ofa December 17, 1971, note thanking Goitein for a box of chocolate (roll 11, slide 503, drawer13 [2.1.1], 1191v).
In addition to writing on cards, Goitein also wrote notes on pieces of paper that he happened to have lying around.
-
-
www.govinfo.gov www.govinfo.gov
-
TIPOFF was created in 1987 for the express purpose of using biographic information drawn from intelligence products for watchlisting purposes. In 1987 TIPOFF began keeping track of suspected terrorists literally with a shoebox and 3 by 5 cards. Since then the program has evolved into a sophisticated interagency counterterrorism tool specifically designed to enhance the security of our nation's borders.
-
- Dec 2022
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Besform plain cards (assorted colours)
Foreign sourced? I can't seen to find them on Google, at least locally.
-
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
The drawers are jammed with jokes typed on 4-by-6-inch cards — 52 drawers, stacked waist-high, like a card catalog of a certain comedian’s life’s work, a library of laughs.
Joan Rivers had an index card catalog with 52 drawers of 4-by-6-inch index cards containing jokes she'd accumulated over her lifetime of work. She had 18 2 drawer stackable steel files that were common during the mid-1900s. Rather than using paper inserts with the label frames on the card catalogs, she used a tape-based label maker to designate her drawers.

Scott Currie, who worked with Melissa Rivers on a book about her mother, Joan Rivers, at the comedian’s former Manhattan office. Many of her papers are stored there.Credit...Hiroko Masuike/The New York Times
Note carefully that the article says 52 drawers, but the image in the article shows a portion of what can be surmised to be 18 2-drawer cabinets for a total of 36 drawers. (14 2-drawer cabinets are pictured, but based on size and perspective, there's one row of 4 2-drawer boxes not shown.)
-
-
www.newyorker.com www.newyorker.com
-
The band began rehearsing in Eno’s house, with Eno acting as “sound manipulator,” a cross between a live-sound engineer and a band member.
Sound manipulator, what a great title for a business card.
-
-
drive.google.com drive.google.com
-
Getting StartedLivable Planet Ltd operates a system that we call role cards. At any time we expect that you willhold in your hand – like a pack of cards – a cluster of role cards, which each contains a set ofresponsibilities and accountabilities towards our shared mission. These role cards will outlinethe skills needed for the role, and what success might look like in it.You are joining Livable Planet Ltd with the following role cards:
The reason why we use role cards is,...
-
-
voiceisalanguage.wordpress.com voiceisalanguage.wordpress.com
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
austinkleon.com austinkleon.com
-
https://austinkleon.com/2018/03/04/card-games/
I'm reminded of early French use of playing cards for note taking here...
-
-
directlyyours.com directlyyours.com
-
1346-4 025719134648 BDY13464 BDY-13464 BDY 13464 Buddy Products Black Single Drawer Card File, 4 x 6, 1346-4
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
edward-slingerland.medium.com edward-slingerland.medium.com
-
Children, who in our post-agricultural age are otherwise pretty useless economically, can actually be usefully employed at this stage. They love cutting things with scissors, and precision is not crucial.
a nod to having "cards of equal size", but that precision isn't necessarily as crucial as we might suppose.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b-Wp0sLpnMY
PVA Glue used in bookbinding, but isn't inexpensive.
- Tacky glue - okay
- rubber cement - not great
- elmer's glue - not great, tears esp. for 2 layers
- Mod podge - pulls nicely and strong
- mod podge hard shell - cracks, not great
- PVA Glue - the best of the group
Recommendations in order: PVA, Tacky Glue, Mod Podge (regular)
Brush on top edge and do two coats. Don't get it down between sheets.
-
- Nov 2022
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Victor Margolin's note taking and writing process
- Collecting materials and bibliographies in files based on categories (for chapters)
- Reads material, excerpts/note making on 5 x 7" note cards
- Generally with a title (based on visual in video)
- excerpts have page number references (much like literature notes, the refinement linking and outlining happens separately later in his mapping and writing processes)
- filed in a box with tabbed index cards by chapter number with name
- video indicates that he does write on both sides of cards breaking the usual rule to write only on one side
- Uses large pad of newsprint (roughly 18" x 24" based on visualization) to map out each chapter in visual form using his cards in a non-linear way. Out of the diagrams and clusters he creates a linear narrative form.
- Tapes diagrams to wall
- Writes in text editor on computer as he references the index cards and the visual map.
"I've developed a way of working to make this huge project of a world history of design manageable."<br /> —Victor Margolin
Notice here that Victor Margolin doesn't indicate that it was a process that he was taught, but rather "I've developed". Of course he was likely taught or influenced on the method, particularly as a historian, and that what he really means to communicate is that this is how he's evolved that process.
"I begin with a large amount of information." <br /> —Victor Margolin
"As I begin to write a story begins to emerge because, in fact, I've already rehearsed this story in several different ways by getting the information for the cards, mapping it out and of course the writing is then the third way of telling the story the one that will ultimately result in the finished chapters."<br /> —Victor Margolin
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Austin Kleon made his own deck of Oblique Strategies by handwriting them onto the front of playing cards with black sharpie.
<script async src="https://platform.twitter.com/widgets.js" charset="utf-8"></script>Making my own Oblique Strategies deck. https://t.co/a1FpNifdLp pic.twitter.com/XsnRBt0GNW
— Austin Kleon (@austinkleon) November 1, 2015
-
-
cccrg.cochrane.org cccrg.cochrane.org
-
Statistical heterogeneity is the term given to differences in the effects of interventions and comesabout because of clinical and/or methodological differences between studies (ie it is a consequenceof clinical and/or methodological heterogeneity). Although some variation in the effects ofinterventions between studies will always exist, whether this variation is greater than what isexpected by chance alone needs to be determined.
If the statistical heterogeneity is larger that what's expected by chance alone, then what does that imply? That there's either clinical or methodological heterogeneity within the pooled studies.
What's the impact of the presence of clinical heterogeneity? The statistical heterogeneity (variation of effects/results of interventions) becomes greater than what's expected by chance alone
What's happens if methodological heterogeneity is present? The statistical heterogeneity (variation of effects/results of interventions) becomes greater than what's expected by chance alone
-
-
www.cisco.com www.cisco.com
-
Scaffolding is the act of providing learners with assistance or support to perform a taskbeyond their own reach if pursued independently when “unassisted.”
Wood, Bruner, & Ross (1976) define scaffolding as what? (Metiri Group, Cisco Sytems, 2008) The act of providing learners with assistance or support to perform a task beyond their own reach if pursued independently when "unassisted."
What term do Wood, Bruner, & Ross (1976) define as "The act of providing learners with assistance or support to perform a task beyond their own reach if pursued independently when 'unassisted.'"? (Metiri Group, Cisco Sytems, 2008) Scaffolding
-
Schemas are chunks of multiple individual units of memory that are linked into a system ofunderstanding
How do Bransford, Brown, & Cocking (2000) define schemas? (Metiri Group, Cisco Sytems, 2008) As chunks of multiple individual units of memory that are linked into a system of understanding
What term is defined by Bransford, Brown, & Cocking (2000) to be "chunks of multiple individual units of memory that are linked into a system of understanding"? (Metiri Group, Cisco Sytems, 2008) Schemas.
-
Learning is defined to be “storage of automated schema in long-term memory.
How is learning defined by Sweller in 2002? (Metiri Group, Cisco Sytems, 2008) The storage of automated schema in long-term memory
What term does Sweller define as the "storage of automated schema in long-term memory"?
-
-
prosimpli.com prosimpli.com
-
https://prosimpli.com/index-card-holder/
Reasonable state-of-the-art of index card holders. Does manage to leave out some of the bleacher display methods, but otherwise not bad.
-
-
-
https://www.ikea.com/us/en/p/kuggis-box-with-lid-transparent-black-00514033/#content
7 x 10.25 x 6"
This is big enough and just about the perfect size for 4 x 6" index cards. The lid has a slight indent to make it easily stackable.

-
-
-
medium.com medium.com
-
Fifty years ago, coinciding with the centennial of the release of Darwin’s manuscript, author Morse Peckham collected all six editions into a single “variorum” text. Peckham painstakingly created a reference system that denotes the modifications and changes between editions. The text was created by Peckham’s careful enumeration of every sentence from every edition, copied onto index cards; from these cards, he carefully assembled them into a final text.
-
-
blog.chain.link blog.chain.link
-
What Is a Blockchain Oracle? A blockchain oracle is a secure piece of middleware that facilitates communication between blockchains and any off-chain system, including data providers, web APIs, enterprise backends, cloud providers, IoT devices, e-signatures, payment systems, other blockchains, and more. Oracles take on several key functions: Listen – monitor the blockchain network to check for any incoming user or smart contract requests for off-chain data. Extract – fetch data from one or multiple external systems such as off-chain APIs hosted on third-party web servers. Format – format data retrieved from external APIs into a blockchain readable format (input) and/or making blockchain data compatible with an external API (output). Validate – generate a cryptographic proof attesting to the performance of an oracle service using any combination of data signing, blockchain transaction signing, TLS signatures, Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) attestations, or zero-knowledge proofs. Compute – perform some type of secure off-chain computation for the smart contract, such as calculating a median from multiple oracle submissions or generating a verifiable random number for a gaming application. Broadcast – sign and broadcast a transaction on the blockchain in order to send data and any corresponding proof on-chain for consumption by the smart contract. Output (optional) – send data to an external system upon the execution of a smart contract, such as relaying payment instructions to a traditional payment network or triggering actions from a cyber-physical system.
Seems related to the paradox of information systems. Add to Anki deck
-
-
pipdecks.com pipdecks.com
-
Something @chrisaldrich mentioned on Reddit as examples of someone selling niche Zettelkasten decks. Seem more like protocol-kasten decks to aid problem-solving in specific contexts.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
https://twitter.com/codexeditor/status/1590314248370286593
Index card and file folder influenced computer user interfaces.
-
-
www.amazon.com www.amazon.com
-
www.shopbrodart.com www.shopbrodart.com
-
These should easily fit 4 x 6" index cards as well as card dividers with taller tabs which commercially don't often get taller than 4 1/2".
See also microfiche divider guides.
Tags
- Brodart
- microfiche
- boxes
- cardboard boxes
- 4 x 6" index cards
- microfiche boxes
- archival materials
- zettelkasten boxes
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
From the beginning I found myself deeply challenged and stuck — freaked out by the blank page. So I started to use my skills as a filmmaker. I note-carded it. I had the notes above my computer, and I got to do a little “X” when I finished the draft of a chapter; it was this really satisfying moment.
Erin Lee Carr talks about using index cards to write a book about her father, but her practice sounds more like index cards with headings as a means of structuring a story and not actually writing the entire work out on cards.
-
-
billyoppenheimer.com billyoppenheimer.com
-
Ronald Reagan notecard


