Thr
Maybe above this paragraph label it "CNA Reflection" so that the reader knows that it is not just a continuation of the context paragraph
Thr
Maybe above this paragraph label it "CNA Reflection" so that the reader knows that it is not just a continuation of the context paragraph
Synthèse de la Séance Plénière du Conseil Économique, Social et Environnemental
La séance plénière du Conseil économique, social et environnemental (CESE) s'est articulée autour de deux axes majeurs :
l'examen et l'adoption unanime d'un avis crucial sur les droits et les besoins fondamentaux de l'enfant,
et une série d'interventions sur des sujets d'actualité reflétant les préoccupations de la société civile.
L'avis intitulé "Satisfaire les besoins fondamentaux des enfants et garantir leurs droits dans tous les temps et espaces de leur vie quotidienne" a été adopté à l'unanimité (130 voix pour).
Conçu en complément des travaux de la Convention Citoyenne sur le même sujet, cet avis dresse un constat sévère de la situation des enfants en France, marquée par des inégalités croissantes (sociales, territoriales, économiques) et un décalage persistant entre les droits proclamés et leur application réelle. Le document met en lumière une société pensée "par et pour les adultes", qui peine à placer l'enfant au cœur de ses préoccupations.
Les préconisations phares incluent l'instauration d'une "clause impact enfance" dans chaque texte de loi, une réforme ambitieuse des rythmes scolaires, la garantie d'un accès équitable aux loisirs et aux vacances, et la création d'un "service public de la continuité éducative" pour coordonner l'ensemble des acteurs.
L'intervention de Claire Hédon, Défenseure des droits, a renforcé ce diagnostic par des données chiffrées alarmantes sur les atteintes aux droits de l'enfant, notamment pour les plus vulnérables.
En amont de ce débat, la séance d'expression libre a permis d'aborder des enjeux variés :
la remise en cause de la légitimité de la participation citoyenne,
les coupes drastiques dans l'aide publique au développement,
les menaces sur le système de santé,
la dérégulation environnementale au niveau européen, les dangers des nouveaux OGM,
la hausse des accidents du travail,
la pression exercée sur les demandeurs d'emploi,
et les appels à une souveraineté alimentaire concrète.
Enfin, la présentation du budget du CESE a révélé une situation financière tendue, marquée par une baisse des dotations de l'État et menacée par de nouvelles coupes potentielles votées par le Sénat, mettant en péril la capacité de l'institution à mener ses missions, notamment l'organisation de futures conventions citoyennes.
Avant l'examen de l'avis sur l'enfance, plusieurs intervenants ont exprimé les préoccupations de leurs groupes respectifs sur des sujets d'actualité.
• Défense de la Participation Citoyenne (Agatha Mel) :
Au nom des organisations étudiantes, une défense de la Convention Citoyenne sur les temps de l'enfant a été formulée, dénonçant les "procès d'illégitimité, d'incompétence et de manipulation" et appelant à un débat sérieux sur le fond du rapport, sans caricaturer le travail des citoyens.
• Aide Publique au Développement (Jean-Marc Boivin) :
Le groupe des associations a alerté sur les coupes "drastiques et disproportionnées" (-60 % en 2 ans) dans le budget de l'aide publique au développement, entraînant la fermeture de 1300 projets, la suppression de 10 000 emplois et impactant plus de 15 millions de personnes.
• Impact sur la Santé (Dominique Joseph) :
La Mutualité Française a qualifié d'irresponsable l'augmentation de la taxe sur les complémentaires santé, la qualifiant de "TVA sur la santé", et a souligné la nécessité d'une réforme de fond du système de protection sociale.
• Dérégulation Environnementale (Florent Compnibus) :
Le groupe environnement a dénoncé le projet législatif européen "Omnibus" comme une "dérégulation massive" et un "abandon pur et simple du principe de précaution", instaurant des autorisations illimitées pour les pesticides et biocides et affaiblissant le devoir de vigilance des entreprises.
• Opposition aux Nouveaux OGM (Éric Meer) :
Le groupe alternative sociale et écologique a critiqué l'accord européen sur les nouvelles techniques génomiques (NGT), y voyant une "fuite en avant technologique" qui favorise le brevetage, la dépendance des paysans et prive les consommateurs de traçabilité.
• Accidents du Travail (Ingrid Clément) :
La CFDT a qualifié 2024 d'"année noire" avec 774 décès au travail (deux par jour), une augmentation de 26 % des accidents pour les femmes, et une hausse des troubles musculosquelettiques et des affections psychiques, appelant à renforcer la prévention primaire.
• Pression sur les Demandeurs d'Emploi (Isabelle Dor) :
Le groupe des associations a relayé des témoignages de personnes suivies par France Travail décrivant "infantilisation", "pression folle" et menaces de radiation, illustrant des situations qualifiées d'ubuesques pour les bénéficiaires du RSA et les travailleurs pauvres.
• Soutien à la Solidarité Syndicale (Alain le corps) :
La CGT a dénoncé la mise en examen de sa secrétaire générale, Sophie Binet, pour avoir utilisé l'expression "les rats quittent le navire", affirmant qu'il s'agit "non pas une injure, mais le constat amer d'un comportement irresponsable".
• Souveraineté Alimentaire (Henriespéré) :
Le groupe de l'agriculture a relayé les propos de la ministre sur la "guerre agricole" qui se prépare, appelant à passer "des discours aux actes" pour relancer les filières agricoles françaises via l'innovation et la réciprocité des normes.
Le cœur de la séance a été consacré à l'avis "Satisfaire les besoins fondamentaux des enfants et garantir leurs droits", élaboré par la commission éducation, culture et communication.
Cet avis constitue la contribution de la société civile organisée en parallèle de la Convention Citoyenne sur les temps de l'enfant, saisie par le Premier ministre.
En introduction, Claire Hédon, Défenseure des droits et des enfants, a livré une intervention dense, soulignant l'écart entre le "droit annoncé et son effectivité".
• Volume des Saisines : L'institution a reçu 3 073 réclamations relatives à des atteintes aux droits de l'enfant en 2024. 30 % de ces réclamations concernent la scolarisation d'élèves en situation de handicap.
• Consultation des Enfants : Pour préparer son rapport 2025, plus de 1 600 enfants et jeunes ont été écoutés, soulignant l'importance de leur parole "trop souvent absente du débat public".
• Accès aux Loisirs : Un chiffre marquant illustre les inégalités massives : 71 % des enfants issus de familles modestes ne pratiquent aucune activité sportive ou culturelle, contre seulement 38 % des familles aisées.
La situation est encore plus critique en Outre-mer, où les équipements sont quatre fois moins nombreux qu'en métropole à Mayotte.
• Temps d'Écran : Le temps passé devant les écrans augmente fortement, atteignant en moyenne 4h48 par jour chez les 11-14 ans (hors école) et jusqu'à 5h10 chez les 16 ans, avec des conséquences graves sur le sommeil et la santé mentale.
• Droit à l'Éducation : La Défenseure a alerté sur les heures d'enseignement perdues, citant le cas d'élèves de CP à Marseille sans cours pendant un mois, et le chiffre de 27 000 jeunes sans affectation au lycée début 2024 sur tout le territoire.
• Impact Climatique : Le réchauffement climatique menace la continuité du service public de l'éducation.
D'ici 2030, près de 7 000 écoles maternelles seront exposées à des vagues de chaleur supérieures à 35°C.
Les rapporteurs ont présenté un projet d'avis structuré autour d'un principe fondamental : l'enfant est une personne à part entière.
Le fil rouge de l'analyse est un triptyque : droits de l'enfant, satisfaction de ses besoins et lutte contre les inégalités.
• Des Droits Peu Effectifs : Malgré la ratification de la Convention internationale des droits de l'enfant, la réalité quotidienne est marquée par des droits non respectés, comme le soulignent les rapports de l'ONU et de la Défenseure des droits.
• Des Inégalités Croissantes : Les inégalités sociales, économiques, territoriales et environnementales percutent de plein fouet la vie des enfants.
34,3 % des familles monoparentales vivent en situation de pauvreté.
À la veille de la rentrée 2025, au moins 2 159 enfants sont restés sans solution d'hébergement.
• Une Société "Adulto-centrée" : L'organisation sociale, notamment les rythmes de travail et les temps scolaires, est pensée pour les adultes, laissant peu de place aux besoins biologiques et psychologiques des enfants.
• L'Enfant "de l'intérieur" : En 20 ans, le périmètre de déplacement autonome des enfants a chuté de plusieurs kilomètres à moins de 300 mètres.
Quatre enfants sur 10 (3-10 ans) ne jouent jamais dehors pendant la semaine.
L'avis formule 19 préconisations pour répondre à ces enjeux. Les plus structurantes sont :
Thématique
Préconisation Phare
Description
Gouvernance et Législation
Créer une clause "impact enfance"
Intégrer dans l'évaluation de chaque projet de loi ou de règlement une analyse de ses conséquences sur les droits et le bien-être des enfants.
Temps Scolaire
Affirmer que le statu quo n'est plus tenable
Appeler à revoir l'organisation des journées et des semaines scolaires, en préconisant une alternance de 7 semaines de cours et 2 semaines de vacances, tout en maintenant 8 semaines l'été.
Droit aux Vacances et Loisirs
Garantir un accès équitable pour tous
Développer une information ciblée, mettre en place une tarification sociale et soutenir financièrement les structures d'accueil collectif pour lutter contre les inégalités d'accès.
Lien à la Nature
Valoriser et accompagner l'éducation "au dehors"
Déployer des aménagements tels que la végétalisation des cours d'école, les aires éducatives et les plans locaux d'éducation à la nature pour reconnecter les enfants à leur environnement.
Coordination des Acteurs
Créer un service public de la continuité éducative
Articuler les outils existants (PEDT, CTG) pour garantir à chaque enfant un accès à des temps éducatifs variés, cohérents et de qualité, en mobilisant l'ensemble des acteurs (école, familles, associations, collectivités).
Parentalité et Travail
Créer un droit attaché aux obligations parentales
Transposer la directive européenne sur l'équilibre vie pro/vie perso pour permettre aux parents de recourir à des formules souples de travail.
Financement
Assurer un effort budgétaire conséquent et pérenne
Reconnaître l'éducation comme un investissement d'avenir et non comme une simple dépense, en garantissant les moyens nécessaires à l'État, la Sécurité sociale et aux collectivités pour mener des politiques publiques ambitieuses.
L'ensemble des groupes politiques et de la société civile présents au CESE ont salué la qualité et l'ambition de l'avis.
Les déclarations ont convergé sur le diagnostic des inégalités croissantes et la nécessité d'une action politique forte.
Le projet d'avis a été adopté à l'unanimité des 130 votants.
En complément, la députée Florence Erroin-Léoté a annoncé son intention de porter une proposition de loi sur le droit au loisir des enfants, s'appuyant sur les travaux de la Convention Citoyenne et du CESE pour faire du temps libre un "lieu éducatif, de mixité, d'émancipation et de démocratie vivante".
La séance s'est conclue par la présentation du budget du CESE, qui a mis en lumière une situation financière préoccupante.
• Contexte de Pression Budgétaire : Le président a rappelé qu'au même moment, le Sénat votait une baisse de 5 millions d'euros du budget du CESE, contre l'avis de sa propre commission des finances et du gouvernement.
• Baisse des Recettes : Le budget présenté montre une érosion continue des recettes, notamment la fin de la dotation spécifique de 4 millions d'euros pour l'organisation des conventions citoyennes.
De plus, les travaux de rénovation du Palais d'Iéna vont priver le CESE d'environ 1,6 million d'euros de recettes de valorisation (location d'espaces) en 2026.
• Un Budget 2026 à l'Équilibre Fragile : Le budget pour 2026 est présenté comme étant à l'équilibre, mais cet équilibre est atteint en n'incluant pas le financement d'une nouvelle convention citoyenne et en réduisant certains postes comme la communication.
• Incapacité à Financer de Nouvelles Missions : Le questeur a été clair : "en l'état, [...] on est demain incapable de refaire une convention citoyenne à 4 millions d'euros".
L'organisation de telles missions dépendra désormais de la capacité du CESE à obtenir des financements ad hoc auprès du gouvernement pour chaque commande.
• Investissement Immobilier Massif : La présentation a souligné que les réserves de trésorerie accumulées sont désormais engagées dans un plan pluriannuel d'investissement indispensable pour la rénovation du bâtiment, rattrapant des décennies de sous-investissement.
Dossier d'Information : L'Impact du Smartphone et de l'IA sur l'Adolescence
Cette synthèse examine l'analyse de l'anthropologue David Le Breton sur les transformations profondes induites par l'omniprésence du smartphone et de l'intelligence artificielle (IA) dans la vie des adolescents.
Le constat central est celui d'une rupture anthropologique majeure, marquée par le remplacement de la "conversation" – un échange incarné, empathique et réciproque – par la "communication" numérique, une interaction désincarnée, utilitariste et source d'isolement.
Les points critiques à retenir sont :
• La Fin de la Conversation : L'interaction en face à face est constamment rompue par les notifications, dévalorisant la présence physique au profit d'un univers virtuel.
Cette fragmentation du lien social direct entraîne une érosion documentée de l'empathie chez les jeunes générations.
• L'Ascension du Compagnon IA : Pour combler le vide affectif et social, les adolescents se tournent vers des chatbots, des "compagnons secrets" virtuels qui offrent une attention constante et sans jugement.
Cette relation, bien que narcissiquement rassurante, amplifie l'isolement et transforme l'utilisateur en produit, ses données étant captées et valorisées.
• Des Conséquences Cognitives et Physiques Sévères : L'exposition massive aux écrans est corrélée à un affaiblissement des capacités de concentration, de lecture approfondie et de pensée critique.
Elle favorise une sédentarité accrue, entraînant des problèmes de santé (douleurs cervicales, myopie) et une baisse drastique de l'activité physique par rapport aux générations précédentes.
• Une Crise de Santé Mentale Planétaire : David Le Breton, s'appuyant sur de multiples travaux, établit un lien direct entre l'explosion de l'anxiété, de la dépression, des tentatives de suicide et des scarifications chez les adolescents depuis 2010 et l'adoption généralisée du smartphone connecté à Internet.
• Enjeux Sociétaux et Éthiques : Au-delà de l'individu, l'analyse pointe vers une homogénéisation culturelle mondiale ("MacWorld"), la vulnérabilité accrue aux fausses nouvelles, et les graves implications éthiques et environnementales de la technologie (travail des enfants, exploitation de métaux rares, pollution des data centers).
En conclusion, loin d'être un simple outil, le smartphone dopé à l'IA façonne une nouvelle anthropologie où la simulation du lien supplante l'expérience réelle, avec des conséquences délétères sur le développement individuel et la cohésion sociale.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
La présente analyse se fonde sur les propos de David Le Breton, professeur émérite d'anthropologie à l'Université de Strasbourg, reconnu pour ses travaux sur les conduites à risque, le corps, et plus récemment sur le ralentissement et la marche.
Son intervention s'inscrit dans une réflexion plus large sur la santé mentale des jeunes et l'impact de l'intelligence artificielle (IA) sur la société.
David Le Breton postule qu'une rupture anthropologique fondamentale a eu lieu autour des années 2008-2009 avec l'avènement de l'Internet à haut débit sur les smartphones.
Ce changement a transformé radicalement l'espace public et les interactions humaines.
• Une "Société Spectrale" : Les villes sont désormais "hantées par des espèces de fantômes qui sont hypnotisés par leur téléphone portable et qui ne voient plus rien du tout à leur entour".
• Perte d'Attention à l'Environnement : Cet état d'hypnose crée des dangers physiques (piétons et cyclistes inattentifs) et sociaux, car l'attention n'est plus portée à l'environnement immédiat ou aux autres personnes présentes.
• Le Monde d'Avant : Il y a une vingtaine d'années, le monde était radicalement différent.
Même avec les premiers téléphones portables, l'attention au monde environnant n'était pas abolie comme elle l'est aujourd'hui par l'hypnose de l'écran du smartphone.
Le cœur de l'analyse de Le Breton repose sur une distinction anthropologique essentielle entre deux modes d'interaction.
Caractéristique
La Conversation
La Communication (numérique)
Cadre
Visage à visage, présence physique.
À distance, anonymat fréquent.
Corps
Central (mimiques, expressions, gestes).
Absent, désincarné.
Temporalité
Imprévisible, inclut le temps du silence et de la réflexion.
Urgence, efficacité, utilitarisme. Le silence est perçu comme une "panne".
Qualité du lien
Écoute, attention, empathie, réciprocité.
Centrée sur soi, instrumentale.
David Le Breton cite son propre ouvrage pour souligner ce point :
La conversation à l'implique de l'empathie c'est-à-dire une capacité à se mettre à la place de l'autre et à ne pas être étranger à ses ressentis.
Cette qualité disparaît dans la communication à distance [...] l'autre se transforme alors en fiction sans épaisseur.
L'intervention initiale d'Axel fournit des chiffres qui contextualisent l'ampleur du phénomène, basés notamment sur un rapport de l'ARCOM d'avril 2025.
Catégorie d'Âge
Temps d'Écran en 2011
Temps d'Écran en 2022/récent
1-6 ans
1h 47min
2h 03min
7-12 ans
2h 51min
4h 12min
13-19 ans
4h 20min
5h 10min
15-24 ans
(non spécifié)
5h 48min (dépasse les 50-64 ans)
50-64 ans
(non spécifié)
5h 27min (principalement TV en direct)
Ces données montrent une augmentation astronomique du temps passé devant les écrans en une décennie, les jeunes de 15-24 ans étant désormais les plus grands consommateurs, principalement via le smartphone. Pour certains adolescents, ce temps peut dépasser les dix heures par jour.
Face à un lien social qui s'effrite et à une désertion affective des proches, l'IA, via les chatbots, offre une solution de substitution qui devient un phénomène central de l'adolescence contemporaine.
• Le "Doudou de Substitution" : L'IA permet de fabriquer un "compagnon secret fictionnel" pour combler un manque affectif.
Le jeune programme ce personnage virtuel (nom, voix, personnalité) pour en faire un interlocuteur idéal.
• Un Bouclier de Sens : Le chatbot est toujours disponible, bienveillant, sans jugement, et procure un sentiment de maîtrise et de reconnaissance.
Il devient un "bouclier de sens pour conjurer les désarrois, les souffrances".
• L'Illusion de la Réciprocité : L'adolescent interagit avec le chatbot comme avec une personne réelle, oubliant qu'il s'agit d'un programme conçu pour capter ses données et le maintenir connecté le plus longtemps possible.
• La Violence de l'Indifférence : Cette quête d'attention virtuelle naît souvent d'un manque d'attention réelle, illustré par l'anecdote poignante d'une petite fille disant à son père hypnotisé par son portable :
Papa je veux que tu m'écoutes avec les yeux.
L'hyper-connexion paradoxalement génère un isolement profond et une dégradation des compétences sociales.
• La Liquidation de l'Interlocuteur : La présence physique d'un ami ou d'un parent est immédiatement "liquidée" dès qu'une notification apparaît.
L'interlocuteur réel a "moins d'épaisseur ontologiquement que les autres virtuels".
• La Simulation du Lien : Les "centaines d'amis" des réseaux sociaux ne valent pas un ou deux amis réels capables d'un geste de réconfort physique.
La communication numérique simule le lien social mais ne crée ni intimité ni raisons de vivre.
• Le Déclin de l'Empathie : Une étude menée par la sociologue Sherry Turkle sur 14 000 étudiants sur 30 ans montre que depuis les années 2000, "les jeunes témoignent d'un moindre intérêt pour les autres".
Les auteurs de l'étude établissent un lien direct entre ce retrait de l'empathie et la croissance de l'accès aux jeux en ligne et aux réseaux sociaux.
La surexposition aux écrans et la délégation de la pensée à l'IA ont des effets directs et mesurables sur le développement des jeunes.
• Difficulté de Lecture : La communication "synchopée, simple, permanente, ultra rapide" rend difficile la lecture de textes longs et élaborés, y compris des SMS de plus de quelques phrases.
• Faible Culture Générale : La croyance que toute information est accessible en un clic décourage l'apprentissage en profondeur.
Les étudiants "peinent à lire simplement quelques pages d'un article ou d'un livre".
• Apprentissage de la Passivité : Le recours systématique à l'IA pour obtenir des réponses immédiates (ex: ChatGPT pour un devoir) empêche le développement de la recherche personnelle, de la nuance et de la pensée critique.
• Externalisation de la Mémoire : L'usage du clavier et la possibilité de tout retrouver en ligne affaiblissent la mémorisation, qui est un processus affectif et contextuel, et non un simple stockage d'informations.
• Sédentarité Extrême : Une recherche du médecin William Bird montre qu'en quelques décennies, la distance parcourue par un enfant de 8 ans autour de son domicile est passée de 9 km à 300 mètres.
• Baisse des Performances Physiques : Les adolescents des années 70 étaient "deux fois plus actifs". Un 800 mètres qui se courait en 3 minutes en prend aujourd'hui 4.
• Problèmes de Santé : Le développement planétaire des douleurs cervicales et dorsales, ainsi que de la myopie, est directement lié à la posture penchée sur l'écran.
David Le Breton conclut son analyse sur un bilan humain alarmant, établissant une corrélation temporelle forte entre la généralisation du smartphone et l'explosion des troubles psychiques chez les jeunes à partir de 2010.
En se référant aux travaux du psychologue Jonathan Haidt ("Génération anxieuse"), il affirme que jamais dans l'histoire on n'a connu une telle ampleur de souffrances adolescentes :
• Anxiété et Dépression
• Sentiment d'Isolement
• Tentatives de Suicide et Suicides
• Scarifications (particulièrement chez les filles)
Cette crise est également visible chez les tout-petits, avec des retards de langage chez des enfants surexposés aux écrans, privés des interactions parentales cruciales à leur développement.
L'impact du smartphone et de l'IA dépasse la sphère individuelle pour toucher l'ensemble de la société.
• Manipulation et Harcèlement : L'IA permet de créer facilement des "deepfakes" ou "deepnudes" pour humilier, discréditer ou faire chanter des individus, les adolescentes étant des victimes fréquentes.
• Homogénéisation Culturelle ("MacWorld") : Les technologies créent une culture mondiale unifiée par les mêmes films, musiques, séries et modes de consommation, liquidant les cultures locales et les savoir-faire traditionnels.
• Hypocrisie de la Silicon Valley : Les dirigeants des géants du numérique protègent leurs propres enfants des technologies qu'ils promeuvent, en les inscrivant dans des écoles (ex: Waldorf) où le numérique est banni, conscients de ses dangers.
• Impacts Environnementaux et Géopolitiques : Le numérique a une empreinte écologique massive (data centers, consommation d'énergie) et repose sur l'exploitation de métaux rares, alimentant des conflits géopolitiques et le travail d'enfants dans certains pays.
Ces aspects sont souvent occultés dans les débats sur le climat.
David Le Breton insiste sur le fait que son analyse n'est pas celle d'un "moraliste" mais celle d'un sociologue et anthropologue qui observe et documente une réalité.
Son travail vise à pointer des faits observables et documentés par de nombreuses études, soulignant que jamais dans l'histoire le lien social n'a été aussi "abîmé".
Le monde hyper-connecté a coïncidé avec le début de "l'hyperindividualisation de nos sociétés", menant au paysage social et psychologique actuel.
hyperspectral Raman imaging (600-1800 cm⁻¹, 873 dimensions with a pixel size of 3 µm)
How did you account for spatial mixing that may occur with the given analyzed spot size? It's possible that a neighboring cell signal could be contributing to the target cell.
we manually selected corresponding cellular keypoints across both imaging modalities. This selection tool then generated a 3×3 transformation matrix to adjust the STARmap images to align with the Raman regions. The manual alignment process utilized a least-squares method, employing a modified two-dimensional version of Horn’s (1987) algorithm to account for differences in translation, scale, rotation, and reflection. For each Raman-STARmap paired sample, hundreds of keypoints were manually selected, and the fitgeotrans function in MATLAB was used to transform the STARmap image to match the Raman region. The imshowpair function was employed iteratively after every 20 keypoints to ensure satisfactory alignment.
I appreciate that this is an important and sometimes tricky problem, but well worth doing! Did you consider using an accuracy metric for the registration?
The backscattered Raman light from the sample passes through two dichroic mirrors (DM1: Semrock LPD01 785RU 25, DM2: Semrock LPD01 785RU 25×36×1.1) and was collected by a multi-mode fiber (Thorlabs M14L 01). The collected signal was delivered to the imaging spectrograph (Holospec f/1.8i, Kaiser Optical Systems) and detected by a thermoelectric cooled, back illuminated and deep depleted CCD (PIXIS: 100BR_eXcelon, Princeton Instruments).
What is the spectral resolution and sampling rate of this system? The datasheet for this spectrograph lists a resolution of 3-6 cm^-1, and if the spectra have 873 dimensions and cover 600-1800 cm^-1, then the spectral sampling rate is around 1.4 cm^-1. Assuming these numbers are roughly correct, this makes it hard to interpret figures that highlight differences between Raman intensities at wavenumbers closer than either of these values (e.g. 1643, 1644, and 1645 cm^-1 in Extended data Fig 11).
Larocco writes: “[...]empathy is an orientation to the other, one thatattunes to some aspect of the other’s feelings or emotions or thoughts[...] yet which may not engage with the other’s otherness at all. [...]Toput the point succinctly: feeling-with is not the same as feeling-for. [...]Empathy, for ethical behavior, is a crucial intersubjective vocalizer, butby itself as an orientation it may not direct the better angels of ournature to direct action.” (Larocco 2018, 3). Larocco here underscoresthe uncertainty around the potential of this empathic positioning, asthere are many possibilities along a spectrum, all the way from authen-tic identification with another to selective empathy that seeks to mis-construe the other as similar to the self, or identifies only with aspectsof the other perceived as similar to the self.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
This work provides a novel statistical model to identify imported malaria cases, which are an important challenge for elimination, particularly in low-transmission areas. This tool was applied in Plasmodium falciparum populations in Mozambique and determined differences in importation rates in 2 low-transmission districts in the South.
Strengths:
The study has several strengths, mainly the development of a novel Bayesian model that integrates genomic, epidemiological, and travel data to estimate importation probabilities. The results showed insights into malaria transmission dynamics, particularly identifying importation sources and differences in importation rates in Mozambique. Finally, the relevance of the findings is to suggest interventions focusing on the traveler population to support efforts for malaria elimination.
Weaknesses:
The study also has some limitations, although the authors have plans to address them. The sample collection was not representative of some provinces, and not all samples had sufficient metadata for the risk factor analysis. Additionally, the authors used a proxy for transmission intensity and assumed some other conditions to calculate the importation probability for specific scenarios. They plan to conduct a new sample collection and include monthly malaria incidence estimates in the future.
Comments on revisions:
- Delete "We added this text to the discussion" in line 302 (Discussion)<br /> - I recommend adding the plans to address limitations indicated in the Response to Reviewers document in the Discussion. This would really strengthen the limitation section.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This study presents a new Bayesian approach to estimate importation probabilities of malaria, combining epidemiological data, travel history, and genetic data through pairwise IBD estimates. Importation is an important factor challenging malaria elimination, especially in low-transmission settings. This paper focuses on Magude and Matutuine, two districts in southern Mozambique with very low malaria transmission. The results show isolation-by-distance in Mozambique, with genetic relatedness decreasing with distances larger than 100 km, and no spatial correlation for distances between 10 and 100 km. But again, strong spatial correlation in distances smaller than 10 km. They report high genetic relatedness between Matutuine and Inhambane, higher than between Matutuine and Magude. Inhambane is the main source of importation in Matutuine, accounting for 63.5% of imported cases. Magude, on the other hand, shows smaller importation and travel rates than Matutuine, as it is a rural area with less mobility. Additionally, they report higher levels of importation and travel in the dry season, when transmission is lower. Also, no association with importation was found for occupation, sex, and other factors. These data have practical implications for public health strategies aiming for malaria elimination, for example, testing and treating travelers from Matutuine in the dry season.
Strengths:
The strength of this study lies in the combination of different sources of data - epidemiological, travel, and genetic data - to estimate importation probabilities, and the statistical analyses.
Weaknesses:
The authors recognize the limitations related to sample size and the biases of travel reports.
We appreciate the review and comment about the manuscript.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
Based on a detailed dataset, the authors present a novel Bayesian approach to classify malaria cases as either imported or locally acquired.