-
-
www.usatoday.com www.usatoday.com
-
"If the Reagans' home in Palisades (Calif.) were burning," Brinkley says, "this would be one of the things Reagan would immediately drag out of the house. He carried them with him all over like a carpenter brings their tools. These were the tools for his trade."
Another example of someone saying that if their house were to catch fire, they'd save their commonplace book (first or foremost).
-
-
forge.medium.com forge.medium.com
-
It's not an exaggeration: Nearly every dollar I've made in my adult life was earned first on the back or front (or both) of an index card.Everything I do, I do on index cards.
-
-
www.instagram.com www.instagram.com
-
https://www.instagram.com/p/CeWV6xBuZUN/?hl=en
Ryan Holiday in the past has made custom 4 x 6" index cards for taking notes for his individual projects.
Pictured: A custom slip with 11 light gray lines, small margins all around, and at the top the printed words: "Courage. Temperance. Justice. Wisdom."
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Billy Oppenheimer, research assistant to Ryan Holiday</span> in The Notecard System: Capture, Organize, and Use Everything You Read, Watch, and Listen To - Billy Oppenheimer (<time class='dt-published'>11/03/2022 16:53:44</time>)</cite></small>
<div style="padding:16px;"> <div style=" display: flex; flex-direction: row; align-items: center;"> <div style="background-color: #F4F4F4; border-radius: 50%; flex-grow: 0; height: 40px; margin-right: 14px; width: 40px;"></div> <div style="display: flex; flex-direction: column; flex-grow: 1; justify-content: center;"> <div style=" background-color: #F4F4F4; border-radius: 4px; flex-grow: 0; height: 14px; margin-bottom: 6px; width: 100px;"></div> <div style=" background-color: #F4F4F4; border-radius: 4px; flex-grow: 0; height: 14px; width: 60px;"></div></div></div><div style="padding: 19% 0;"></div> <div style="display:block; height:50px; margin:0 auto 12px; width:50px;"><svg width="50px" height="50px" viewBox="0 0 60 60" version="1.1" xmlns="https://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="https://www.w3.org/1999/xlink"><g stroke="none" stroke-width="1" fill="none" fill-rule="evenodd"><g transform="translate(-511.000000, -20.000000)" fill="#000000"><g><path d="M556.869,30.41 C554.814,30.41 553.148,32.076 553.148,34.131 C553.148,36.186 554.814,37.852 556.869,37.852 C558.924,37.852 560.59,36.186 560.59,34.131 C560.59,32.076 558.924,30.41 556.869,30.41 M541,60.657 C535.114,60.657 530.342,55.887 530.342,50 C530.342,44.114 535.114,39.342 541,39.342 C546.887,39.342 551.658,44.114 551.658,50 C551.658,55.887 546.887,60.657 541,60.657 M541,33.886 C532.1,33.886 524.886,41.1 524.886,50 C524.886,58.899 532.1,66.113 541,66.113 C549.9,66.113 557.115,58.899 557.115,50 C557.115,41.1 549.9,33.886 541,33.886 M565.378,62.101 C565.244,65.022 564.756,66.606 564.346,67.663 C563.803,69.06 563.154,70.057 562.106,71.106 C561.058,72.155 560.06,72.803 558.662,73.347 C557.607,73.757 556.021,74.244 553.102,74.378 C549.944,74.521 548.997,74.552 541,74.552 C533.003,74.552 532.056,74.521 528.898,74.378 C525.979,74.244 524.393,73.757 523.338,73.347 C521.94,72.803 520.942,72.155 519.894,71.106 C518.846,70.057 518.197,69.06 517.654,67.663 C517.244,66.606 516.755,65.022 516.623,62.101 C516.479,58.943 516.448,57.996 516.448,50 C516.448,42.003 516.479,41.056 516.623,37.899 C516.755,34.978 517.244,33.391 517.654,32.338 C518.197,30.938 518.846,29.942 519.894,28.894 C520.942,27.846 521.94,27.196 523.338,26.654 C524.393,26.244 525.979,25.756 528.898,25.623 C532.057,25.479 533.004,25.448 541,25.448 C548.997,25.448 549.943,25.479 553.102,25.623 C556.021,25.756 557.607,26.244 558.662,26.654 C560.06,27.196 561.058,27.846 562.106,28.894 C563.154,29.942 563.803,30.938 564.346,32.338 C564.756,33.391 565.244,34.978 565.378,37.899 C565.522,41.056 565.552,42.003 565.552,50 C565.552,57.996 565.522,58.943 565.378,62.101 M570.82,37.631 C570.674,34.438 570.167,32.258 569.425,30.349 C568.659,28.377 567.633,26.702 565.965,25.035 C564.297,23.368 562.623,22.342 560.652,21.575 C558.743,20.834 556.562,20.326 553.369,20.18 C550.169,20.033 549.148,20 541,20 C532.853,20 531.831,20.033 528.631,20.18 C525.438,20.326 523.257,20.834 521.349,21.575 C519.376,22.342 517.703,23.368 516.035,25.035 C514.368,26.702 513.342,28.377 512.574,30.349 C511.834,32.258 511.326,34.438 511.181,37.631 C511.035,40.831 511,41.851 511,50 C511,58.147 511.035,59.17 511.181,62.369 C511.326,65.562 511.834,67.743 512.574,69.651 C513.342,71.625 514.368,73.296 516.035,74.965 C517.703,76.634 519.376,77.658 521.349,78.425 C523.257,79.167 525.438,79.673 528.631,79.82 C531.831,79.965 532.853,80.001 541,80.001 C549.148,80.001 550.169,79.965 553.369,79.82 C556.562,79.673 558.743,79.167 560.652,78.425 C562.623,77.658 564.297,76.634 565.965,74.965 C567.633,73.296 568.659,71.625 569.425,69.651 C570.167,67.743 570.674,65.562 570.82,62.369 C570.966,59.17 571,58.147 571,50 C571,41.851 570.966,40.831 570.82,37.631"></path></g></g></g></svg></div><div style="padding-top: 8px;"> <div style=" color:#3897f0; font-family:Arial,sans-serif; font-size:14px; font-style:normal; font-weight:550; line-height:18px;">View this post on Instagram</div></div><div style="padding: 12.5% 0;"></div> <div style="display: flex; flex-direction: row; margin-bottom: 14px; align-items: center;"><div> <div style="background-color: #F4F4F4; border-radius: 50%; height: 12.5px; width: 12.5px; transform: translateX(0px) translateY(7px);"></div> <div style="background-color: #F4F4F4; height: 12.5px; transform: rotate(-45deg) translateX(3px) translateY(1px); width: 12.5px; flex-grow: 0; margin-right: 14px; margin-left: 2px;"></div> <div style="background-color: #F4F4F4; border-radius: 50%; height: 12.5px; width: 12.5px; transform: translateX(9px) translateY(-18px);"></div></div><div style="margin-left: 8px;"> <div style=" background-color: #F4F4F4; border-radius: 50%; flex-grow: 0; height: 20px; width: 20px;"></div> <div style=" width: 0; height: 0; border-top: 2px solid transparent; border-left: 6px solid #f4f4f4; border-bottom: 2px solid transparent; transform: translateX(16px) translateY(-4px) rotate(30deg)"></div></div><div style="margin-left: auto;"> <div style=" width: 0px; border-top: 8px solid #F4F4F4; border-right: 8px solid transparent; transform: translateY(16px);"></div> <div style=" background-color: #F4F4F4; flex-grow: 0; height: 12px; width: 16px; transform: translateY(-4px);"></div> <div style=" width: 0; height: 0; border-top: 8px solid #F4F4F4; border-left: 8px solid transparent; transform: translateY(-4px) translateX(8px);"></div></div></div> <div style="display: flex; flex-direction: column; flex-grow: 1; justify-content: center; margin-bottom: 24px;"> <div style=" background-color: #F4F4F4; border-radius: 4px; flex-grow: 0; height: 14px; margin-bottom: 6px; width: 224px;"></div> <div style=" background-color: #F4F4F4; border-radius: 4px; flex-grow: 0; height: 14px; width: 144px;"></div></div></div>
<script async src="//www.instagram.com/embed.js"></script>
I used to do this sort of practice before, but I used buckslips instead.
-
- Oct 2022
-
Local file Local file
-
he three-by-five inch slipsof thin paper eventually filled about eighty wooden file drawers.And he classified the notes day by day, under topical-chronologicalheadings that eventually extended from 4639 B.C. to 1949, theyear after his death.
Frederic L. Paxson kept a collection of 3 x 5 " slips of thin paper that filled eighty wooden file drawers which he organized using topical-chronologic headings spanning 4639 BCE to 1949.
-
-
www.gutenberg.org www.gutenberg.org
-
Les murs du cabinet de travail, le plancher, le plafond même portaient des liasses débordantes, des cartons démesurément gonflés, des boîtes où se pressait une multitude innombrable de fiches, et je contemplai avec une admiration mêlée de terreur les cataractes de l'érudition prêtes à se rompre. —Maître, fis-je d'une voix émue, j'ai recours à votre bonté et à votre savoir, tous deux inépuisables. Ne consentiriez-vous pas à me guider dans mes recherches ardues sur les origines de l'art pingouin? —Monsieur, me répondit le maître, je possède tout l'art, vous m'entendez, tout l'art sur fiches classées alphabétiquement et par ordre de matières. Je me fais un devoir de mettre à votre disposition ce qui s'y rapporte aux Pingouins. Montez à cette échelle et tirez cette boîte que vous voyez là-haut. Vous y trouverez tout ce dont vous avez besoin. J'obéis en tremblant. Mais à peine avais-je ouvert la fatale boîte que des fiches bleues s'en échappèrent et, glissant entre mes doigts, commencèrent à pleuvoir. Presque aussitôt, par sympathie, les boîtes voisines s'ouvrirent et il en coula des ruisseaux de fiches roses, vertes et blanches, et de proche en proche, de toutes les boîtes les fiches diversement colorées se répandirent en murmurant comme, en avril, les cascades sur le flanc des montagnes. En une minute elles couvrirent le plancher d'une couche épaisse de papier. Jaillissant de leurs inépuisables réservoirs avec un mugissement sans cesse grossi, elles précipitaient de seconde en seconde leur chute torrentielle. Baigné jusqu'aux genoux, Fulgence Tapir, d'un nez attentif, observait le cataclysme; il en reconnut la cause et pâlit d'épouvante. —Que d'art! s'écria-t-il. Je l'appelai, je me penchai pour l'aider à gravir l'échelle qui pliait sous l'averse. Il était trop tard. Maintenant, accablé, désespéré, lamentable, ayant perdu sa calotte de velours et ses lunettes d'or, il opposait en vain ses bras courts au flot qui lui montait jusqu'aux aisselles. Soudain une trombe effroyable de fiches s'éleva, l'enveloppant d'un tourbillon gigantesque. Je vis durant l'espace d'une seconde dans le gouffre le crâne poli du savant et ses petites mains grasses, puis l'abîme se referma, et le déluge se répandit sur le silence et l'immobilité. Menacé moi-même d'être englouti avec mon échelle, je m'enfuis à travers le plus haut carreau de la croisée.
France, Anatole. L’Île Des Pingouins. Project Gutenberg 8524. 1908. Reprint, Project Gutenberg, 2005. https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/8524/pg8524.html
Death by Zettelkasten!!
(Coming soon to a theater near you...)
In the preface to the novel Penguin Island (L'Île des Pingouins. Calmann-Lévy, 1908) by Nobel prize laureate Anatole France, a scholar is drowned by an avalanche of index cards which formed a gigantic whirlpool streaming out of his card index (Zettelkasten).
Link to: Historian Keith Thomas has indicated that he finds it hard to take using index cards for excerpting and research seriously as a result of reading this passage in the satire Penguin Island.<br /> https://hypothes.is/a/rKAvtlQCEe2jtzP3LmPlsA
Translation via: France, Anatole. Penguin Island. Translated by Arthur William Evans. 8th ed. 1908. Reprint, New York, NY, USA: Dodd, Mead & Co., 1922. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Penguin_Island/6UpWAvkPQaEC?hl=en&gbpv=0
Small changes in the translation by me, comprising only adding the word "index" in front of the occurrences of card to better represent the historical idea of fiches used by scholars in the late 1800s and early 1900s, are indicated in brackets.
The walls of the study, the floor, and even the ceiling were loaded with overflowing bundles, paste board boxes swollen beyond measure, boxes in which were compressed an innumerable multitude of small [index] cards covered with writing. I beheld in admiration mingled with terror the cataracts of erudition that threatened to burst forth.
“Master,” said I in feeling tones, “I throw myself upon your kindness and your knowledge, both of which are inexhaustible. Would you consent to guide me in my arduous researches into the origins of Penguin art?"
“Sir," answered the Master, “I possess all art, you understand me, all art, on [index] cards classed alphabetically and in order of subjects. I consider it my duty to place at your disposal all that relates to the Penguins. Get on that ladder and take out that box you see above. You will find in it everything you require.”
I tremblingly obeyed. But scarcely had I opened the fatal box than some blue [index] cards escaped from it, and slipping through my fingers, began to rain down.
Almost immediately, acting in sympathy, the neighbouring boxes opened, and there flowed streams of pink, green, and white [index] cards, and by degrees, from all the boxes, differently coloured [index] cards were poured out murmuring like a waterfall on a mountain-side in April. In a minute they covered the floor with a thick layer of paper. Issuing from their in exhaustible reservoirs with a roar that continually grew in force, each second increased the vehemence of their torrential fall. Swamped up to the knees in cards, Fulgence Tapir observed the cataclysm with attentive nose. He recognised its cause and grew pale with fright.
“ What a mass of art! ” he exclaimed.
I called to him and leaned forward to help him mount the ladder which bent under the shower. It was too late. Overwhelmed, desperate, pitiable, his velvet smoking-cap and his gold-mounted spectacles having fallen from him, he vainly opposed his short arms to the flood which had now mounted to his arm-pits . Suddenly a terrible spurt of [index] cards arose and enveloped him in a gigantic whirlpool. During the space of a second I could see in the gulf the shining skull and little fat hands of the scholar; then it closed up and the deluge kept on pouring over what was silence and immobility. In dread lest I in my turn should be swallowed up ladder and all I made my escape through the topmost pane of the window.
-
-
-
Filing is a tedious activity and bundles of unsorted notes accumulate. Some of them get loose and blow around the house, turning up months later under a carpet or a cushion. A few of my most valued envelopes have disappeared altogether. I strongly suspect that they fell into the large basket at the side of my desk full of the waste paper with which they are only too easily confused.
Relying on cut up slips of paper rather than the standard cards of equal size, Keith Thomas has relayed that his slips often "get loose and blow around the house, turning up months later under a carpet or cushion."
He also suspects that some of his notes have accidentally been thrown away by falling off his desk and into the nearby waste basket which camouflages his notes amongst similar looking trash.
-
Since Anatole France’s description in Penguin Island of the scholar drowned by an avalanche of his own index cards, it has been hard to take them seriously.
In Penguin Island, Anatole France describes a scholar drowned by an avalanche of their own index cards!
-
-
www.flotsamandfork.com www.flotsamandfork.com
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Does anyone else work in project-based systems instead? .t3_y2pzuu._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/m_t_rv_s__n https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/y2pzuu/does_anyone_else_work_in_projectbased_systems/
Historically, many had zettelkasten which were commonplace books kept on note cards, usually categorized by subject (read: "folders" or "tags"), so you're not far from that original tradition.
Similar to your work pattern, you may find the idea of a "Pile of Index Cards" (PoIC) interesting. See https://lifehacker.com/the-pile-of-index-cards-system-efficiently-organizes-ta-1599093089 and https://www.flickr.com/photos/hawkexpress/albums/72157594200490122 (read the descriptions of the photos for more details; there was also a related, but now defunct wiki, which you can find copies of on Archive.org with more detail). This pattern was often seen implemented in the TiddlyWiki space, but can now be implemented in many note taking apps that have to do functionality along with search and tags. Similarly you may find those under Tiago Forte's banner "Building a Second Brain" to be closer to your project-based/productivity framing if you need additional examples or like-minded community. You may find that some of Nick Milo's Linking Your Thinking (LYT) is in this productivity spectrum as well. (Caveat emptor: these last two are selling products/services, but there's a lot of their material freely available online.)
Luhmann changed the internal structure of his particular zettelkasten that created a new variation on the older traditions. It is this Luhmann-based tradition that many in r/Zettelkasten follow. Since many who used the prior (commonplace-based) tradition were also highly productive, attributing output to a particular practice is wrongly placed. Each user approaches these traditions idiosyncratically to get them to work for themselves, so ignore naysayers and those with purist tendencies, particularly when they're new to these practices or aren't aware of their richer history. As the sub-reddit rules indicate: "There is no [universal or orthodox] 'right' way", but you'll find a way that is right for you.
-
-
www.flickr.com www.flickr.com
-
riclav 16y Do you implement any kind of analogue "trackback"? In other words, does 2006.7.14 18.06 know that it has been linked to? If not, would there be value in having this kind of function?
The original PoIC didn't include bi-directional links, but the idea was brought up and considered.
-
-
mleddy.blogspot.com mleddy.blogspot.com
-
Google "Hawk Sugano" and "PoIC" for the reinvention and updating of a system much in use by the Japanese (Umedao author) and Germans (Buhmann author) in the Sixties and Seventies. Neither of these works has been translated into English...apparently Japan and Germany are jealously holding on to their State Secrets ;)
This post was via Den https://www.blogger.com/profile/15319877273178044093
What are these references to Umedao and Buhmann? Quck searches don't yield much. Need to look deeper.
-
-
www.flickr.com www.flickr.com
-
GTD Card Icon : Square (check box)Tag : 4th block. Squared as open-loop first, and filled later as accomplished. The GTD is advanced To-Do system proposed by David Allen. Next action of your project is described and processed through a certain flow. The GTD cards are classified into this class. 4th block is squared as open-loop first, and filled later as accomplished. The percentage of GTD Cards in my dock is less than 5 %.
-
-
unclutterer.com unclutterer.com
-
Brief explanation of the Pile of Index Cards system, but without significant depth.
-
I’m with Iris (and Jane) about the PoIC system — I don’t understand how the system works once it is set up. It’s a shame as it might be very useful. Ideally, I’d like to set it up with notebooks in Evernote instead of actual index cards and boxes (the last thing I need in my life is more paper clutter). That way it would be easily searchable, too).
As is apparently often in describing new organizing systems (commonplace books, zettelkasten, PoIC, etc.), not everyone is going to understand it the first time, or even understand what is going on or why one would want to use it.
This post by Susan is such an example.
Susan does almost immediately grasp that this might be something one could transfer into a digital system however, particularly for the search functionality.
-
-
web.archive.org web.archive.org
-
Several months back I'd thought about adapting the 43 folders system to a zettelkasten sort of system. I'm obviously not the first to have done so.
-
-
www.flickr.com www.flickr.com
-
https://www.flickr.com/photos/aki_oda/2684257358/
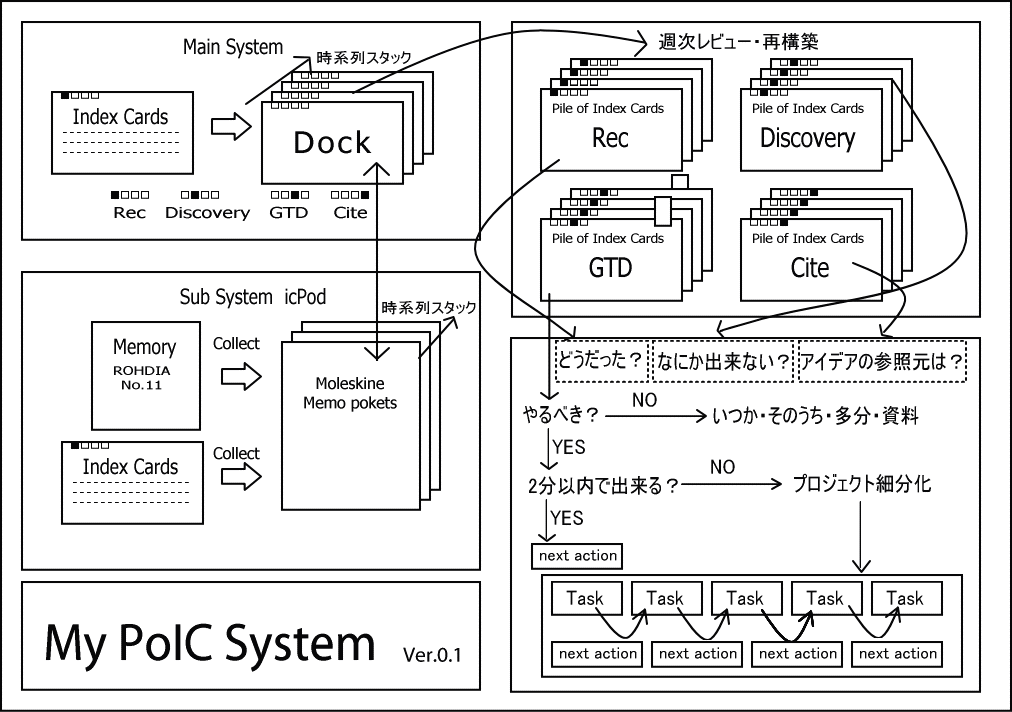
Visual diagram of PoIC system, similar to 43 folders and GTD systems.
-
-
www.flickr.com www.flickr.comkf3331
-
https://www.flickr.com/photos/36761543@N02/
Kf333 falls into the tradition of PoIC which they associated directly.
They photographed and saved their cards into Flickr.
-
-
lifehacker.com lifehacker.com
-
https://lifehacker.com/the-pile-of-index-cards-system-efficiently-organizes-ta-1599093089
LifeHacker covers the Hawk Sugano's Pile of Index Cards method, which assuredly helped promote it to the GTD and productivity crowd.
One commenter notices the similarities to Ryan Holiday's system and ostensibly links to https://thoughtcatalog.com/ryan-holiday/2013/08/how-and-why-to-keep-a-commonplace-book/
Two others snarkily reference using such a system to "keep track of books in the library [,,,] Sort them out using decimal numbers on index cards in drawers or something..." and "I need to tell my friend Dewey about this! He would run with it." Obviously they see the intellectual precursors and cousins of the method, though they haven't looked at the specifics very carefully.
One should note that this may have been one of the first systems to mix information management/personal knowledge management with an explicit Getting Things Done set up. Surely there are hints of this in the commonplace book tradition, but are there any examples that go this far?
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Posted byu/raphaelmustermann9 hours agoSeparate private information from the outline of academic disciplines? .t3_xi63kb._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } How does Luhmann deal with private Zettels? Does he store them in a separate category like, 2000 private. Or does he work them out under is topics in the main box.I can´ find informations about that. Anyway, you´re not Luhmann. But any suggestions on how to deal with informations that are private, like Health, Finances ... does not feel right to store them under acadmic disziplines. But maybe it´s right and just a feeling which come´ out how we "normaly" store information.
I would echo Bob's sentiment here and would recommend you keep that material like this in a separate section or box all together.
If it helps to have an example, in 2006, Hawk Sugano showed off a version of a method you may be considering which broadly went under the title of Pile of Index Cards (or PoIC) which combined zettelkasten and productivity systems (in his case getting things done or GTD). I don't think he got much (any?!) useful affordances out of mixing the two. In fact, from what I can see looking at later iterations of his work and how he used it, it almost seems like he spent more time and energy later attempting to separate and rearrange them to get use out of the knowledge portions as distinct from the productivity portions.
I've generally seen people mixing these ideas in the digital space usually to their detriment as well—a practice I call zettelkasten overreach.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
there might be a miscellaneous division, which wouldserve as a "tickler" and which might even be equipped with a set ofcalendar guides so that the "follow-up" system may be used.
An example of a ticker file in the vein of getting things done (GTD) documented using index cards and a card file from 1917. Sounds very familiar to the Pile of Index Cards (PoIC) from the early 2000s.
-
-
zettelkasten.de zettelkasten.de
-
image courtesy hawkexpress on flickr
Interesting to see the first post on zettelkasten.de in 2013 has a photo of hawkexpress' Pile of Index Cards (PoIC) in it.

This obviously means that Christian Tietze had at least a passing familiarity with that system, though it differed structurally from Luhmann's version of zettelkasten.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.comYouTube1
-
https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=pile+of+index+card
Doesn't look like there's any of the "original" PoIC material on YouTube, but some examples of related practices to check into.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Bouttes contributedfrequently to Barthes’s seminar and gave an unusual paper at thecolloque de Cerisy called ‘Le diamantfoudre’ (‘The diamond-lightning’). He was darkly dazzling, strange, sombre, unexpected.Barthes thought he had something of Des Esseintes about him,witness an anecdote noted in his card index diary: ‘J.L.: in a phasewhere, in the restaurant, he deconstructs the menus, greatlyshocking the waiters. The other evening, at Prunier’s, oysters andoyster gratin, yesterday, at Le Balzar, oeuf en gelée and oysters,coffee ice cream and ice cream.’59
- BNF, NAF 28630, ‘Grand fichier’, 3 January 1975.
Roland Barthes' biographer Tiphaine Samoyault quotes portions of what he calls Barthes' card index diary.
This can also be seen in the published cards which comprise Barthes' Mourning Diary about the period following his mother's death.
Are there other people who've used their card index as a diary the way that some use it for productivity?
-
-
Local file Local file
-
In one way, the cards’ uniform size and format was part of Deutsch’sdream to produce a systematic method of research and writing.
-
Deutsch’s focus on facts was commonplace among professional US historians atthis time, as was his conception of the ‘fact’ as a small item that could fit onto the sizeof an index card (Daston, 2002).
Find this quote and context!
-
‘He knows everything that’s happened fromB’reshis [Genesis] to today’, it went, ‘and it really isn’t work to him – it’s merely play’,a sentiment later expressed when one colleague wrote of Deutsch’s ‘game of cards’(Margolis, 1921).3
Apparently a colleague wrote about Deutsch's "game of cards" as a description of hit use of a zettelkasten. The play here is reminiscent of the joy Ahrens talks about when doing research/reading/writing (2017).
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Dwyer, Edward J. “File Card Efficiency.” Journal of Reading 26, no. 2 (1982): 171–171.
Ease of use in writing and grading with short assignments by using 4 x 6" index cards in classrooms.
This sounds like some of the articles from 1912 and 1917 about efficiency of card indexes for teaching.
I'm reminded of some programmed learning texts that were card-based (or really strip-based since they were published in book form) in the 1960s and 1970s. Thse books had small strips with lessons or questions on the front with the answers on the reverse. One would read in strips through the book from front to back and then start the book all over again on page one on the second row of strips and so on.
-
-
archive.org archive.org
-
Unlike many manuals on note taking, Goutor suggest a few methods of note categorization beyond adding typical headwords. These include adding top or side edge notches using a paper punch, colored cards, or adding colored flags. However he does note some potential problems and limitations of these methods including being cumbersome or limiting (by colors available, for example). (p31-32)
-
For the second time Goutor mentions using different size cards for different note types, but doesn't specifically advise for it or provide a reason. Perhaps his advice for consistency and card size applies only to cards of particular types? (p28)
link to: https://hypothes.is/a/XPphjkNZEe2s3i9VV4qt1g
Incidentally he also specifically mentions 7x9" cards here too. How frequently used were these as a standard?
-
While he previously recommended using note cards of the same size, the examples in Goutor (1980) have 3x5" cards for bibliographic notes and 5x7" or larger cards for content notes. (p19, 21)
Is there a reason stated anywhere here for this discrepancy or change? One would ostensibly keep them in different places/sections of one's card index, but does the size difference help to differentiate the two to aid in sorting? Is the larger card intended to hold more long form writing?
Goutor is in Canada, so were 5x7" cards more common or standardized there in the late 1970s and early 80s?
A5 measures 148 × 210 millimeters or 5.83 × 8.27 inches, so is a bit larger than 5x7".
5x7" is a more standard photo size, so was this chosen as the result of storage options from the photography space?
5x7" is scantly available in America in 2022, but only from Hamilco. A few others make cardstock in that size but not specifically as index cards.
-
Goutor comments, like many before him, that it is common to take notes on notebook paper in longer form, but that this is inadvisable as it is much harder to impose a useful order or classification on such work. He does mention scissors as a means of cutting up such notes, but comments that "a mass of slips of paper of varying sizes [can be] difficult to arrange and potentially useless unless care has been taken to note the source of each separate entry."
He also repeats the frequent admonitions that one should take notes only on one side and to use cards of a uniform size.
(p6)
Tags
- color codes
- edge-notched cards
- note card sizes
- subject headings
- Canada
- note taking advice
- write only on one side
- 7 x 9" index cards
- 5 x 7" index cards
- open questions
- notebooks
- paper standards
- categorization
- consistency
- note taking affordances
- 3 x 5" index cards
- types of notes
- cards of equal size
- classification
- Herman Hollerith
Annotators
URL
-
-
Local file Local file
-
A career-line study of the presidents, all cabinet members,and all members of the Supreme Court. This 1 'already have onIBM cards from the constitutional period through Truman'ssecond term, but I want to expand the items used and analyze itafresh.
Notice that it's not just notes, but data on IBM cards that he's using for research here. This sort of data analysis is much easier now, but is also of the sort detailed by Beatrice Webb in her scientific note taking.
-
- Sep 2022
-
-
Thesheets must always be of equal size, or at least of equal height in order not to get stuck or beoverlooked when manually searching for sheets or adding them.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Posted byu/jackbaty4 hours agoCard sizes .t3_xib133._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; } I've been on-again/off-again with paper for PKM, but one thing remains consistent each time: I don't enjoy using 4x6 index cards. I much prefer 3x5-inch cards. I realize that it's irrational, but there it is.My question is if I dive into building an antinet, will I regret using 3x5 cards? I already have hundreds of them. I have dividers, holders, and storage boxes for them. I just prefer how they _feel_, as weird as that sounds.I'd like to hear if people are using 3x5 cards successfully or if you've come to regret it.
While it may be slightly more difficult to find larger metal/wood cases for the 4x6 or 5x8 cards, it's a minor nuisance and anyone who wants them will eventually find the right thing for them. Beyond this, choose the card size that feels right to you.
If you don't have an idea of what you need or like, try things out for 10-20 cards and see how it works for you, your handwriting size, and general needs. People have been using 3x5, 4x6, and even larger for hundreds of years without complaining about any major issues. If Carl Linnaeus managed to be okay with 3x5, which he hand cut by the way, I suspect you'll manage too.
Of course I won't mention to the Americans the cleverness of the A6, A5, A4 paper standards which allows you to fold the larger sizes in half to get the exact next smaller size down. Then you might get the benefit of the smaller size as well as the larger which could be folded into your collection of smaller cards, you just have to watch out for accidentally wrapping ("taco-ing") a smaller card inside of a larger one and losing it. I suppose you could hand cut your own 5" x 6" larger cards to do this if you found that you occasionally needed them.
For the pocketbook conscious, 3x5 does have the benefit of lower cost as well as many more options and flexibility than larger sizes.
At least commercial card sizes are now largely standardized, so you don't have deal with changing sizes the way Roland Barthes did over his lifetime.
My personal experience and a long history of so many manuals on the topic saying "cards of the same size" indicates that you assuredly won't have fun mixing different sized slips together. I personally use 3x5" cards in a waste book sense, but my main/permanent collection is in 4x6" format. Sometimes I think I should have done 3 x 5, but it's more like jealousy than regret, particularly when it comes to the potential of a restored fine furniture card catalog. But then again...
-
-
Local file Local file
-
As I write this book, for instance, I am sitting in a small room, beforea laptop computer, surrounded by books, papers, and magazines—all ofwhich I am, in some metaphorical sense, “in conversation with” (in muchthe same way I am also in conversation with you, my imagined reader).But what I am actually doing is working with a set of materials—lookingfor books on my shelves and flipping through them, folding pages over ormarking them with Post-its, retyping passages, filing and retrieving print-outs and photocopies, making notes in margins and on index cards, and,of course, composing, cutting, pasting, formatting, revising, and printingblocks of prose. I am, that is, for the most part, moving bits of text and paperaround.
Joseph Harris uses a mélange of materials to make his writing including books, papers, magazines, from which he is copying sections out, writing in margins, making notes on index cards and then moving those pieces of text and pieces of paper (the index cards, and possibly Post-it notes) around to create his output.
He doesn't delineate a specific process for his excerpting or note taking practice. How does he organize his notes? Is he just pulling them from piles around him? Is there a sense of organization at all?
-
-
web.archive.org web.archive.org
-
https://web.archive.org/web/20080412071219/http://eastgate.com/catalog/Briefcase.html
Eastgate systems used to make a "3x5 Card Briefcase" to capture short notes on the go which could later "be scanned or transcribed to Tinderbox."
Tinderbox was one of the first digital tools to be used in a way very similar to zettelkasten of old, particularly by academics, who are a large portion of their power user base.
-
-
www.connectedtext.com www.connectedtext.com
-
By the way, Luhmann's system is said to have had 35.000 cards. Jules Verne had 25.000. The sixteenth-century thinker Joachim Jungius is said to have had 150.000, and how many Leibniz had, we do not know, though we do know that he had one of the most ingenious piece of furniture for keeping his copious notes.
Circa late 2011, he's positing Luhmann had 35,000 cards and not 90,000.
Jules Verne used index cards. Joachim Jungius is said to have had 150,000 cards.
-
-
www.getfrictionless.com www.getfrictionless.com
-
Capture Cards (red) 4.00 Beautifully Useful 3″ x 5″ Index Cards (Pack of 100)I created my Capture Cards to help make it easier for me to capture ideas, make notes, and record tasks as they happen. Good tools have a way of removing frustration and stress from a workflow, and for me, these cards do just that.Just enough structure to help you capture, but not enough to get in the way.They’re printed full-bleed on 70lb (heavy and durable) premium smooth white cover stock, and you get 100 2-sided cards in each pack. They feel great in your hand, yet hold up well in your pocket.
https://web.archive.org/web/20140707053048/http://www.getfrictionless.com/products/capture-cards-red
Simple index cards, but sold with a purpose in mind: capturing notes!
One is reminded here of waste books and fleeting notes.
Image:<br />