Strengths:
The proposed Bayesian approach for case classification is simple, well justified, and allows the integration of parasite genomics, travel history, and epidemiological data. The work is well-written, very organized, and brings important contributions both to malaria control efforts in Mozambique and to the scientific community. Understanding the origin of cases is essential for designing more effective control measures and elimination strategies.
Weakness:
While the authors aim to classify cases as imported or locally acquired, the work lacks a quantification of the contribution of each case type to overall transmission.
The method presented here allows for classifying individual cases according to whether the infection occurred locally or was imported during a trip. By definition, it does not look to secondary infections after an importation event. Our next step is to conduct outbreak investigation to quantify the impact of importation events on the overall transmission, but this activity goes beyond the scope of this manuscript. We clarify this in the discussion section.
The Bayesian rationale is sound and well justified; however, the formulation appears to present an inconsistency that is replicated in both the main text and the Supplementary Material.
Thank you for pointing out the inconsistency in the final formula. In fact, the final formula corresponds to P(IA | G), instead of P(IA), so:
instead of
We have now corrected this error in the new version of the manuscript.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
The authors present an important approach to identify imported P. falciparum malaria cases, combining genetic and epidemiological/travel data. This tool has the potential to be expanded to other contexts. The data was analyzed using convincing methods, including a novel statistical model; although some recognized limitations can be improved. This study will be of interest to researchers in public health and infectious diseases.
Strengths:
The study has several strengths, mainly the development of a novel Bayesian model that integrates genomic, epidemiological, and travel data to estimate importation probabilities. The results showed insights into malaria transmission dynamics, particularly identifying importation sources and differences in importation rates in Mozambique. Finally, the relevance of the findings is to suggest interventions focusing on the traveler population to help efforts for malaria elimination.
Weaknesses:
The study also has some limitations. The sample collection was not representative of some provinces, and not all samples had sufficient metadata for risk factor analysis, which can also be affected by travel recall bias. Additionally, the authors used a proxy for transmission intensity and assumed some conditions for the genetic variable when calculating the importation probability for specific scenarios. The weaknesses were assessed by the authors.
We acknowledge the limitations commented by the reviewer. We have the following plans to address the limitations. We will repeat the study for our data collected in 2023, which this time contains a good representation of all the provinces of Mozambique, and completeness of the metadata collection was ensured by implementing a new protocol in January 2023. Regarding the proxy for transmission intensity, we will refine the model by integrating monthly estimates of malaria incidence (previously calibrated to address testing and reporting rates) from the DHIS2 data, taking also into account the date of the reported cases in the analysis.
Reviewing Editor Comments:
The reviewers have made specific suggestions that could improve the clarity and accuracy of this report.
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Abstract, lines 36, 37 and 38: "Spatial genetic structure and connectivity were assessed using microhaplotype-based genetic relatedness (identity-by-descent) from 1605 P. falciparum samples collected (...)", but only 540 samples were successfully sequenced, therefore used in spatial genetic structure and connectivity analysis.
The 540 samples refer to those from Maputo province and are described in Fig. 1. The Spatial and connectivity analyses also included the samples from the rest of the provinces from the multi-cluster sampling scheme. Sample sizes from these provinces are described in Suppl. Table 2, and the total between them and the 540 samples from Maputo are the 1605 samples mentioned in the abstract. We specify this number in the caption of Sup. Fig. 4, and add it now into Fig. 3
(2) In the Introduction, some epidemiological context about Magude and Matutuine could be added. It is only mentioned in the Discussion section (lines 265-269).
We have added some context about both districts in the introduction now.
(3) In the Discussion, lines 241-244, could the lack of structure mean no barriers for gene flow due to high mobility in short distances? Maybe it could only be resolved with a large number of samples.
This could be an explanation (we mention it in the new version), although it is not something we can prove, or at least in this study.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
The work is well written, very organized, and brings important contributions both to malaria control efforts in Mozambique and to the scientific community. Based on detailed datasets from Mozambique, the authors present a novel Bayesian approach to classify malaria cases as either imported or locally acquired. Understanding the origin of cases is essential for designing more effective control measures and elimination strategies. My review focuses on the Bayesian approach as well as on a few aspects of the presentation of results.
The authors combine travel history, parasite genetic relatedness, and transmission intensity from different areas to compute the probability of infection occurring in the study area, given the P. falciparum genome. The Bayesian rationale is sound and well justified; however, the formulation appears to present an inconsistency that is replicated in both the main text and the Supplementary Material. According to Bayes' Rule:
P(I_A |G) = (P(I_A) ∙ P(G|I_A)) / (P(G)),
with
P(I_A) = K ∙ T_A ∙ PR_A,
P(G│I_A) = R'_A,
and assuming
P(I_A│G) + P(I_B│G) = 1,
the expression,
(T_A ∙ PR_A ∙ R'_A) / (T_A ∙ PR_A ∙ R'_A + T_B ∙ PR_B ∙ R'_B)
appears to refer to P(I_A│G), not to P(I_A) (as indicated in the main text and Supplementary Material).
P(I_A│G) + P(I_B│G) = (P(I_A) ∙ P(G|I_A) + P(I_B) ∙ P(G|I_B)) / P(G) = 1
⇒P(G) = P(I_A) ∙ P(G|I_A) + P(I_B) ∙ P(G|I_B)
⇒P(G) = K ∙ T_A ∙ PR_A ∙ R'_A + K ∙ T_B ∙ PR_B ∙ R'_B
⇒P(I_A│G) = (T_A ∙ PR_A ∙ R'_A) / (T_A ∙ PR_A ∙ R'_A + T_B ∙ PR_B ∙ R'_B)
Please clarify this.
As mentioned in a previous comment, we acknowledge this point from the reviewer. In fact, the final formula corresponds to P(IA | G), instead of P(IA), so:
instead of
We have now corrected this error in the new version of the manuscript and in the supplementary information.
Additional comments:
(1) Figure 3A has a scale that includes negative values, which is not reasonable for R.
We agree that R estimates are not compatible with negative values. The intention of this scale was to show the overall mean R in the centre, in white, so that blue colours represented values below the average and red values above the average. However, we proceeded to update the figures according to your recommendations.
(2) I suggest using a common scale from 0 to 0.12 (maximum values among panels) across panels A, C, and D, as well as in Sup Fig 3, to facilitate comparison.
We updated the figures according to the recommendations.
(3) The x-axis labels in Figure 3A and Supplementary Figure 2A are not aligned with the x-axis ticks.
We updated the figures so that the alignment in the x-axis is clear.
(4) Supplementary Figure 5 would be better presented if the data were divided into four separate panels.
We have divided the figure into four separate panels.
(6) Figure 5D is not referenced in the main text.
We missed the mention, which is now fixed in the new version.
(7) The authors state: "No significant differences in R were found comparing parasite samples from Magude and the rest of the districts." However, Supplementary Figure 3 shows statistically significant relatedness between parasites from Magude and Matutuine. Please clarify this.
Answer: we added clarity to this sentence which was indeed confusing.
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Introduction: More background info about malaria in Mozambique would be appreciated.
We included some contextualisation about malaria in Mozambique and our study districts.
(2) Why were most of the samples collected from children? Is malaria most prevalent in that group? Information could be added in the introduction.
Children are usually considered an appropriate sentinel group for malaria surveillance for several reasons. First, most malaria cases reported from symptomatic outpatient visits are children, especially in areas with moderate to high burden. Second (and probably the cause for the first reason), their lower immunity levels, due to lower time of exposure, and their immature system, provides a cleaner scenario of the effects of malaria, since the body response is less adapted from past exposures. Finally, as a vulnerable population, they deserve a stronger focus in surveillance systems. We added a comment in the introduction referring to them as a common sentinel group for surveillance.
(3) Minor: Check spaces in the text (for example, line 333 and the start of the Discussion).
Thank you for noticing, we fixed in in the new version
(4) Minor: In my case, the micro (u) symbol can be observed in Word, but not in PDF.
One of the symbols produced an error, we hope that the new version is correct now.
(5) Were COI calculations with MOIRE performed across provinces and regions, or taking all samples as one population?
Wwe took all samples as one population. However, we validated that the same results (reaching equivalent numbers and the same conclusions) were obtained when run across different populations (regions or provinces). We mention this in the manuscript now.
(6) Have you tested lower values than 0.04 for PR in Maputo?
This would not have had any impact in the classification. Only two individuals reported a trip to Maputo city (where we assumed PR=0.04), and none of them were classified as imported. If lower values of PR were assumed, their probabilities of importation would have reduced, so that we would still obtain no imported cases.
(7) Map (Supplementary Figure 1): Please, improve the resolution (like in the zoom in) and add a scale and a compass rose.
We improved the resolution of the map. We did not add a scale and a compass rose, but labelled the coordinates as longitude and latitude to clarify the scale and orientation of the map. We added this in the rest of the maps of the manuscript as well.
(8) In this work, Pimp values were bimodal to 0 or 1, making the classification easy. I wonder in other scenarios, where Pimp values are more intermediate (0.4-0.6), is the threshold at 0.5 still useful? Is there another way, like having a confidence interval of Pimp, to ensure the final classification? A discussion on this topic may be appreciated.
In this case, we would recommend doing probabilistic analyses, keeping the probability of being imported as the final outcome, and quantifying the importation rates from the weighted sum of probabilities across individuals. We added this clarification in the Methods section: “ In case of obtaining a higher fraction of intermediate values (0.4-0.6), weighted sums of individual probabilities would be more appropriate to better quantify importation rates.”
(9) Results: More details per panel, not as the whole figure (Figure 2B, Figure 3A, etc) in the manuscript would be appreciated.
We appreciate the comment and added more details
(10) Figure 3: Please, add a color legend in panel B (not only in the caption, but in the panel, such as in A, C, D).
We added a color legend in panel B.
(11) Do the authors recommend routine surveillance to detect importation in Mozambique, or are these results solid enough to propose strategies? How possible is it that importation rates vary in the future in the south? If so, how feasible is it to implement all this process (including the amplicon sequencing) routinely?
We added the following text in the discussion: “While these results propose programmatic strategies for the two study districts, routine surveillance to detect importation in Mozambique would allow for identifying new strategies in other districts aiming for elimination, as well as monitoring changes in importation rates in Magude and Matutuine in the future. If scaling molecular surveillance is not feasible, travel reports could be integrated in the routing surveillance to extrapolate the case classification based on the results of this study. “
(12) Which other proxies of transmission intensity could have been used?
Better proxies of transmission intensity could be malaria incidence at the monthly level from national surveillance systems, or estimates of force of infection, for example from the use of molecular longitudinal data if available. We added this text in the discussion.
(13) Can this strategy be applied to P. vivax-endemic areas outside Africa?
This new method can also be applied to P. vivax-endemic areas outside Africa. Symptomatic P. vivax cases are not necessarily reflecting recent infections, so that travel reports might need to cover longer time periods, which does not require any essential adaptation to the method. We added this text to the discussion.
By 15 May 2014 and every six years thereafter the Commissionshall present to the European Parliament and to the Council areport on the implementation of this Directive based, inter alia,on reports from Member States in accordance with Article 21(2)and (3).Where necessary, the report shall be accompanied by proposalsfor Community action
replaced, by a one time(!) eval after 6 years.
By way of derogation from Article 11(1), Member States maylimit public access to spatial data sets and services through theservices referred to in points (b) to (e) of Article 11(1), or to thee-commerce services referred to in Article 14(3), where suchaccess would adversely affect any of the following
changed to Member States may limit public access to spatial data sets and services where such access could adversly affect any of the following:
The description of the existing data themes referred to inAnnexes I, II and III may be adapted in accordance with theregulatory procedure with scrutiny referred to in Article 22(3), inorder to take into account the evolving needs for spatial data insupport of Community policies that affect the environment.25.4.2007 EN Official Journal of the European Union L 108/5
Replaced by The Commission is empowered to adopt delegated acts in accordance with Article 22a in order to amend Annexes I, II and III by adapting the description of the existing data themes in the light of technological and economic developments
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer globally and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths. Colonoscopy and fecal immunohistochemical testing are among the early diagnostic tools that have significantly enhanced patient survival rates in CRC. Methylation dysregulation has been identified in the earliest stages of CRC, offering a promising avenue for screening, prediction, and diagnosis. The manuscript entitled "Early Diagnosis and Prognostic Prediction of Colorectal Cancer through Plasma Methylation Regions" by Zhu et al. presents that a panel of genes with methylation pattern derived from cfDNA (27 DMRs), serving as a noninvasive detection method for CRC early diagnosis and prognosis.
Strengths:
The authors provided evidence that the 27 DMRs pattern worked well in predicting CRC distant metastasis, and the methylation score remarkably increased in stage III-IV.
Weaknesses:
The major concerns are the design of DMR screening, the relatively low sensitivity of this DMR pattern in detecting early-stage CRC, the limited size of the cohorts, and the lack of comparison with the traditional diagnosis test.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for their thorough evaluation and constructive feedback on our manuscript. We are encouraged that the reviewer found our 27-DMR panel promising for predicting distant metastasis and for its performance in late-stage CRC. We have carefully considered the weaknesses pointed out and have made revisions to address these concerns, which we believe have significantly strengthened our paper.
We agree with the reviewer that achieving high sensitivity for early-stage disease is the ultimate goal for any noninvasive screening test. Detecting the minute quantities of cfDNA shed from early-stage tumors is a well-recognized challenge in the field. Although the sensitivity of our current panel for early-stage CRC is modest, its core strengths, lie in its capability to also detect advanced adenomas and its excellent performance in assessing CRC metastasis and prognosis. Furthermore, we have now added a direct comparative analysis of our 27-DMR panel against the most widely used clinical serum biomarker for CRC, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), using samples from the same patient cohorts. Our results demonstrate that 27-DMR methylation score significantly outperforms CEA in diagnostic accuracy for early-stage CRC (64% vs. 18%) (Table s7). And in the Discussion section, we have also acknowledged our limitations and suggest that future studies are warranted to combine the cfDNA methylation model with commonly used clinical markers, such as CEA and CA19-9, with the aim of improving the sensitivity for early diagnosis.
We acknowledge the reviewer's concern regarding the cohort size and validation in larger, prospective, multi-center cohorts is essential before this panel can be considered for clinical application. We have explicitly stated this as a limitation of our study in the Discussion section and have highlighted the need for future large-scale validation studies (Page 18, Lines 367-373). We once again thank the reviewer for their insightful comments, which have allowed us to substantially improve our manuscript. We hope that the revised version is now suitable for publication.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
This work presents a 27-region DMR model for early diagnosis and prognostic prediction of colorectal cancer using plasma methylation markers. While this non-invasive diagnostic and prognostic tool could interest a broad readership, several critical issues require attention.
Major Concerns:
(1) Inconsistencies and clarity issues in data presentation
(a) Sample size discrepancies
The abstract mentions screening 119 CRC tissue samples, while Figure 1 shows 136 tissues. Please clarify if this represents 119 CRC and 17 normal samples.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for this careful observation and for pointing out the inconsistency. We apologize for the error and the confusion it caused. Regarding Figure 1: The reviewer is correct. The number 136 in the original Figure 1 was an error. This was due to an inadvertent double-counting of the tumor samples that were used in the differential analysis against adjacent normal tissues. The actual number of tissue samples used in this analysis is 89. We have now corrected this value in the revised Figure 1.
Regarding the Abstract: The 119 CRC tissue samples mentioned in the abstract represents the total number of unique tumor samples analyzed across all stages of our study. This number is composed of two cohorts: the initial 15 pairs of tissues used for preliminary screening, and the subsequent 89 tissue samples used for validation, totaling 119 samples. We have ensured all sample numbers are now consistent throughout the revised manuscript.
The plasma sample numbers vary across sections: the abstract cites 161 samples, Figure 1 shows 116 samples, and the Supplementary Methods mentions 77 samples (13 Normal, 15 NAA, 12 AA, 37 CRC).
We sincerely thank the reviewer for their meticulous review and for identifying these inconsistencies in the plasma sample numbers. We apologize for this oversight and the lack of clarity.
Figure 1 & Supplementary Methods (77 samples): The number 116 in the original Figure 1 was a clerical error. The correct number is 77, which is the cohort used for our differential methylation analysis. This number is now consistent with the Supplementary Methods. This cohort is composed of 13 Normal, 15 NAA, 12 AA, and 37 CRC samples. The figure has been revised accordingly.
Abstract (161 samples): The total of 161 plasma samples mentioned in the abstract is the sum of two distinct sample sets used for different stages of our analysis: The 77 samples (13 Normal, 15 NAA, 12 AA, 37 CRC) used for the differential analysis. An additional 84 samples (33 Normal, 51 CRC) which served as the training set for the LASSO regression model. We have now clarified these distinctions in the text and ensured consistency across the abstract, figures, and methods sections.
(b) Methodological inconsistencies
The Supplementary Material reports 477 hypermethylated sites from TCGA data analysis (Δβ>0.20, FDR<0.05), but Figure 1 indicates 499 sites.
The manuscript states that analyzing TCGA data across six cancer types identified 499 CRC-specific methylation sites, yet Figure 1 shows 477. Please also explain the rationale for selecting these specific cancer types from TCGA.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for their sharp observation and for highlighting these inconsistencies. We apologize for this clerical error, which occurred when labeling the figure. The numbers 477 and 499 in Figure 1 were inadvertently swapped and the text in Supplementary Material is correct. We have now corrected this error throughout the manuscript to ensure clarity and consistency. We deeply regret the confusion this has caused.
Regarding the rationale for selecting the cancer types:
The selection of colorectal, esophageal, gastric, lung, liver, and breast cancers was based on the following strategic criteria to ensure the stringent identification of CRC-specific markers. Firstly, esophageal, gastric, liver, and colorectal cancers all originate from the gastrointestinal tract and share developmental and functional similarities. Comparing CRC against these closely related cancers allowed us to filter out general GI-tract-related methylation patterns and isolate those that are truly unique to colorectal tissue. Secondly, we included lung and breast cancer as they are two of the most common non-GI malignancies worldwide with distinct tissue origins. This helps ensure our identified markers are not just pan-cancer methylation events but are specific to CRC, even when compared against highly prevalent cancers from different lineages. Finally, these six cancer types have some of the largest and most complete datasets available in the TCGA database, including high-quality methylation data. This provided a robust statistical foundation for a reliable cross-cancer comparison. We hope this explanation clarifies our methodology. Thank you again for your valuable feedback.
"404 CRC-specific DMRs" mentioned in the main text while "404 MCBs" in Figure 1, the authors need to clarify if these terms are interchangeable or how MCBs are defined.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for pointing out this important inconsistency in terminology. We apologize for the confusion this has caused and for the error in Figure 1. The two terms are closely related in our study. The final 404 markers are technically DMRs that were identified through an analysis of MCBs. To avoid confusion, we have decided to unify the terminology. The manuscript has now been revised to consistently use "DMRs", which is the most accurate final descriptor. The label in Figure 1 has been corrected accordingly.
(2) Methodological documentation
The Results section requires a more detailed description of marker identification procedures and justification of methodological choices.
Figure 3 panels need reordering for sequential citation.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable suggestion. We agree that the original Results section lacked sufficient detail regarding the marker identification procedures and the justification for our methodological choices. To address this, we have substantially rewritten the "Methylation markers selection" subsection. This revised section provides a clear, step-by-step narrative of our marker discovery. The revised text now integrates the specific methodological details and statistical criteria. For instance, we now explicitly describe the three-pronged approach for the initial TCGA data mining and the specific criteria (Δβ, FDR, log2FC) for each, and the analysis methodology such as Wilcoxon test and LASSO regression analysis. We believe this detailed narrative now provides the necessary description and justification for our methodological choices directly within the results, significantly improving the clarity and logical flow of our manuscript. This revision can be found on (Page 9-11, Lines 180-195, 202-213). We hope these changes fully address the reviewer's concerns.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out the citation order of the panels in Figure 3. This was a helpful suggestion for improving the clarity of our manuscript. We have now reordered the panels in Figure 3 to ensure they are cited sequentially within the text. These adjustments have been made in the "Development and validation of the CRC diagnosis model" subsection of the Results (Page 11, lines 224-230). We appreciate the reviewer's attention to detail.
(3) Quality control and data transparency
No quality control metrics are presented for the in-house sequencing data (e.g., sequencing quality, alignment rate, BS conversion rate, coverage, PCA plots for each cohort).
The analysis code should be publicly available through GitHub or Zenodo.
At a minimum, processed data should be made publicly accessible to ensure reproducibility.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for their valuable and constructive feedback regarding quality control and data transparency. We fully agree that these elements are crucial for ensuring the robustness and reproducibility of our research. As the reviewer suggested, we have made all processed data and the key quality control metrics for each sample including sequencing quality scores, bisulfite (BS) conversion rates, and sequencing coverage publicly available to ensure the reproducibility of our findings. The analysis was performed using standard algorithms as detailed in the Methods section. While we are unable to host the code in a public repository at this time, all analysis scripts are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The data has been deposited in the National Genomics Data Center (NGDC) and is accessible under the accession number OMIX009128. This information is now clearly stated in the "Data and Code Availability" section of the manuscript. We thank the reviewer again for pushing us to improve our manuscript in this critical aspect.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This article provides a model for early diagnosis and prognostic prediction of Colorectal Cancer and demonstrates its accuracy and usability. However, there are still some minor issues that need to be revised and paid attention to.
Strengths:
A large amount of external datasets were used for verification, thus demonstrating robustness and accuracy. Meanwhile, various influencing factors of multiple samples were taken into account, providing usability.
Weaknesses:
There are notable language issues that hinder readability, as well as a lack of some key conclusions provided.
We are very grateful to the reviewer for their positive assessment of our study and for the constructive feedback provided. We are particularly encouraged that the reviewer recognized the strengths of our work, especially the robustness demonstrated through extensive external validation and the practical usability of our model. Regarding the weaknesses, we have taken the comments very seriously and have thoroughly revised the manuscript. We sincerely apologize for the language issues that hindered readability in our initial submission. To address this, the entire manuscript has undergone a comprehensive round of professional language polishing and editing. We have carefully reviewed and revised the text to improve clarity, flow, and grammatical accuracy. Besides, we agree that the conclusions could be stated more explicitly. To rectify this, we have substantially revised the final paragraph of the Discussion and the Conclusion section (Page 14-18, lines 279-305, 319-334, 346-348, 358-360, 367-379). We now more clearly summarize the main findings of our study, emphasize the clinical significance and potential applications of our model, and provide clear take-home messages. We thank you again for your time and insightful comments, which have been invaluable in improving the quality of our paper. We hope the revised manuscript now meets the standards for publication.
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
Detail comments are outlined below:
(1) In this study, the authors have highlighted methylated cfDNA as a noninvasive approach for CRC early diagnosis. However, the small size of cohorts for plasma screening, particularly the sample number of NAA and AA , may cause bias in the selection of DMRs. This bias may lead to inappropriate DMRs for early diagnosis. Furthermore, the similar issues for the training set with a high percentage of late-stage CRC, no AA or NAA samples were included. This absence may be the key factor in screening changed methylated cfDNA that can predict the early stages of CRC.
We are very grateful to the reviewer for this insightful methodological critique. We agree that cohort composition and sample size are critical factors in the development of robust biomarkers, and we appreciate the opportunity to clarify our study design and the interpretation of our results.
We agree with the reviewer that the number of precancerous lesion samples (NAA and AA) in our initial plasma screening cohort was limited. This is a valid point. However, it is important to contextualize the role of this step within our overall multi-stage marker selection funnel. The markers evaluated in this plasma cohort were not discovered from this small sample set alone. They were the result of a rigorous pre-selection process based on large-scale public TCGA data and our own tissue-level sequencing. This robust, tissue-based validation ensured that only the most promising CRC-specific markers were advanced for plasma testing. Therefore, while the plasma cohort was modest in size, its purpose was to confirm the circulatory detectability of markers already known to have a strong tissue-of-origin signal, thereby mitigating the potential bias from a smaller discovery set.
Our primary aim was to first build a model that could robustly and accurately identify a definitive cancer-specific methylation signal. By training the model on clear-cut invasive cancer cases versus healthy controls, we could isolate the most powerful and specific markers for established malignancy. Our working hypothesis was that these strong cancer-specific methylation patterns are initiated during the precursor stages and would therefore be detectable, albeit at lower levels, in precancerous lesions. Unfortunately, the panel could only identify a limited proportion of precancerous lesions (48.4% in the NAA group and 52.2% in the AA group). We fully agree with the reviewer's sentiment that including a larger and more balanced set of precancerous lesions in future training cohorts could potentially optimize a model specifically for adenoma detection. We have now explicitly added this point to our Discussion section, highlighting it as an important direction for future research (Page 18, lines 367-373).
(2) The sensitivity of 27 DMRs in the external validation set (for NAA, AA and CRC 0-Ⅱare 48.4%. 52.2% and 66.7%, respectively) were much lower compared with previously published studies, like ColonES assay (DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101717) and ColonSecure test (DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01866-z). The 27 DMRs from the layered screening process did not show superior performance in a small population of an external validation cohort. Therefore, it is unlikely that this DMR pattern will be applicable to the general population in the future.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for their insightful comments and for providing a thorough comparison with the highly relevant ColonES and ColonSecure assays. This has given us an important opportunity to clarify the unique contributions and specific clinical applications of our 27-DMR panel.
We acknowledge the reviewer's point that the sensitivities of our panel for precancerous lesions (NAA: 48.4%, AA: 52.2%), while substantial, are numerically lower than those reported by the excellent ColonES assay (AA: 79.0%). However, it is important to clarify that while the ColonES and ColonSecure tests are outstanding benchmarks designed primarily for early detection and screening, the primary objective and contribution of our study were slightly different. Our model demonstrated an exceptional ability to predict distant metastasis with an AUC of 0.955 and a strong capacity for predicting overall prognosis with an AUC of 0.867. Our goal was to develop a multi-functional, biologically-rooted biomarker panel that not only contributes to early detection but, more importantly, provides crucial information for post-diagnosis patient management, including staging, risk stratification, and prognostication, from a single preoperative sample. We believe this ability to preoperatively identify high-risk patients who may require more aggressive treatment or intensive surveillance is the key contribution of our work. It provides a distinct clinical utility that complements, rather than directly competes with, pure screening assays.
We agree with the reviewer that our external validation was performed on a limited cohort, and we have acknowledged this as a limitation in our Discussion section. However, the purpose of this validation was to provide a proof-of-concept for the panel's performance across its multiple functions. The promising and exceptionally high-performing results in the prognostic domain strongly warrant further validation in larger, prospective, multi-center cohorts.
(3) The 27 DMRs pattern worked well in predicting CRC distant metastasis, and the methylation score remarkably increased in stage III-IV. In contrast, the increase of AA and 0-II groups was very mild in the validation cohort. This observation raises concerns regarding the study design, particularly in the context of the layered screening process and sample assigning.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for this insightful and critical comment. We agree with the reviewer's observation that the methylation score increased more remarkably in late-stage (III-IV) CRC compared to the milder increase in adenoma (AA) and early-stage (0-II) CRC in the validation cohort. However, the observed pattern is biologically plausible and consistent with the nature of colorectal cancer progression. Carcinogenesis is a multi-step process involving the gradual accumulation of genetic and epigenetic alterations. The methylation changes we identified are likely associated with tumor progression and metastasis. Therefore, it is expected that advanced, metastatic cancers (Stage III-IV), which have undergone significant biological changes, would exhibit a much stronger and more robust methylation signal compared to pre-cancerous lesions (adenomas) or early-stage, non-metastatic cancers (Stage 0-II). The "mild" increase in early stages reflects the initial, more subtle epigenetic alterations, while the "remarkable" increase in late stages reflects the extensive changes required for invasion and metastasis. We believe this graduated increase actually strengthens the validity of our methylation signature, as it mirrors the underlying biological progression of the disease. We hope this response and the corresponding revisions address the reviewer's comments.
(4) The authors did not provide the 27 DMRs prediction efficacy comparison with other noninvasive CRC assays, like a CEA and a FIT test.