-
-
mleddy.blogspot.com mleddy.blogspot.com
-
I've been spelunking through your posts from roughly the decade from 2005 onward which reference your interest in index cards. Thanks for unearthing and writing about all the great index card material from that time period. Have you kept up with your practices?
I noticed that at least one of your posts had a response by MK (Manfred Kuehn, maintainer of the now defunct Taking Note blog (2007-2018). Was it something you read at the time or kept up with?
Have you been watching the productivity or personal knowledge management space since roughly 2017 where the idea of the Zettelkasten (slip box or card index) has taken off (eg. https://zettelkasten.de/, Sonke Ahren's book How to Take Smart Notes, Obsidian.md, Roam Research, etc.?) I'd be curious to hear your thoughts on them or even what your practice has meant over time.
Thanks again.
Cheers! -CJA
-
-
The casting director Marion Dougherty, in the documentary Casting By (dir. Tom Donahue, 2012): “I would keep the three-by-five card. I would put down anything that hit my mind.” The card for Dustin Hoffman (whose first screen appearance was in an episode of Naked City) notes Bob Duval’s (Robert Duvall’s) judgment that Hoffman is “v.g.” — very good. Notice the name of Blair Brown in the third screenshot. The Days and Nights of Molly Dodd is an Orange Crate Art and Musical Assumptions favorite.
The documentary Casting By (2012) shows casting director Marion Dougherty's 3 x 5" index card collection which she used for casting notes. In particular they show an example card for Dustin Hoffman with his details. In Hoffman's case, his card included the older telephone numbers with exchanges (EN2-6933 or Endicott2 6933), so these cards may have also served a contact purpose similar to more modern rolodexes. Different from them however, Dougherty's also included heights, credits, and other observations relevant to the casting process.
 Screen capture from the movie
Screen capture from the movie
-
-
www.flickr.com www.flickr.com
-
indexcard (情報カード).
Japanese translation of index card
-
-
musicalassumptions.blogspot.com musicalassumptions.blogspot.com
-
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Michael Leddy</span> in Orange Crate Art: Writing and index cards (<time class='dt-published'>09/15/2022 10:38:15</time>)</cite></small>
Elaine Fine is Michael Leddy's wife.
-
-
www.takenote.space www.takenote.space
-
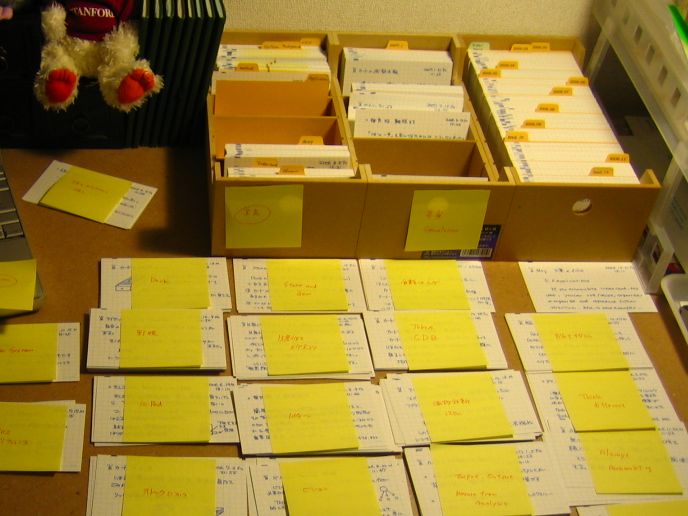
I didn't see/couldn't find this image in the Life archive, but it was obviously contemporanous to the others

-
-
mleddy.blogspot.com mleddy.blogspot.com
-
The Field Notes journal serves as RAM, the index cards as HDD, metaphorically speaking...(brain is CPU).
Den analogizes their note taking system to computing on 2010-11-11 8:43 PM.
-
-
mleddy.blogspot.com mleddy.blogspot.com
-
Pen + Gear Graph-Ruled Index Cards. They’re a bit on the thin side, but they take ink well, without feathering or bleeding through. And they’re printed with a very fine light-blue grid (five squares to the inch) that doesn’t get in the way of what one is writing or drawing or mapping. These cards are much better than Oxford or Staples grid cards, and a fraction of the cost of Exacompta: 48¢ for 100 cards. Highly recommended.
https://mleddy.blogspot.com/2017/08/index-card-recommendation.html
Walmart has these index cards, but only in 3x5" format.
-
-
mleddy.blogspot.com mleddy.blogspot.com
-
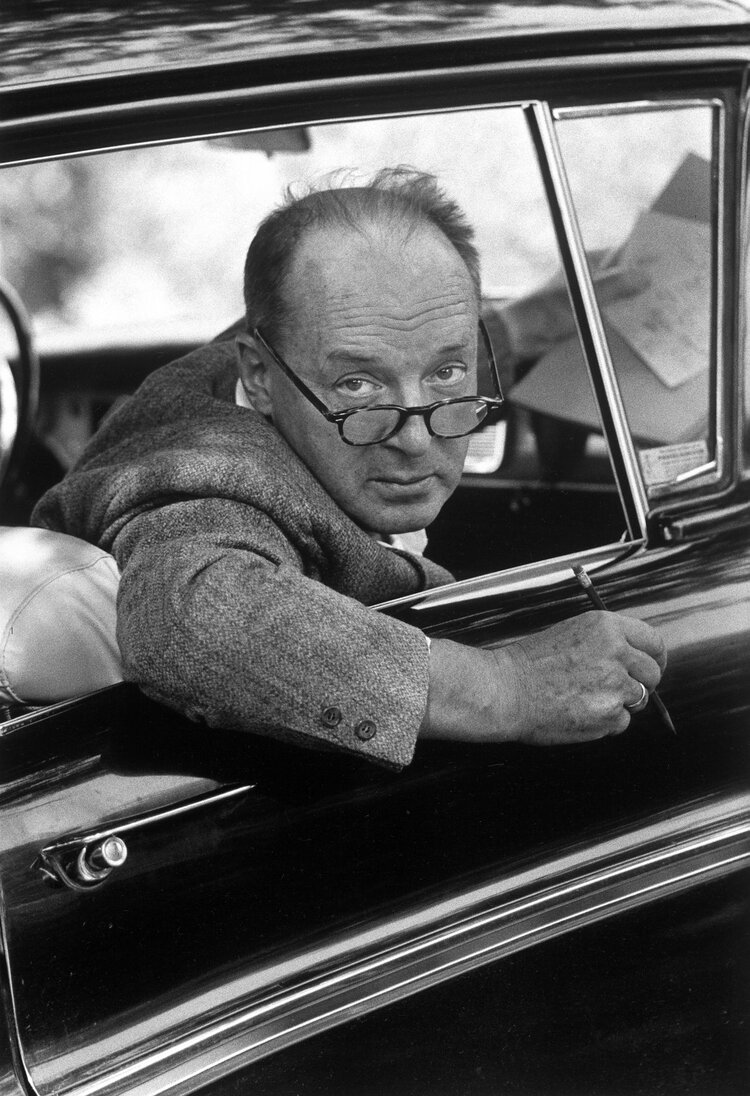
I’m not sure how to explain the photograph — that might be a cardfile, not a shoebox. The number of blue lines per card in the Pale Fire passage suggests that John Shade used 6 x 4 cards. It looks like Nabokov in the car has 6 x 4s too.
What size index cards did Vladimir Nabokov use?
See also: series of Nabokov photos of him and index cards.
-
After a leisurely lunch, prepared by the German cook who came with the house, I would spend another four-hour span in a lawn chair, among the roses and mockingbirds, using lined index cards and a Blackwing pencil, for copying and recopying, rubbing out and writing anew, the scenes I had imagined in the morning. Foreword to Lolita: A Screenplay (1973)
-
-
images.google.com images.google.com
-
Author Vladimir Nabokov's doodlings.Location:Ithaca, NY, USDate taken:September 1958Photographer:Carl Mydans
-
-
images.google.com images.google.com
-
Author Vladimir Nabokov's researched materials on file cards for his book 'Lolita'.Location:Ithaca, NY, USDate taken:September 1958Photographer:Carl Mydans
-
-
images.google.com images.google.com
-
Author Vladimir Nabokov at work, writing on index cards in his car.Location:Ithaca, NY, USDate taken:September 1958Photographer:Carl MydansSize:1280 x 889 pixels (17.8 x 12.3 inches)
-
- Aug 2022
-
www.amazon.com www.amazon.com
-
When Vladimir Nabokov died in 1977, he left instructions for his heirs to burn the 138 handwritten index cards that made up the rough draft of his final and unfinished novel, The Original of Laura. But Nabokov’s wife, Vera, could not bear to destroy her husband’s last work, and when she died, the fate of the manuscript fell to her son. Dmitri Nabokov, now seventy-five—the Russian novelist’s only surviving heir, and translator of many of his books—has wrestled for three decades with the decision of whether to honor his father’s wish or preserve for posterity the last piece of writing of one of the greatest writers of the twentieth century.
Nabokov's wishes were that his heirs burn the index cards on which he had handwritten the beginning of his unfinished novel The Original of Laura. His wife Vera, not able to destroy her husband's work, couldn't do it, so the decision fell to their son Dimitri. Having translated many of his father's works previously, Dimitri Nabokov ultimately allowed Penguin the right to publish the unfinished novel.
-
-
uni-bielefeld.de uni-bielefeld.de
-
A-6 format
This is 4-1/8 x 5-7/8 in which is close to the American 4x6 inch index card.
-
-
-
The most suitable format seems to be DIN A6 (14.8 x 10.5 cm).
Or roughly 4 x 6".
-
Kartenwächter[card guards], also called alarm cards.
-
another advantage to the small size: A6 (14.8 x 10.5 cm) has exactly the samemeasurements as the official German Reich postcard does, which is also the maximum sizepermitted for private post cards. What follows from this is the fact that one can easily addpost cards with scientific or non-scientific content into the sequence of sheets without havingto copy them.
-
For use on the desk, papersheets are the right choice.
paper over card in terms of sheet thickness, particularly over time
-
The sheet box
Interesting choice of translation for "Die Kartei" by the translator. Some may have preferred the more direct "file".
Historically for this specific time period, while index cards were becoming more ubiquitous, most of the prior century researchers had been using larger sheets and frequently called them either slips or sheets based on their relative size.
Beatrice Webb in 1926 (in English) described her method and variously used the words “cards”, “slips”, “quarto”, and “sheets” to describe notes. Her preference was for quarto pages which were larger pages which were likely closer to our current 8.5 x 11” standard than they were to even larger index cards (like 4 x 6".
While I have some dissonance, this translation makes a lot of sense for the specific time period. I also tend to translate the contemporaneous French word “fiches” of that era as “sheets”.
See also: https://hypothes.is/a/OnCHRAexEe2MotOW5cjfwg https://hypothes.is/a/fb-5Ngn4Ee2uKUOwWugMGQ
-
-
threadreaderapp.com threadreaderapp.com
-
I am sponsored by Big Notecard.
-
-
-
Forcertainlyagreatervarietyofcards,clippings,andsuchlikecan befiledbehind 4x6slipsthan behind3x5's.
A benefit of 4 x 6" cards is that clippings and other items can often be more easily filed along with them as opposed to the smaller 3 x 5" cards.
-
shall I adopt the 3x5 slip or the 4x61
Dow indicates in 1924 that 3 x 5" and 4 x 6" are both commonly had in a range of materials the US as well as boxes or cases to keep them in. He does mention that one can also cut their own paper, indicating that this is a possibility.
-
-
www.heise.de www.heise.de
-
Mit der Normierung von Karteikarten für die Karteikästen eigener Fabrikation machte Dewey sich um die Weiterentwicklung der Verzettelungstechniken verdient, ohne etwas damit zu verdienen. Um den ökonomischen Ruin zu verhindern, stellte das Library Bureau im Jahr 1888 die eigene Buchführung vom traditionellen Verbuchungssystem auf das schnellere und kostengünstigere System des "card index" um. Der "Technologietransfer zwischen Bibliothek und Büro" (Krajewski), nämlich die Buchführung in Zettelkästen, wird ein Erfolgsschlager: Banken und Versicherungen, Stahl- und Eisenbahnunternehmen übernehmen das Karteisystem und damit auch die Karteikästen von Deweys Firma.
With the standardization of index cards for the filing boxes of his own manufacture, Dewey earned himself the further development of the routing techniques without earning anything with it. In order to prevent economic ruin, the Library Bureau switched its own bookkeeping from the traditional accounting system to the faster and more cost-effective system of the "card index" in 1888. The "technology transfer between library and office" (Krajewski), namely bookkeeping in card boxes, is a hit: banks and insurance companies, steel and railway companies take over the card system and thus also the card boxes from Dewey's company.
This is a fascinating way of making one's product indispensable. Talk about self-dogfooding!
Sounds similar to the way that some chat messaging productivity apps were born (Slack was this way?). The company needed a better way to communicate internally and so built it's own chat system which they sold to others.
-
-
-
By the earlytwentieth century advice manuals on research methods recommended takingnotes on index cards.141
Here Blair quotes Chavigny and Heyde, but crucially leaves out Bernheim, Langlois & Seignobos, and Beatrice Webb.
Check the others, specifically for index card references, but Webb uses slips or sheets (and often larger ones).
-
-
-
Devices for note-taking. In taking notes of reading,use slips of paper the size of the standard library card(8 x 6 in.). For more extended notes and for typewrittennotes, the standard half-sheet (6% x 8% in.) is usually themost satisfactory sire. For special purposes still larger sheetsare sometimes essential. In any extended investi ation theuse of different colored sli s or different coloref inks forcertain classes of notes w i g often prove a convenient andtime-savin device. It is especially desirable, thus, to dis-tinguish bifliogra hical data from subject matter. Each slipshould contain onyy a single note. Put a topical heading atthe top of each slip of subject notes and a reference to thevolume and page of the authority quoted.
The transcription on this from .pdf via Hypothesis is dreadful! In particular for the card sizes. The actual text reads as:
- Devices for note-taking. In taking notes of reading, use slips of paper the size of the standard library card (3 x5 in.). For more extended notes and for typewritten notes, the standard half-sheet (5 1/2 x 8 1/2 in.) is usually the most satisfactory size. For special purposes still larger sheets are sometimes essential. In any extended investigation the use of different colored slips or different colored inks for certain classes of notes will often prove a convenient and time-saving device. It is especially desirable, thus, to distinguish bibliographical data from subject matter. Each slip should contain only a single note. Put a topical heading at the top of each slip of subject notes and a reference to the volume and page of the authority quoted.
-
-
render.plexus.earth render.plexus.earth
-
https://render.plexus.earth/
-
-
www.ischool.berkeley.edu www.ischool.berkeley.edu
-
Historical Hypermedia: An Alternative History of the Semantic Web and Web 2.0 and Implications for e-Research. .mp3. Berkeley School of Information Regents’ Lecture. UC Berkeley School of Information, 2010. https://archive.org/details/podcast_uc-berkeley-school-informat_historical-hypermedia-an-alte_1000088371512. archive.org.
https://www.ischool.berkeley.edu/sites/default/files/audio/2010-10-20-vandenheuvel_0.mp3

Interface as Thing - book on Paul Otlet (not released, though he said he was working on it)
- W. Boyd Rayward 1994 expert on Otlet
- Otlet on annotation, visualization, of text
- TBL married internet and hypertext (ideas have sex)
- V. Bush As We May Think - crosslinks between microfilms, not in a computer context
- Ted Nelson 1965, hypermedia
t=540
- Michael Buckland book about machine developed by Emanuel Goldberg antecedent to memex
- Emanuel Goldberg and His Knowledge Machine: Information, Invention, and Political Forces (New Directions in Information Management) by Michael Buckland (Libraries Unlimited, (March 31, 2006)
- Otlet and Goldsmith were precursors as well
four figures in his research: - Patrick Gattis - biologist, architect, diagrams of knowledge, metaphorical use of architecture; classification - Paul Otlet, Brussels born - Wilhelm Ostwalt - nobel prize in chemistry - Otto Neurath, philosophher, designer of isotype
Paul Otlet
- wrote bibliography on law
- book: Something on Bibliography #wanttoread
- universal decimal classification system
- mundaneum
- Le Corbusier - architect worked with Otlet for building for Mundaneum; See: https://socks-studio.com/2019/05/05/the-shape-of-knowledge-the-mundaneum-by-paul-otlet-and-henri-la-fontaine/
Otlet was interested in both the physical as well as the intangible aspects of the Mundaneum including as an idea, an institution, method, body of work, building, and as a network.<br /> (#t=1020)
Early iPhone diagram?!?