Thank you for this valuable suggestion. We agree that comparing our model with established non-invasive assays is crucial for demonstrating its clinical potential. Following your advice, we have now included a direct comparison of the diagnostic performance between our model and the traditional tumor marker, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), using the external validation cohort. The results show that our model has a significantly higher sensitivity for detecting early-stage colorectal cancer and adenomas compared to CEA. This detailed comparison has been added as Table s7 in the supplementary materials, and the corresponding description has been incorporated into the Results section of our manuscript (Page 12, lines 234-236). Regarding the Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT), we unfortunately could not perform a direct statistical comparison because very few individuals in our cohort had undergone FIT. A comparison based on such a small sample size would lack statistical power and might not yield meaningful conclusions. We have acknowledged this as a limitation of our study in the Discussion section.We believe these additions and clarifications have substantially strengthened our manuscript. Thank you again for your constructive feedback.
(5) The authors did not explicitly describe how they assigned the plasma samples to the distinct sets, nor did they specify the criteria for the plasma screen set, training set, and validation set. The detailed information for the patient grouping should be listed.
Responce: Thank you for this essential feedback. We agree that a transparent and detailed description of the sample allocation process is crucial for the manuscript. We apologize for the previous lack of clarity and have now revised the Methods section to address this. Our patient cohorts were assigned to the screening, training, and validation sets based on a chronological splitting strategy. Specifically, samples were allocated based on the date of collection in a consecutive manner. This approach was chosen to minimize selection bias and to provide a more realistic, forward-looking assessment of the model's performance, simulating a prospective validation scenario. The screening set comprised 89 tissue samples and 77 plasma samples collected between June to December 2020. The primary purpose of this set was for the initial discovery and screening of potential methylation markers. The training set and validation set included 165 plasma samples collected from December 2020 to July 2022. The external validation cohort comprised 166 plasma samples collected from from July 2022 to December 2022. The subsection titled "Study design and samples" within the Methods section of the revised manuscript, which now contains all of this detailed information (Page 6, lines 116-133). We believe this detailed explanation now makes our study design clear and transparent. Thank you again for helping us improve our manuscript.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
The manuscript requires significant language editing to improve clarity and readability. We recommend that the authors seek professional editing services for revision.
Thank you for your constructive comments on the language of our manuscript. We apologize for any lack of clarity in the previous version. To address this, we have performed a thorough revision of the manuscript. The text has been carefully reviewed and edited by a native English-speaking colleague who is an expert in our research field. We have focused on correcting all grammatical errors, improving sentence structure, and refining the phrasing throughout the document to enhance readability. We are confident that these extensive revisions have significantly improved the clarity of the manuscript. We hope you will find the current version much easier to read and understand.
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) However, I think the abstract part of the article is too detailed and should be more concise and shortened. It is not necessary to show detailed values but to summarize the results.
Thank you for this valuable suggestion. We agree that the previous version of the abstract was overly detailed and that a more concise summary would be more effective for the reader. Following your advice, we have substantially revised the abstract. We have removed the specific numerical values (such as detailed statistics) and have instead focused on summarizing the key findings and their broader implications (Page 3, lines 54-60, 64-66, 70-72). The revised abstract is now shorter and provides a clearer, high-level overview of our study's background, methods, main results, and conclusions. We believe these changes have significantly improved its readability and impact. We hope you will find the current version more appropriate.
(2) Figure 4, the color in the legend and plot are not the same, and should be revised.
Thank you for your careful attention to detail and for pointing out the color inconsistency in Figure 4. We apologize for this oversight. We have now corrected the figure as you suggested, ensuring that the colors in the legend perfectly match those in the plot. The revised Figure 4 has been updated in the manuscript. We appreciate your help in improving the quality of our figures.
(3) Please pay attention to the article format, such as the consistency of fonts and punctuation marks. (For example, Lines 75 and Line 230).
Thank you for your meticulous review and for pointing out the inconsistencies in our manuscript's formatting. We sincerely apologize for these oversights and any inconvenience they may have caused. Following your feedback, we have carefully corrected the specific issues you highlighted. Furthermore, we have conducted a thorough proofread of the entire manuscript to ensure consistency in all fonts, punctuation marks, and overall adherence to the journal's formatting guidelines. We appreciate your help in improving the presentation and professionalism of our paper.
However, due to software limitations, it was not possible to correct standard errors for the complex survey design (via the Jackknife method for ICILS, Fay’s method for PISA, or cluster-robust estimation). At present, the lavaan package does not support: 1) the use of robust estimators for categorical variables in conjunction with clustering; 2) the simultaneous use of sampling weights combined with clustering; and 3) the implementation of replicate variance estimation methods.
No es necesario entrar en este detalle. Pero si se va a decir, hay que usar citas para fundamentar.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Taylar Hammond and colleagues identified new regulators of the G1/S transition of the cell cycle. They did so by screening publicly available data from the Cancer Dependency Map and identified FAM53C as a positive regulator of the G1/S transition. Using biochemical assays they then show that FAM53 interacts with the DYRK1A kinase to inhibit its function. They show in RPE1 cells that loss of FAMC53 leads to a DYRK1A + P53-dependent cell cycle arrest. Combined inactivation of FAM53C and DYRK1A in a TP53-null background caused S-phase entry with subsequent apoptosis. Finally the authors assess the effect of FAM53C deletion in a cortical organoid model, and in Fam53c knockout mice. Whereas proliferation of the organoids is indeed inhibited, mice show virtually no phenotype.
The authors have revised the manuscript, and I respond here point-by-point to indicate which parts of the revision I found compelling, and which parts were less convincing. So the numbering is consistent with the numbering in my first review report.
(1) The p21 knockdowns are a valuable addition, and the claim that other p53 targets than p21 are involved in the FAMC53 RNAi-mediated arrest is now much more solid. Minor detail: if S4D is a quantification of S4C, it is hard to believe that the quantification was done properly (at least the DYRK1Ai conditions). Perhaps S4C is not the best representative example, or some error was made?
(2a) I appreciate the decision to remove the cyclin D1 phosphorylation data. A more nuanced model now emerges. It is not clear to me however why the Protein Simple immunoassay was used for experiments with RPE cells, and not the cortical organoids. Even though no direct claims are made based on the phospho-cyclin D data in Figure 5E+G, showing these data suggests that FAM53C deletion increases DYRK1A-mediated cyclin D1 phosphorylation. I find it tricky to show these data, while knowing now that this effect could not be shown in the RPE1 cells.<br /> (2b) The quantifications of the immunoassays are not convincing. In multiple experiments, the HSP90 levels vary wildly, which indicates big differences in protein loading if HSP90 is a proper loading control. This is for example problematic for the interpretation of figure 3F and S3I. The cyclin D1 "bands" look extremely similar between siCtrl and siFAM53C (Fig S3I), in fact the two series of 6 samples with different dosages of DYRK1Ai look seem an identical repetition of each other. I did not have to option to overlay them, but it would be important to check if a mistake was made here. The cyclin D1 signals aside, the change in cycD1/HSP90 ratios seems to be entirely caused by differences in HSP90 levels. Careful re-analysis of the raw data and more equal loading seem necessary. The same goes (to a lesser extent) for S3J+K.<br /> (2c) the new model in Fig S4L: what do the arrows at the right FAM53C and p53 that merge a point straight towards S-phase mean? They suggest that p53 (and FAM53C) directly promote S-phase progression, but most likely this is not what the authors intended with it.
(3) Clear; nicely addressed.
(4) Thank you for correcting.
(5) I appreciate that the authors are now more careful to call the IMPC analysis data preliminary. This is acceptable to me, but nevertheless, I suggest the authors to seriously consider taking this part entirely out. The risk of chance finding and the extremely skewed group sizes (as reviewer #2 had pointed out) hamper the credibility of this statistical analysis.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
In this study Hammond et al. investigated the role of Dual-specificity Tyrosine Phosphorylation regulated Kinase 1A (DYRK1) in G1/S transition. By exploiting Dependency Map portal, they identified a previously unexplored protein FAM53C as potential regulator of G1/S transition. Using RNAi, they confirmed that depletion of FAM53C suppressed proliferation of human RPE1 cells and that this phenotype was dependent on the presence protein RB. In addition, they noted increased level of CDKN1A transcript and p21 protein that could explain G1 arrest of FAM53C-depleted cells but surprisingly, they did not observe activation of other p53 target genes. Proteomic analysis identified DYRK1 as one of the main interactors of FAM53C and the interaction was confirmed in vitro. Further, they showed that purified FAM53C blocked the ability of DYRK1 to phosphorylate cyclin D in vitro although the activity of DYRK1 was likely not inhibited (judging from the modification of FAM53C itself). Instead, it seems more likely that FAM53C competes with cyclin D in this assay. Authors claim that the G1 arrest caused by depletion of FAM53C was rescued by inhibition of DYRK1 but this was true only in cells lacking functional p53. This is quite confusing as DYRK1 inhibition reduced the fraction of G1 cells in p53 wild type cells as well as in p53 knock-outs, suggesting that FAM53C may not be required for regulation of DYRK1 function. Instead of focusing on the impact of FAM53C on cell cycle progression, authors moved towards investigating its potential (and perhaps more complex) roles in differentiation of IPSCs into cortical organoids and in mice. They observed a lower level of proliferating cells in the organoids but if that reflects an increased activity of DYRK1 or if it is just an off-target effect of the genetic manipulation remains unclear. Even less clear is the phenotype in FAM53C knock-out mice. Authors did not observe any significant changes in survival nor in organ development but they noted some behavioral differences. Weather and how these are connected to the rate of cellular proliferation was not explored. In the summary, the study identified previously unknown role of FAM53C in proliferation but failed to explain the mechanism and its physiological relevance at the level of tissues and organism. Although some of the data might be of interest, in current form the data is too preliminary to justify publication.
Major comments:
(1) Whole study is based on one siRNA to Fam53C and its specificity was not validated. Level of the knock down was shown only in the first figure and not in the other experiments. The observed phenotypes in the cell cycle progression may be affected by variable knock-down efficiency and/or potential off target effects.
(2) Experiments focusing on the cell cycle progression were done in a single cell line RPE1 that showed a strong sensitivity to FAM53C depletion. In contrast, phenotypes in IPSCs and in mice were only mild suggesting that there might be large differences across various cell types in the expression and function of FAM53C. Therefore, it is important to reproduce the observations in other cell types.
(3) Authors state that FAM53C is a direct inhibitor of DYRK1A kinase activity (Line 203), however this model is not supported by the data in Fig 4A. FAM53C seems to be a good substrate of DYRK1 even at high concentrations when phosphorylations of cyclin D is reduced. It rather suggests that DYRK1 is not inhibited by FAM53C but perhaps FAM53C competes with cyclin D. Further, authors should address if the phosphorylation of cyclin D is responsible for the observed cell cycle phenotype. Is this Cyclin D-Thr286 phosphorylation, or are there other sites involved?
(4) At many places, information on statistical tests is missing and SDs are not shown in the plots. For instance, what statistics was used in Fig 4C? Impact of FAM53C on cyclin D phosphorylation does not seem to be significant. IN the same experiment, does DYRK1 inhibitor prevent modification of cyclin D?
(5) Validation of SM13797 compound in terms of specificity to DYRK1 was not performed.
(6) A fraction of cells in G1 is a very easy readout but it does not measure progression through the G1 phase. Extension of the S phase or G2 delay would indirectly also result in reduction of the G1 fraction. Instead, authors could measure the dynamics of entry to S phase in cells released from a G1 block or from mitotic shake off.
Comments to the revised manuscript:
In the revised version of the manuscript, authors addressed most of the critical points. They now include new data with depletion of FAM53C using single siRNAs that show small but significant enrichment of population of the G1 cells. This G1 arrest is likely caused by a combined effects on induction of p21 expression and decreased levels of cyclin D1. Authors observed that inhibition of DYRK1 rescued cyclin D1 levels in FAM53 depleted cells suggesting that FAM53C may inhibit DYRK1. This possibility is also supported by in vitro experiments. On the other hand, inhibition of DYRK1 did not rescue the G1 arrest upon depletion of FAM53C, suggesting that FAM53C may have also DYRK1-independent role in G1. Functional rescue experiments with cyclin D1 mutants and detection of DYRK1 activity in cells would be necessary to conclusively explain the function of FAM53C in progression through G1 phase but unfortunately these experiments were technically not possible. Knock out of FAM53C in iPSCs and in mice suggest that FAM53C may have additional functions besides the cell cycle control and/or that adaptation may have occurred in these model systems. Overall, the study implicated FAM53C in fine tuning DYRK1 activity in cells that may to some extent influence the progression through G1 phase. In addition, FAM53C may also have DYRK1 and cell cycle independent functions that remain to be addressed by future studies.
Author response:
(1) General Statements
We thank the Reviewers for a fair review of our work and helpful suggestions. We have significantly revised the manuscript in response to these suggestions. We provide a point-by-point response to the Reviewers below but wanted to highlight in our response a recurring concern related to the strong cell cycle arrest observed upon the acute FAM53C knock-down being different than the limited phenotypes in other contexts, including the knockout mice and DepMap data.
First, we now show that we can recapitulate the strong G1 arrest resulting from the FAM53C knock-down using two independent siRNAs in RPE-1 cells, supporting the specificity of the effects.
Second, the G1 arrest that results from the FAM53C knock-down is also observed in cells with inactive p53, suggesting it is not due to a non-specific stress response due to “toxic” siRNAs. In addition, the arrest is dependent on RB, which fits with the genetic and biochemical data placing FAM53C upstream of RB, further supporting a specific phenotype.
Third, we have performed experiments in other human cells, including cancer cell lines. As would be expected for cancer cells, the G1 arrest is less pronounced but is still significant, indicating that the G1 arrest is not unique to RPE-1 cells.
Fourth, it is not unexpected that compensatory mechanisms would be activated upon loss of FAM53C during development or in cancer – which may explain the lack of phenotypes in vivo or upon long-term knockout. This has been true for many cell cycle regulators, either because of compensation by other family members that have overlapping functions, or by a larger scale rewiring of signaling pathways.
(2) Point-by-point description of the revisions
Reviewer #1 (Evidence, reproducibility and clarity):
Summary:
Taylar Hammond and colleagues identified new regulators of the G1/S transition of the cell cycle.
They did so by screening public available data from the Cancer Dependency Map, and identified FAM53C as a positive regulator of the G1/S transition. Using biochemical assays they then show that FAM53 interacts with the DYRK1A kinase to inhibit its function. DYRK1A in its is known to induce degradation of cyclin D, leading the authors to propose a model in which DYRK1Adependent cyclin D degradation is inhibited by FAM53C to permit S-phase entry. Finally the authors assess the effect of FAM53C deletion in a cortical organoid model, and in Fam53c knockout mice. Whereas proliferation of the organoids is indeed inhibited, mice show virtually no phenotype.
Major comments:
The authors show convincing evidence that FAM53C loss can reduce S-phase entry in cell cultures, and that it can bind to DYRK1A. However, FAM53 has multiple other binding partners and I am not entirely convinced that negative regulation of DYRK1A is the predominant mechanism to explain its effects on S-phase entry. Some of the claims that are made based on the biochemical assays, and on the physiological effects of FAM53C are overstated. In addition, some choices made methodology and data representation need further attention.
(1) The authors do note that P21 levels increase upon FAM53C. They show convincing evidence that this is not a P53-dependent response. But the claim that " p21 upregulation alone cannot explain the G1 arrest in FAM53C-deficient cells (line 138-139) is misleading. A p53-independent p21 response could still be highly relevant. The authors could test if FAM53C knockdown inhibits proliferation after p21 knockdown or p21 deletion in RPE1 cells.
The Reviewer raises a great point. Our initial statement needed to be clarified and also need more experimental support. We have performed experiments where we knocked down FAM53C and p21 individually, as well as in combination, in RPE-1 cells. These experiment show that p21 knock-down is not sufficient to negate the cell cycle arrest resulting from the FAM53C knockdown in RPE-1 cells (Figure 4B,C and Figure S4C,D).
We now extended these experiments to conditions where we inhibited DYRK1A, and we also compared these data to experiments in p53-null RPE-1 cells. Altogether, these experiments point to activation of p53 downstream of DYRK1A activation upon FAM53C knock-down, and indicate that p21 is not the only critical p53 target in the cell cycle arrest observed in FAM53C knock-down cells (Figure 4 and Figure S4).
(2) The authors do not convincingly show that FAM53C acts as a DYRK1A inhibitor in cells. Figures 4B+C and S4B+C show extremely faint P-CycD1 bands, and tiny differences in ratios. The P values are hovering around the 0.05, so n=3 is clearly underpowered here. Total CycD1 levels also correlate with FAM53C levels, which seems to affect the ratios more than the tiny pCycD1 bands. Why is there still a pCycD1 band visible in 4B in the GFP + BTZ + DYRK1Ai condition? And if I look at the data points I honestly don't understand how the authors can conclude from S4C that knockdown of siFAM53C increases (DYRK1A dependent) increases in pCycD1 (relative to total CycD1). In figure 5C, no blot scans are even shown, and again the differences look tiny. So the authors should either find a way to make these assays more robust, or alter their claims appropriately.
We appreciate these comments from the Reviewer and have significantly revised the manuscript to address them.
The analysis of Cyclin D phosphorylation and stability are complicated by the upregulation of p21 upon FAM53C knock-down, in particular because p21 can be part of Cyclin D complexes, which may affect its protein levels in cells (as was nicely showed in a previous study from the lab of Tobias Meyer – Chen et al., Mol Cell, 2013). Instead of focusing on Cyclin D levels and stability, we refocused the manuscript on RB and p53 downstream of FAM53C loss.
We removed previous panel 4B from the revised manuscript. For panels 4E and S4B (now panels S3J and S3K)), we used a true “immunoassay” (as indicated in the legend – not an immunoblot), which is much more quantitative and avoids error-prone steps in standard immunoblots (“Western blots”). Briefly, this system was developed by ProteinSimple. It uses capillary transfer of proteins and ELISA-like quantification with up to 6 logs of dynamic range (see their web site https://www.proteinsimple.com/wes.html). The “bands” we show are just a representation of the luminescence signals in capillaries. We made sure to further clarify the figure legends in the revised manuscript.
The representative Western blot images for 5C-D (now 5F-G) in the original submission are shown in Figure 5E, we apologize if this was not clear. The differences are small, which we acknowledge in the revised manuscript. Note that several factors can affect Cyclin D levels in cells, including the growth rate and the stage of the cell cycle. Our FACS analysis shows that normal organoids have ~63% of cells in G1 and ~13% in S phase; the overall lower proportion of S-phase cells in organoids may make the immunoblot difference appear smaller, with fewer cycling cells resulting in decreased Cyclin D phosphorylation.
Nevertheless, the Reviewer brings up a good point and comments from this Reviewer and the others made us re-think how to best interpret our results. As discussed above, we re-read carefully the Meyer paper and think that FAM53C’s role and DYRK1A activity in cells may be understood when considering levels of both CycD and p21 at the same time in a continuum. While our genetic and biochemical data support a role for FAM53C in DYRK1A inhibition, it is likely that the regulation of cell cycle progression by FAM53C is not exclusively due to this inhibition. As discussed above and below, we noted an upregulation of p21 upon FAM53C knock-down, and activation of p53 and its targets likely contributes significantly to the phenotypes observed. We added new experiments to support this more complex model (Figure 4 and Figure S4, with new model in S4L).
(3) The experiments to test if DYRK1A inhibition could rescue the G1 arrest observed upon FAM53C knockdown are not entirely convincing either. It would be much more convincing if they also perform cell counting experiments as they have done in Figures 1F and 1G, to complement the flow cytometry assays. I suggest that the authors do these cell counting experiments in RPE1 +/- P53 cells as well as HCT116 cells. In addition, did the authors test if P21 is induced by DYRK1Ai in HCT116 cells?
We repeated the experiments with the DYRK1A inhibitor and counted the cells. In p53-null RPE1 cells, we found that cell numbers do not increase in these conditions where we had observed a cell cycle re-entry (Fig. 4E), which was accompanied by apoptotic cell death (Fig. S4I). Thus, cells re-enter the cell cycle but die as they progress through S-phase and G2/M. We note that inhibition of DYRK1A has been shown to decrease expression of G2/M regulators (PMID: 38839871), which may contribute to the inability of cells treated to DYRK1Ai to divide. Because our data in RPE-1 cells showed that p21 knock-down was not sufficient to allow the FAM53C knock-down cells to re-enter the cell cycle, we did not further analyze p21 in HCT-116 cells.
(4) The data in Figure 5C and 5D are identical, although they are supposed to represent either pCycD1 ratios or p21 levels. This is a problem because at least one of the two cannot be true. Please provide the proper data and show (representative) images of both data types.
We apologize for these duplicated panels in the original submission. We now replaced the wrong panel with the correct data (Fig. 5F,G).
(5) Line 246: "Fam53c knockout mice display developmental and behavioral defects." I don't agree with this claim. The mutant mice are born at almost the expected Mendelian ratios, the body weight development is not consistently altered. But more importantly, no differences in adult survival or microscopic pathology were seen. The authors put strong emphasis on the IMPC behavioral analysis, but they should be more cautious. The IMPC mouse cohorts are tested for many other phenotypes related to behavior and neurological symptoms and apparently none of these other traits were changed in the IMPC Famc53c-/- cohort. Thus, the decreased exploration in a new environment could very well be a chance finding. The authors need to take away claims about developmental and behavioral defects from the abstract, results and discussion sections; the data are just too weak to justify this.
We agree with the Reviewer that, although we observed significant p-values, this original statement may not be appropriate in the biological sense. We made sure in the revised manuscript to carefully present these data.
Minor comments:
(6) Can the authors provide a rationale for each of the proteins they chose to generate the list of the 38 proteins in the DepMap analysis? I looked at the list and it seems to me that they do not all have described functions in the G1/S transition. The analysis may thus be biased.
To address this point, we updated Table S1 (2nd tab) to provide a better rationale for the 38 factors chosen. Our focus was on the canonical RB pathway and we included RB binding proteins whose function had suggested they may also be playing a role in the G1/S transition. We do agree that there is some bias in this selection (e.g., there are more RB binding factors described) but we hope the Reviewer will agree with us that this list and the subsequent analysis identified expected factors, including FAM53C. Future studies using this approach and others will certainly identify new regulators of cell cycle progression.
(7) Figure 1B is confusing to me. Are these just some (arbitrarily) chosen examples? Consider leaving this heatmap out altogether, of explain in more detail.
We agree with the Reviewer that this panel was not necessarily useful and possibly in the wrong place, and we removed it from the manuscript. We replaced it with a cartoon of top hits in the screen.
(8) The y-axes in Figures 2C, 2D, 2E, and 4D are misleading because they do not start at 0. Please let the axis start at 0, or make axis breaks.
We re-graphed these panels.
(9) Line 229: " Consequences ... brain development." This subheader is misleading, because the in vitro cortical organoid system is a rather simplistic model for brain development, and far away from physiological brain development. Please alter the header.
We changed the header to “Consequences of FAM53C inactivation in human cortical organoids in culture”.
(10) Figure S5F: the gating strategy is not clear to me. In particular, how do the authors know the difference between subG1 and G1 DAPI signals? Do they interpret the subG1 as apoptotic cells? If yes, why are there so many? Are the culturing or harvesting conditions of these organoids suboptimal? Perhaps the authors could consider doing IF stainings on EdU or BrdU on paraffin sections of organoids to obtain cleaner data?
Thank you for your feedback. The subG1 population in the original Figure S5F represents cells that died during the dissociation step of the organoids for FACS analysis. To address this point, we performed live & dead staining to exclude dead cells and provide clearer data. We refined gating strategy for better clarity in the new S5F panel.
(11) Figure S6A; the labeling seems incorrect. I would think that red is heterozygous here, and grey mutant.
We fixed this mistake, thank you.
Reviewer #1 (Significance):
The finding that the poorly studied gene FAM53C controls the G1/S transition in cell lines is novel and interesting for the cell cycle field. However, the lack of phenotypes in Famc53-/- mice makes this finding less interesting for a broader audience. Furthermore, the mechanisms are incompletely dissected. The importance of a p53-indepent induction of p21 is not ruled out. And while the direct inhibitory interaction between FAM53C and DYRK1A is convincing (and also reported by others; PMID: 37802655), the authors do not (yet) convincingly show that DYRK1A inhibition can rescue a cell proliferation defect in FAM53C-deficient cells.
Altogether, this study can be of interest to basic researchers in the cell cycle field.
I am a cell biologist studying cell cycle fate decisions, and adaptation of cancer cells & stem cells to (drug-induced) stress. My technical expertise aligns well with the work presented throughout this paper, although I am not familiar with biolayer interferometry.
Reviewer #2 (Evidence, reproducibility and clarity):
Summary
In this study Hammond et al. investigated the role of Dual-specificity Tyrosine Phosphorylation regulated Kinase 1A (DYRK1) in G1/S transition. By exploiting Dependency Map portal, they identified a previously unexplored protein FAM53C as potential regulator of G1/S transition. Using RNAi, they confirmed that depletion of FAM53C suppressed proliferation of human RPE1 cells and that this phenotype was dependent on the presence protein RB. In addition, they noted increased level of CDKN1A transcript and p21 protein that could explain G1 arrest of FAM53Cdepleted cells but surprisingly, they did not observe activation of other p53 target genes. Proteomic analysis identified DYRK1 as one of the main interactors of FAM53C and the interaction was confirmed in vitro. Further, they showed that purified FAM53C blocked the ability of DYRK1 to phosphorylate cyclin D in vitro although the activity of DYRK1 was likely not inhibited (judging from the modification of FAM53C itself). Instead, it seems more likely that FAM53C competes with cyclin D in this assay. Authors claim that the G1 arrest caused by depletion of FAM53C was rescued by inhibition of DYRK1 but this was true only in cells lacking functional p53. This is quite confusing as DYRK1 inhibition reduced the fraction of G1 cells in p53 wild type cells as well as in p53 knock-outs, suggesting that FAM53C may not be required for regulation of DYRK1 function. Instead of focusing on the impact of FAM53C on cell cycle progression, authors moved towards investigating its potential (and perhaps more complex) roles in differentiation of IPSCs into cortical organoids and in mice. They observed a lower level of proliferating cells in the organoids but if that reflects an increased activity of DYRK1 or if it is just an off target effect of the genetic manipulation remains unclear. Even less clear is the phenotype in FAM53C knock-out mice. Authors did not observe any significant changes in survival nor in organ development but they noted some behavioral differences. Weather and how these are connected to the rate of cellular proliferation was not explored. In the summary, the study identified previously unknown role of FAM53C in proliferation but failed to explain the mechanism and its physiological relevance at the level of tissues and organism. Although some of the data might be of interest, in current form the data is too preliminary to justify publication.
Major points
(1) Whole study is based on one siRNA to Fam53C and its specificity was not validated. Level of the knock down was shown only in the first figure and not in the other experiments. The observed phenotypes in the cell cycle progression may be affected by variable knock-down efficiency and/or potential off target effects.
We thank the Reviewer for raising this important point. First, we need to clarify that our experiments were performed with a pool of siRNAs (not one siRNA). Second, commercial antibodies against FAM53C are not of the best quality and it has been challenging to detect FAM53C using these antibodies in our hands – the results are often variable. In addition, to better address the Reviewer’s point and control for the phenotypes we have observed, we performed two additional series of experiments: first, we have confirmed G1 arrest in RPE-1 cells with individual siRNAs, providing more confidence for the specificity of this arrest (Fig. S1B); second, we have new data indicating that other cell lines arrest in G1 upon FAM53C knock-down (Fig. S1E,F and Fig. 4F).
(2) Experiments focusing on the cell cycle progression were done in a single cell line RPE1 that showed a strong sensitivity to FAM53C depletion. In contrast, phenotypes in IPSCs and in mice were only mild suggesting that there might be large differences across various cell types in the expression and function of FAM53C. Therefore, it is important to reproduce the observations in other cell types.
As mentioned above, we have new data indicating that other cell lines arrest in G1 upon FAM53C knock-down (three cancer cell lines) (Fig. S1E,F and Fig. 4F).
(3) Authors state that FAM53C is a direct inhibitor of DYRK1A kinase activity (Line 203), however this model is not supported by the data in Fig 4A. FAM53C seems to be a good substrate of DYRK1 even at high concentrations when phosphorylations of cyclin D is reduced. It rather suggests that DYRK1 is not inhibited by FAM53C but perhaps FAM53C competes with cyclin D. Further, authors should address if the phosphorylation of cyclin D is responsible for the observed cell cycle phenotype. Is this Cyclin D-Thr286 phosphorylation, or are there other sites involved?