(roughly) armchair to do the things in the web of life (Nelson quote) (get full quote and source for use) (circa 19:30)
compares Otlet to TBL
Michael Buckland 1991 <s>internet of things</s> coinage - did I hear this correctly? https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_things lists different coinages
Turns out it was "information as thing"<br /> See: https://hypothes.is/a/kXIjaBaOEe2MEi8Fav6QsA
sugane brierre and otlet<br /> "everything can be in a document"<br /> importance of evidence
The idea of evidence implies a passiveness. For evidence to be useful then, one has to actively do something with it, use it for comparison or analysis with other facts, knowledge, or evidence for it to become useful.
transformation of sound into writing<br /> movement of pieces at will to create a new combination of facts - combinatorial creativity idea here. (circa 27:30 and again at 29:00)<br /> not just efficiency but improvement and purification of humanity
put things on system cards and put them into new orders<br /> breaking things down into smaller pieces, whether books or index cards....
Otlet doesn't use the word interfaces, but makes these with language and annotations that existed at the time. (32:00)
Otlet created diagrams and images to expand his ideas
Otlet used octagonal index cards to create extra edges to connect them together by topic. This created more complex trees of knowledge beyond the four sides of standard index cards. (diagram referenced, but not contained in the lecture)
Otlet is interested in the "materialization of knowledge": how to transfer idea into an object. (How does this related to mnemonic devices for daily use? How does it relate to broader material culture?)
Otlet inspired by work of Herbert Spencer
space an time are forms of thought, I hold myself that they are forms of things. (get full quote and source) from spencer influence of Plato's forms here?
Otlet visualization of information (38:20)
S. R. Ranganathan may have had these ideas about visualization too
atomization of knowledge; atomist approach 19th century examples:S. R. Ranganathan, Wilson, Otlet, Richardson, (atomic notes are NOT new either...) (39:40)
Otlet creates interfaces to the world - time with cyclic representation - space - moving cube along time and space axes as well as levels of detail - comparison to Ted Nelson and zoomable screens even though Ted Nelson didn't have screens, but simulated them in paper - globes
Katie Berner - semantic web; claims that reporting a scholarly result won't be a paper, but a nugget of information that links to other portions of the network of knowledge.<br /> (so not just one's own system, but the global commons system)
Mention of Open Annotation (Consortium) Collaboration:<br /> - Jane Hunter, University of Australia Brisbane & Queensland<br /> - Tim Cole, University of Urbana Champaign<br /> - Herbert Van de Sompel, Los Alamos National Laboratory annotations of various media<br /> see:<br /> - https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311366469_The_Open_Annotation_Collaboration_A_Data_Model_to_Support_Sharing_and_Interoperability_of_Scholarly_Annotations - http://www.openannotation.org/spec/core/20130205/index.html - http://www.openannotation.org/PhaseIII_Team.html
trust must be put into the system for it to work
coloration of the provenance of links goes back to Otlet (~52:00)
Creativity is the friction of the attention space at the moments when the structural blocks are grinding against one another the hardest. —Randall Collins (1998) The sociology of philosophers. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press (p.76)
Tags
- atomic notes
- Hypothes.is
- mnemonic devices
- S. R. Ranganathan
- Michael Buckland
- Tim Berners-Lee
- materialization of knowledge
- Mundaneum
- hypermedia
- Web 2.0
- material culture
- listen
- atomic ideas
- Paul Otlet
- Emanuel Goldberg
- octagonal index cards
- semantic web
- atomist philosophy
- Le Corbusier
- index cards
- Herbert Spencer
- memex
- Ted Nelson
- idea links
- Herbert Van de Sompel
- Open Annotation Collaboration
- Otto Neurath
- Tim Cole
- Charles van den Heuvel
- Jane Hunter
- Vannevar Bush
- Randall Collins
- evidence
- references
- Wilhelm Ostwalt
- Universal Decimal Classification
- W. Boyd Rayward
Annotators
URL
-
-
socks-studio.com socks-studio.com
-

Notice the octagonal shape of this rooms which mirrors in some ways the octagonal index cards mentioned by Charles van den Heuvel in his Regents Lecture (2008) which Otlet used to link via subject headings. You'll see here subject headings on the walls of the architecture to match.
link to: - https://hypothes.is/a/8e9hThZ4Ee2hWAcV1j5B9w
-
-
wiki.c2.com wiki.c2.com
-
used for project management. The logistics for the Gulf War were managed on index cards. Read "Moving Mountains" by Lt. General George Pagonis.
Example of index cards used for project management.
-
-
www.popularmechanics.com www.popularmechanics.com
-
https://www.popularmechanics.com/culture/a19379/a-short-history-of-the-index-card/
Broad history essay but doesn't dig into the weeds. Feels a lot like a few other essays I've seen of this sort. Content farmish...
-
-
multimediaman.blog multimediaman.blog
-
In 1895, the Belgians Paul Otlet (1868-1944) and Henri La Fontaine founded the International Institute of Bibliography (IIB) and began working on something they called the Universal Bibliographic Repertory (UBR), an enormous catalog based on index cards. Funded by the Belgian government, the UBR involved the collection of books, articles, photographs and other documents in order to create a one-of-a-kind international index.
-
In 1896, Dewey formed a partnership with Herman Hollerith and the Tabulating Machine Company (TMC) to provide the punch cards used for the electro-mechanical counting system of the US government census operations. Dewey’s relationship with Hollerith is significant as TMC would be renamed International Business Machines (IBM) in 1924 and become an important force in the information age and creator of the first relational database.
-
After thirty years of working with notebooks, Linnaeus began to experiment with a filing system of information recorded on separate sheets of paper.
Carl Linnaeus used notebooks for thirty years before beginning to experiment with information written on slips of paper.
-
-
lifehacker.com lifehacker.com
-
I know a lot of people use Evernote for this but I think physical is better. You want to be able to move the stuff around.
Holiday prefers physical index cards over digital systems like Evernote because he wants to have the ability to "move the stuff around."
-
-
-
Alternate index card holding furniture for display?<br /> https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/wffvs4/alternate_index_card_holding_furniture_for_display/
Separate from boxes for long term card holding storage, does anyone have any suggestions they like for organizing or temporarily displaying cards?
I've got a couple card tray rack organizers (originally intended for playing cards, but great for zettels) which I generally like.

I've also seen Levenger's note card "bleachers" which are similar, but more expensive. - Note Card Bleachers - Portable Note Card Bleachers - Nantucket Bamboo Compact Bleachers
 Levenger index card bleacher for compactly displaying index cards in an array on a desk so that portions are visible but that they don't take up space.
Levenger index card bleacher for compactly displaying index cards in an array on a desk so that portions are visible but that they don't take up space.Does anyone have anything else they like for compact working/displaying aside from laying cards out on tables/desks?
Do you have other methods for this sort of organization or layout of ideas visually? Corkboards, magnetic whiteboards/walls, other?
-
-
universitylifecafe.k-state.edu universitylifecafe.k-state.edu
-
https://universitylifecafe.k-state.edu/bookshelf/academicskills/indexcardstudysystem.html
Natalie Umberger is writing about an "index card study system" in an academic study skills context, but it's an admixture of come ideas from Cornell Notes and using index cards as flashcards.
The advice to "Review your notes and readings frequently, so the material is 'fresh.' " is a common one (through at least the 1980s to the present), though research on the mere-exposure effect indicates that it's not as valuable as other methods.
How can we stamp out the misconception that this sort of review is practical?
-
-
www.preservearticles.com www.preservearticles.com
-
This page seems to be broadly copied from the book Secretarial Practice and Company Law by Arun Kumar and Rachana Sharma (Atlantic Publishers & Distributors (P) Limited, 1998) # and specifically page 529.
It contains no other history or references that I can immediately see. The book seems to be written for a secretarial audience in India in the 1990's, and while interesting not otherwise pertinent to immediate to my historical questions.
-
- Jul 2022
-
Local file Local file
-
THE ART OF NOTE-TAKING
Beatrice Webb's suggestions: - Use sheets of paper and not notebooks, specifically so one can re-arrange, shuffle, and resort one's notes - She uses quarto pages as most convenient (quarto sizes have varied over time, but presumably hers were in the range of 8.5 x 11" sheets of paper, and thus rather large compared to index cards
It takes some careful attention, but her description of her method and how she used it in a pre-computer era is highly indicative of the fact that Beatrice Webb was actively creating a paper database system which she could then later query to compile data to either elicit insight or to prove answers to particular questions.
She specifically advises that one keep one and only one sort of particular types of data on each card whether that be dates, locations, subjects, or categories of facts. This is directly equivalent to the modern database design of only keeping one value in a particular field. As a result, each sheet within her notes might be equivalent to a row of related data which might contain a variety of different types of individual data. By not mixing data on individual sheets one can sort and resort their tables and effectively search through them without confusing data types.
Her work and examples here would have been in the period of 1890 and 1910 (she specifically cites that this method was used for her research on the "principles of 1834" which was subsequently published as English Poor Law Policy in 1910) at a time after Basile Bouchon and Joseph Marie Jacquard and contemporaneously with Herman Hollerith who were using punched cards for some of this sort of work.
-
An instance may be given of the necessity of the “ separate sheet ” system.Among the many sources of information from which we constructed our bookThe Manor and the Borough were the hundreds of reports on particular boroughsmade by the Municipal Corporation Commissioners in 1835 .These four hugevolumes are well arranged and very fully indexed; they were in our own possession;we had read them through more than once; and we had repeatedly consulted themon particular points. We had, in fact, used them as if they had been our own boundnotebooks, thinking that this would suffice. But, in the end, we found ourselvesquite unable to digest and utilise this material until we had written out every oneof the innumerable facts on a separate sheet of paper, so as to allow of the mechanicalabsorption of these sheets among our other notes; of their complete assortment bysubjects; and of their being shuffled and reshuffled to test hypotheses as to suggestedco-existences and sequences.
Webb's use case here sounds like she's got the mass data, but that what she really desired was a database which she could more easily query to do her work and research. As a result, she took the flat file data and made it into a manually sortable and searchable database.
-
By the method of note-taking that I have described, it was practicableto sort out all our thousands of separate pieces of paper according toany, or successively according to all, of these categories or combinationof categories
The broad description of Beatrice Webb's note taking system sounds almost eerily like the idea behind edge notched cards, however in her case she was writing note in particular locations on cards in an effort to help her cause rather than putting physical punch holes into them.
-
“ Every one agrees nowadays ”, observethe most noted French writers on the study of history, “ that it is advisable to collectmaterials on separate cards or slips of paper. . . . The advantages of this artifice areobvious; the detachability of the slips enables us to group them at will in a host ofdifferent combinations; if necessary, to change their places; it is easy to bring textsof the same kind together, and to incorporate additions, as they are acquired, in theinterior of the groups to which they belong ” (Introduction to the Study of History,by Charles Langlois and Charles Seignobos, translated by C. G. Berry, 1898, p.103). “
Tags
- flat files
- slips
- punched cards
- edge-notched cards
- Joseph Marie Jacquard
- search
- combinations
- note taking methods
- databases
- computer science
- intellectual history
- Charles Seignobos
- discovery
- note taking
- note taking affordances
- Charles Langlois
- archives
- index cards
- Basile Bouchon
- Beatrice Webb
- Herman Hollerith
- 1898
Annotators
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Punched_card
Link to Beatrice Webb's use of note taking methods as a means of data storage, search, and sort in the early 1900s.
-
-
www.ibm.com www.ibm.comIBM Docs1
-
Quarto 215 x 275 mm
roughly 8.46 inches x 10.8 inches or about the size of an 8.5 x 11" sheet
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
Over the course of his intellectual life, from about 1943 until hissudden death in 1980, Barthes built a card index consisting of morethan 12,250 note cards – the full extent of this collection was notknown until access to it was granted to the manuscript researchers ofthe Institut Mémoires de l’édition contemporaine (IMEC) inFrance (Krapp, 2006: 363).3
Roland Barthes accumulated a card index of more than 12,250 note cards beginning in 1943 which were held after his death in 1980 at the Institut Mémoires de l’édition contemporaine (IMEC) in France.
Barthes' dates 12 November 1915 – 26 March 1980 age 64
He started his card index at roughly age 28 and at around the same time which he began producing written work. (Did he have any significant writing work or publications prior to this?)
His card collection spanned about 37 years and at 12,250 cards means that was producing on average 0.907 cards per day. If we don't include weekends, then he produced 1.27 cards per day on average. Compare this with Ahrens' estimate of 6 cards a day for Niklas Luhmann.
With this note I'm starting the use of a subject heading (in English) of "card index" as a generic collection of notes which are often kept in one or more boxes. This is to distinguish it from the more modern idea of zettelkasten in the Luhmann framing which also connotes a dense set of links between the cards themselves, though this may not have been the case historically. Card index is also specifically separate from 'index card' which is an individual instance of an item that might be found in a card index. At present, I'm unaware of a specific word in English which defines the broader note taking context or portions thereof relating to index cards in the same way that a zettelkasten implies. This may be the result of the broad use of index cards for so many varying uses in the early 20th century. For these other varying uses I'll try to differentiate them henceforth with the generic 'index card files' which might also be used to describe the containers in which cards might be found.
-
-
www.zylstra.org www.zylstra.org
-
https://www.zylstra.org/blog/2022/06/spring-83/
I've been thinking about this sort of thing off and on myself.
I too almost immediately thought of Fraidyc.at and its nudge at shifting the importance of content based on time and recency. I'd love to have a social reader with additional affordances for both this time shifting and Ton's idea of reading based on social distance.
I'm struck by the seemingly related idea of @peterhagen's LindyLearn platform and annotations: https://annotations.lindylearn.io/new/ which focuses on taking some of the longer term interesting ideas as the basis for browsing and chewing on. Though even here, one needs some of the odd, the cutting edge, and the avant garde in their balanced internet diet. Would Spring '83 provide some of this?
I'm also struck by some similarities this has with the idea of Derek Siver's /now page movement. I see some updating regularly while others have let it slip by the wayside. Still the "board" of users exists, though one must click through a sea of mostly smiling and welcoming faces to get to it the individual pieces of content. (The smiling faces are more inviting and personal than the cacophony of yelling and chaos I see in models for Spring '83.) This reminds me of Stanley Meyers' frequent assertion that he attempted to design a certain "sense of quiet" into the early television show Dragnet to balance the seeming loudness of the everyday as well as the noise of other contemporaneous television programming.
The form reminds me a bit of the signature pages of one's high school year book. But here, instead of the goal being timeless scribbles, one has the opportunity to change the message over time. Does the potential commercialization of the form (you know it will happen in a VC world crazed with surveillance capitalism) follow the same trajectory of the old college paper facebook? Next up, Yearbook.com!
Beyond the thing as a standard, I wondered what the actual form of Spring '83 adds to a broader conversation? What does it add to the diversity of voices that we don't already see in other spaces. How might it be abused? Would people come back to it regularly? What might be its emergent properties?
It definitely seems quirky and fun in and old school web sort of way, but it also stresses me out looking at the zany busyness of some of the examples of magazine stands. The general form reminds me of the bargain bins at book stores which have the promise of finding valuable hidden gems and at an excellent price, but often the ideas and quality of what I find usually isn't worth the discounted price and the return on investment is rarely worth the effort. How might this get beyond these forms?
It also brings up the idea of what other online forms we may have had with this same sort of raw experimentation? How might the internet have looked if there had been a bigger rise of the wiki before that of the blog? What would the world be like if Webmention had existed before social media rose to prominence? Did we somehow miss some interesting digital animals because the web rose so quickly to prominence without more early experimentation before its "Cambrian explosion"?
I've been thinking about distilled note taking forms recently and what a network of atomic ideas on index cards look like and what emerges from them. What if the standard were digital index cards that linked and cross linked to each other, particularly in a world without adherence to time based orders and streams? What does a new story look like if I can pull out a card either at random or based on a single topic and only see it or perhaps some short linked chain of ideas (mine or others) which come along with it? Does the choice of a random "Markov monkey" change my thinking or perspective? What comes out of this jar of Pandora? Is it just a new form of cadavre exquis?
This standard has been out for a bit and presumably folks are experimenting with it. What do the early results look like? How are they using it? Do they like it? Does it need more scale? What do small changes make to the overall form?
For more on these related ideas, see: https://hypothes.is/search?q=tag%3A%22spring+%2783%22
Tags
- atomic notes
- read
- cadavre exquis
- Now Now Now
- web standards
- atomic idea links
- experimental fiction
- quiet
- yearbooks
- alternate universes
- Derek Sivers
- calmness
- media studies
- Markov monkey
- narrative forms
- Dragnet
- Lindy library
- Spring '83
- experimental media
- Fraidyc.at
- index cards
- combinatorial creativity
- Pandora's box
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.remastery.net www.remastery.net
-
Beyond the cards mentioned above, you should also capture any hard-to-classify thoughts, questions, and areas for further inquiry on separate cards. Regularly go through these to make sure that you are covering everything and that you don’t forget something.I consider these insurance cards because they won’t get lost in some notebook or scrap of paper, or email to oneself.
Julius Reizen in reviewing over Umberto Eco's index card system in How to Write a Thesis, defines his own "insurance card" as one which contains "hard-to-classify thoughts, questions, and areas for further inquiry". These he would keep together so that they don't otherwise get lost in the variety of other locations one might keep them
These might be akin to Ahrens' "fleeting notes" but are ones which may not easily or even immediately be converted in to "permanent notes" for one's zettelkasten. However, given their mission critical importance, they may be some of the most important cards in one's repository.
link this to - idea of centralizing one's note taking practice to a single location
Is this idea in Eco's book and Reizen is the one that gives it a name since some of the other categories have names? (examples: bibliographic index cards, reading index cards (aka literature notes), cards for themes, author index cards, quote index cards, idea index cards, connection cards). Were these "officially" named and categorized by Eco?
May be worthwhile to create a grid of these naming systems and uses amongst some of the broader note taking methods. Where are they similar, where do they differ?
Multi-search tools that have full access to multiple trusted data stores (ostensibly personal ones across notebooks, hard drives, social media services, etc.) could potentially solve the problem of needing to remember where you noted something.
Currently, in the social media space especially, this is not a realized service.
-
Even the sloppiest manuscript would bring twenty new cards for my hoard.
This quote is similar to the broad idea (source(s)?) that one can learn something even from the worst books or the man who's a fool.
I've excerpted the portion of the quote that appears before this in the past. See: https://hyp.is/jqug2tNlEeyg2JfEczmepw/3stages.org/c/gq_title.cgi?list=1045&ti=Foucault%27s%20Pendulum%20(Eco)
Tags
- quotes
- card index
- search
- note taking methods
- fleeting notes
- note taking why
- card index for writing
- tools for thought affordances
- zettelkasten
- insurance cards
- multi-search
- learning
- fleeting ideas
- permanent notes
- Umberto Eco
- types of notes
- fools
- index cards
- IndieWeb search
- note taking process
Annotators
URL
-
- Jun 2022
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bP7AXjA4O6U
meh... nothing new here for me
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
u/sscheper in writing your book, have you thought about the following alternative publishing idea which I'm transcribing from a random though I put on a card this morning?
I find myself thinking about people publishing books in index card/zettelkasten formats. Perhaps Scott Scheper could do this with his antinet book presented in a traditional linear format, but done in index cards with his numbers, links, etc. as well as his actual cards for his index at the end so that readers could also see the power of the system by holding it in their hands and playing with it?
It could be done roughly like Edward Powys Mathers' Cain's Jawbone or Henry Korn's Pontoon Manifesto? Perhaps numbered consecutively to make it easier to bring back into that format, but also done with your zk numbering so that people could order it and use it that way too? This way you get the book as well as a meta artifact of what the book is about as an example of how to do such a thing for yourself. Maybe even make a contest for a better ordering for the book than the one you published it in ?
Link to: - https://hyp.is/6IBzkPfeEeyo9Suq-ZmCKg/www.scientificamerican.com/article/reading-paper-screens/
-
-
www.scientificamerican.com www.scientificamerican.com
-
surveys indicate that screens and e-readers interfere with two other important aspects of navigating texts: serendipity and a sense of control.
Based on surveys, readers indicate that two important parts of textual navigation are sense of control and serendipity.
http://books.google.com/books/about/Electronic_journal_literature.html?id=YSFlAAAAMAAJ
How does the control over a book frame how we read? What does "power over" a book look like compared to "power with"?
What are the tools for thought affordances that paper books provide over digital books and vice versa?
I find myself thinking about people publishing books in index card/zettelkasten formats. Perhaps Scott Scheper could do this with his antinet book presented in a linear format, but done in index cards with his numbers, links, etc. as well as his actual cards for his index so that readers could also see the power of the system by holding it in their hands and playing with it.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Luhmann’s zettelkasten use case .t3_vlape5._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; } I was just thinking… I wonder what Luhmann’s use case for his zettelkasten was. By this I mean, was his original use for it for knowledge development, then his papers/books came as a successful bi-product? Or was his original intention to use it to actually write books/papers in the first place… Does anyone have any insight on this?
When asked by Bielefeld University to report on his research projects, Luhmann famously replied:
“Theory of society; duration: 30 years; costs: none”.
In this there is a tremendously large nod to his zettelkasten to permit this work to be done.
Though technically at the current price of $11.78 for 1,000 index cards on Amazon right now and a total of 92,000 cards, Luhmann should have better budgeted 1083.76 for the paper not to mention the cost of pens and pencils.
Luhmann, N. (1997). Die Gesellschaft der Gesellschaft (2 vols). Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Suhrkamp. Published in translation as Theory of society (2 vols.). Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press 2012–2013.
-
-
www.iemoji.com www.iemoji.com
-
The fact that there are three discrete emoji for the - card file box 🗃️ - card index dividers 🗂️ - card index (aka rolodex) 📇
indicate the importance of these older analog tools, even in a more modern digital space.
-
-
-
Sometimes the goal is nothing more than a personal mantra such as “keep itsimple” or “something perfect” or “economy” to remind me of what I was thinkingat the beginning if and when I lose my way. I write it down on a slip of paper and it’sthe first thing that goes into the box.
-
The second was “makedance pay for the dancers.” I’ve always been resentful of the fact that some of theso-called elite art forms can’t survive on their own without sponsorship andsubsidies. It bothers me that dance companies around the world are not-for-profitorganizations and that dancers, who are as devoted and disciplined as any NFL orNBA superstar, are at the low end of the entertainment industry’s income scale. Iwanted this Broadway-bound project not only to elevate serious dance in thecommercial arena but also to pay the dancers well. So I wrote my goals for theproject, “tell a story” and “make dance pay,” on two blue index cards and watchedthem float to the bottom of the Joel box.
Given the importance of dance in oral cultures, what, why, and how has dance moved to be one of the seemingly lowest and least well paid art forms in modern society?
How might modern dance regain its teaching and mnemonic status in our culture?
-
-
-
You may prefer notebooks to cards for note taking-very well:use what you like, but invariably; it will save you time andannoyance. If you use cards , use small ones (3" x 5") so that youuse a separate card for each fact, title, or memorandum toyourself. The cards are then easily shuffled for grouping. If youuse a notebook, leave a margin for the key word, letter, or num-ber which you will insert later as an index to the contents.
-
- May 2022
-
www.uni-bielefeld.de www.uni-bielefeld.de
-
The pixel portrait of Niklas Luhmann was created by Sebastian Zimmer (CCeH) using the software AndreaMosaic from the image of 1271 slips of paper from the 'Zettelkasten'.
 © Alexander Kluge/ Universität Bielefeld*
© Alexander Kluge/ Universität Bielefeld*
-
-
via3.hypothes.is via3.hypothes.is
-
Despite the librarian card-theoreticalrecommendation of only using cardboard or strong paper as a bearer of information,17Luhmann relies on plain typewriter paper for spatial economy, which can quickly lead,however, to the deterioration of the medium with frequent browsing.
For Luhmann's time, the librarian recommendation for substrate was either cardboard or strong paper as the carrier for information, but he eschewed this recommendation in favor of plain typewriter paper because it took up less space. This came at the cost of deterioration of many of his cards through regular use however.
-
According to this, the arrangement consists of “wooden boxes with drawers that pullout in the front, and cards in octavo format ” (= DIN A5).
Luhmann's zettelkasten collection of cards was in octavo format, aka DIN A5 (148mm x 210mm or 5.8" x 8.3").
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Between 1930 to 1980,Labrousse, Daumard, and Kuznets carried out their research almostexclusively by hand, on file cards.
Piketty indicates that Ernest Labrousse, Adeline Daumard, and Simon Kuznets carried out their economic and historical research almost exclusively by hand using file cards.
Are their notes still extant? What did their systems look like? From whom did they learn them?
Tags
Annotators
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
The first early modern card index was designed by Thomas Harrison (ca 1640s). Harrison's manuscript on The Ark of Studies[5] (Arca studiorum) was edited and improved by Vincent Placcius in his well-known handbook on excerpting methods (De arte excerpendi, 1689).
-
-
Local file Local file
-
The last element in his file system was an index, from which hewould refer to one or two notes that would serve as a kind of entrypoint into a line of thought or topic.
Indices are certainly an old construct. One of the oldest structured examples in the note taking space is that of John Locke who detailed it in Méthode nouvelle de dresser des recueils (1685), later translated into English as A New Method of Organizing Common Place Books (1706).
Previously commonplace books had been structured with headwords done alphabetically. This meant starting with a preconceived structure and leaving blank or empty space ahead of time without prior knowledge of what would fill it or how long that might take. By turning that system on its head, one could fill a notebook from front to back with a specific index of the headwords at the end. Then one didn't need to do the same amount of pre-planning or gymnastics over time with respect to where to put their notes.
This idea combined with that of Konrad Gessner's design for being able to re-arrange slips of paper (which later became index cards based on an idea by Carl Linnaeus), gives us an awful lot of freedom and flexibility in almost any note taking system.
Building blocks of the note taking system
- atomic ideas
- written on (re-arrangeable) slips, cards, or hypertext spaces
- cross linked with each other
- cross linked with an index
- cross linked with references
are there others? should they be broken up differently?
Godfathers of Notetaking
- Aristotle, Cicero (commonplaces)
- Seneca the Younger (collecting and reusing)
- Raymond Llull (combinatorial rearrangements)
- Konrad Gessner (storage for re-arrangeable slips)
- John Locke (indices)
- Carl Linnaeus (index cards)
-
-
-
In §§ 4–5, I examine the socio-evolutionary circumstances under which a closed combinatory, such as the one triggered by the Llullian art, was replaced by an open-ended combinatory, such as the one triggered by a card index based on removable entries. In early modernity, improvement in abstraction compelled scholars to abandon the idea that the order of knowledge should mirror the order of nature. This development also implied giving up the use of space as a type of externalization and as the main rule for checking consis-tency.
F*ck! I've been scooped!
Apparently I'm not the only one who has noticed this, though I notice that he doesn't cite Frances A. Yates, which would have certainly been the place for having come up with this historical background (at least that's where I found it.)
The Llullian arts can be more easily practiced with ideas placed on moveable index cards than they might be with ideas stored in one's own memory. Thus the index card as a tool significantly decreases the overhead and provides an easier user interface for permuting one's ideas and combining them. This decrease in mental work appearing at a time of information overload also puts specific pressure on the older use of the art of memory to put it out of fashion.
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
i started creating and using notecards and this isn't like 2006.
Scott P. Scheper left off of notebooks and started using note cards in 2006.
-
- Apr 2022
-
-
https://ello.co/dredmorbius/post/u4dgr0tkxk4tk9npuvex5a
<small><cite class='h-cite ht'>↬ <span class='p-author h-card'>Dave Gauer</span> in Inspiration for the virtual box of cards - ratfactor (<time class='dt-published'>02/27/2022 14:21:56</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
-
INTERVIEWER: Could you say something of your work habits?Do you write to a preplanned chart? Do you jump from onesection to another, or do you move from the beginning throughto the end?NABOKOV: The pattern of the thing precedes the thing. I fill inthe gaps of the crossword at any spot I happen to choose. Thesebits I write on index cards until the novel is done. My schedule
is flexible, but I am rather particular about my instruments: lined Bristol cards and well sharpened, not too hard, pencils capped with erasers.
Nabokov on his system of writing.
-
Mr. Nabokov’s writing method is to compose his stories and novels on index cards,shuffling them as the work progresses since he does not write in consecutive order.Every card is rewritten many times. When the work is completed,the cards in final order, Nabokov dictates from them to his wifewho types it up in triplicate.
Vladimir Nabokov's general writing method consisted of composing his material on index cards so that he could shuffle them as he worked as he didn't write in consecutive order. He rewrote and edited cards many times and when the work was completed with the cards in their final order, Nabokov dictated them to his wife Vera who would type them up in triplicate.
-
-
boffosockobooks.com boffosockobooks.com
-
-
Local file Local file
-
It is notinsignificant either that among the illustrations of the Roland Barthes par RolandBarthes there are a series of facsimile reproductions of the author’s handwriting,analogic reproductions of linguistic graphemes, pieces of writing silenced,abstracted from the universe of discourse by their photographic reproduction. Inparticular, as we have seen, the three index cards are reproduced not for the sakeof their content, not for their signified, but for a reality-effect value for which ourexpanding taste, says Barthes, encompasses the fashion of diaries, of testimonials,of historical documents, and, most of all, the massive development of photogra-
phy. In that sense, the reproduction of these three slips ironically resonates, if on a different scale, with the world tour of the mask of Tutankhamen. It refers, if not to the magic silence of a relic, at least to the ghostly parergonal quality of what French language calls a reliquat.
Hollier argues that Barthes' reproduced cards are not only completely divorced from their original context and use, but that they are reproduced for the sheen of reality and artistic fashion they convey to the reader. So much thought, value, and culture is lost in the worship of these items in this setting compared to their original context.
This is closely linked to the same sort of context collapse highlighted by the photo of Chief William Berens seated beside the living stones of his elders in Tim Ingold's Why Anthropology Matters. There we only appreciate the sense of antiquity, curiosity, and exoticness of an elder of a culture that is not ours. These rocks, by very direct analogy, are the index cards of the zettelkasten of an oral culture.
 Chief William Berens seated beside the living stones of his elders; a picture taken by A. Irving Hallowell in 1930, between Grand Rapids and Pikangikum, Ontario, Canada. (American Philosophical Society)
Chief William Berens seated beside the living stones of his elders; a picture taken by A. Irving Hallowell in 1930, between Grand Rapids and Pikangikum, Ontario, Canada. (American Philosophical Society) -
Hollier, Denis. “Notes (On the Index Card).” October 112, no. Spring (2005): 35–44. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3397642
Read: 2022-04-20 15:36
Interesting material on Barthes' use of note cards, though not in depth. Some interesting discussion on the idea of autobiography from a philosophical perspective.
The first five sections were interesting to me, the last two a bit denser and not as clear or interesting without additional context.
-
Roland Barthes par Roland Barthes. This time, the index cards werealready there. One of the pages of illustrations of the volume reproduces three ofthem in facsimile. The text doesn’t comment on them, doesn’t even allude tothem. There is just a caption: “Reversal: of scholarly origin, the index card endsup following the twists and turns of the drive.”
In his book Roland Barthes par (by) Roland Barthes, Barthes reproduces three of his index cards in facsimile. The text doesn't comment or even allude to them, they're presented only with the captions "Reversal: of scholarly origin, the note follows the various twists and turns of movement." "...outside...", and "...or at a desk".
In this setting, the card index proves itself the most direct co-author as it physically appears in Barthes' autobiography!
-
In his practice, Leiris wrote,Duchamp demonstratesall the honesty of a gambler who knows that the game only has meaningto the extent that one scrupulously observes the rules from the very out-set. What makes the game so compelling is not its final result or how wellone performs, but rather the game in and of itself, the constant shiftingaround of pawns, the circulation of cards, everything that contributes tothe fact that the game—as opposed to a work of art—never stands still.
particularly:
but rather the game in and of itself, the constant shifting around of pawns, the circulation of cards, everything that contributes to the fact that the game--as opposed to a work of art--never stands still.
This reminds me of some of the mnemonic devices (cowrie shells) that Lynne Kelly describes in combinatorial mnemonic practice. These are like games or stories that change through time. And these are fairly similar to the statistical thermodynamics of life and our multitude of paths through it. Or stories which change over time.
Is life just a game?
there's a kernel of something interesting here, we'll just need to tie it all together.
Think also of combining various notes together in a zettelkasten.
Were these indigenous tribes doing combinatorial work in a more rigorous mathematical fashion?
Tags
- context collapse
- Denis Hollier
- Michel Leiris
- read
- cards
- talking rocks
- note taking in oral cultures
- games
- game of life
- reality
- life
- autobiography
- references
- orality
- William Berens
- combinatorics
- Roland Barthes
- Lynne Kelly
- card index as autobiography
- zettelkasten
- note taking
- card index as co-author
- gambling
- art
- index cards
- reliquat
- cowrie shells
- combinatorial creativity
- memory
Annotators
-
-
www.newyorker.com www.newyorker.com
-
Embarrassed and almost guilty because sometimes I feel that my mourning is merely a susceptibility to emotion. But all my life haven’t I been just that: moved?