We revised the text of the manuscript to include the possibility that FAM53C could act as a competitive substrate and/or an inhibitor.
We removed most of the Cyclin D phosphorylation/stability data from the revised manuscript. As the Reviewers pointed out, some of these data were statistically significant but the biological effects were small. As discussed above in our response to Reviewer #1, the analysis of Cyclin D phosphorylation and stability are complicated by the upregulation of p21 upon FAM53C knockdown, in particular because p21 can be part of Cyclin D complexes, which may affect its protein levels in cells (as was nicely showed in a previous study from the lab of Tobias Meyer – Chen et al., Mol Cell, 2013). Instead of focusing on Cyclin D levels and stability, we refocused the manuscript on RB and p53 downstream of FAM53C loss.
We note, however, that we used specific Thr286 phospho-antibodies, which have been used extensively in the field. Our data in Figure 1 with palbociclib place FAM53C upstream of Cyclin D/CDK4,6. We performed Cyclin D overexpression experiments but RPE-1 cells did not tolerate high expression of Cyclin D1 (T286A mutant) and we have not been able to conduct more ‘genetic’ studies.
(4) At many places, information on statistical tests is missing and SDs are not shown in the plots. For instance, what statistics was used in Fig 4C? Impact of FAM53C on cyclin D phosphorylation does not seem to be significant. In the same experiment, does DYRK1 inhibitor prevent modification of cyclin D?
As discussed above, we removed some of these data and re-focused the manuscript on p53-p21 as a second pathway activated by loss of FAM53C.
(5) Validation of SM13797 compound in terms of specificity to DYRK1 was not performed.
This is an important point. We had cited an abstract from the company (Biosplice) but we agree that providing data is critical. We have now revised the manuscript with a new analysis of the compound’s specificity using kinase assays. These data are shown in Fig. S3F-H.
(6) A fraction of cells in G1 is a very easy readout but it does not measure progression through the G1 phase. Extension of the S phase or G2 delay would indirectly also result in reduction of the G1 fraction. Instead, authors could measure the dynamics of entry to S phase in cells released from a G1 block or from mitotic shake off.
The Reviewer made a good point. As discussed in our response to Reviewer #1, with p53-null RPE-1 cells, we found that cell numbers do not increase in these conditions where we had observed a cell cycle re-entry (Fig. 4E), which was accompanied by apoptotic cell death (Fig. S4I). Thus, cells re-enter the cell cycle but die as they progress through S-phase and G2/M. We note that inhibition of DYRK1A has been shown to decrease expression of G2/M regulators (PMID: 38839871), which may contribute to the inability of cells treated to DYRK1Ai to divide.
Because our data in RPE-1 cells showed that p21 knock-down was not sufficient to allow the FAM53C knock-down cells to re-enter the cell cycle, we did not further analyze p21 in HCT-116 cells. These data indicate that G1 entry by flow cytometry will not always translate into proliferation.
Other points:
(7) Fig. 2C, 2D, 2E graphs should begin with 0
We remade these graphs.
(8) Fig. 5D shows that the difference in p21 levels is not significant in FAM53C-KO cells but difference is mentioned in the text.
We replaced the panel by the correct panel; we apologize for this error.
(9) Fig. 6D comparison of datasets of extremely different sizes does not seem to be appropriate
We agree and revised the text. We hope that the Reviewer will agree with us that it is worth showing these data, which are clearly preliminary but provide evidence of a possible role for FAM53C in the brain.
(10) Could there be alternative splicing in mice generating a partially functional protein without exon 4? Did authors confirm that the animal model does not express FAM53C?
We performed RNA sequencing of mouse embryonic fibroblasts derived from control and mutant mice. We clearly identified fewer reads in exon 4 in the knockout cells, and no other obvious change in the transcript (data not shown). However, immunoblot with mouse cells for FAM53C never worked well in our hands. We made sure to add this caveat to the revised manuscript.
Reviewer #2 (Significance):
Main problem of this study is that the advanced experimental models in IPSCs and mice did not confirm the observations in the cell lines and thus the whole manuscript does not hold together. Although I acknowledge the effort the authors invested in these experiments, the data do not contribute to the main conclusion of the paper that FAM53C/DYRK1 regulates G1/S transition.
Reviewer #3 (Evidence, reproducibility and clarity:
This paper identifies FAM53C as a novel regulator of cell cycle progression, particularly at the G1/S transition, by inhibiting DYRK1A. Using data from the Cancer Dependency Map, the authors suggest that FAM53C acts upstream of the Cyclin D-CDK4/6-RB axis by inhibiting DYRK1A. Specifically, their experiments suggest that FAM53C Knockdown induces G1 arrest in cells, reducing proliferation without triggering apoptosis. DYRK1A Inhibition rescues G1 arrest in P53KO cells, suggesting FAM53C normally suppresses DYRK1A activity. Mass Spectrometry and biochemical assays confirm that FAM53C directly interacts with and inhibits DYRK1A. FAM53C Knockout in Human Cortical Organoids and Mice leads to cell cycle defects, growth impairments, and behavioral changes, reinforcing its biological importance.
Strength of the paper:
The study introduces a novel cell cycle control signalling module upstream of CDK4/6 in G1/S regulation which could have significant impact. The identification of FAM53C using a depmap correlation analysis is a nice example of the power of this dataset. The experiments are carried out mostly in a convincing manner and support the conclusions of the manuscript.
Critique:
(1) The experiments rely heavily on siRNA transfections without the appropriate controls. There are so many cases of off-target effects of siRNA in the literature, and specifically for a strong phenotype on S-phase as described here, I would expect to see solid results by additional experiments. This is especially important since the ko mice do not show any significant developmental cell cycle phenotypes. Moreover, FAM53C does not show a strong fitness effect in the depmap dataset, suggesting that it is largely non-essential in most cancer cell lines. For this paper to reach publication in a high-standard journal, I would expect that the authors show a rescue of the S-phase phenotype using an siRNA-resistant cDNA, and show similar S-phase defects using an acute knock out approach with lentiviral gRNA/Cas9 delivery.
We thank the Reviewer for this comment. Please refer to the initial response to the three Reviewers, where we discuss our use of single siRNAs and our results in multiple cell lines. Briefly, we can recapitulate the G1 arrest upon FAM53C knock-down using two independent siRNAs in RPE-1 cells. We also observe the same G1 arrest in p53 knockout cells, suggesting it is not due to a non-specific stress response. In addition, the arrest is dependent on RB, which fits with the genetic and biochemical data placing FAM53C upstream of RB, further supporting a specific phenotype. Human cancer cell lines also arrest in G1 upon FAM53C knock-down, not just RPE-1 cells. Finally, we hope the Reviewer will agree with us that compensatory mechanisms are very common in the cell cycle – which may explain the lack of phenotypes in vivo or upon long-term knockout of FAM53C.
(2) The S-phase phenotype following FAM53C should be demonstrated in a larger variety of TP53WT and mutant cell lines. Given that this paper introduces a new G1/S control element, I think this is important for credibility. Ideally, this should be done with acute gRNA/Cas9 gene deletion using a lentiviral delivery system; but if the siRNA rescue experiments work and validate an on-target effect, siRNA would be an appropriate alternative.
We now show data with three cancer cell lines (U2OS, A549, and HCT-116 – Fig. S1E,F and Fig. 4F), in addition to our results in RPE-1 cells and in human cortical organoids. We note that the knock-down experiments are complemented by overexpression data (Fig. 1G-I), by genetic data (our original DepMap screen), and our biochemical data (showing direct binding of FAM53C to DYRK1A).
(3) The western blot images shown in the MS appear heavily over-processed and saturated (See for example S4B, 4A, B, and E). Perhaps the authors should provide the original un-processed data of the entire gels?
For several of our panels (e.g., 4E and S4B, now panels S3J and S3K)), we used a true “immunoassay” (as indicated in the legend – not an immunoblot), which is much more quantitative and avoids error-prone steps in standard immunoblots (“Western blots”). Briefly, this system was developed by ProteinSimple. It uses capillary transfer of proteins and ELISA-like quantification with up to 6 logs of dynamic range (see their web site https://www.proteinsimple.com/wes.html). The “bands” we show are just a representation of the luminescence signals in capillaries. We made sure to further clarify the figure legends in the revised manuscript.
Data in 4A are also not a western blot but a radiograph.
For immunoblots, we will provide all the source data with uncropped blots with the final submission.
(4) A critical experiment for the proposed mechanism is the rescue of the FAM53C S-phase reduction using DYRK1A inhibition shown in Figure 4. The legend here states that the data were extracted from BrdU incorporation assays, but in Figure S4D only the PI histograms are shown, and the S-phase population is not quantified. The authors should show the BrdU scatterplot and quantify the phenotype using the S-phase population in these plots. G1 measurements from PI histograms are not precise enough to allow for conclusions. Also, why are the intensities of the PI peaks so variable in these plots? Compare, for example, the HCT116 upper and lower panels where the siRNA appears to have caused an increase in ploidy.
We apologize for the confusion and we fixed these errors, for most of the analyses, we used PI to measure G1 and S-phase entry. We added relevant flow cytometry plots to supplemental figures (Fig. S1G, H, I, as well as Fig. S4E and S4K, and Fig. S5F).
(5) There's an apparent contradiction in how RB deletion rescues the G1 arrest (Figure 2) while p21 seems to maintain the arrest even when DYRK1A is inhibited. Is p21 not induced when FAM53C is depleted in RB ko cells? This should be measured and discussed.
This comment and comments from the two other Reviewers made us reconsider our model. We re-read carefully the Meyer paper and think that DYRK1A activity may be understood when considering levels of both CycD and p21 at the same time in a continuum (as was nicely showed in a previous study from the lab of Tobias Meyer – Chen et al., Mol Cell, 2013). While our genetic and biochemical data support a role for FAM53C in DYRK1A inhibition, it is obvious that the regulation of cell cycle progression by FAM53C is not exclusively due to this inhibition. As discussed above and below, we noted an upregulation of p21 upon FAM53C knock-down, and activation of p53 and its targets likely contributes significantly to the phenotypes observed. We added new experiments to support this more complex model (Figure 4 and Figure S4, with new model in S4L).
Reviewer #3 (Significance):
In conclusion, I believe that this MS could potentially be important for the cell cycle field and also provide a new target pathway that could be relevant for cancer therapy. However, the paper has quite a few gaps and inconsistencies that need to be addressed with further experiments. My main worry is that the acute depletion phenotypes appear so strong, while the gene is nonessential in mice and shows only a minor fitness effect in the depmap screens. More convincing controls are necessary to rule out experimental artefacts that misguide the interpretation of the results.
We appreciate this comment and hope that the Reviewer will agree it is still important to share our data with the field, even if the phenotypes in mice are modest.
As a consequence of the amendments set out above in relation to network services,interoperability and data sharing, it is furthermore proposed to repeal the following relatedimplementing acts, by way of the applicable procedure, and to delete the correspondingempowerments:(1) Commission Regulation (EC) No 976/2009 as regards Network Services21(2) Commission Regulation (EU) No 1089/2010 on interoperability of spatial data setsand services22, and(3) Commission Regulation (EU) No 268/2010 on data and service sharing23.(4) Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2019/1372 implementing Directive2007/2/EC as regards monitoring and reporting24.
I read this as taking out all INSPIRE obligations, whereas the HVD reg builds on these pre-existing obligations. (Stating that sharing data / services must be open)- [ ] Crosscheck if HVD states an explicit independent mandate, without reference to INSPIRE mandates. #geonovumtb #10mins #belangrijkeerst
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
In the manuscript of Cotten et al., the authors study the 2-thiolation of tRNA in bacterial antibiotic resistance. The wildtype organism, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, downregulates 2-thiolation as a response to antibiotics targeting the ribosome. In this manuscript, the authors show that a knockout of tusB causes slower translation. They provide evidence on the mechanisms of the slowing by determining transcription and translation, ribosome profiling and performing codon-usage analysis. They successfully determined that 2 codons are drivers of the translation slowdown, and the data is highly conclusive. Technically, I have nothing to criticize.
Strengths:
All in all, the study is very well made, and the writing is clear and concise. It covers a wide array of state-of-the-art analyses to unravel the interplay of tRNA modifications in translation.
Weaknesses:
The only question that remains to be asked is why the slowed translation leads to a better survival of the bacteria under antibiotic stress. In my opinion, the mechanism itself remains unclear. Thus, the statement that "We expect that this reduction in ribosomal proteins is globally reducing the translational capacity of the cell and is responsible for inducing tolerance to ribosome and RNA polymerase-targeting antibiotics" does not truly emphasize the remaining open question of why slowed translation favors survival. Therefore, I would recommend a minor text revision.
Author response:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Cotton et al. investigated the role of tusB in antibiotic tolerance in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. They used the IP2226 strain and introduced appropriate mutations and complementation constructs. Assays were performed to measure growth rates, antibiotic tolerance, tRNA modification, gene expression and proteomic profiles. In addition, experiments to measure ribosome pausing and bioinformatic analysis of codon usage in ribosomal proteins provided in-depth mechanistic support for the conclusions.
Strengths:
The findings are consistent with the authors having uncovered new mechanistic insights into bacterial antibiotic tolerance mediated by reducing ribosomal protein abundance.
Weaknesses:
Since the WT strain grows faster than the tusB mutant, there is a question of how growth rate, per se, impacts some of the analysis done. The authors should address this issue. In addition, it may not be essential, but would analysis of another slow-growing mutant (in some other antibiotic tolerance pathway if available) serve as a good control in this context?
We would like to thank the reviewer for their time spent reviewing our manuscript and for their positive review. We plan to address their comment as to how growth rate impacts the analyses and plan to incorporate another slow-growing mutant in the revised version of the manuscript.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study addresses a critical clinical challenge-bacterial antibiotic tolerance (a key driver of treatment failure distinct from genetic resistance)-by uncovering a novel regulatory role of the conserved s2U tRNA modification in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Its strengths are notable and lay a solid foundation for understanding phenotypic drug tolerance. The study is the first to link s2U tRNA modification loss to antibiotic tolerance, specifically targeting translation/transcription-inhibiting antibiotics (doxycycline, gentamicin, rifampicin). By establishing a causal chain - s2U deficiency → codon-specific ribosome pausing (at AAA/CAA/GAA) → reduced ribosomal protein translation → global translational suppression → tolerance - it expands the functional landscape of tRNA modifications beyond canonical translation fidelity, filling a gap in how RNA epigenetics shapes bacterial stress adaptation.
Strengths:
This study makes a valuable contribution to understanding tRNA modification-mediated antibiotic tolerance.
Weaknesses:
There are several limitations that weaken the robustness of the study's mechanistic conclusions. Addressing these gaps would significantly enhance its impact and translational potential.
We would like to thank the reviewer for their time spent reviewing our manuscript, and for both their positive comments about the significance and novelty of this work as well as their critiques. We plan to address their specific recommendations in the revised manuscript by focusing on the contribution of specific ribosomal proteins (i.e. the 30S subunit protein, S13) through overexpression, codon replacement, and stability experiments. We also plan to design experiments to assess in vivo relevance and assess possible impacts on other pathways involved in antibiotic tolerance.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
In the manuscript of Cotten et al., the authors study the 2-thiolation of tRNA in bacterial antibiotic resistance. The wildtype organism, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, downregulates 2-thiolation as a response to antibiotics targeting the ribosome. In this manuscript, the authors show that a knockout of tusB causes slower translation. They provide evidence on the mechanisms of the slowing by determining transcription and translation, ribosome profiling and performing codon-usage analysis. They successfully determined that 2 codons are drivers of the translation slowdown, and the data is highly conclusive. Technically, I have nothing to criticize.
Strengths:
All in all, the study is very well made, and the writing is clear and concise. It covers a wide array of state-of-the-art analyses to unravel the interplay of tRNA modifications in translation.
Weaknesses:
The only question that remains to be asked is why the slowed translation leads to a better survival of the bacteria under antibiotic stress. In my opinion, the mechanism itself remains unclear. Thus, the statement that "We expect that this reduction in ribosomal proteins is globally reducing the translational capacity of the cell and is responsible for inducing tolerance to ribosome and RNA polymerase-targeting antibiotics" does not truly emphasize the remaining open question of why slowed translation favors survival. Therefore, I would recommend a minor text revision.
We would like to thank the reviewer for their time spent reviewing our manuscript and for their positive review of the technical aspects, experimental design, and writing. We will incorporate their suggested text revision into the revised manuscript, and will add to this statement if additional planned experiments shed light on this remaining question.
0.9.15
バージョン0.9.17が出たので更新します。
.
トル ですよね
最新バージョンのPython
ここへのコメントが適切か分かりませんが、uv python コマンドの紹介も欲しいなと思いました。 「uv で python 環境を管理する」みたいな
コマンドラインツールを作るためのプロジェクトを作成する
--app はコマンドラインツールを作るためのオプションではなさそうです
This project kind is for web servers, scripts, and command-line interfaces. https://docs.astral.sh/uv/reference/cli/#uv-init--app
。
uvで作成する仮想環境は、基本的にvenvで作るやつと同じだよ、みたいな説明がほしいかな
uv-example-script
.py は付けない?
てプロジェクト
Pythonプロジェクト
とか最初は書いておいた方がいいかなと
uv init
この手前に全体を俯瞰したいので、uvで提供しているコマンド一覧がほしい。
全部紹介しないなら、そのうち本書ではこれを紹介するよ、とか言ってほしい
。
これを紹介しているので、あえてバージョン指定してのインストールは教えなくてもいいかなと
特定のバージョンのuvをインストールする場合は
これ必要な場合ってありますか?説明しなくてもいいかなと思った
Pythonの標準パッケージマネージャーはpipですが、
pipはパッケージインストーラーであってマネージャーじゃないかなという意見
https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/
あー、でもpipの方に「パッケージを管理する」って書いてるのか、じゃあこのままでいいかなぁ
Today's simplification package is composed of six legislative proposals.
6 legislative proposals (but press release lists 5)
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
eLife Assessment:
This valuable study examines how mammals descend effectively and securely along vertical substrates. The conclusions from comparative analyses based on behavioral data and morphological measurements collected from 21 species across a wide range of taxa are convincing, making the work of interest to all biologists studying animal locomotion.
We would like to greatly thank the two reviewers for their time in reviewing this work, and for their valuable comments and suggestions that will help to improve this manuscript.
Overall, we agree with the weaknesses raised, which are mainly areas for consideration in future studies: to study more species, and in a natural habitat context.
We will nevertheless add a few modifications to improve the manuscript, notably by making certain figures more readable, and adding definitions and bibliography in the main text concerning gait characteristics.
We also provide brief comments on each point of weakness raised by the reviewers below, in blue.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This unique study reports original and extensive behavioral data collected by the authors on 21 living mammal taxa in zoo conditions (primates, tree shrew, rodents, carnivorans, and marsupials) on how descent along a vertical substrate can be done effectively and securely using gait variables. Ten morphological variables reflecting head size and limb proportions are examined in relationship to vertical descent strategies and then applied to reconstruct modes of vertical descent in fossil mammals.
Strengths:
This is a broad and data-rich comparative study, which requires a good understanding of the mammal groups being compared and how they are interrelated, the kinematic variables that underlie the locomotion used by the animals during vertical descent, and the morphological variables that are associated with vertical descent styles. Thankfully, the study presents data in a cogent way with clear hypotheses at the beginning, followed by results and a discussion that addresses each of those hypotheses using the relevant behavioral and morphological variables, always keeping in mind the relationships of the mammal groups under investigation. As pointed out in the study, there is a clear phylogenetic signal associated with vertical descent style. Strepsirrhine primates much prefer descending tail first, platyrrhine primates descend sideways when given a choice, whereas all other mammals (with the exception of the raccoon) descend head first. Not surprisingly, all mammals descending a vertical substrate do so in a more deliberate way, by reducing speed, and by keeping the limbs in contact for a longer period (i.e., higher duty factors).
Weaknesses:
The different gait patterns used by mammals during vertical descent are a bit more difficult to interpret. It is somewhat paradoxical that asymmetrical gaits such as bounds, half bounds, and gallops are more common during descent since they are associated with higher speeds and lower duty factors. Also, the arguments about the limb support polygons provided by DSDC vs. LSDC gaits apply for horizontal substrates, but perhaps not as much for vertical substrates.
We analyzed gait patterns using methods commonly found in the literature and discussed our results accordingly. However, the study of limbs support polygons was indeed developed specifically for studying locomotion on horizontal supports, and may not be applicable for studying vertical locomotion, which is in fact a type of locomotion shared by all arboreal species. In the future, it would be interesting to consider new methods for analyzing vertical gaits.
The importance of body mass cannot be overemphasized as it affects all aspects of an animal's biology. In this case, larger mammals with larger heads avoid descending head-first. Variation in trunk/tail and limb proportions also covaries with different vertical descent strategies. For example, a lower intermembral index is associated with tail-first descent. That said, the authors are quick to acknowledge that the five lemur species of their sample are driving this correlation. There is a wide range of intermembral indices among primates, and this simple measure of forelimb over hindlimb has vital functional implications for locomotion: primates with relatively long hindlimbs tend to emphasize leaping, primates with more even limb proportions are typically pronograde quadrupeds, and primates with relatively long forelimbs tend to emphasize suspensory locomotion and brachiation. Equally important is the fact that the intermembral index has been shown to increase with body mass in many primate families as a way to keep functional equivalence for (ascending) climbing behavior (see Jungers, 1985). Therefore, the manner in which a primate descends a vertical substrate may just be a by-product of limb proportions that evolved for different locomotor purposes. Clearly, more vertical descent data within a wider array of primate intermembral indices would clarify these relationships. Similarly, vertical descent data for other primate groups with longer tails, such as arboreal cercopithecoids, and particularly atelines with very long and prehensile tails, should provide more insights into the relationship between longer tail length and tail-first descent observed in the five lemurs. The relatively longer hallux of lemurs correlates with tail-first descent, whereas the more evenly grasping autopods of platyrrhines allow for all four limbs to be used for sideways descent. In that context, the pygmy loris offers a striking contrast. Here is a small primate equipped with four pincer-like, highly grasping autopods and a tail reduced to a short stub. Interestingly, this primate is unique within the sample in showing the strongest preference for head-first descent, just like other non-primate mammals. Again, a wider sample of primates should go a long way in clarifying the morphological and behavioral relationships reported in this study.
We agree with this statement. In the future, we plan to study other species, particularly large-bodied ones with varied intermembral indexes.
Reconstruction of the ancient lifestyles, including preferred locomotor behaviors, is a formidable task that requires careful documentation of strong form-function relationships from extant species that can be used as analogs to infer behavior in extinct species. The fossil record offers challenges of its own, as complete and undistorted skulls and postcranial skeletons are rare occurrences. When more complete remains are available, the entire evidence should be considered to reconstruct the adaptive profile of a fossil species rather than a single ("magic") trait.
We completely agree with this, and we would like to emphasize that our intention here was simply to conduct a modest inference test, the purpose of which is to provide food for thought for future studies, and whose results should be considered in light of a comprehensive evolutionary model.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This paper contains kinematic analyses of a large comparative sample of small to medium-sized arboreal mammals (n = 21 species) traveling on near-vertical arboreal supports of varying diameter. This data is paired with morphological measures from the extant sample to reconstruct potential behaviors in a selection of fossil euarchontaglires. This research is valuable to anyone working in mammal locomotion and primate evolution.
Strengths:
The experimental data collection methods align with best research practices in this field and are presented with enough detail to allow for reproducibility of the study as well as comparison with similar datasets. The four predictions in the introduction are well aligned with the design of the study to allow for hypothesis testing. Behaviors are well described and documented, and Figure 1 does an excellent job in conveying the variety of locomotor behaviors observed in this sample. I think the authors took an interesting and unique angle by considering the influence of encephalization quotient on descent and the experience of forward pitch in animals with very large heads.
Weaknesses:
The authors acknowledge the challenges that are inherent with working with captive animals in enclosures and how that might influence observed behaviors compared to these species' wild counterparts. The number of individuals per species in this sample is low; however, this is consistent with the majority of experimental papers in this area of research because of the difficulties in attaining larger sample sizes.
Yes, that is indeed the main cost/benefit trade-off with this type of study. Working with captive animals allows for large comparative studies, but there is a risk of variations in locomotor behavior among individuals in the natural environment, as well as few individuals per species in the dataset. That is why we plan and encourage colleagues to conduct studies in the natural environment to compare with these results. However, this type of study is very time-consuming and requires focusing on a single species at a time, which limits the comparative aspect.
Figure 2 is difficult to interpret because of the large amount of information it is trying to convey.
We agree that this figure is dense. One possible solution would be to combine species by phylogenetic groups to reduce the amount of information, as we did with Fig. 3 on the dataset relating to gaits. However, we believe that this would be unfortunate in the case of speed and duty factor because we would have to provide the complete figure in SI anyway, as the species-level information is valuable. We therefore prefer to keep this comprehensive figure here and we will enlarge the data points to improve their visibility, and provide the figure with a sufficiently high resolution to allow zooming in on the details.
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
As indicated in the first section above, this is a strong comparative study that addresses important questions, relative to the evolution of arboreal locomotion in primates and close mammal relatives. My recommendations should be taken in the context of improving a manuscript that is already generally acceptable.
(1) The terms symmetrical and asymmetrical gaits should be briefly defined in the main text (not just in the Methods section) by citing work done by Hildebrand and other relevant studies. To that effect, the statement on lines 96-97 about the convergence of symmetrical gaits is unclear. What does "Symmetrical gaits have evolved convergently in rodents, scandentians, carnivorans, and marsupials" mean? Symmetrical gaits such as the walk, run, trot, etc., are pretty the norm in most mammals and were likely found in metatherians and basal eutherians. This needs clarification. On line 239, the term "ambling" is used in the context of related asymmetrical gaits. To be clear, the amble is a type of running gait involving no whole-body aerial phase and is therefore a symmetrical gait (see Schmitt et al., 2006).
We have added a definition of the terms symmetrical and asymmetrical gaits and added references in the introduction such as: “Symmetrical gaits are defined as locomotor patterns in which the footfalls of a girdle (a pair of fore- or hindlimbs) are evenly spaced in time, with the right and left limbs of a pair of limbs being approximately 50% out of phase with each other (Hildebrand, 1966, 1967). Symmetrical gaits can be further divided into two types: diagonal-sequence gaits, in which a hindlimb footfall is followed by that of the contralateral forelimb, and lateral-sequence gaits, in which a hindlimb footfall is followed by that of the ipsilateral forelimb (Hildebrand, 1967; Shapiro and Raichlen, 2005; Cartmill et al., 2007b). In contrast, asymmetrical gaits are characterized by unevenly spaced footfalls within a girdle, with the right and left limbs moving in near synchrony (Hildebrand, 1977).” Now found in lines 87-94.
We corrected the sentence such as “Symmetrical gaits are also common in rodents, scandentians, etc..” Now found in line 107.
Thank you for pointing this out. We indeed did not use the right term to mention related asymmetrical gaits with increased duty factors. We removed the term « ambling » and the associated reference here. Now found in line 256.
(2) Correlations are used in the paper to examine how brain mass scales with body mass. It is correct to assume that a correlation significantly different from 0 is indicative of allometry (in this case, positive). That said, lines are used in Figure S2 that go through the bivariate scatter plot. The vast majority of scaling studies rely on regression techniques to calculate and compare slopes, which are different statistically from correlations. In this case, a slope not significantly different from 1.0 would support the hypothesis of isometry based on geometric similarity (as brain mass and body mass are two volumes). The authors could refer to the work of Bob Martin and the 1985 edited book by Jungers and contributions therein. These studies should also be cited in the paper.
Thank you for recommending us this better suited method. We replaced the correlations with major axis orthogonal regressions, as recommended by Martin and Barbour 1989. We found a positive slope for all species significantly different from 1 (0.36), indicating a negative allometry (we realized we were mistaken about the allometry terminology, initially reporting a “positive allometry” instead of a positive correlation).
We corrected in the manuscript in the Results and Methods sections, and cited Martin and Barbour 1989 such as:
“To ensure that the EQs of the different species studied are comparable and meaningful, we tested the allometry between the brain and body masses in our dataset following [84] and found a significant and positive slope for all species (major axis orthogonal regression on log transformed values: slope = 0.36, r<sup>2</sup> = 0.92, p = 5.0.10<sup>-12</sup>), indicating a negative allometry (r = 0.97, df = 19, p = 2.0.10<sup>-13</sup>), and similar allometric coefficients when restricting the analysis to phylogenetic groups (Fig. S2).” Now found in lines 289-298.