-
Struck by the abstract nature of absence; yet it’s so painful, lacerating. Which allows me to understand abstraction somewhat better: it is absence and pain, the pain of absence—perhaps therefore love?

-
—How strange: her voice, which I knew so well, and which is said to be the very texture of memory (“the dear inflection…”), I no longer hear. Like a localized deafness…

-
—”Never again, never again!” —And yet there’s a contradiction: “never again” isn’t eternal, since you yourself will die one day. “Never again” is the expression of an immortal. (Images courtesy Michel Salzedo.)

-
I was fortunate enough to see—and now share with you—a handful of these diaries from 1977 in their original, hand-written form. (A collection of more than three hundred entries, entitled “Mourning Diary,” will be published by Hill and Wang next month.)
Hill and Wang published Mourning Diary by Roland Barthes on October 12, 2010. It is a collection of 330 entries which he wrote following the death of his mother Henriette in 1977.
Kristina Budelis indicates that she saw them in person and reproduced four of them as index card-like notes in The New Yorker (September 2010).
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
In one interview, Barthes lists the fragment among the ‘twenty keywords’ most important to him (see Barthes, 1991: 205-211).
-
Krapp argues that, despite its ‘respectablelineage’, the card index generally ‘figures only as an anonymous,furtive factor in text generation, acknowledged – all the way into thetwentieth century – merely as a memory crutch’ (361).2 A keyreason for this is due to the fact that the ‘enlightened scholar isexpected to produce innovative thought’ (361); knowledgeproduction, and any prostheses involved in it, ‘became and remaineda private matter’ (361).
'Memory crutch' implies a physical human failing that needs assistance rather than a phrase like aide-mémoire that doesn't draw that same attention.
-
In a remarkable essay on precursors to hypertext, Peter Krapp(2006) provides a useful overview of the development of the indexcard and its use by various thinkers, including Locke, Leibniz, Hegel,and Wittgenstein, as well as by those known to Barthes and part of asimilar intellectual milieu, including Michel Leiris, Georges Perec,and Claude Lévi-Strauss (Krapp, 2006: 360-362; Sieburth, 2005).1
Peter Krapp created a list of thinkers including Locke, Leibniz, Hegel, Wittgenstein, Barthes, Michel Leiris, Georges Perec, and Lévi-Strauss who used index cards in his essay Hypertext Avant La Lettre on the precursors of hypertext.
see also: Krapp, P. (2006) ‘Hypertext Avant La Lettre’, in W. H. K. Chun & T. Keenan (eds), New Media, Old Theory: A History and Theory Reader. New York: Routledge: 359-373.
Notice that Krapp was the translator of Paper Machines About Cards & Catalogs, 1548 – 1929 (MIT Press, 2011) by Marcus Krajewski. Which was writing about hypertext and index cards first? Or did they simply influence each other?
-
arthes’ use ofindex cards has been documented elsewhere (Krapp, 2006; Hollier,2005; Calvet, 1994)
Roland Barthes' use of index cards has been documented by the following:
Krapp, P. (2006) ‘Hypertext Avant La Lettre’, in W. H. K. Chun & T. Keenan (eds), New Media, Old Theory: A History and Theory Reader. New York: Routledge: 359-373.
Hollier, D. (2005) ‘Notes (on the Index Card)’, October 112 (Spring): 35-44.
Calvet, J.-L. (1994) Roland Barthes: A Biography. Trans. S. Wykes. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
-
Calvet, J.-L. (1994) Roland Barthes: A Biography. Trans. S. Wykes.Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
Includes some research on the use Roland Barthes made of index cards for note taking to create his output.
-
Krapp, P. (2006) ‘Hypertext Avant La Lettre’, in W. H. K. Chun & T.Keenan (eds), New Media, Old Theory: A History and Theory Reader.New York: Routledge: 359-373.
-
Denis Hollier, in an essayon index card use by Barthes and Michel Leiris, argues that Leiris’use of index cards in writing his autobiography results in ‘asecondary, indirect autobiography, originating not from thesubject’s innermost self, but from the stack of index cards (theautobiographical shards) in the little box on the author’s desk’(Hollier, 2005: 39).
Wait, what?! Someone's written an essay on index card use by these two?!
Tags
- memory crutch
- Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz
- external scaffolding
- Michel Leiris
- paper machines
- want to read
- Denis Hollier
- external structures for thought
- Georges Perec
- Georg Hegel
- Ludwig Wittgenstein
- fragments
- hypertext
- Marcus Krajewski
- Peter Krapp
- innovation
- autobiography
- insight
- prostheses
- zettelkasten
- Roland Barthes
- note taking
- aide-mémoire
- thinking
- scaffolding
- index cards
- Claude Lévi-Strauss
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.loc.gov www.loc.gov
-
Nabokov’s working notecards for “Lolita.”
Nabokov used index cards for his research and writing. In one index card for research on Lolita, he creates a "weight-heigh-age table for girls of school age" to be able to specify Lolita's measurements. He also researched the Colt catalog of 1940 to get gun specifications to make those small points realistic in his writing.


-
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Colin Marshall</span> in The Notecards on Which Vladimir Nabokov Wrote Lolita: A Look Inside the Author's Creative Process | Open Culture (<time class='dt-published'>04/10/2022 12:18:34</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
www.openculture.com www.openculture.com
-
https://www.openculture.com/2014/02/the-notecards-on-which-vladimir-nabokov-wrote-lolita.html
Some basic information about Vladimir Nabokov's card file which he was using to write The Origin of Laura and a tangent on cards relating to Lolita.
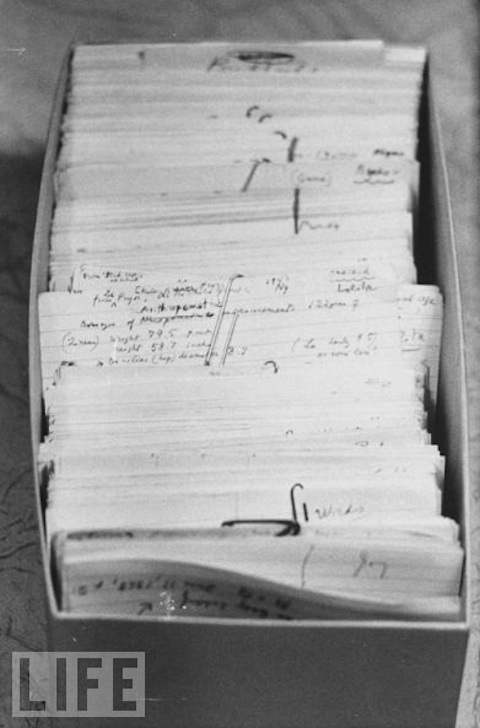


-
-
www.researchgate.net www.researchgate.net
-
Henri Cartier-Bresson, Roland Barthes, 1963. © PAR79520 Henri CartierBresson/Magnum Photos.
A photo of Roland Barthes from 1963 featured in Picturing Barthes: The Photographic Construction of Authorship (Oxford University Press, 2020) DOI: 10.5871/bacad/9780197266670.003.0007
There appears to be in index card file behind him in the photo, which he may have used for note taking in the mode of a zettelkasten.