- “To control that brain allometry is homogeneous among all phylogenetic groups, to be able to compare EQ between species, we computed major axis orthogonal regressions, following the recommendation of Martin and Barbour [84], between the Log transformed brain and body masses, over all species and by phylogenetic group using the sma package in R (Fig. S2).” Now found in lines 336-338.
We also changed Figure S2 in Supplementary Information accordingly.
(3) Trunk length is used as the denominator for many of the indices used in the study. In this way, trunk length is considered to be a proxy for body size. There should be a demonstration that trunk length scales isometrically with body mass in all of the mammals compared. If not the case, some of the indices may not be directly comparable.
We did not use trunk length as a proxy for body mass, but to compute geometric body proportions in order to test whether intrinsic body proportions could be related to vertical descent behaviors, namely the length of the tail and of the fore- and hindlimbs relative to the animal. We chose those indices to quantify the capability of limbs to act as levers or counterweights to rotate the animals for this specific question of vertical descent behavior. We therefore do not think that body mass allometry with respect to trunk length is relevant to compare these indices across species here. Also, we don’t expect that trunk length (which is a single dimension) would scale isometrically with body mass, which scales more as a volume.
(4) Given the numerous comparisons done in this study, a Bonferroni correction method should be considered to mitigate type I error (accepting a false positive).
We had already corrected all our statistical tests using the Benjamini-Hochberg method to control for false positives; see the SuppTables Excel file for the complete results of the statistical analyses. We chose this method over the Bonferroni correction because the more modern and balanced Benjamini-Hochberg procedure is better suited for analyses involving a large number of hypotheses.
(5) The terms "arm" and "leg" used in the main text and Table 1 are anatomically incorrect. Instead, the terms "forelimb" and hindlimb" should be used as they include the length sum of the stylopod, zeugopod, and autopod.
Indeed, thank you for pointing that out. We have corrected this error within the manuscript as well as in the figures 4 and S3.
(6) On p. 14, the authors make the statement that the postcranial anatomy of Adapis and Notharctus remains undescribed. The authors should consult the work of Dagosto, Covert, Godinot and others.
We did not state that the postcranial remains of Adapis and Notharctus have not been described. However, we were unfortunately unable to find published illustrations of the known postcranial elements that could be reliably used in this study. To avoid any misunderstanding, we removed the sentence such as: “However, we could not find suitable illustrations of the known postcranial elements of these species in the literature that could be reliably incorporated into this study. Thus, we only included their reconstructed body mass and EQ,..”. Now found in lines 393-397.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Line 65/69 - Perchalski et al. 2021 is a single-author publication, so no et al. or w/ colleagues.
Indeed. This has been corrected in the manuscript, now found in lines 65 and 70.
(2) Lines 96-98 - Is it appropriate to say that the use of symmetrical gaits are examples of convergent evolution? There's less burden of evidence to state that these are shared behaviors, rather than suggesting they independently evolved across all those groups.
We agree with this and corrected the sentence such as “Symmetrical gaits are also common in rodents, scandentians, etc..” Now found in line 107.
(3) Line 198 - I am confused by how to interpret (-16,36 %) compared to how other numbers are presented in the rest of the paragraph.
To avoid confusion, we rephrased this sentence such as: “In contrast, primates did not significantly reduce their speed compared to ascents when descending sideways or tail-first (Fig. 2A, SuppTables B).” Now found in lines 207-209.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This study investigates how Rhino, a chromatin-associated HP1-family protein essential for germline piRNA biogenesis in Drosophila, is initially recruited to specific genomic loci. Although canonical dual-strand piRNA clusters such as 42AB, 38C, 80F, and 102F produce the majority of germline piRNAs, the mechanisms guiding Rhino to these regions remain poorly understood. To explore the earliest steps of Rhino loading, the authors use a doxycycline-inducible Rhino transgene in OSC cells, a system that expresses only the primary Piwi pathway and therefore provides an experimentally accessible, epigenetically naïve context distinct from the endogenous germline environment. Through a combination of inducible Rhino expression, knockdown of selected Drosophila PRMTs (DARTs), ChIP-seq, small RNA sequencing, and imaging, the authors propose that asymmetric arginine-methylated histones, particularly those deposited by DART4, contribute to defining initial sites of Rhino association. They identify a subset of Rhino-bound loci, termed DART4-dependent piRNA source loci (piSL), which lose Rhino, Kipferl, and piRNA production upon DART4 depletion and may represent nascent or transitional piRNA clusters. Overall, the study provides intriguing evidence for a link between ADMA histone marks and de novo Rhino recruitment, particularly in the simplified OSC context, and offers new candidate loci for further exploration of early piRNA-cluster chromatin dynamics.
Strengths:
This study offers important insights into how asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) histone marks contribute to the initial recruitment of Rhino, a Drosophila HP1-family protein essential for dual-strand piRNA cluster specification. Using an integrative approach that includes ectopic expression of a Rhino transgene in OSC cells, germline knockdown of DART4 in Drosophila ovaries, ChIP-seq, small RNA-seq, and imaging, the authors show that ADMA marks particularly H3R17me2a and H4R3me2acorrelate with Rhino binding at the boundaries of canonical piRNA clusters and at DART4-dependent piRNA source loci (piSL). These piSL may represent nascent or transitional piRNA-generating regions. Overall, the dataset presented here provides a valuable resource for understanding the chromatin features associated with the emergence and maturation of piRNA clusters.
Weaknesses:
Despite the strengths of the study, several important limitations remain. Although Rhino binding correlates with ADMA-enriched boundaries, the data do not directly demonstrate that these histone marks are required for Rhino spreading, leaving the mechanistic relationship correlative rather than causal. The DART4-dependent piRNA source loci identified here produce only low levels of piRNAs, and their functional contribution remains uncertain. In addition, redundancy among DART family methyltransferases remains unresolved: only DART4 was tested in the germline, and effective knockdown of DART1 or other DARTs could not be achieved, limiting the ability to evaluate whether ADMA-histones more broadly regulate Rhino recruitment at canonical clusters. Consequently, the current dataset primarily supports DART4-dependent effects at a small subset of evolutionarily young loci, and both the model and the title may overstate the generality of this mechanism across the full repertoire of dual-strand piRNA clusters.
In conclusion, this study is carefully executed and puts forward compelling hypotheses regarding the early chromatin environment that may underlie piRNA cluster formation. The findings will be relevant to researchers interested in genome regulation, small RNA biology, and chromatin-mediated transposon control.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1(Public review):
Summary:
In this study, the authors aim to understand how Rhino, a chromatin protein essential for small RNA production in fruit flies, is initially recruited to specific regions of the genome. They propose that asymmetric arginine methylation of histones, particularly mediated by the enzyme DART4, plays a key role in defining the first genomic sites of Rhino localization. Using a combination of inducible expression systems, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and genetic knockdowns, the authors identify a new class of Rhinobound loci, termed DART4 clusters, that may represent nascent or transitional piRNA clusters.
Strengths:
One of the main strengths of this work lies in its comprehensive use of genomic data to reveal a correlation between ADMA histones and Rhino enrichment at the border of known piRNA clusters. The use of both cultured cells and ovaries adds robustness to this observation. The knockdown of DART4 supports a role for H3R17me2a in shaping Rhino binding at a subset of genomic regions.
Weaknesses:
However, Rhino binding at, and piRNA production from, canonical piRNA clusters appears largely unaffected by DART4 depletion, and spreading of Rhino from ADMArich boundaries was not directly demonstrated. Therefore, while the correlation is clearly documented, further investigation would be needed to determine the functional requirement of these histone marks in piRNA cluster specification.
The study identify piRNA cluster-like regions called DART4 clusters. While the model proposes that DART4 clusters represent evolutionary precursors of mature piRNA clusters, the functional output of these clusters remains limited. Additional experiments could help clarify whether low-level piRNA production from these loci is sufficient to guide Piwi-dependent silencing.
In summary, the authors present a well-executed study that raises intriguing hypotheses about the early chromatin context of piRNA cluster formation. The work will be of interest to researchers studying genome regulation, small RNA pathways, and the chromatin mechanisms of transposon control. It provides useful resources and new candidate loci for follow-up studies, while also highlighting the need for further functional validation to fully support the proposed model.
We sincerely thank Reviewer #1 for the thoughtful and constructive summary of our work. We appreciate the reviewer’s recognition that our study provides a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between ADMA-histones and Rhino localization, and that it raises intriguing hypotheses about the early chromatin context of piRNA cluster formation.
We fully agree with the reviewer that our data primarily demonstrate correlation between ADMA-histones and Rhino localization, rather than direct causation. In response, we have carefully revised the text throughout the manuscript to avoid overstatements implying causality (details provided below).
We also acknowledge the reviewer’s important point that the functional requirement of ADMA-histones for piRNA clusters specification remains to be further established. We have now added the discussion about our experimental limitations (page 18).
Overall, we have revised the manuscript to present our findings more cautiously and transparently, emphasizing that our data reveal a correlation between ADMA-histone marks and the initial localization of Rhino, rather than proving a direct mechanistic requirement. We thank the reviewer again for highlighting these important distinctions.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
This study seeks to understand how the Rhino factor knows how to localize to specific transposon loci and to specific piRNA clusters to direct the correct formation of specialized heterochromatin that promotes piRNA biogenesis in the fly germline. In particular, these dual-strand piRNA clusters with names like 42AB, 38C, 80F, and 102F generate the bulk of ovarian piRNAs in the nurse cells of the fly ovary, but the evolutionary significance of these dual-strand piRNA clusters remains mysterious since triple null mutants of these dual-strand piRNA clusters still allows fly ovaries to develop and remain fertile. Nevertheless, mutants of Rhino and its interactors Deadlock, Cutoff, Kipferl and Moonshiner, etc, causes more piRNA loss beyond these dual-strand clusters and exhibit the phenotype of major female infertility, so the impact of proper assembly of Rhino, the RDC, Kipferl etc onto proper piRNA chromatin is an important and interesting biological question that is not fully understood.
This study tries to first test ectopic expression of Rhino via engineering a Dox-inducible Rhino transgene in the OSC line that only expresses the primary Piwi pathway that reflects the natural single pathway expression the follicle cells and is quite distinct from the nurse cell germline piRNA pathway that is promoted by Rhino, Moonshiner, etc. The authors present some compelling evidence that this ectopic Rhino expression in OSCs may reveal how Rhino can initiate de novo binding via ADMA histone marks, a feat that would be much more challenging to demonstrate in the germline where this epigenetic naïve state cannot be modeled since germ cell collapse would likely ensue. In the OSC, the authors have tested the knockdown of four of the 11 known Drosophila PRMTs (DARTs), and comparing to ectopic Rhino foci that they observe in HP1a knockdown (KD), they conclude DART1 and DART4 are the prime factors to study further in looking for disruption of ADMA histone marks. The authors also test KD of DART8 and CG17726 in OSCs, but in the fly, the authors only test Germ Line KD of DART4 only, they do not explain why these other DARTs are not tested in GLKD, the UAS-RNAi resources in Drosophila strain repositories should be very complete and have reagents for these knockdowns to be accessible.
The authors only characterize some particular ADMA marks of H3R17me2a as showing strong decrease after DART4 GLKD, and then they see some small subset of piRNA clusters go down in piRNA production as shown in Figure 6B and Figure 6F and Supplementary Figure 7. This small subset of DART4-dependent piRNA clusters does lose Rhino and Kipferl recruitment, which is an interesting result.
However, the biggest issue with this study is the mystery that the set of the most prominent dual-strand piRNA clusters. 42AB, 38C, 80F, and 102F, are the prime genomic loci subjected to Rhino regulation, and they do not show any change in piRNA production in the GLKD of DART4. The authors bury this surprising negative result in Supplementary Figure 5E, but this is also evident in no decrease (actually an n.s. increase) in Rhino association in Figure 5D. Since these main piRNA clusters involve the RDC, Kipferl, Moonshiner, etc, and it does not change in ADMA status and piRNA loss after DART4 GLKD, this poses a problem with the model in Figure 7C. In this study, there is only a GLKD of DART4 and no GLKD of the other DARTs in fly ovaries.
One way the authors rationalize this peculiar exception is the argument that DART4 is only acting on evolutionarily "young" piRNA clusters like the bx, CG14629, and CG31612, but the lack of any change on the majority of other piRNA clusters in Figure 6F leaves upon the unsatisfying concern that there is much functional redundancy remaining with other DARTs not being tested by GLKD in the fly that would have a bigger impact on the other main dual-strand piRNA clusters being regulated by Rhino and ADMA-histone marks.
Also, the current data does not provide convincing enough support for the model Figure 7C and the paper title of ADMA-histones being the key determinant in the fly ovary for Rhino recognition of the dual-strand piRNA clusters. Although much of this study's data is well constructed and presented, there remains a large gap that no other DARTs were tested in GLKD that would show a big loss of piRNAs from the main dual-strand piRNA clusters of 42AB, 38C, 80F, and 102F, where Rhino has prominent spreading in these regions.
As the manuscript currently stands, I do not think the authors present enough data to conclude that "ADMA-histones [As a Major new histone mark class] does play a crucial role in the initial recognition of dual-strand piRNA cluster regions by Rhino" because the data here mainly just show a small subset of evolutionarily young piRNA clusters have a strong effect from GLKD of DART4. The authors could extensively revise the study to be much more specific in the title and conclusion that they have uncovered this very unique niche of a small subset of DART4-dependent piRNA clusters, but this niche finding may dampen the impact and significance of this study since other major dual-strand piRNA clusters do not change during DART4 GLKD, and the authors do not show data GLKD of any other DARTs. The niche finding of just a small subset of DART-4-dependent piRNA clusters might make another specialized genetics forum a more appropriate venue.
We are deeply grateful to Reviewer #2 for the detailed and insightful review that carefully situates our study in the broader context of Rhino-mediated piRNA cluster regulation. We appreciate the reviewer’s recognition that our inducible Rhino expression system in OSCs provides a valuable model to explore de novo Rhino recruitment under a simplified chromatin environment.
At the same time, we agree that the current data mainly support a role for DART4 in regulating a subset of evolutionarily young piRNA clusters, and do not demonstrate a requirement for ADMA-histones at the major dual-strand piRNA clusters such as 42AB or 38C. We have therefore revised the title and main conclusions to more accurately reflect the scope of our findings.
We agree with the reviewer that functional redundancy among DARTs may explain why major dual-strand piRNA clusters are unaffected by DART4 GLKD. Indeed, we have tried DART1 GLKD in the germline, which shows collapse of Rhino foci in OSCs.For DART1 GLKD, two approaches were possible:
(1) Crossing the BDSC UAS-RNAi line (ID: 36891) with nos-GAL4.
(2) Crossing the VDRC UAS-RNAi line (ID: 110391) with nos-GAL4 and UAS-Dcr2.
The first approach was not feasible because the UAS-RNAi line always arrived as dead on arrival (DOA) and could not be maintained in our laboratory. The second approach did not yield effective and stable knockdown (as follows).
DART8 and CG17726 did not alter Rhino foci in OSC knockdown experiments; therefore, we did not attempt germline knockdown (GLKD) of these DARTs in the ovary. We agree with the reviewer’s opinion that there are piRNA source loci where Rhino localization depends on DART1, and that simultaneous depletion of multiple DARTs may indeed reveal additional positive results because ADMA-histones such as H3R8me2a may be completely eliminated by the knockdown of multiple DARTs. At the same time, we note that many evolutionarily conserved piRNA clusters show a loss of ADMA accumulation compared with evolutionarily young piRNA clusters, with levels that are comparable to the background input in ChIP-seq reads. Therefore, conserved clusters such as 42AB and 38C may no longer be regulated by ADMA. Even if multiple DARTs function redundantly to regulate ADMA, it may be difficult to disrupt Rhino localization at such conserved piRNA clusters by depletion of DARTs. While disruption of Rhino localization at conserved clusters like 42AB and 38C may be challenging, we cannot exclude the possibility that DART depletion affects Rhino binding at less conserved piRNA clusters, where ADMA modification remains detectable. We added clarifications in the Discussion to acknowledge the potential redundancy with other DARTs and to note that further knockdown experiments in the germline will be necessary to test this model comprehensively (page 18).
We appreciate the reviewer’s critical feedback, which has helped us refine the message and strengthen the interpretative balance of the paper.
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
In multiple places, the link between ADMA histones and Rhino recruitment is presented in terms that imply causality. Please revise these statements to reflect that, in most cases, the evidence supports correlation rather than direct functional necessity. Similarly, statements suggesting that ADMA histones promote Rhino spreading should be revised unless supported by direct evidence.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for the insightful comments. We recognize that these suggestions are crucial for improving the manuscript, and we have revised it accordingly to address the concerns. The specific revisions we made are detailed below.
(1) Page 1, line 14: The original sentence “in establishing the sites” was changed to “may establish the potential sites.”
(2) Page 4, lines 11-12: The original sentence “genomic regions where Rhino binds at the ends and propagates in the areas in a DART4-dependent manner, but not stably anchored” was changed to “genomic regions that have ADMA-histones at their ends and exhibit broad Rhino spreading across their internal regions in a DART4dependent manner”
(3) Page4, lines 12-15: The original sentence “Kipferl is present at the regions but not sufficient to stabilize Rhino-genomic binding after Rhino propagates.” was changed to “In contrast to authentic piRNA clusters, Kipferl was lost together with Rhino upon DART4 depletion in these regions, suggesting that Kipferl by itself is not sufficient to stabilize Rhino binding; rather, their localization depends on DART4.”
(4) Page4, lines17-18: The original sentence “are considered to be primitive clusters” was changed to “might be nascent dual-strand piRNA source loci”.
(5) Page 8, line 7: The original sentence “Involvement of ADMA-histones in the genomic localization of Rhino was implicated.” was changed to “Correlation of ADMA-histones in the genomic localization of Rhino was implicated.”
(6) Page 8, lines 19-21: The original sentence “These results suggest that ADMAhistones, together with H3K9me3, contribute significantly and specifically to the recruitment of Rhino to the ends of dual-strand clusters in OSCs.” was changed to “These results raise the possibility that ADMA-histones, together with H3K9me3, may contribute specifically to the recruitment of Rhino to the ends of dual-strand clusters in OSCs.”
(7) Page 10, lines 11-13: The original sentence “These results suggest that DART1 and DART4 are involved in Rhino recruitment at distinct genomic sites through the decreases in ADMA-histones in each of their KD conditions (H4R3me2a and H3R17me2a, respectively).” was changed to ”These results suggest that DART1 and DART4 could contribute to Rhino recruitment at distinct genomic sites through the decreases in ADMA-histones in each of their KD conditions (H4R3me2a and H3R17me2a, respectively).”
(8) Page 13, line 2: The original sentence “Genomic regions where Rhino spreads in a DART4-dependent manner, but not stably anchored, produce some piRNAs“ was changed to “Genomic regions where Rhino binds broadly in a DART4-dependent manner, but not stably anchored, produce some piRNAs”
(9) Page 13, lines 21-22: The original sentence “These results support the hypothesis that ADMA-histones are involved in the genomic binding of Rhino both before and after Rhino spreading, resulting in stable genome binding.” was changed to “These results raise the possibility that a subset of Rhino localized to genomic regions correlating with ADMA-histones may serve as origins of spreading.”
(10) Page 16, lines 6-8: The original sentence “In this study, we took advantage of cultured OSCs for our analysis and found that chromatin marks (i.e., ADMA-histones) play a crucial role in the loading of Rhino onto the genome.” was changed to “In this study, we took advantage of cultured OSCs for our analysis and found that chromatin marks (i.e., bivalent nucleosomes containing H3K9me3 and ADMA-histones) appear to contribute to the initial loading of Rhino onto the genome.”
(11) Page16, line 12: The original sentence “We propose that the process of piRNA cluster formation begins with the initial loading of Rhino onto bivalent nucleosomes containing H3K9me3 and ADMA-histones (Fig. 7C). In OSCs, the absence of Kipferl and other necessary factors means that Rhino loading into the genome does not proceed to the next step.” was removed.
Major points
(1) Clarify the limited colocalization between Rhino and H3K9me3 in OSCs. The observation that FLAG-Rhino foci show minimal overlap with H3K9me3 in OSCs appears inconsistent with the proposed model by the authors in the discussion, in which Rhino is initially recruited to bivalent nucleosomes bearing both H3K9me3 and ADMA marks. This discrepancy should be addressed.
We thank the reviewer’s insightful comments. Indeed, ChIP-seq shows that Rhino partially overlaps with H3K9me3 (Fig. 1F), but immunofluorescence did not reveal any detectable overlap (Fig. 1A). We interpret this discrepancy as arising from the fact that immunofluorescence primarily visualizes H3K9me3 foci that are localized as broad domains in the genome, such as those at centromeres, pericentromeres, or telomeres (named chromocenters), whereas the sharp and interspersed H3K9me3 signals along chromosome arms are difficult to detect by immunofluorescence. We now have these explanations in the revised text (page 6).
(2) Please indicate whether the FLAG-Rhino used in OSCs has been tested for functionality in vivo-for example, by rescuing Rhino mutant phenotypes. This is particularly relevant given that no spreading is observed with this construct.
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point. We have not directly tested the functionality of FLAG-Rhino construct used in OSCs in living Drosophila fly; i.e., it has not been used to rescue Rhino mutant phenotypes in flies. We acknowledge that FLAGRhino has not previously been expressed in OSCs, and that its localization pattern in OSCs differs from that observed in ovaries, where Rhino is endogenously expressed. However, several lines of evidence suggest that the addition of the N-terminal FLAG tag is unlikely to compromise Rhino function
(1) In previous studies, N-terminally tagged Rhino (e.g., 3xFLAG-V5-Precision-GFPRhino) was expressed in a living Drosophila ovary and was shown to localize properly to piRNA clusters, indicating that the tag does not prevent Rhino from binding its genomic targets (Baumgartner et al., 2022; eLife. Fig. 3 supplement 1G).
(2) In Drosophila S2 cells, FLAG-tagged tandem Rhino chromodomains construct was shown to bind H3K9me3/H3K27me3 bivalent chromatin, demonstrating that the FLAG tag does not impair this fundamental chromatin interaction (Akkouche et al., 2025; Nat Struct Mol Biol. Fig. 4b).
(3) GFP-tagged Rhino has been demonstrated to rescue the transposon derepression phenotype of Rhino mutant flies, further supporting that the addition of tags does not abolish its in vivo function. (Parhad et al., 2017; Dev Cell. Fig.1D).
Therefore, we interpret the partial localization of FLAG-Rhino in OSCs as reflecting the specific chromatin environment and regulatory context of OSCs rather than functional impairment due to the FLAG tag.
(3) Given the low levels of piRNA production and the absence of measurable effects on transposon expression or fertility upon DART4 knockdown, the rationale for classifying these regions as piRNA clusters should be clearly stated. Additional experiments could help clarify whether low-level piRNA production from these loci is sufficient to guide Piwidependent silencing. The authors should also consider and discuss the possibility that some of these differences may reflect background-specific genomic variation rather than DART4-dependent regulation per see.
We thank the reviewer for the insightful comments. As noted, DART4 knockdown did not measurably affect transposon expression or fertility. piRNAs generated from DART4associated clusters associate with Piwi but are insufficient for target repression. Although loss of DART4 largely eliminated piRNAs from these clusters, the cluster-derived transcripts themselves were unchanged. To clarify this point, we now refer to these regions as DART4-dependent piRNA-source loci (DART4 piSLs) in the revised text. We also acknowledge that some observed differences may reflect strain-specific genomic variation and have added this caveat on page 16.
(4) The authors should describe the genomic context of DART4 clusters in more detail. Specifically, it would be helpful to indicate whether these regions overlap with known transposable elements, gene bodies, or intergenic regions, and to report the typical size range of the clusters. Are any of the piRNAs produced from these clusters predicted to target known transcripts?
We thank the reviewer’s insightful comments. The overlap of DART4 piSL with transposable elements, gene bodies, and intergenic regions is shown in the right panel of Supplementary Fig. 6E (denoted as “Rhino reduced regions in DART4 GLKD” in the figure). The typical size range of these clusters is presented in Supplementary Fig. 6G. The annotation of piRNA reads derived from these piSL is shown in the right panel of Supplementary Fig. 6F, indicating that most of them appear to target host genes. The specific genes and transposons matched by the piRNAs produced from DART4 piSL are listed in Supplementary Table 8.
(5) While correlations between Rhino and ADMA histone marks (especially H3R8me2a,H3R17me2a, H4R3me2a) are robust, many ADMA-enriched regions do not recruit Rhino. Please discuss this observation and consider the possible involvement of additional factors.
We thank the reviewer’s insightful comments. As pointed out, not all ADMA-enriched regions recruit Rhino; rather, Rhino is recruited only at sites where ADMAs overlap with H3K9me3. Furthermore, the combination of H3K9me3 and ADMAs alone does not fully account for the specificity of Rhino recruitment, suggesting the involvement of additional co-factors (for example, other ADMA marks such as H3R42me2a, or chromatininteracting proteins). In addition, since histone modifications—including arginine methylation—have the possibility that they are secondary consequences of modifications on other proteins rather than primary regulatory events, it is possible that DART1/4 contribute to Rhino recruitment not only through histone methylation but also via arginine methylation of non-histone chromatin-interacting factors. However, methylation of HP1a does not appear to be involved (Supplementary Fig. 3G). We have added new sentences about these points in the Discussion section (page 18).
(6) The manuscript states that Kipferl is present at DART4 clusters but does not stabilize Rhino binding. Please specify which experimental results support this conclusion and explain.
We apologize for the lack of clarity regarding Kipferl data. Supplementary Fig. 7A and 7B show that Kipferl localizes at major DART4 piSL. This Kipferl localization is lost together with Rhino upon DART4 GLKD, indicating that Rhino localization at DART4 piSL depends on DART4 rather than on Kipferl. From these results, we infer that, unlike at authentic piRNA clusters, Kipferl may not be sufficient to stabilize the association of Rhino with the genome at DART4 piSL. We have added this interpretation on page 14.
Minor points
(1) Figure 1D: Please specify which piRNA clusters are included in the metaplot - all clusters, or only the major producers?
We thank the reviewer for the question. The metaplot was not generated from a predefined list of “all” piRNA clusters or only the “major producers.” Instead, it was constructed from Rhino ChIP–seq peaks (“Rhino domains”) that are ≥1.5 kb in length.These Rhino domains mainly correspond to the subregions within major dual-strand clusters (e.g., 42AB, 38C) as well as additional clusters such as 80F, 102F, and eyeless, among others. We have provided the full list of domains and their corresponding piRNA clusters (with genomic coordinates) in Supplementary Table 9 and added the additional explanation in Fig. 1d legend.
(2) Supplemental Figure 5E is referred to as 5D in the main text.
We corrected the figure citations on pages 11-12: the reference to Supplementary Fig. 5E has been changed to 5D, and the reference to Supplementary Fig. 5F has been changed to 5E.
(3) Supplemental Figure 7C: The color legend does not match the pie chart, which may confuse readers.
We thank the reviewer for the helpful comment. We are afraid we were not entirely sure what specific aspect of the legend was confusing, but to avoid any possible misunderstanding, we revised Supplemental Fig. 7C so that the color boxes in the legend now exactly match the corresponding colors in the pie chart. We hope this modification improves clarity.
(4) Since the manuscript focuses on the roles of DART1 and DART4, including their expression profiles in OSCs and ovaries would help contextualize the observed phenotypes. Please consider adding this information if available.
We thank the reviewer for the suggestion. We have now included a scatter plot comparing RNA-seq expression in OSCs and ovaries (Supplementary Fig. 3H). In these datasets, DART1 is strongly expressed in both tissues, whereas DART4 shows no detectable reads. Notably, ref. 28 reports strong expression of both DART1 and DART4 in ovaries by western blot and northern blot. In our own qPCR analysis in OSCs, DART4 expression is about 3% of DART1, which, although low, may still be sufficient for functional roles such as modification of H3R17me2a (Fig. 3C, Supplementary Fig. 3F and 3I). We have added these new data and additional explanation in the revised manuscript (page 11).
(5) Several of the genome browser snapshots, particularly scale and genome coordinates, are difficult to read.