link to journal article notes on:
Wilken, Rowan. “The Card Index as Creativity Machine.” Culture Machine 11 (2010): 7–30. https://culturemachine.net/creative-media/
-
-
-
anadvocate for the index card in the early twentieth century, for example, called forthe use of index cards in imitation of “accountants of the modern school.”32
Zedelmaier argues that scholarly methods of informa- tion management inspired bureaucratic information management; see Zedelmaier (2004), 203.
Go digging around here for links to the history of index cards, zettelkasten, and business/accounting.
-
- Mar 2022
-
buttondown.email buttondown.email
-
René Descartes designed a deck of playing cards that also functioned as flash cards to learn geometry and mechanics. (King of Clubs from The use of the geometrical playing-cards, as also A discourse of the mechanick powers. By Monsi. Des-Cartes. Translated from his own manuscript copy. Printed and sold by J. Moxon at the Atlas in Warwick Lane, London. Via the Beinecke Library, from which you can download the entire deck.)
My immediate thought is that this deck of cards was meant as a memory palace. I'm curious what training in rhetoric/memory methods Descartes must have had?
-
- Feb 2022
-
niklas-luhmann-archiv.de niklas-luhmann-archiv.de
-
9/8g Hinter der Zettelkastentechnik steht dieErfahrung: Ohne zu schreiben kann mannicht denken – jedenfalls nicht in anspruchsvollen,selektiven Zugriff aufs Gedächtnis voraussehendenZusammenhängen. Das heißt auch: ohne Differenzen einzukerben,kann man nicht denken.
Google translation:
9/8g The Zettelkasten technique is based on experience: You can't think without writing—at least not in contexts that require selective access to memory.
That also means: you can't think without notching differences.
There's something interesting about the translation here of "notching" occurring on an index card about ideas which can be linked to the early computer science version of edge-notched cards. Could this have been a subtle and tangential reference to just this sort of computing?
The idea isn't new to me, but in the last phrase Luhmann tangentially highlights the value of the zettelkasten for more easily and directly comparing and contrasting the ideas on two different cards which might be either linked or juxtaposed.
Link to:
- Graeber and Wengrow ideas of storytelling
-
Shield of Achilles and ekphrasis thesis
-
https://hypothes.is/a/I-VY-HyfEeyjIC_pm7NF7Q With the further context of the full quote including "with selective access to memory" Luhmann seemed to at least to make space (if not give a tacit nod?) to oral traditions which had methods for access to memories in ways that modern literates don't typically give any credit at all. Johannes F.K .Schmidt certainly didn't and actively erased it in Niklas Luhmann’s Card Index: The Fabrication of Serendipity.
-
-
-
In fact, my allegiance to Scrivener basically boils down to just three tricks that the software performs, but those tricks are so good that I’m more than willing to put up with all the rest of the tool’s complexity.Those three tricks are:Every Scrivener document is made up of little cards of text — called “scrivenings” in the lingo — that are presented in an outline view on the left hand side of the window. Select a card, and you see the text associated with that card in the main view.If you select more than one card in the outline, the combined text of those cards is presented in a single scrolling view in the main window. You can easily merge a series of cards into one longer card.The cards can be nested; you can create a card called, say, “biographical info”, and then drag six cards that contain quotes about given character’s biography into that card, effectively creating a new folder. That folder can in turn be nested inside another folder, and so on. If you select an entire folder, you see the combined text of all the cards as a single scrolling document.
Steven Johnson identifies the three features of Scrivener which provide him with the most value.
Notice the close similarity of these features to those of a traditional zettelkasten: cards of text which can be linked together and rearranged into lines of thought.
One difference is the focus on the creation of folders which creates definite hierarchies rather than networks of thought.
-
-
-
In preparing these instructions, Gaspard-Michel LeBlond, one of their authors, urges the use of uniform media for registering titles, suggesting that “ catalog materials are not diffi cult to assemble; it is suffi cient to use playing cards [. . .] Whether one writes lengthwise or across the backs of cards, one should pick one way and stick with it to preserve uniformity. ” 110 Presumably LeBlond was familiar with the work of Abb é Rozier fi fteen years earlier; it is unknown whether precisely cut cards had been used before Rozier. The activity of cutting up pages is often mentioned in prior descrip-tions.
In published instructions issued on May 8, 1791 in France, Gaspard-Michel LeBlond by way of standardization for library catalogs suggests using playing cards either vertically or horizontally but admonishing catalogers to pick one orientation and stick with it. He was likely familiar with the use of playing cards for this purpose by Abbé Rozier fifteen years earlier.
-
4. What follows is the compilation of the basic catalog; that is, all book titles are copied on a piece of paper (whose pagina aversa must remain blank) according to a specifi c order, so that together with the title of every book and the name of the author, the place, year, and format of the printing, the volume, and the place of the same in the library is marked.
Benedictine abbot Franz Stephan Rautenstrauch (1734 – 1785) in creating the Catalogo Topographico for the Vienna University Library created a nine point instruction set for cataloging, describing, and ordering books which included using paper slips.
Interesting to note that the admonishment to leave the backs of the slips (pagina aversa), in the 1780's seems to make its way into 20th century practice by Luhmann and others.
-
Rozier chances upon the labor-saving idea of producing catalogs according to Gessner ’ s procedures — that is, transferring titles onto one side of a piece of paper before copying them into tabular form. Yet he optimizes this process by dint of a small refi nement, with regard to the paper itself: instead of copying data onto specially cut octavo sheets, he uses uniformly and precisely cut paper whose ordinary purpose obeys the contingent pleasure of being shuffl ed, ordered, and exchanged: “ cartes à jouer. ” 35 In sticking strictly to the playing card sizes available in prerevolutionary France (either 83 × 43 mm or 70 × 43 mm), Rozier cast his bibliographical specifi cations into a standardized and therefore easily handled format.
Abbé François Rozier cleverly transferred book titles onto the blank side of French playing cards instead of cut octavo sheets as a means of indexing after being appointed in 1775 to index the holdings of the Académie des Sciences in Paris.
-
Therefore, they were frequently used as lottery tickets, marriage and death announcements, notepads, or busi-ness cards.
With blank backs, French playing cards in the late 1700s were often used as lottery tickets, marriage and death announcements, notepads, and business cards.
-
Playing cards offer numerous advantages: only after 1816 do their hitherto unmarked backs (fi gure 3.1) assumed a Tarot pattern.
Prior to 1816 in France playing cards (cartes à jouer) had unmarked backs and thereafter contained a Tarot pattern.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
cut out paper as Luhmann hadto.
On the back of his notes, you will find not only manuscript drafts, but also old bills or drawings by his children. [footnote]
While it's possible that Luhmann may have cut some of his own paper, by the time he was creating his notes the mass manufacture of index cards of various sizes was ubiquitous enough that he should never have had to cut his own. He certainly wasn't forced to manufacture them the way Carl Linnaeus had to.
-
- Jan 2022
-
-
Here, the card index func-tions as a ‘thinking machine’,67 and becomes the best communication partner for learned men.68
From a computer science perspective, isn't the index card functioning like an external memory, albeit one with somewhat pre-arranged linked paths? It's the movement through the machine's various paths that is doing the "thinking". Or the user's (active) choices that create the paths creates the impression of thinking.
Perhaps it's the pre-arranged links where the thinking has already happened (based on "work" put into the system) and then traversing the paths gives the appearance of "new" thinking?
How does this relate to other systems which can be thought of as thinking from a complexity perspective? Bacteria perhaps? Groups of cells acting in concert? Groups of people acting in concert? Cells seeing out food using random walks? etc?
From this perspective, how can we break out the constituent parts of thought and thinking? Consciousness? With enough nodes and edges and choices of paths between them (or a "correct" subset of paths) could anything look like thinking or computing?
-
-
stevenson.ucsc.edu stevenson.ucsc.edu
-
ow about using a scratch pad slightly smaller than the page-size of the book -- so that the edges of the sheets won't protrude?
Interesting to note here that he suggests a scratch pad rather than index cards here given his own personal use of index cards.
-
- Dec 2021
-
luhmann.surge.sh luhmann.surge.sh
-
index card file
Given the use case that Niklas Luhmann had, the translation of zettelkasten into English is better read as "index card file" rather than the simpler and more direct translation "slip box".
While it's not often talked about in the recent contexts, there is a long history of using index cards for note taking in the United States and the idea of an index card file was once ubiquitous. There has been such a long span between this former ubiquity and our digital modernity that the idea of a zettelkasten seems like a wondrous new tool, never seen before. As a result, people in within social media, the personal knowledge management space, or the tools for thought space will happily use the phrase zettelkasten as if it is the hottest and newest thing on the planet.
-
-
aegir.org aegir.org
-
An absolutely beautiful design for short notes.
This is the sort of theme that will appeal to zettelkasten users who are building digital gardens. A bit of the old mixed in with the new.
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Pete Moor </span> in // pimoore.ca (<time class='dt-published'>12/24/2021 18:02:15</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
-
Commonplaces were no longer repositories of redundancy, but devices for storing knowledge expansion.
With the invention of the index card and atomic, easily moveable information that can be permuted and re-ordered, the idea of commonplacing doesn't simply highlight and repeat the older wise sayings (sententiae), but allows them to become repositories of new and expanding information. We don't just excerpt anymore, but mix the older thoughts with newer thoughts. This evolution creates a Cambrian explosion of ideas that helps to fuel the information overload from the 16th century onward.
-
Through an inner structure of recursive links and semantic pointers, a card index achieves a proper autonomy; it behaves as a ‘communication partner’ who can recommend unexpected associations among different ideas. I suggest that in this respect pre-adaptive advances took root in early modern Europe, and that this basic requisite for information pro-cessing machines was formulated largely by the keyword ‘order’.
aliases for "topical headings": headwords keywords tags categories
-
-
-
An analogous situation is the use of visiting cards: “ One arrives at one of the famous spas, a couple of hours after arriving one sends out a few hundred visiting cards, and the same day one is introduced to the whole society of the resort, and acquainted with two to three hundred people as if one had already lived
with them for many years.” 62
What ever happened to visiting cards? They should make a resurgence in the social media space, n'cest pas?
-
One more thing ought to be explained in advance: why the card index is indeed a paper machine. As we will see, card indexes not only possess all the basic logical elements of the universal discrete machine — they also fi t a strict understanding of theoretical kinematics . The possibility of rear-ranging its elements makes the card index a machine: if changing the position of a slip of paper and subsequently introducing it in another place means shifting other index cards, this process can be described as a chained mechanism. This “ starts moving when force is exerted on one of its movable parts, thus changing its position. What follows is mechanical work taking place under particular conditions. This is what we call a machine . ” 11 The force taking effect is the user ’ s hand. A book lacks this property of free motion, and owing to its rigid form it is not a paper machine.
The mechanical work of moving an index card from one position to another (and potentially changing or modifying links to it in the process) allows us to call card catalogues paper machines. This property is not shared by information stored in codices or scrolls and thus we do not call books paper machines.
-
Foucault proclaimed in a footnote: “ Appearance of the index card and development of the human sciences: another invention little celebrated by historians. ”
from Foucault 1975, p. 363, n. 49; see Foucault 1966, pp. XV and passim for discourse analysis.
Is he talking here about the invention of the index card about the same time as the rise of the scientific method? With index cards one can directly compare and contrast two different ideas as if weighing them on a balance to see which carries more weight. Then the better idea can win while the lesser is discarded to the "scrap heap"?
-
Here, I also briefl y digress and examine two coinciding addressing logics: In the same decade and in the same town, the origin of the card index cooccurs with the invention of the house number. This establishes the possibility of abstract representation of (and controlled access to) both texts and inhabitants.
Curiously, and possibly coincidently, the idea of the index card and the invention of the house number co-occur in the same decade and the same town. This creates the potential of abstracting the representation of information and people into numbers for easier access and linking.
-
What differs here from other data storage (as in the medium of the codex book) is a simple and obvious principle: information is available on separate, uniform, and mobile carriers and can be further arranged and processed according to strict systems of order.
The primary value of the card catalogue and index cards as tools for thought is that it is a self-contained, uniform and mobile carrier that can be arranged and processed based on strict systems of order. Books have many of these properties, but the information isn't as atomic or as easily re-ordered.
-
s Alan Turing proved only years later, these machines merely need (1) a (theoretically infi nite) partitioned paper tape, (2) a writing and reading head, and (3) an exact
procedure for the writing and reading head to move over the paper segments. This book seeks to map the three basic logical components of every computer onto the card catalog as a “ paper machine,” analyzing its data processing and interfaces that may justify the claim, “Card catalogs can do anything!”
Purpose of the book.
A card catalog of index cards used by a human meets all the basic criteria of a Turing machine, or abstract computer, as defined by Alan Turing.
-
“ Card catalogs can do anything ” — this is the slogan Fortschritt GmbH
What a great quote to start off a book like this!
-
- Nov 2021
-
docs.google.com docs.google.com
-
Now that we're digitizing the Zettelkasten we often find dated notes that say things like "note 60,7B3 is missing". This note replaces the original note at this position. We often find that the original note is maybe only 20, 30 notes away, put back in the wrong position. But Luhmann did not start looking, because where should he look? How far would he have to go to maybe find it again? So, instead he adds the "note is missing"-note. Should he bump into the original note by chance, then he could put it back in its original position. Or else, not.
Niklas Luhmann had a simple way of dealing with lost cards by creating empty replacements which could be swapped out if found later. It's not too dissimilar to doing inventory in a book store where mischievous customers pick up books, move them, or even hide them sections away. Going through occasionally or even regularly or systematically would eventually find lost/misfiled cards unless they were removed entirely from the system (similar to stolen books).
-
So the big secret then is, how did he know that this note here exists? How could he remember that this existing note was relevant to the new one he was writing? A mystery we haven't solved yet.
I'm surprised to see/hear this!
How did Niklas Luhmann cross link his notes? Apparently researchers don't quite know, but I'd suggest that in working with them diligently over time, he'd have a reasonable internal idea from memory in addition to working with his indices and his outline cards.
The cards in some sense form a physical path through which he regularly traverses, so he's making a physical memory palace (or songline) out of index cards.
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
on advocate for the index card in the early twentieth century called for animitation of “accountants of the modern schoolY”1
Paul Chavigny, Organisation du travail intellectuel: Recettes pratiques a` l’usage des e ́tudiants de toutes les faculte ́s et de tous les travailleurs (Paris, 1920)
Chavigny was an advocate for the index card in note taking in imitation of "accountants of the modern school". We know that the rise of the index card was hastened by the innovation of Melvil Dewey's company using index cards as part of their internal accounting system, which they actively exported to other companies as a product.
-
- Sep 2021
-
finiteeyes.net finiteeyes.net
-
Offloading can be far more complex, however, and doesn’t necessarily involve language. For example, “when we use our hands to move objects around, we offload the task of visualizing new configurations onto the world itself, where those configurations take tangible shape before our eyes” (243-244).
This is one of the key benefits over the use of index cards in moving toward a zettelkasten from the traditional commonplace book tradition. Rearranging one's ideas in a separate space.
Raymond Llull attempted to do this within his memory in the 12th century, but there are easier ways of doing this now.
-
-
ivankreilkamp.com ivankreilkamp.com
- Aug 2021
-
kimberlyhirsh.com kimberlyhirsh.com
-
https://kimberlyhirsh.com/2018/06/29/a-starttofinish-literature.html
Great overview of a literature review with some useful looking links to more specifics on note taking methods.
Most of the newer note taking tools like Roam Research, Obsidian, etc. were not available or out when she wrote this. I'm curious how these may have changed or modified her perspective versus some of the other catch-as-catch-can methods with pen/paper/index cards/digital apps?
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
I remember also seeing this as an indexing system for index cards in 2007. https://www.flickr.com/photos/hawkexpress/sets/72157594200490122/
It's not too dissimilar a pattern from the early 20th century edge-notched cards which were used to make sorting collections easier. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edge-notched_card Of course doing this for a notebook isn't going to work as easily.
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
-
In her book Parti-colored Blocks for a Quilt, writer Marge Piercy described how she used needle cards instead of a notebook: .mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}I keep neither a journal nor a notebook. I have a memory annex which serves my purposes. It uses edge-notched cards. Edge-notched cards are cards which have holes around the borders as opposed to machine punch cards which are punched through the body. The cards are sorted with knitting needles. I have a nice sophisticated system which I call the "General Practitioner."[12]
Interesting to see that Marge Piercy used an edge-notched card system for personal use in the manner of a commonplace book.
See reference: Piercy, Marge (1982). Parti-colored blocks for a quilt. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. pp. 27–28. doi:10.3998/mpub.7442. ISBN 0472063383. OCLC 8476006.
-
-
www.connectedtext.com www.connectedtext.com
-
In writing my dissertation and working on my first book, I used an index card system, characterized by the "one fact, one card" maxim, made popular by Beatrice Webb. [4]
I've not come across Beatrice Webb before, but I'm curious to see what her system looks like based on this statement.
From the footnotes:
She observed in the appendix to her My Apprenticeship of 1926, called The Art of Note-Taking: "It is difficult to persuade the accomplished graduate of Oxford or Cambridge that an indispensable instrument in the technique of sociological enquiry - seeing that without it any of the methods of acquiring facts can seldom be used effectively - is the making of notes" Webb, Beatrice (1926) My Apprenticeship (London: Longmans, Green, and Co.), pp. 426-7.
-
-
wiki.c2.com wiki.c2.com
-
-
To me, the greatest benefit of IndexCards is that they force you to not write too much. This is a big help to those of us who are still squishing the bitter juice of BigDesignUpFront from our brains. The expense and rarity of vellum played a similar role in MedievalArchitecture.
-
This is one of the points made in TheMythOfThePaperlessOffice -- that workplaces often shift from more efficient paper-based technologies to less efficient electronic technologies (electronic technologies can be either more or less efficient, of course) because computers symbolize The Future, Progress, and a New Way Of Doing Things. An office on the move, that's what an office that uses cutting-edge technology is. Not an office that is stuck in the past. And the employees are left to cope with the less productive, but shinier, New Way. -- ApoorvaMuralidhara
New technologies don't always have the user interface to make them better than old methods.
-
-
web.archive.org web.archive.org
-
In 2003, Ross's family gave his journals, papers, and correspondence to the British Library, London. Then, in March 2004, on the last day of the W. Ross Ashby Centenary Conference, they announced the intention to make his journal available on the Internet. Four years later, this website fulfilled that promise, making this previously unpublished work available on-line.
The journal consists of 7,189 numbered pages in 25 volumes, and over 1,600 index cards. To make it easy to browse purposefully through so many images, extensive cross-linking has been added that is based on the keywords in Ross's original keyword index.
This definitely sounds like a commonplace book. Also an example of one which has been digitized.
-
-
edwardbetts.com edwardbetts.com
-
Now, whenever I have a thought worth capturing, I write it on an index card in either marker pen or biro (depending on the length of the thought), and place in the relevant box. I use index cards for books, blogs, conversations I overhear at the club, memories, etc. They’re in my coat pocket when I fetch the kids from school. I leave them handy in the locker at the swimming pool (where I do much of my best thinking). And I run with them. Sound weird? Well, I’m in good company. Ryan Holiday[116], Anne Lamott[117], Robert Greene[118], Oliver Burkeman[119], Ronald Reagan, Vladimir Nabokov[120] and Ludwig Wittgenstein[121] all use (d) the humble index card to catalogue and organise their thoughts. If you’re serious about embarking on this digital journey, buy a hundred-pack of 127 x 76mm ruled index cards for less than a pound, rescue a shoebox from the attic and stick a few marker-penned notecards on their end to act as dividers. Write a “My Digital Box” label on the top of the shoebox, and you’re off.
apparently a quote from Reset: How to Restart Your Life and Get F.U. Money by David Sawyer FCIPR.
Notes about users of index card based commonplace books.
-
-
groups.google.com groups.google.com
-
I am also interested in the work and method of Ross Ashby. His card index and notebooks have been put online by the British Commputer Society. I am fascinated by his law of requisite variety and how variety relates to complexity and its unfolding in general and in relation to design.
Sounds like Ross Ashby kept a commonplace book here.
Could be worth looking into: http://www.rossashby.info/ and digging further.
-