We apologize for the difficulty in reading several of the genome browser snapshots in the original submission. We have re-generated the relevant figures using IGV, which provides clearer visualization of scale and genome coordinates. The previous images have been replaced with the improved versions in the revised manuscript.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) The authors need to elaborate on what this sentence means, as it is very unclear what they are describing about Rhino residency: "The results show that Rhino in OSCs tends to reside in the genome where Rhino binds locally in the ovary (Fig. 1C)."
We apologize for the lack of clarity in the original sentence. The text has been revised as follows:
”Rhino expressed in OSCs bound predominantly to genomic sites exhibiting sharp and interspersed Rhino localization patterns in the ovary, while showing little localization within broad Rhino domains, including major piRNA clusters.”
In addition, to clarify the behavior of Rhino at broad domains, we have added the phrase “the terminal regions of broad domains, such as major piRNA clusters” to the subsequent sentence.
(2) The red correlation line is very confusing in Figure 5F. What sort of line does this mean in this scatter plot?
We apologize for the lack of clarity regarding the red line in Fig. 5F. The red line represents the least-squares linear regression fit to the data points, calculated using the lm() function in R, and was added with abline() to illustrate the correlation between ctrl GLKD and DART4 GLKD values. In the revised figure, we have clarified this in the legend by specifying that it is a regression line.
(3) There is no confirmation of the successful knockdown of the various DARTs in the OSCs.
We thank the reviewer for the comment. The knockdown efficiency of the various DARTs in OSCs was confirmed by RT–qPCR. The data are now shown in Supplementary Fig. 3J.
(4) What is the purpose of an unnumbered "Method Figure" in the supplementary data file? Why not just give it a number and mention it properly in the text?
We thank the reviewer for the suggestion. We have now assigned a number to the previously unnumbered "Method Figure" and have included it as Supplementary Fig. 9.
The figure is now properly cited in the Methods section.
(5) For Figure 5A, those fly strain numbers in the labels are better reserved in the Methods, and a more appropriate label is to describe the GAL4 driver and the UAS-RNAi construct by their conventional names.
We thank the reviewer for the suggestion. The labels in Fig. 5A have been updated to use the conventional names of the GAL4 drivers and UAS-RNAi constructs. Specifically, they now read Ctrl GLKD (nos-GAL4 > UAS-emp) and DART4 GLKD (nos-GAL4 > UASDART4). The original fly strain numbers are listed in the Methods section.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
In this paper, authors used MEFs expressing the R1441G mutant of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), a mutant associated with the early onset of Parkinson's disease. They report that in these cells LAMP2 fluorescence is higher but BMP fluorescence is lower, MVE size is reduced and that MVEs contain less ILVs. They also report that LAMP2-positive EVs are increased in mutant cells in a process sensitive to LRRK2 kinase inhibition but are further increased by glucocerebrosidase (GCase) inhibition, and that total di-22:6-BMP and total di-18:1-BMP are increased in mutant LRRK2 MEFs compared to WT cells by mass spectrometry. They also report that LRRK2 kinase inhibition partially restores cellular BMP levels, and that GCase inhibition further increased BMP levels, and that in EVs from the LRRK2 mutant, LRRK2 inhibition decreases BMP while GCase inhibition has the opposite effect. Moreover, they report that BMP increase is not due to increased BMP synthesis, although authors observe that CLN5 is increased in LRRK2 mutant cells. Finally, they report that GW4869 decreases EV release and exosomal BMP, while bafilomycin A1 increases EV release. They conclude that LRRK2 regulates BMP levels (in cells) and release (via EVs). They also conclude that the process is modulated by GCase in LRRK2 mutant cells, and that these studies may contribute to the use of BMP-positive EVs as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease and associated treatments.
Strengths:
This is a potentially interesting paper,. However, I had comments that authors needed to address to clarify some aspects of their study.
Weaknesses:
(1) The authors seem to have missed the point in their reply to my first comment. They mention the paper by Stuffers et al., who reports that endosome biogenesis continues without ESCRT. This is a nice paper, but it is irrelevant to the subject at hand. In my initial comment, I drew the author's attention to an apparent contradiction: higher LAMP2 staining in R1441G LRRK2 knock-in MEFs and yet smaller MVEs with a reduced surface area. LAMP2 being one of the major glycoproteins of MVE's limiting membrane, one would have expected lower LAMP2 staining if cells contain fewer and smaller MVEs. Authors now state that elevated LAMP2 expression in cells expressing R1441G reflects a cell type-specific effect (differential penetrance of LRRK2 signaling on lysosomal biogenesis), because amounts of LAMP1 and CD63 are similar in cells from LRRK2 G2019S PD patients and control cells (new Fig 7A-F). However, authors still conclude that LRRK2 modulates the lysosomal network, including LAMP2 and CLN5. Does it?
Similarly, the mass spec analysis of BMP (Fig S1H) does not support the data in Fig 1. Does this Table include all major isoforms found in these cells? If so, the dominant isoform is by far the di-18:1 isoform in wt and R1441G cells (at least 10X more abundant than other isoforms). Now, di-18:1-BMP is roughly 4X more abundant in R1441G cells when compared to wt cells, while BMP is reduced by half in R1441G cells (light microscopy in Fig 1). Authors argue that light microscopy may only detects a so-called antibody accessible pool. What is this? And why would this pool decrease in R1441G cells when LAMP2 is higher? Alternatively, they argue that the anti-BMP antibody may be less specific and detect other analytes. As I had already mentioned, this makes no sense, since the observed signal is lower and not higher. If authors do not trust their light microscopy analysis, why show the data?
(2) Cells contain 3 LAMP2 isoforms. Which one is upregulated and/or secreted in exosomes?
(3) The new Fig S4A is far from convincing. How were cells fractionated and what are the gradients (not described in Methods)? CD63 (presumably endolysosomes) is spread over fractions 8 - 13. LRRK2 (fractions 8-9) does not copurify with CD63. The bulk of LRRK2 is at the bottom (presumably cytosol if this is a floatation gradient), and a minor fraction moves into the gradient. CLN5 is even less clear since the bulk is also at the bottom with a tiny fraction only between LRRK2 and CD63. Also, why do authors conclude that a considerable pool of newly synthesized CLN5 did not reach its final destination at the endolysosome and may instead be retained in the ER? Where is the ER on the gradient?
(4) Fig S4B shows blots of whole cell lysates from CTRL and LRRK2 mutant-derived fibroblasts: 6 lanes are shown but without captions, containing varying amounts of calnexin and CD63. In addition, the blots look very dirty. Where is CD63? Is it the minor band at ≈37 kD (as in Fig S4A)? Or the major band below the 50kD marker? What are the other bands on these blots? As a result, the quantification shown in the bar graph does not mean much.
(5) The cell content of 18.1-BMP is increased approx. 5X by BafA1 (Fig 6C) but amounts of 18.1-BMP secreted in EVs hardly changes (Fig 6E). Since BMP is mostly present as 18.1 isoform (22:6-BMP being only a minor species, Fig S1H), does it mean that BafA1 does not increase BMP secretion and/or only a minor fraction of total cellular BMP is secreted in exosomes?
Comments on revisions:
How come 0.2 mmol/L of 22:6 and 18:1 fatty acid both correspond to 65 µg/mL (Fig 4A)?
It is stated in the Legend of Fig4 that long (B-C) and short (D) chase time points are shown as fold change. There is no panel D in the figure.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
eLife Assessment
This useful study presents the potentially interesting concept that LRRK2 regulates cellular BMP levels and their release via extracellular vesicles, with GCase activity further modulating this process in mutant LRRK2-expressing cells. However, the evidence supporting the conclusions remains incomplete, and certain statistical analyses are inadequate. This work would be of interest to cell biologists working on Parkinson's disease.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Even though mutations in LRRK2 and GBA1 (which encodes the protein GCase) increase the risk of developing Parkinson's disease (PD), the specific mechanisms driving neurodegeneration remain unclear. Given their known roles in lysosomal function, the authors investigate how LRRK2 and GCase activity influence the exocytosis of the lysosomal lipid BMP via extracellular vesicles (EVs). They use fibroblasts carrying the PDassociated LRRK2-R1441G mutation and pharmacologically modulate LRRK2 and GCase activity.
Strengths:
The authors examine both proteins at endogenous levels, using MEFs instead of cancer cells. The study's scope is potentially interesting and could yield relevant insights into PD disease mechanisms.
Weaknesses:
Many of the authors' conclusions are overstated and not sufficiently supported by the data. Several statistical errors undermine their claims. Pharmacological treatment is very long, leading to potential off-target effects. Additionally, the authors should be more rigorous when using EV markers.
We thank the reviewer for these valuable observations. In the revised manuscript, we have addressed each of these points as follows:
(1) Conclusions and data support – We carefully revised our text throughout the manuscript to ensure that all conclusions are better supported by the presented data. For instance, we now explicitly state that while pharmacological modulation supports the regulatory role of LRRK2 activity in EV-mediated BMP release, we have softened our conclusions concerning the contribution of GCase in this model (see revised Results and Discussion sections).
(2) Statistical analyses – We reanalyzed experiments involving more than two groups and replaced simple t-tests with non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis tests followed by Dunn’s post hoc comparisons. This approach, described in the updated figure legends (e.g., Figure 2D-F and H-J), provides a more rigorous statistical framework that accounts for small sample sizes and variability typical of EV quantifications.
(3) Pharmacological treatment duration – Prolonged MLi-2 treatments have been extensively used in the field without evidence of significant off-target effects. Several studies, including Fell et al. (2015, J Pharmacol Exp Ther 355:397-409), De Wit et al. (2019, Mol Neurobiol 56:5273-5286), Ho et al. (2022, NPJ Parkinson’s Dis 8:115),Tengberg et al. (2024, Neurobiol Dis 202:106728), and Jaimon et al. (2025, Sci Signal 18:eads5761), have applied long-term (24-48 h) MLi-2 treatments at comparable concentrations without detecting toxicity or off-target alterations, including in MEFs (Ho et al., 2022; Dhekne et al., 2018, eLife 7:e40202). In our study, 48-hour incubations were necessary to sustain full LRRK2 inhibition throughout the extracellular vesicle (EV) collection period. EV biogenesis, BMP biosynthesis, and packaging into EVs are timedependent processes; therefore, extended incubation and collection periods (48 h) were required to allow downstream effects of LRRK2 inhibition on BMP production and release to manifest, and to obtain sufficient EV material for biochemical and lipidomic analyses. This experimental design also reflects our and others’ previous observations in humans and non-human primates, where urinary BMP changes are associated with chronic or subchronic LRRK2 inhibitor treatment (Baptista MAS, Merchant K, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2020, 12:eaav0820; Jennings D, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2022, 14:eabj2658; Maloney MT, et al. Mol Neurodegener. 2025, 20:89). Importantly, under these conditions, we did not observe significant changes in cell viability or morphology, supporting that the treatment was well tolerated. We have clarified this rationale in the revised Methods section to emphasize that the prolonged incubation reflects the experimental design for EV isolation rather than a requirement for achieving LRRK2 inhibition.
(4) EV markers – We and others have reported enrichment of Flotillin-1 and LAMP proteins in isolated small EV fractions (Kowal et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2018; Mathieu et al., 2021; Ferreira et al., 2022). Moreover, LAMP proteins have been reported to be more enriched in EVs of endolysosomal origin (Mathieu et al., 2021). To further strengthen this point, we performed new experiments using a CD63-pHluorin sensor combined with TIRF microscopy, which allowed real-time visualization of CD63-positive exosome release. These new data (now presented in Figure 7, Panels G-I; Videos 1 and 2) confirm increased CD63-positive EV release in LRRK2 mutant fibroblasts, which was reversed by LRRK2 inhibition with MLi-2. The CD63-positive compartment was also largely BMPpositive (new Figure 7D, F, G), reinforcing our conclusions and providing additional rigor in EV marker validation.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
In this paper, the authors used MEFs expressing the R1441G mutant of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), a mutant associated with the early onset of Parkinson's disease. They report that in these cells LAMP2 fluorescence is higher but BMP fluorescence is lower, MVE size is reduced, and that MVEs contain less ILVs. They also report that LAMP2-positive EVs are increased in mutant cells in a process sensitive to LRRK2 kinase inhibition but are further increased by glucocerebrosidase (GCase) inhibition, and that total di-22:6-BMP and total di-18:1-BMP are increased in mutant LRRK2 MEFs compared to WT cells by mass spectrometry. They also report that LRRK2 kinase inhibition partially restores cellular BMP levels, and that GCase inhibition further increases BMP levels, and that in EVs from the LRRK2 mutant, LRRK2 inhibition decreases BMP while GCase inhibition has the opposite effect. Moreover, they report that the BMP increase is not due to increased BMP synthesis, although the authors observe that CLN5 is increased in LRRK2 mutant cells. Finally, they report that GW4869 decreases EV release and exosomal BMP, while bafilomycin A1 increases EV release. They conclude that LRRK2 regulates BMP levels (in cells) and release (via EVs). They also conclude that the process is modulated by GCase in LRRK2 mutant cells, and that these studies may contribute to the use of BMP-positive EVs as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease and associated treatments.
Strengths:
This is an interesting paper, which provides novel insights into the biogenesis of exosomes with exciting biomedical potential. However, I have comments that authors need to address to clarify some aspects of their study.
Weaknesses:
(1) The intensity of LAMP2 staining is increased significantly in cells expressing the R1441G mutant of LRRK2 when compared to WT cells (Figure 1C). Yet mutant cells contain significantly smaller MVEs with fewer ILVs, and the MVE surface area is reduced (Figure 1D-F). This is quite surprising since LAMP2 is a major component of the limiting membrane of late endosomes. Are other proteins of endo-lysosomes (eg, LAMP1, CD63, RAB7) or markers (lysotracker) also decreased (see also below)?
As referenced in our original manuscript, several previous studies have reported endolysosomal morphological and homeostatic defects in cells harboring pathogenic LRRK2 mutations. LAMP2 can be upregulated as part of a lysosomal biogenesis or stress response (e.g., via MiT/TFE transcription factors such as TFEB; Sardiello et al., Science 2009, 325:473-477), whereas ILV biogenesis is primarily controlled by ESCRT- and SMPD3-dependent pathways that are regulated independently of MiT/TFE-driven transcriptional programs. Indeed, Stuffers et al. (Traffic 2009, 10:925-937) demonstrated that depletion of key ESCRT subunits markedly inhibited ILV formation while concomitantly increasing LAMP2 expression, highlighting the mechanistic dissociation between LAMP2 abundance and ILV number. In our study, we observed a similar pattern in R1441G LRRK2 MEFs, in which elevated LAMP2 staining and protein levels occurred despite a reduction in MVE size and ILV number. We interpret this as a compensatory lysosomal biogenesis response.
Our revised manuscript now includes new immunofluorescence data for BMP, LAMP1 and CD63 (New Figure 7, Panels A-F) together with biochemical analysis of CD63 protein levels (New Supplemental Figure 4, Panel B) in human skin fibroblasts derived from healthy donors and LRRK2 G2019S PD patients. Quantitative analysis of these experiments revealed no statistically significant differences in total cellular levels of either LAMP1 or CD63 between groups. However, we observed a consistent decrease in BMP immunostaining intensity (New Figure 7, Panel A and B), in agreement with our findings in mouse fibroblasts. We therefore propose that the elevated LAMP2 expression observed in the engineered MEF clone expressing R1441G may reflect a cell type-specific effect, potentially linked to differential penetrance of LRRK2 signaling on the lysosomal biogenesis response. We have updated the Results and Discussion section of the manuscript to incorporate and clarify these findings.
(2) LRRK2 has been reported to interact with endolysosomal membranes. Does the R1441G mutant bind LAMP2- and/or BMP-positive membranes?
We agree that LRRK2 has been reported to associate dynamically with endolysosomal membranes, particularly under conditions of endolysosomal stress or damage (Eguchi T, et al. PNAS 2018, 115:E9115-E9124; Bonet-Ponce L, et al. Sci Adv. 2020, 6:eabb2454; Wang X, et al. Elife. 2023, 12:e87255).
Nevertheless, to explore whether LRRK2 associates with BMP-positive endolysosomes, we performed subcellular fractionation followed by biochemical analysis of endolysosomal fractions, since our available LRRK2 antibodies did not provide reliable immunofluorescence signals. These experiments were carried out using human skin fibroblasts derived from both healthy controls and Parkinson’s disease patients carrying the LRRK2-G2019S mutation. In both control and mutant fibroblasts, a pool of LRRK2 was detected in fractions positive for the BMP synthase CLN5 and the endolysosomal marker CD63 (New Supplementary Figure 4, Panel A), supporting the localization of LRRK2 to endolysosomal membranes that are likely BMP-enriched. Our manuscript’s Results and Methods sections have been updated accordingly.
Does the mutant affect endolysosomes?
As referenced in our original manuscript, several studies have reported that pathogenic LRRK2 mutations can lead to endolysosomal defects. Consistent with these reports, we also observed morphological alterations in endolysosomes of cells expressing mutant LRRK2, including reduced MVE size and fewer ILVs, as shown in Figure 1D–F. These observations are in agreement with previously described phenotypes associated with pathogenic LRRK2 variants. Furthermore, in mutant LRRK2 MEFs, and now in humanderived fibroblasts (see new Figure 7, Panel A and B), we observed a decrease in BMP immunostaining signal.
(3) Immunofluorescence data indicate that BMP is decreased in mutant LRRK2expressing cells compared to WT (Figure 1A-B), but mass spec data indicate that di-22:6BMP and di-18:1-BMP are increased (Figure 3). Authors conclude that the BMP pool detected by mass spec in mutant cells is less antibody-accessible than that present in wt cells, or that the anti-BMP antibody is less specific and that it detects other analytes. This is an awkward conclusion, since the IF signal with the antibody is lower (not higher): why would the antibody be less specific? Could it be that the antibody does not see all BMP isoforms equally well? Moreover, the observations that mutant cells contain smaller MVEs (Figure 1D-F) with fewer ILVs are consistent with the IF data and reduced BMP amounts. This needs to be clarified.
As previously reported by us (Lu et al., J Cell Biol 2022;221:e202105060) and others (Berg AL, et al. Cancer Lett. 2023, 557:216090), discrepancies can occur between BMP levels detected by immunofluorescence and those quantified by mass spectrometry. This is because immunostaining reflects the pool of antibody-accessible BMP, whereas lipidomics measures the total cellular content of all BMP molecular species, irrespective of their distribution or accessibility.
We agree that the anti-BMP antibody may not detect all BMP isoforms equally well. Differences in acyl chain composition (such as the degree of saturation or chain length) can alter the stereochemistry of BMP and, consequently, epitope accessibility to antibody binding.
In addition, in a personal communication with Monther Abu-Remaileh (Stanford University), we were informed that the antibody may also cross-react with other lipid species in endolysosomes. Nevertheless, since there is no formal evidence supporting this, we have removed the sentence in the Discussion section stating “Alternatively, the antibody may also detect non-BMP analytes” to avoid any potential misinterpretations. In its place, we have added a short statement noting that “not all BMP isoforms may be detected equally well”.
Mass spectrometry data are only shown for two BMP species (di-22:6, di-18:1). What are the major BMP isoforms in WT cells? The authors should show the complete analysis for all BMP species if they wish to draw quantitative conclusions about the amounts of BMP in wt and mutant cells. Finally, BMP and PG are isobaric lipids. Fragmentation of BMPs or PGs results in characteristic fingerprints, but the presence of each daughter ion is not absolutely specific for either lipid. This should be clarified, e.g., were BMP and PG separated before mass spec analysis? Was PG affected? The authors should also compare the BMP data with mass spec data obtained with a control lipid, e.g., PC.
Regarding BMP isoforms, our targeted UPLC-MS/MS analyses revealed that 2,2′-di-22:6-BMP (sn2/sn2′) and 2,2′-di-18:1-BMP (sn2/sn2′) are the predominant BMP isoforms in MEF cells, consistent with previous reports showing docosahexaenoyl (22:6; DHA) and oleoyl (18:1) BMP as the most abundant isoforms. Across diverse mammalian cells and tissues, BMP typically exhibits a fatty acid composition dominated by oleoyl, with polyunsaturated fatty acids (particularly DHA) also contributing substantially. Enrichment of DHA-containing BMP species has been observed in multiple systems, including rat uterine stromal cells, PC12 cells, THP-1 and RAW macrophages, as well as in rat and human liver. This consistent presence of oleoyl- and docosahexaenoyl-containing BMP species across tissues indicates that these acyl chains are conserved features influencing the lipid’s structural and functional characteristics (Kobayashi et al. J Biol Chem, 2002; Hullin-Matsuda et al. Prostaglandins Leukotriens Essent Fatty Acids, 2009; Thompson et al. Int J Toxicol. 2012; Delton-Vandenbroucke et al. J Lipid Res, 2019).
Nevertheless, we have included a Table (Panel H in updated Supplemental Figure 1) showing other BMP species that were also detected in our lipidomics analysis. Overall, dioleoyl (18:1)- and di-docosahexaenoyl (22:6)-BMP species were the most abundant in MEF cells, whereas di-arachidonoyl (20:4)- and di-linoleoyl (18:2)-BMP isoforms were present at lower levels. Consistently, R1441G LRRK2 MEFs displayed higher levels of dioleoyl- and di-docosahexaenoyl-BMP compared with WT cells, and these elevations were reduced following LRRK2 kinase inhibition with MLi-2. Data from three independent representative experiments are shown, and the manuscript has been revised accordingly to include these results.
Regarding the separation of BMP and PG species, we confirm that BMP and PG were chromatographically resolved prior to MS/MS detection using a validated UPLC-MS/MS method developed by Nextcea, Inc. PG exhibits a substantially longer LC retention time than BMP, ensuring complete baseline separation. This approach (established by Nextcea nearly two decades ago and later validated through a multi-year collaboration with the U.S. FDA to clinically qualify di-22:6-BMP as a biomarker) prevents any ambiguity arising from the isobaric nature of BMP and PG species. No changes in PG levels were detected under any experimental conditions.
Finally, we employed isotope-labeled BMP as an internal standard to ensure robust normalization across samples. These additional details and references cited above have been included in the revised Methods and References sections to further clarify the analytical rigor of our lipidomics workflow.
(4) It is quite surprising that the amounts of labeled BMP continue to increase for up to 24h after a short 25min pulse with heavy BMP precursors (Figure 4B).
In these isotope-labeling experiments, it is important to note (as described in our original manuscript) that two distinct pools of metabolically labeled BMP species were detected: semi-labeled BMP (with only one heavy isotope-labeled fatty acyl chain) and fully-labeled BMP (with both fatty acyl chains labeled). We consider the fully-labeled BMP pool to provide the most reliable readout for BMP turnover, as it showed a rapid decline after a 1h chase (decreasing by more than 50% within 8 h in all conditions), reaching its lowest levels at the end of the 48-h chase period.
The apparent increase in semi-labeled BMP species over time may be explained by continued incorporation of labeled precursors following the initial pulse. Specifically, once existing semi-labeled and fully-labeled BMP molecules are degraded by PLA2G15 (Nyame K, et al. Nature 2025, 642:474-483), the resulting isotope-labeled lysophosphatidylglycerol (LPG) and fatty acids could be recycled and re-enter a new round of BMP biosynthesis, leading to a gradual accumulation of semi-labeled BMP such as di-18:1-BMP. Why would this reasoning not also apply to the fully-labeled species? Once the pulse is completed, newly incorporated non-labeled fatty acyl chains present in the cellular pool can compete with labeled ones during subsequent rounds of lipid remodeling or synthesis. As a result, the probability of generating semi-labeled BMP molecules becomes higher than that of forming fully-labeled species. Consistent with this, our data show an increase in only semi-labeled BMP species (but not in fully-labeled ones) up to 24 hours after the pulse. We have added a clarification regarding this point in the revised manuscript.
(5) It is argued that upregulation of CLN5 may be due to an overall upregulation of lysosomal enzymes, as LAMP2 levels were also increased (Figure 2A, C, E). Again, this is not consistent with the observed decrease in MVE size and number (Figure 1D-F). As mentioned above, other independent markers of endo-lysosomes should be analyzed (eg, LAMP1, CD63, RAB7), and/or other lysosomal enzymes (e.g. cathepsin. D).
Our revised manuscript now includes new immunofluorescence data for BMP, LAMP1 and CD63 (New Figure 7, Panels A-F) together with biochemical analysis of CD63 protein levels (New Supplemental Figure 4, Panel B) in human skin fibroblasts derived from healthy controls and LRRK2 G2019S PD patients. Quantitative analysis of these experiments revealed no statistically significant differences in total cellular levels of either LAMP1 or CD63 between groups. However, our results consistently show increased CLN5 protein levels in both mouse and human fibroblast cell lines harboring pathogenic LRRK2 mutations. Upregulation of CLN5 may reflect a compensatory effect from loss of BMP via EV exocytosis. As discussed above, the elevated LAMP2 signal observed in the engineered MEF clone expressing R1441G could represent a cell type-specific effect, potentially linked to differential penetrance of LRRK2 signaling on the lysosomal biogenesis response. Our Results and Discussion sections have been updated accordingly.
(6) The authors report that the increase in BMP is not due to an increase in BMP synthesis (Figure 4), although they observe a significant increase in CLN5 (Figure 5A) in LRRK2 mutant cells. Some clarification is needed.
In our original manuscript, we proposed that although CLN5 protein levels are increased in R1441G LRRK2 MEFs, the absence of significant changes in BMP synthesis rates (Figure 4B, C) may reflect either limited substrate availability or that CLN5 is already operating near its maximal enzymatic capacity. Our new subcellular fractionation data (new Figure 7, Panel A) further indicate that, despite a relative increase in total CLN5 levels in G2019S LRRK2 human fibroblasts, the amount of CLN5 associated with endolysosomes remains comparable between mutant LRRK2 and control cells. This suggests that a considerable fraction of upregulated CLN5 may not localize to endolysosomes, potentially accumulating in the endoplasmic reticulum due to enhanced translation or impaired trafficking. Unfortunately, the available anti-CLN5 antibody did not yield reliable immunofluorescence signals, preventing us from directly confirming this possibility. Nevertheless, in light of our new data (new Supplemental Figure 4A), we have included a clarification in the revised manuscript discussing this possibility as well.
(7) Authors observe that both LAMP2 and BMP are decreased in EVs by GW4869 and increased by bafilomycin (Figure 6). Given my comments above on Figure 1, it would also be nice to illustrate/quantify the effects of these compounds on cells by immunofluorescence.
We appreciate the reviewer’s suggestion. We have previously published immunofluorescence data showing increased BMP accumulation in endolysosomes following treatment with bafilomycin A1 Lu A, et al. J Cell Biol. 2009, 184:863-879). However, in the present study, our lipidomics analyses revealed a decrease in both di22:6-BMP and di-18:1-BMP species in cells treated with this compound. As discussed above, this apparent discrepancy likely reflects methodological differences between immunofluorescence, which detects only antibody-accessible BMP pools, and lipidomics, which quantifies total cellular BMP content.
Moreover, in a recent study (Andreu Z, et al. Nanotheranostics 2023, 7:1-21), BMP levels were analyzed by immunofluorescence in cells treated with spiroepoxide, a potent and selective irreversible inhibitor of nSMase (different from GW4869) known to block EV release. Spiroepoxide-treated cells showed decreased BMP immunostaining; a result that, again, does not align with mass spectrometry data revealing increased cellular BMP levels upon GW4869 treatment. Notably, in that study, spiroepoxide was used instead of GW4869 because the intrinsic autofluorescence of GW4869 could potentially interfere with the immunofluorescence BMP signal.
We therefore consider lipidomics measurements to provide a more reliable and quantitative representation of BMP dynamics under these conditions.
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
Major concerns:
(1) 48 h for MLi2 treatment seems too long. LRRK2 kinase activity is inhibited with much shorter incubation times. The longer the incubation, the more likely off-target effects are. The authors should repeat these experiments with 1-2 h of MLi2.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable comment. We acknowledge that MLi-2 is a potent and selective LRRK2 kinase inhibitor that achieves near-complete target engagement within a few hours of treatment. However, prolonged exposure has been widely used in the field without evidence of significant off-target effects. Several studies, including Fell et al. (2015, J Pharmacol Exp Ther 355:397-409), De Wit et al. (2019, Mol Neurobiol 56:5273-5286), Ho et al. (2022, NPJ Parkinson’s Dis 8:115), Tengberg et al. (2024, Neurobiol Dis 202:106728), and Jaimon et al. (2025, Sci Signal 18:eads5761), have employed long-term (24-48 h) MLi-2 treatments at comparable concentrations without detecting toxicity or off-target alterations, including in MEFs (Ho et al., 2022; Dhekne et al., 2018, eLife 7:e40202).
In our study, 48-hour incubations were necessary to sustain full LRRK2 inhibition throughout the extracellular vesicle (EV) collection period. EV biogenesis, BMP biosynthesis, and packaging into EVs are time-dependent processes; therefore, extended incubation and collection periods (48 h) were required to allow downstream effects of LRRK2 inhibition on BMP production and release to manifest, and to obtain sufficient EV material for biochemical and lipidomic analyses. This experimental design also reflects our and others’ previous observations in humans and non-human primates, where urinary BMP changes are associated with chronic or subchronic LRRK2 inhibitor treatment (Baptista MAS, Merchant K, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2020, 12:eaav0820; Jennings D, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2022, 14:eabj2658; Maloney MT, et al. Mol Neurodegener. 2025, 20:89). Importantly, under these conditions, we did not observe significant changes in cell viability or morphology, supporting that the treatment was well tolerated.
We have clarified this rationale in the revised Methods section to emphasize that the prolonged incubation reflects the experimental design for EV isolation rather than a requirement for achieving LRRK2 inhibition.
(2) Is there a reason why the authors don't include CD81, CD63, and Syntenin-1 in their study as an EV marker? Using solely Flotilin-1 does not seem to be enough to justify their claims.
We actually used not only Flotillin-1 but also LAMP2 as EV markers in our study. While both Flotillin-1 and LAMP2 detection on EVs may vary depending on the cell type, we and others have reported enrichment of Flotillin-1 and LAMP proteins in isolated small EV fractions (Kowal et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2018; Mathieu et al., 2021; Ferreira et al., 2022). In particular, one of these studies reported that “LAMP1-positive subpopulations of EVs represent MVB/lysosome-derived exosomes, which also contain syntenin-1.” Therefore, our choice of EV markers (LAMP2 and Flotillin-1) is consistent with those previously and reliably used to characterize small EVs.
Nevertheless, to further address the reviewer’s concern, we performed additional experiments using a CD63-based fluorescence sensor (CD63-pHluorin), which, combined with TIRF microscopy, enables real-time visualization of CD63-positive exosome release. These experiments were conducted in control and LRRK2-mutant fibroblasts, and the data are presented in new Figure 7 (Panels G-I; Videos 1 and 2). We have also included all relevant references and clarified this point in the revised manuscript.
(3) Indeed, to quantify the amount of certain proteins in EVs, the authors should normalize them by CD63 or CD81.
Protein normalization in isolated EV fractions is indeed challenging. Although tetraspanins such as CD63 and CD81 are commonly enriched in EVs, their abundance can vary considerably across EV subpopulations, cell types, and experimental conditions, making them unreliable as universal normalization markers (Théry et al., J Extracell Vesicles, 2018; Margolis & Sadovsky, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2019). Current guidelines from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV), as described in the Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018; Théry C, et al. JExtracell Vesicles. 2018, 7:1535750) and updated in MISEV2024 (Welsh JA, et al. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024, 13:e12404), recommend reporting multiple EV markers rather than relying on a single protein for normalization. They also suggest ensuring comparable experimental conditions by using the same number of cells at the start of the experiment and normalizing EV data to cell number or whole-cell lysate protein content at the end of the experiment, among other approaches.
In our study, we normalized EV data to whole-cell lysate (WCL) protein content, as this approach accounts for differences in EV production due to variations in cell number or treatment conditions and is commonly used in the field (Kowal et al., PNAS, 2016; Mathieu et al., Nat Commun, 2021). We also included Flotillin-1 and LAMP2 as EV markers, both of which have been validated as molecular markers of small EV subpopulations.
(4) Hyper normalization in WB quantification in Figure 2E-G is statistically incorrect, as it assumes that one group (in this case, R1441G ctrl) has no variability at all, which is not biologically possible. The authors should repeat the quantification without hypernormalizing one of their groups. This issue is prevalent across the whole manuscript.
We understand the concern regarding “hyper-normalization” (i.e., expressing all values relative to one condition set to 1), which may mask variability in the reference group. However, it is standard practice in immunoblotting analysis to express data relative to a control condition for comparison, as variations in membrane transfer, exposure time, and signal development can differ across blots. In our case, the data are expressed as relative levels (arbitrary units) rather than absolute quantitative values. To facilitate comparison between datasets and account for inter-experimental variation, we continued to express values relative to the mutant LRRK2 MEF condition.
On the other hand, in lipidomics experiments, despite using the same number of seeded cells and identical extraction and analysis protocols, minor biological and technical variability was observed across independent replicates. This variability is inherent to the experimental system and is now explicitly represented in the new table included in Supplemental Figure 1F, which compiles three independent representative lipidomics experiments showing quantitative BMP levels across different conditions.
(5) The authors perform a t-test in Figure 2E-G when comparing more than 2 groups, which is wrong. The authors should use a two-way ANOVA as they are comparing genotype and treatment.
We appreciate the reviewer’s comment and agree with this observation. The MLi-2 and CBE experiments were performed independently and in separate experimental runs; therefore, we have reanalyzed these datasets separately rather than combining them in a two-way ANOVA. To properly compare more than two groups within each dataset, we have now applied a Kruskal-Wallis test followed by an uncorrected Dunn’s post hoc test (Figure 2 D-F and H-J). This non-parametric approach is more appropriate for our data structure, as EV experiments are usually subject to high variability and immunoblot quantifications involving small sample sizes (n≈6) do not always meet the assumptions of normality or equal variance. The Kruskal-Wallis test does not assume normality or equal variances, making it more robust for small, variable biological datasets. The statistical analyses and figure legend have been updated in the revised manuscript accordingly.
In addition, since our CBE treatments yielded statistically non-significant data, we have softened our conclusions throughout the manuscript concerning the contribution of GCase activity to EV-mediated BMP release modulation.
(6) There is a very strong reduction in flotillin-1 in R1441G cells vs WT (Figure 2G) in the EV fraction. That reduction is further exacerbated with MLi2, which likely means it is not kinase activity dependent. Can the authors comment on that?
We agree with the reviewer that Flotillin-1 showed a different behavior compared with LAMP2 in these experiments. As recommended by the MISEV guidelines (Théry C, et al. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018; 7:1535750; Welsh JA, et al. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024, 13:e12404), it is important to analyze more than one EV-associated protein marker. We examined LAMP2, which, together with LAMP1, has been reported to be specifically enriched in EVs of endolysosomal origin (exosomes; Mathieu et al., Nat Commun. 2021, 12:4389 ). In contrast, Flotillin-1 is also associated with small EVs but may represent a distinct EV subpopulation from those positive for LAMP proteins (Kowal J, et al. PNAS 2016, 113:E968-E977).
Nevertheless, the biochemical analysis of isolated EV fractions was complemented by our lipidomics data and, in the revised version, by TIRF microscopy analysis of exosome release in control and G2019S LRRK2 human fibroblasts (new Figure 7, Panels G-I; Videos 1 and 2). In this analysis, we confirmed increased exocytosis of CD63-pHluorin– positive endolysosomes in G2019S LRRK2 human fibroblasts compared to controls, an effect that was reversed by MLi-2 treatment. The CD63-pHluorin–positive compartment of these cells was also largely positive for BMP (new Figure 7G). Collectively, these findings further support the regulatory role of LRRK2 activity in EV-mediated BMP secretion.
(7) In Figure 2C, the authors should express that the LAMP2-EV and flotillin-1 EV fractions from the WB are highly exposed. As presently presented, it is slightly misleading.
We thank the reviewer for this comment. In EV preparations, the amount of protein recovered is typically very low. Therefore, although we loaded all the EV protein obtained from each sample, the immunoblots for LAMP2 and Flotillin-1 in EV fractions required longer exposure times to visualize clear signals across all conditions. We have now indicated in the corresponding figure legend that these EV blots are long-exposure blots to facilitate signal detection and avoid any potential misunderstanding.
(8) If Figure 2C and D are from two different experiments, they should not be plotted together in Figure 2E-G. You cannot compare the effect of MLi2 vs CBE if done in completely different experiments.
We appreciate the reviewer’s comment and agree with this observation. The MLi-2 and CBE experiments were performed independently and in separate experimental runs; therefore, we have reanalyzed these datasets separately rather than combining them in a two-way ANOVA. To properly compare more than two groups within each dataset, we have now applied a Kruskal-Wallis test followed by an uncorrected Dunn’s post hoc test (Figure 2 D-F and H-J). This non-parametric approach is more appropriate for our data structure, as EV experiments are usually subject to high variability and immunoblot quantifications involving small sample sizes (n≈6) do not always meet the assumptions of normality or equal variance. The Kruskal-Wallis test does not assume normality or equal variances, making it more robust for small, variable biological datasets. The revised statistical analyses and figure legends have been updated accordingly in the manuscript.
(9) The authors state that "For the R1441G MEF cells, MLi-2 decreased EV concentration while CBE increased EV particles per ml, in agreement with the effects observed in our biochemical analysis." As Figure S1D shows no statistical significance, the authors don't have sufficient evidence to make this claim.
We apologize for this overstatement. We have revised the text to clarify that, although the differences did not reach statistical significance, a consistent trend toward decreased EV concentration upon MLi-2 treatment and increased EV release following CBE treatment was observed in R1441G MEF cells.
(10) "Altogether, given that BMP is specifically enriched in ILVs (which become exosomes upon release), the data presented above support our biochemical analysis (Figure 2C, D, F) and suggest a role for LRRK2 and GCase in modulating BMP release in association with LAMP2-positive exosomes from MEF cells." As Figure 3E shows no statistical difference of BMP on EVs upon CBE treatment, this sentence is not accurate and should be reframed. Furthermore, the authors claim an increase in EV-LAMP2 in R1441G cells compared to WT, however, the amount of BMP in EVs of R1441G cells vs WT is unchanged with a non-significant reduction. This contradiction does not support the authors' conclusions and really puts into question their whole model.
We thank the reviewer for this observation. After reanalyzing our biochemical data from isolated EV fractions (see new Panels D-F and H-J) using an improved statistical approach, we found that although EV-associated LAMP2 levels were consistently elevated in untreated R1441G LRRK2 MEFs compared to WT cells, CBE treatment only produced a non-significant trend toward increased EV-associated LAMP2 compared to untreated R1441G LRRK2 cells. Accordingly, we have revised the sentence to read as follows:
“Altogether, given that BMP is specifically enriched in ILVs (which become exosomes upon release), the data presented above support our biochemical analysis (Figure 2C, E, G, I) and suggest that LRRK2 activity regulates BMP release in association with LAMP2positive exosomes, whereas GCase activity appears to have a more variable effect under the tested conditions.”
We also agree with the reviewer that, in our MEF model, the amount of BMP in EVs of R1441G cells vs WT is unchanged with a non-significant reduction. However, pharmacological modulation supports our conclusion that BMP release is modulated by LRRK2 activity. Specifically, treatment with the LRRK2 inhibitor MLi-2 decreased EVassociated BMP and LAMP2 levels in R1441G LRRK2 MEFs, and our new data (new Figure 7, Panel G-I; Videos 1 and 2) show increased exocytosis of CD63-pHluorin– positive endolysosomes in G2019S LRRK2 human fibroblasts compared to controls, an effect that was reversed by MLi-2 treatment. The CD63-pHluorin–positive compartment of these cells was also largely positive for BMP (new Figure 7G).
In light of the reviewer’s comment about CBE treatment, we have softened our conclusions throughout the manuscript concerning the contribution of GCase activity in this model.
(11) In Figure 5, 16 h of MLi2 treatment is too long and can lead to off-target effects. I would advise reducing it to 1-4 h.
Prolonged MLi-2 treatments have been extensively used in the field without evidence of significant off-target effects. Several studies, including Fell et al. (2015, J Pharmacol Exp Ther 355:397-409), De Wit et al. (2019, Mol Neurobiol 56:5273-5286), Ho et al. (2022, NPJ Parkinson’s Dis 8:115), Tengberg et al. (2024, Neurobiol Dis 202:106728), and Jaimon et al. (2025, Sci Signal 18:eads5761), have applied long-term (24-48 h) MLi-2 treatments at comparable concentrations without detecting toxicity or off-target alterations, including in MEFs (Ho et al., 2022; Dhekne et al., 2018, eLife 7:e40202). Moreover, the data presented in Figure 5 demonstrate a reduction in CLN5 protein levels in both MEFs and human fibroblasts following MLi-2 treatment, confirming the specificity of the observed effects in LRRK2 mutant cells.
(12) "Our data suggest that BMP is exocytosed in association with EVs and that LRRK2 and GCase activities modulate BMP secretion." Again, cells carrying the R1441G mutation have the same amount of BMP in EVs than WT. This sentence is not factually accurate. Accordingly, CBE did not change the amount of BMP in EVs.
We thank the reviewer for this observation and agree that, in our MEF model, the amount of BMP in EVs from R1441G LRRK2 cells is comparable to that observed in WT cells. However, pharmacological modulation supports our conclusion that BMP release is modulated by LRRK2 activity. Specifically, treatment with the LRRK2 inhibitor MLi-2 decreased EV-associated BMP levels in R1441G LRRK2 MEFs, and our new data (new Figure 7G-I; Videos 1 and 2) show increased exocytosis of CD63-pHluorin–positive endolysosomes in G2019S LRRK2 human fibroblasts compared to controls, an effect that was reversed by MLi-2 treatment. The CD63-pHluorin–positive compartment of these cells was also largely positive for BMP (new Figure 7G). These findings further support the regulatory role of LRRK2 activity in EV-mediated BMP secretion. In addition, in light of the reviewer’s comment about CBE treatment, we have softened our conclusions throughout the paper concerning the contribution of GCase activity in this model.
(13) Figure 6; EV release should have been monitored by more accurate markers such as CD63 and CD81.
We thank the reviewer for this comment. We and others (Kowal et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2018; Mathieu et al., 2021; Ferreira et al., 2022) have reported enrichment of Flotillin-1 and LAMP proteins in isolated small EV fractions. In particular, one of these studies (Mathieu et al., Nat Commun. 2021), in which bafilomycin A1 was also used (to boost exosome release), reported that “LAMP1-positive subpopulations of EVs represent MVB/lysosome-derived exosomes, which also contain syntenin-1.” Altogether, our choice of EV markers (LAMP2 and Flotillin-1) is consistent with those previously and accurately used to characterize EVs. We have now included all relevant references in the revised manuscript to further clarify this point.
(14) Figure 6 suggests that exosomal BMP is controlled by EV release. I would think that is rather obvious.
We agree that the finding that exosomal BMP release is influenced by EV secretion may appear “obvious.” However, our intention in Figure 6 was to provide direct experimental evidence confirming this relationship using pharmacological modulators of EV release. Specifically, inhibition of EV secretion with GW4869 reduced exosomal BMP levels, whereas stimulation with bafilomycin A1 increased them. These data were important to establish a causal link between EV trafficking and BMP export, thereby validating our model and supporting the interpretation that LRRK2 regulates BMP homeostasis through EV-mediated exocytosis, which is further modulated, to some extent, by GCase activity.
Minor concerns:
(1) Figure 1: Change colors to be color blind friendly.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful suggestion. We have adjusted the colors in Figure 1 to be color-blind friendly. In addition, we have applied the same color-blind friendly palette to the new immunofluorescence data presented in new Figure 7, Panel A and D.
(2) More consistency on "Xmin" vs "X min" would be appreciated.
We thank the reviewer for this observation. We have revised the manuscript to ensure consistent formatting of time indications throughout the text and figures, using the standardized format “X min.”
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Figure 2C-D. Were equal amounts of protein loaded in each lane?
Equal protein amounts were loaded in lanes corresponding to whole-cell lysate (WCL) fractions and normalized based on α-Tubulin levels.
For the extracellular vesicle (EV) fractions, all protein recovered from EV pellets after isolation was loaded. In all EV-related experiments, we seeded the same number of EVproducing cells per condition, and the resulting EV-derived data (from both immunoblotting and lipidomics analyses) were normalized to the corresponding whole cell lysate (WCL) protein content to ensure comparability across conditions.
All these technical details have been included in the Materials section of our revised manuscript.
(2) The authors refer to the papers of Medoh et al (ref 43) and Singh et al. (44) for the key role of CLN5 in the BMP biosynthetic pathway. However, Medoh et al reported that CLN5 is the lysosomal BMP synthase. In contrast, Singh et al. reported that PLD3 and PLD4 mediate the synthesis of SS-BMP, and did not find any role for CLN5.
To avoid any confusion or misinterpretation of our findings regarding CLN5 and given that we do not analyze PLD3 or PLD4 in our study, we have decided to replace the reference to Singh et al. with Bulfon D. et al. (Nat. Commun. 2024, 15:9937) instead. This last work, conducted by an independent group distinct from the one that originally described CLN5, also validated CLN5 as the sole BMP synthase in cells.
Also, authors mention that bafilomycin A1 (B-A1) dramatically boosts EV exocytosis, referring to Kowal et al., 2016 (ref 35) and Lu et al., 2018 (ref 45). However, this is not shown in Kowal et al.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out this mistake. We apologize for the incorrect citation and have now corrected the reference. The statement regarding the effect of bafilomycin A1 on EV exocytosis now appropriately refers to Mathieu et al., 2021 and Lu et al., 2018.
(3) Page 7, it is stated that "No statistically significant differences in intracellular BMP levels were observed in WT LRRK2 MEFs upon LRRK2 or GCase inhibition(Supplemental Figure 1D, E)". The authors probably mean "Supplemental Figure 1F, G"
We thank the reviewer for noting this error. We have corrected the text to refer to panels F and G of Supplemental Figure 1, which correspond to the relevant data. We have also revised the reference to panel I of Supplemental Figure 1 accordingly.
The goal is acquiring many experiences. The side effects include entertainment and increased skill.
I love this. <3
The HTTP response must return the file as a binary object, not as HTML or plain text. Set the Content-Type header to application/octet-stream to indicate this is a binary file download.
to be changed to:
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The manuscript entitled "Adaptation of endothelial cells to microenvironment 1 topographical cues through lysyl oxidase like-2-mediated basement membrane scaffolding" by Marchand et al., aims to determine the impact of LOXL2 on the dynamic formation of vascular basement membranes (BMs).
Strengths:
This manuscript includes a nice combination of different methods and presents the results in an appropriate manner.
Furthermore, the results clearly demonstrate an impact of LOXL2 on collagen IV-fibronectin organization and topography. Finally, the proper arrangement of collagen IV-fibronectin impacts cell alignment.
Weaknesses:
An open question for this reviewer is what the real take-home message of the present study is? Can the authors deliver novel insight into BM formation transferable to the in vivo situation? Why do the authors not see a "real" BM? Could it be that in vivo endothelial cells do not build the vascular BM alone? Thus, are additional cell types needed? And what will happen then if LOXL2 expression is altered?
Major comments:
(1) Can the authors show that LOXL2 cross-links fibronectin and collagen IV?
(2) The authors stated that LOXL2 depletion affects cytoskeleton arrangements and cell shape. Could it be that this is simply a secondary effect mediated primarily through the altered cross-linking of fibronectin and collagen IV?
(3) Can the authors perform cell adhesion studies on CDMs derived from wild-type versus LOXL2-deficient cells?
(4) Line 226-230: Can the authors provide the proliferation data of wildtype and LOXL2-depleted cells supporting their Src and Akt activity findings?
(5) Line 298-299: The authors made a statement about laminin. Can the authors think of a co-culture of wild-type versus LOXL2-depleted endothelial cells in combination with pericytes or fibroblasts, as these cells contribute to the efficient assembly of a functional vascular basement membrane (10.1182/blood-2009-05-222364). Here, you can determine the impact of altered fibronectin-collagen IV cross-linking on laminin network formation. This will affect their conclusion in lines 299-304, as these facts are solely based on endothelial cells.
(6) Suggestion: can the authors supplement recombinant LOXL2 protein in its active version to the LOXL2-depleted endothelial cells to rescue the observed changes? And further compare LOXL2 enzymatic function with LOXL2 protein harbouring Zn instead of Cu, making it enzymatic inactive. Here, the authors might be able to strengthen their hypothesis that LOXL2 might bridge fibronectin and collagen IV or link both proteins.
(7) There are grammatical errors in the manuscript that the authors should work on.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
This important study shows that basement membrane (BM) generation is a key event mediating cell 3D organization in response to microenvironmental cues. Such a mechanism participates in the endothelial cell capacity to organize into a capillary vessel segment through the shift of interactions with the interstitial ECM to interactions with vascular BM. This is particularly important for the developing, sprouting vasculature. The authors conclusively show, using TIRF and atomic force microscopy substantiated by 3D sprouting assays, that the lysyl oxidase Loxl2 plays a key role herein. With respect to translation into clinical practice, the dysregulation of adherens junctions and barrier properties associated with Loxl2 dysfunction mediated defects in BM supports its involvement in the progression of long-term microvascular diseases.
An outstanding question not answered in the current MS is how Loxl2 integrates into the Dll4-Notch mediated control of tip-stalk-phalanx cell differentiation in the developing (embryonic) vasculature. The authors focused a lot on Loxl2 loss of function; however, in a (patho)physiological context, Loxl2 gain of function would be relevant. Loxl2 is a hypoxia target and Loxl2 accumulates in the ECM upon hypoxic stress (as occurs during ischemic CVD, stroke/heart infarct). It would be interesting to know how Loxl2 gain-of-function impacts BM assembly, endothelial behavior, mechanosensing, and vessel angiogenic remodeling.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
The authors have investigated the myelination pattern along the axons of chick avian cochlear nucleus. It has already been shown that there are regional differences in the internodal length of axons in the nucleus magnocellularis. In the tract region across the midline, internodes are longer than in the nucleus laminaris region. Here the authors suggest that the difference in internodal length is attributed to heterogeneity of oligodendrocytes. In the tract region oligodendrocytes would contribute longer myelin internodes, while oligodendrocytes in the nucleus laminaris region would synthesize shorter myelin internodes. Not only length of myelin internodes differs, but also along the same axon unmyelinated areas between two internodes may vary. This is an interesting contribution since all these differences contribute to differential conduction velocity regulating ipsilateral and contralateral innervation of coincidence detector neurons. However, the demonstration falls rather short of being convincing.
Significance:
The authors suggest that the difference in internodal length is attributed to heterogeneity of oligodendrocytes. In the tract region oligodendrocytes would contribute longer myelin internodes, while oligodendrocytes in the nucleus laminaris region would synthesize shorter myelin internodes. Not only length of myelin internodes differs, but also along the same axon unmyelinated areas between two internodes may vary. This is an interesting contribution since all these differences contribute to differential conduction velocity regulating ipsilateral and contralateral innervation of coincidence detector neurons.
Editors' note: The authors have written an effective rebuttal to the previous round of reviews.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the previous reviews
Reviewer #3:
Comments on revised version:
This revised version is in large improved and the responses to reviewers' comments are generally relevant. However, the response regarding pre-nodes is not satisfactory. I understand that the authors prefer to avoid further experimentations, but I think this is an important point that needs to be clarified. Exploring stages between E12 and E15 are therefore of importance. When carefully examining some of the figures (Fig. 1E or 2D) I think that at E15 they may well be pre-nodes formation prior to myelin deposition, on structure the authors considered to be heminodes. To be convincing they should use double or triple labeling with, in addition to the nodal proteins (ankG and/or Nav pan), a good myelin marker such as antiPLP. The rat monoclonal developed by late Pr Ikenaka would give a sharper staining than the anti MAG they used. (I assume the clone must still be available in Okazaki ).
We appreciate your insightful comment regarding the possible presence of pre-nodal clusters along NM axons and your kind suggestion to use the PLP antibody (clone AA3; Yamamura et al., J Neurochem, 1991). We have obtained this monoclonal antibody from Dr. Kenji Tanaka previously in Okazaki and confirmed that it works well in chicken tissues. However, since this clone recognizes both PLP and DM-20 isoforms, it labels not only myelin-forming oligodendrocytes (MFOLs) but also newly formed oligodendrocytes (NFOLs) (Yokoyama et al., J Neurochem, 2025). Therefore, it is not ideal for determining whether nodal protein clusters are formed before myelin deposition.
Instead, we performed double immunostaining for MAG and AnkG between E12 and E15 to clarify the temporal relationship between myelin maturation and node formation. The results showed that detectable AnkG clusters along NM axons began to appear very sparsely around E13, coinciding with the emergence of MAG signals, and became more prominent with development. This temporal pattern does not match the definition of pre-nodal clusters, which are formed prior to myelination.
Although we cannot completely rule out the possibility of undetectable pre-nodal clusters or those composed of molecules other than AnkG, our results support the view that pre-nodal clusters are unlikely to play a major role in determining the regional difference in nodal spacing along NM axons. These new data have been added as Figure 2—figure supplement 1, and the relevant sections in the Results, Discussion, and Figure legend have been revised accordingly (page 5, line 4; page 10, line 7; page 29, line 1).
Researchers have found that attractiveness is one factor.3 Studies have found that good-looking people tend to be seen as having positive personality traits and higher intelligence.4 One study even found that jurors were less likely to believe that attractive people were guilty of criminal behavior.5
it's undeniable that people's decision was largely influenced by one's appearance.
Fisher said she was handcuffed anyway, before being released around 3 a.m. and was told anyone with an outstanding warrant, even if it was unrelated to immigration, would not be released.
I find it's interesting because the government merely arrests of all "suspects" without making any preparations.
Female triple-transgenic AD (3xTg-AD)
DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-7769003/v1
Resource: (MMRRC Cat# 034830-JAX,RRID:MMRRC_034830-JAX)
Curator: @AleksanderDrozdz
SciCrunch record: RRID:MMRRC_034830-JAX
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
The authors attempted to clarify the impact of N protein mutations on ribonucleoprotein (RNP) assembly and stability using analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) and mass photometry (MP). These complementary approaches provide a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying processes. Both SV-AUC and MP results consistently showed enhanced RNP assembly and stability due to N protein mutations.<br /> The overall research design appears well planned, and the experiments were carefully executed.
Strengths:
SV-AUC, performed at higher concentrations (3 µM), captured the hydrodynamic properties of bulk assembled complexes, while MP provided crucial information on dissociation rates and complex lifetimes at nanomolar concentrations. Together, the methods offered detailed insights into association states and dissociation kinetics across a broad concentration range. This represents a thorough application of solution physicochemistry.
Weaknesses:
Unlike AUC, MP observes only a part of solution. In MP, bound molecules are accumulated on the glass surface (not dissociated) thus concentration in solution should change as time develops. How does such concentration change impact the result shown here?
Comments on revisions:
The response from the authors is appropriate and reasonable.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript investigates how mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (N) alter ribonucleoprotein (RNP) assembly, stability, and viral fitness. The authors focus on mutations such as P13L, G214C, G215C combining biophysical assays (SV-AUC, mass photometry, CD spectroscopy, EM), VLP formation, and reverse genetics. They propose that SARS-CoV-2 exploits "fuzzy complex" principles, where distributed weak interfaces in disordered regions allow both stability and plasticity, with measurable consequences for viral replication.
Strengths:
* The paper demonstrates a comprehensive integration of structural biophysics, peptide/protein assays, VLP systems, and reverse genetics.
* Identification of both de novo (P13L) and stabilizing (G214C/G215C) interfaces provides a mechanistic insight into RNP formation.
* Strong application of the "fuzzy complex" framework to viral assembly, showing how weak/disordered interactions support evolvability, is a significant conceptual advance in viral capsid assembly.
* Overall, the study provides a mechanistic context for mutations that have arisen in major SARS-CoV-2 variants (Omicron, Delta, Lambda) and a mechanistic basis for how mutations influence phenotype via altered biomolecular interactions.
Weaknesses:
The weaknesses are shared via detailed comments to follow.
Comments on revisions:
The authors have addressed the criticisms of the original manuscript satisfactorily.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public Review):
Summary:
The authors attempted to clarify the impact of N protein mutations on ribonucleoprotein (RNP) assembly and stability using analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) and mass photometry (MP). These complementary approaches provide a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying processes. Both SV-AUC and MP results consistently showed enhanced RNP assembly and stability due to N protein mutations.
The overall research design appears well planned, and the experiments were carefully executed.
Strengths:
SV-AUC, performed at higher concentrations (3 µM), captured the hydrodynamic properties of bulk assembled complexes, while MP provided crucial information on dissociation rates and complex lifetimes at nanomolar concentrations. Together, the methods offered detailed insights into association states and dissociation kinetics across a broad concentration range. This represents a thorough application of solution physicochemistry.
We thank the Reviewer for this positive assessment.
Weaknesses:
Unlike AUC, MP observes only a part of the solution. In MP, bound molecules are accumulated on the glass surface (not dissociated), thus the concentration in solution should change as time develops. How does such concentration change impact the result shown here?
We agree with the Reviewer that the concentration in solution above the surface will change with time; however, the impact of surface adsorption turns out to be negligible. To show this we have added a calculation as Supplementary Methods that is based on the number of imaged adsorption events, the fraction of imaged area to total surface area, and the initial sample volume and concentration. Under our experimental conditions the reduction is less than 1%, which is well within the range of experimental concentration errors.
This is in line with the observation that surface adsorption of proteins to glass is critical and needs to be prevented when working at picomolar concentrations (Zhao H, Mayer ML, Schuck P. 2014. Analysis of protein interactions with picomolar binding affinity by fluorescence-detected sedimentation velocity. Anal Chem 86:3181–3187. doi:10.1021/ac500093m), but is ordinarily negligible when working at the mid nanomolar concentration range. The difference in the MP experiments is that where usually the surface adsorption to glass and plastic is invisible, it is being imaged and quantified in MP. The negligible impact of surface adsorption on solution concentration in typical MP experiments is also in line with the results of several studies that have successfully measured dissociation constants of binding equilibria by MP (Young G et al., Science 360 (2018) 432; Wu & Piszczeck, Anal Biochem 592 (2020) 113575; Solterman et al. Angewandte Chemie 59 (2020) 10774) with samples in the 5-50 nM range and similar experimental setup. It should be noted that in the MP experiments no surface functionalization is employed, in contrast to optical biosensors that utilize surface-immobilized ligands and polymeric matrices and thereby enhance the surface binding capacity.
Even though this depletion effect is negligible under ordinary MP conditions, the Reviewer raises a good point and readers may have a similar question with this novel technique. For this reason, we have added in the MP section of the Methods the sentence “In either configuration, the impact of surface binding on the sample concentration is < 1% and negligible, as described in the Supplementary Methods S1.” and added the detailed calculations in the Supplement accordingly. The use of SV as a traditional, orthogonal technique and the observation of consistent results with those of MP should further dispel readers’ methodological concerns in this point.
Reviewer #2 (Public Review):
Summary:
In this manuscript, the authors apply a variety of biophysical and computational techniques to characterize the effects of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 N protein on the formation of ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs). They find convergent evolution in multiple repeated independent mutations strengthening binding interfaces, compensating for other mutations that reduce RNP stability but which enhance viral replication.
Strengths:
The authors assay the effects of a variety of mutations found in SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern using a variety of approaches, including biophysical characterization of assembly properties of RNPs, combined with computational prediction of the effects of mutations on molecular structures and interactions. The findings of the paper contribute to our increasing understanding of the principles driving viral self-assembly, and increase the foundation for potential future design of therapeutics such as assembly inhibitors.
Thank you for highlighting the strengths of our paper and the potential impact on future design of therapeutics.
Weaknesses:
For the most part, the paper is well-written, the data presented support the claims made, and the arguments are easy to follow. However, I believe that parts of the presentation could be substantially improved. I found portions of the text to be overly long and verbose and likely could be substantially edited; the use of acronyms and initialisms is pervasive, making parts of the exposition laborious to follow; and portions of the figures are too small and difficult to read/understand.
We are glad the Reviewer concurs the data support our conclusions, and finds the arguments easy to follow. We appreciate the comment that the work was not optimally presented. To address this point, we have identified multiple opportunities to streamline the text without jeopardizing the clarity. We have also rewritten the end of the Introduction.
As recommended, we have reduced and harmonized the use of acronyms and abbreviations throughout the text to improve readability. Specifically, we have now spelled out nucleic acid (NA), intrinsically disordered regions (IDR), full-length (FL), AlphaFold (AF3), and variants of concern (VOC).
Finally, we have improved the presentation of most figures, adding labels and new panels, and increased the label font sizes to facilitate more detailed inspections of the data.
Reviewer #3 (Public Review):
This manuscript investigates how mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (N) alter ribonucleoprotein (RNP) assembly, stability, and viral fitness. The authors focus on mutations such as P13L, G214C, and G215C, combining biophysical assays (SV-AUC, mass photometry, CD spectroscopy, EM), VLP formation, and reverse genetics. They propose that SARS-CoV-2 exploits "fuzzy complex" principles, where distributed weak interfaces in disordered regions allow both stability and plasticity, with measurable consequences for viral replication.
Strengths:
(1) The paper demonstrates a comprehensive integration of structural biophysics, peptide/protein assays, VLP systems, and reverse genetics.
(2) Identification of both de novo (P13L) and stabilizing (G214C/G215C) interfaces provides a mechanistic insight into RNP formation.
(3) Strong application of the "fuzzy complex" framework to viral assembly, showing how weak/disordered interactions support evolvability, is a significant conceptual advance in viral capsid assembly.
(4) Overall, the study provides a mechanistic context for mutations that have arisen in major SARS-CoV-2 variants (Omicron, Delta, Lambda) and a mechanistic basis for how mutations influence phenotype via altered biomolecular interactions.
We are grateful for these comments highlighting this work as a significant conceptual advance.
Weaknesses:
(1) The arrangement of N dimers around LRS helices is presented in Figure 1C, but the text concedes that "the arrangement sketched in Figure 1C is not unique" (lines 144-146) and that AF3 modeling attempts yielded "only inconsistent results" (line 149).
The authors should therefore present the models more cautiously as hypotheses instead. Additional alternative arrangements should be included in the Supplementary Information, so the readers do not over-interpret a single schematic model.
We agree that in the absence of high-resolution structures the RNP models are hypothetical, and have now emphasized this in the Results, following the Reviewer’s recommendation. To present alternative arrangements that satisfy the biophysical constraints upfront, we have promoted the previous Supplementary Figure 11 showing different models to the first Supplementary Figure, and expanded it with examples of different oligomers. In this way it is referenced early on in the Results and in the legend to Figure 1C. We agree this strengthens the manuscript, as one of the take-home messages is the inherent polydispersity of the RNPs.
The fact that AF3 can only provide inconsistent results will not come as a surprise, given the substantial disordered regions of the complex, and is a drawback of AF3 rather than our structural model. We slightly emphasized this point so as to clarify that the presentation of the AF3-based RNP structure serves solely as supporting evidence that our hypothetical model is sterically reasonable.
The new Results paragraph reads:
“As suggested in the cartoon of Figure 1C, this supports the hypothesis of a three-dimensional arrangement with a central LRS oligomer with symmetry properties and dimensions similar to low resolution EM images of model RNPs (Carlson et al., 2022, 2020) and cryo-ET of RNPs in virions (Klein et al., 2020; Yao et al., 2020). It should be noted, however, that the arrangement sketched in Figure 1C is not unique and other subunit orientations could be envisioned that satisfy all constraints from experimentally observed binding interfaces, including different oligomers and anti-parallel subunits as illustrated in Supplementary Figure S1. Extending previous ColabFold structural predictions that show multiple N-protein dimers self-assembled via the LRS coiled-coils (Zhao et al., 2023), we attempted the AlphaFold modeling of RNPs combining multiple N dimers with SL7 RNA ligands, mimicking our biophysical assembly model. Current AlphaFold restrictions limit the prediction to pentamers of N-protein dimers with 10 copies of SL7 RNA. While only inconsistent results were obtained – which is not surprising given the large intrinsically disordered regions exceed the predictive power of AlphaFold – some models did produce an overall RNP organization similar to Figure 1C, suggesting such an arrangement is at least sterically reasonable with regard to possible N-protein subunit orientations in an RNP (Supplementary Figure S2)”
(2) Negative-stained EM fibrils (Figure 2A) and CD spectra (Figure 2B) are presented to argue that P13L promotes β-sheet self-association. However, the claim could benefit from more orthogonal validation of β-sheet self-association. Additional confirmation via FTIR spectra or ThT fluorescence could be used to further distinguish structured β-sheets from amorphous aggregation.
We completely agree that the application of multiple orthogonal biophysical methods can strengthen the conclusions. In addition to EM fibrils and CD spectra (a classical gold standard technique for protein secondary structure in solution), we already have support from ColabFold modeling, as well as NMR results from the Zweckstetter lab showing the potential for for β-sheet-like conformations.
Furthermore, we believe the evidence for the absence of ‘amorphous aggregates’ is very strong, as this would be inconsistent with the long-range order required to create the visibly fibrillar morphology in EM, and amorphous aggregates would be inconsistent with the increased solution viscosity. In this context, it is also highly relevant that the β-sheet-like secondary structure recorded by CD is concentration-dependent and reversible upon dilution. The long-range spatial order of fibrils is consistent with the formation of secondary structure in solution.
In addition, it must be kept in mind that what we see is specific to N-arm peptides carrying the P13L mutation (in EM, CD, and structural prediction) and does not occur in the other two N-arm peptides (ancestral N-arm and N-arm with deletion of 31-33), linker peptides, or C-arm peptides.
Most importantly, as elaborated in more detail below, we do not claim that fibril formation is physiologically relevant. At the heart of this – in the context of the evolution of fuzzy complexes – is that the P13L mutation creates additional weak protein-protein interactions. Indeed, the assembly of fibrils geometrically requires at least two interfaces for each subunit. These weak interactions are at play physiologically in the context of the disordered RNP particles, and in macromolecular condensates, but not in the formation of fibrils. Therefore, while we appreciate the suggestion for FTIR spectra ThT staining, we are afraid further emphasis on the fibril structure might confuse the reader, and therefore we would rather clarify upfront that these fibrillar assemblies are not thought to form in vivo from full-length protein, but merely demonstrate the presence of N-arm self-association interfaces in the model of truncated peptides.
Accordingly, we have amended the Results paragraph reporting the fibrils:
“Thus, the N-arm mutation P13L is responsible for the formation of fibrils in N-arm peptides after prolonged storage. Some of these N-arm fibrils exhibit a twisted morphology with width of »5 nm (Figure 2A), in some instances exhibiting patterns of strand breaks. Such fibrils are frequently encountered in proteins that can stack β-sheets, such as in amyloids (Paravastu et al., 2008). While we have not observed fibril formation in the context of full-length N, and have no evidence such fibrils are physiologically relevant, their occurrence in solutions of truncated N-arm peptide nonetheless demonstrates the introduction of ordered N-arm self-association interfaces in conformations of P13L mutants.”
And more completely summarized experimental evidence prior to describing the ColabFold prediction results (which previously did not include mention of the NMR):
“Finally, confirming the interpretation of the EM images and the CD data, as well as the b-structure propensity reported from NMR data (Zachrdla et al., 2022), the structural prediction of N[10-20]:P13L in ColabFold displayed oligomers with stacking b-sheets …”
(3) In the main text, the authors alternate between emphasizing non-covalent effects ("a major effect of the cysteines already arises in reduced conditions without any covalent bonds," line 576) and highlighting "oxidized tetrameric N-proteins of N:G214C and N:G215C can be incorporated into RNPs". Therefore, the biological relevance of disulfide redox chemistry in viral assembly in vivo remains unclear. Discussing cellular redox plausibility and whether the authors' oxidizing conditions are meant as a mechanistic stress test rather than physiological mimicry could improve the interpretation of these results.
The paper could benefit if the authors provide a summary figure or table contrasting reduced vs. oxidized conditions for G214C/G215C mutants (self-association, oligomerization state, RNP stability). Explicitly discuss whether disulfides are likely to form in infected cells.
We thank the Reviewer for raising this most interesting point. The reason why the biological relevance of N dilsulfides remains unclear is simply that this is still unknown, unfortunately. Recently, Kubinski et al. have strongly argued for the formation of disulfides in infected cells, but in our view the evidence remains weak since the majority of disulfide bonds in that work presented as post-lysis artifacts, and it appears the non-covalent effects alone could explain the physiological observations. We aimed for a balanced presentation and wrote in the relevant Results section:
“Covalent disulfide bonds in the LRS in non-reducing conditions were found to further promote LRS oligomerization. However, there is no conclusive data yet whether covalent bonds in the LRS occur in vivo, or any G215C effect is entirely non-covalent due to the significant strengthening of LRS helix oligomerization (see Discussion).”
Despite the uncertainty regarding physiological disulfide bond formation, we believe it is useful to ask whether covalently crosslinked N dimers would aid or constrain RNP assembly in our biophysical model. We have now better explained this motivation in the Results section describing the RNP experiments:
“Even though it is still unclear whether disulfide bonds of N cysteine mutants form in vivo, we were curious about the impact of disulfide-linked oligomers of the cysteine mutants on their RNP structure and stability in our biophysical assembly model.”
The referenced paragraph from the Discussion reads:
“Regarding the cysteine mutations that have been repeatedly introduced in the LRS prior to the rise of the Omicron VOCs, it is an open question whether they lead to covalent bonds in vivo or in the VLP assay. While examples of disulfide-linked viral nucleocapsid proteins have been reported (Kubinski et al., 2024; Prokudina et al., 2004; Wootton and Yoo, 2003), a methodological difficulty in their detection is artifactual disulfide bond formation post-lysis of infected cells (Kubinski et al., 2024; Wootton and Yoo, 2003). However, our results clearly show that a major effect of the cysteines already arises in reduced conditions without any covalent bonds, through extension of the LRS helices, and concomitant redirection of the disordered N-terminal sequence. While oxidized tetrameric N-proteins of N:G214C and N:G215C can be incorporated into RNPs, the covalent bonds provided only marginally improved RNP stability. Interestingly, the introduction of cysteines imposes preferences of RNP oligomeric states dependent on oxidation state, consistent with our MD simulations highlighting the impact of cysteine orientation of 214C versus 215C relative to the hydrophobic surface of the LRS helices. Overall, considering potentially detrimental structural constraints from covalent bonds on LRS clusters seeding RNPs, energetic penalties on RNP disassembly, as well as the required monomeric state of the LRS helix for interaction with the NSP3 Ubl domain (Bessa et al., 2022), at present it is unclear to what extent the formation of disulfide linkages between LRS helices would be beneficial or detrimental in the viral life cycle.”
We feel that this text addresses the Reviewer’s comment, and that expanding the existing discussion further would conflict with other recommendations to shorten and focus the text.
Finally, we have addressed the valuable suggestion of a new table summarizing the oligomeric state and self-association of the different cysteine mutants by inserting a new column in the existing Table 1 reporting all species’ oligomeric state at low micromolar concentrations. In this way they can be compared at a glance with the other mutants as well. A more detailed comparison of the concentration-dependent size-distribution is provided in Figure 4.
(4) VLP assays (Figure 7) show little enhancement for P13L or G215C alone, whereas Figure 8 shows that P13L provides clear fitness advantages. This discrepancy is acknowledged but not reconciled with any mechanistic or systematic rationale. The authors should consider emphasizing the limitations of VLP assays and the sources of the discrepancy with respect to Figure 8.
We thank the Reviewer for this comment, which highlights a very important point.
For clarification and to improve the cohesion of the manuscript we have inserted a reference to the Discussion after the presentation of the VLP results, which provides a natural transition to the following description of the reverse genetics experiments:
“As expanded on in the Discussion, the failure to observe enhancement by P13L alone may be related to limitations of the VLP assay in sensitivity, including the restriction to a single round of infection, and protein expression levels.”
This references a paragraph in the Discussion about the limitations of the VLP assay in general and the reasons we believe the enhancement by P13L alone was not picked up:
“…While this assay has been widely used for rapid assessment of spike protein and N variants (Syed et al., 2021), it has limitations due to the addition of non-genomic RNA and the lack of double membrane vesicles from which gRNA emerges through the NSP3/NSP4 pore complex potentially poised for packaging (Bessa et al., 2022; Ke et al., 2024; Ni et al., 2023). It should also be recognized that the results do not directly reflect the relative efficiency of RNP assembly only, since protein expression levels, their localization, and their posttranslational modifications are not controlled for. Susceptibility for such factors might be exacerbated with mutations that modulate weak protein interactions. For example, as shown previously (Syed et al., 2024; Zhao et al., 2024), a GSK3 inhibitor inhibiting N-protein phosphorylation significantly enhances VLP formation and eliminates the advantage provided for by the N:G215C mutation relative to the ancestral N – presumably due to an increase in assembly-competent, non-phosphorylated N-protein erasing an affinity advantage. A similar process may be underlying the absent or marginal improvement in VLP readout from the cysteine LRS mutants and P13L at the achieved transfection level in the present work, and the enhanced signal from R203K/G204R and R203M (the latter being consistent with previous reports (Li et al., 2025; Syed et al., 2021)) modulating protein phosphorylation. Nonetheless, mirroring the results of the biophysical in vitro experiments, the addition of RNP-stabilizing P13L and G214C mutations on top of R203K/G204R led to a significantly larger VLP signal.
The VLP assay may be limited in sensitivity to mutation effects due to its restriction to a single round of infection. To avoid this and other potential limitations of the VLP assay for the study of viral packaging, for the key mutation N:P13L we carried out reverse genetics experiments. These showed the sole N:P13L mutation significantly increases viral fitness (Figure 8).”
(5) Figures 5 and 6 are dense, and the several overlays make it hard to read. The authors should consider picking the most extreme results to make a point in the main Figure 5 and move the other overlays to the Supplementary. Additionally, annotating MP peaks directly with "2×, 4×, 6× subunits" can help non-experts.
We completely agree with the Reviewer – these figures were very dense. To mitigate this problem without having the reader to switch back-and-forth to the supplement, we subdivided the panels of Figure 5 and showed only a subset of curves in each. In this way the data are easier to read while still readily compared. It is a large figure, but it contains the key data for the present work and is therefore worthwhile to have in one place. For the MP histogram data we also have inserted the suggested peak labels. Similarly, we have split Figure 6A into two panels for clarity.
(6) The paper has several names and shorthand notations for the mutants, making it hard to keep up. The authors could include a table that contains mutation keys, with each shorthand (Ancestral, Nο/No, Nλ, etc.) mapped onto exact N mutations (P13L, Δ31-33, R203K/G204R, G214C/G215C, etc.). They could then use the same glyphs (Latin vs Greek) consistently in text and figure labels.
Yes, we agree this is a problem and we apologize for the confusion. However, it is not possible to refer exclusively to either Latin or Greek terminology, which we feel would be even more detrimental to readability (the former being exhaustively lengthy and the latter being imprecise). But we have used a rational system: If the complete set of mutations of a variant are present, then its Greek letter will be used as an abbreviation, and otherwise we use Latin amino acid/position indicators for individual mutations or combinations thereof. Unfortunately, previously we inadvertently failed to explicitly mention this, and we are most grateful for the Reviewer to point this out.
We have now rectified this by including upfront the sentence:
“We will adopt a nomenclature where the complete set of defining mutations of a variant will be referred to by its Greek letter, i.e., N:P13L/R203K/G204R/G214C is N<sub>λ</sub>, and analogously the set of Omicron mutations N:P13L/Δ31-33/R203K/G204R are referred to as N<sub>ο</sub>; see Table 1”
This will define the two shorthands N<sub>λ</sub> and N<sub>ο</sub> used. Furthermore, as suggested and pointed to in the text, Table 1 does provide the keys to mutation and variants, including the information in which variant any of the other mutations studied here occur.
(7) The EM fibrils (Figure 2A) and CD spectra (Figure 2B) were collected at mM peptide concentrations. These are far above physiological levels and may encourage non-specific aggregation. Similarly, the authors mention" ultra-weak binding energies that require mM concentrations to significantly populate oligomers". On the other hand, the experiments with full-length protein were performed at concentrations closer to biologically relevant concentrations in the micromolar range. While I appreciate the need to work at high concentrations to detect weak interactions, this raises questions about physiological relevance.
This is indeed an important point to clarify. We agree that much lower nucleocapsid protein concentrations are present in the cytosol on average, and these were used in our RNP assembly experiments. However, there are at least two important physiologically relevant cases where high local N concentrations do occur:
(1) Once assembled in RNPs, the disordered N-terminal extensions are locally at a very high concentration within the volume they can explore while tethered to the NTD. A back-of-the-envelope calculation assuming 12 N-protein subunits confining 12 N-terminal extensions to the volume of a single RNP (≈14x14x14 nm<sup>3</sup> by cryoEM; Klein et al 2020) leads to an effective concentration of 7.4 mM. Obviously the N-arm peptides are not completely free and there will be constraints that would hinder or promote encounter complex probability, but interfaces with mM Kd are clearly strong enough to populate Narm-Narm contacts extending from N-protein in the RNP.
Additionally, any interaction where N-proteins are brought in close proximity could allow weak N-arm interactions to provide additional stability. Besides the RNP, we demonstrate this in our Results for nucleic-acid liganded N tetramers (Figure 4B), but this might similarly occur in complexes with NSP3 or host proteins. Generally, it is quite common that small additional binding energies play important roles in the modulation of multivalent protein complexes.
(2) Within the macromolecular condensate the local concentration will be substantially higher than on average within the infected cell. While we do not know its precise concentration, it is well-established that the sum of many ultra-weak interactions is driving the formation of this dense liquid phase. In our previous eLife paper (Nguyen et al., 2024) we have shown LLPS is suppressed with the R203K/G204R mutation, but it is ‘rescued’ with the additional P13L/del31-33 mutation of the Omicron variant showing strong LLPS. Similarly, LLPS is suppressed by the LRS mutant L222P, but rescued in conjunction with P13L. This is another biologically relevant scenario where weak interactions are critical.
We have emphasized these points in the revised manuscript as described below.
Specifically:
(a) Could some of the fibril/β-sheet features attributed to P13L (Figure 2A-C) reflect non-specific aggregation at high concentrations rather than bona fide self-association motifs that could play out in biologically relevant scenarios?
We understand this concern from the experience with proteins that often have limited solubility and tendencies to aggregate, sometimes accompanied by unfolding and driven by hydrophobic interactions, or clustering on the path to LLPS. However, we are struggling to reconcile the picture of non-specific aggregation with the context of our P13L N-arm peptides. The term ‘non-specific aggregation’ implies the idea of amorphous aggregates, which we would contend is inconsistent with the observed geometry of fibrils, which exhibit long-range order. In addition, non-specific aggregation does not lead to increased solution viscosity, which we describe, but fibril formation does. Another connotation of ‘aggregates’ is irreversibility. However, we find the beta-sheet-like conformation seen at 1 mM becomes significantly more disordered when the same sample is diluted to 0.4 mM peptide. This is consistent with a reversible self-association driven by a conformational change toward ordered secondary structure.
To highlight the reversibility, we have clarified the description: “Interestingly, diluting the 1 mM sample (solid) to a concentration of 0.4 mM (dashed) reveals a large shift in the far-UV spectra … both indicative of a significant increase of disorder upon dilution. This is consistent with the stabilization of b-sheets in a reversible, strongly cooperative self-association process with an effective K<sub>D</sub> in the high mM to low mM range.”
We have also inserted a concentration conversion to mg/ml units, which shows even 1 mM of peptides is only ~5 mg/ml, i.e. not excessively high. “While the ancestral N-arm at »1 mM (» 4.6 mg/ml) concentrations exhibits CD spectra with a minimum at »200 nm typical of disordered conformations (black)”
With regard to the question of specificity, we have studied similar N-arm peptides without P13L mutations and with the 31-33 deletion under equivalent conditions. But we observe the reversible self-association, conformational change, and fibril formation only for those containing the P13L mutation, consistent with ColabFold predictions. Neither did we observe fibrils with disordered C-arm peptides.
How these weak self-association motifs in the N-arm can be physiologically relevant in the context of full-length protein modulating the stability of multi-molecular complexes and enhancing LLPS was outlined above, and further clarified in the manuscript as detailed below.
(b) How do the authors justify extrapolating from the mM-range peptide behaviors to the crowded but far lower effective concentrations in cells?
As pointed out above, the key to this question is the local preconcentration as the N-arm peptides are tethered to the rest of protein in the context of flexible multi-molecular assemblies. Another mechanism to consider is the formation of condensates. The response to the next comment will expand on this.
The authors should consider adding a dedicated section (either in Methods or Discussion) justifying the use of high concentrations, with estimation of local concentrations in RNPs and how they compare to the in vitro ranges used here. For concentration-dependent phenomena discussed here, it is vital to ensure that the findings are not artefacts of non-physiological peptide aggregation..
The use of high concentration in biophysical experiments is quite common, for example, in NMR or crystallography, insofar as they elucidate molecular properties. We believe this is obvious; the Reviewer will certainly agree with us, and this does not require further elaboration. The property observed in this case is the existence of specific, weak protein self-association interfaces in the N-arm.
Our response to the Reviewer’s point 7(a) addresses the distinction between artefactual aggregation and self-association of N-arm peptides. The relevance of these weak protein self-association interfaces in the context of the full-length protein is the second underlying question.
As we have previously stated in a dedicated Results paragraph:
“In contrast to the modulation of the coiled-coil LRS interfaces, the de novo creation of the N-arm self-association interface through beta-sheet interactions enabled by P13L cannot be readily observed in full-length N-protein at low M concentrations. Similar to the ancestral LRS interface, it provides only ultra-weak binding energies that require mM concentrations to significantly populate oligomers. This is fully consistent with the previous observation by SV-AUC that neither N:P13L,31-33 nor N<sub>o</sub> with the full set of Omicron mutations show any significant higher-order self-association at low M concentrations, whereas at high local concentrations – as observed in phase-separated droplets – they can modulate and cooperatively enhance self-association processes (Nguyen et al., 2024). (If fact, P13L can substitute for the LRS promoting LLPS, as observed in the rescue of LLPS by N:P13L,31-33/L222P mutants whereas N:L222P LRS-abrogating mutants are deficient in LLPS.) Another process that increases the local concentration of N-arm chains is the tetramerization of full-length N-protein. As described earlier, occupancy of the NA-binding site in the NTD allosterically promotes self-assembly of the LRS into higher oligomers (Zhao et al., 2021). We hypothesized that these oligomers may be cooperatively stabilized by additional N-arm interactions in P13L mutants.”
To state completely unambiguously why weak interfaces are important, we have followed the Reviewer’s suggestion and added an additional clarification already earlier, at the end of the P13L Results section:
“While this self-association interface in the P13L N-arm is weak and its direct observation in biophysical experiments requires mM concentrations, which far exceed average intracellular concentration of N, such weak interactions can become highly relevant physiologically when high local concentrations are prevailing, for example, when the disordered extension is preconcentrated while tethered within macromolecular assemblies as in the RNP, or in macromolecular condensates.”
Furthermore, we have added early in the Discussion:
“Even though the solution affinity of the N-arm P13L interface is ultra-weak, the average local concentration of N-arm chains across the RNP volume (in a back-of-the-envelope calculation assuming a ≈14 nm cube (Klein et al., 2020) with a dodecameric N cluster) is ≈7.4 mM, such that disordered N-arm peptides could well create populations of N-arm clusters stabilizing RNPs through this interface. However, besides the RNP-stabilizing mutants we have also observed unexpected RNP destabilization by the ubiquitous R203K/G204R double mutation, which may be caused by the introduction of additional charges close to the self-association interface in the LRS. In our experiments, this destabilization is more than compensated for by the P13L mutation. (Another scenario where ultra-weak interactions can have a critical impact is in molecular condensates. We previously reported the suppression of LLPS by the R203K/G204R mutation, which is rescued by the additional P13L/Δ31-33 mutation (Nguyen et al., 2024). This is consistent with compensatory weak stabilizing and destabilizing impacts of weak interactions on the RNP observed here.)”
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the Authors):
In Figure 1B, it is unclear what the orange lines connecting polypeptides represent, as well as the zig-zag orange lines in the N-arm.
We thank the Reviewer for this comment. We intended this to represent regions of self-association but recognize the patterned background is confusing. We have changed this now to solid-colored backgrounds, and indicated this in the figure legend:
“Regions of self-association are indicated by shaded backgrounds.”
Regarding presentation, in Figure 5 (MP), the relationship between mass and oligomer size should be shown more clearly.
We agree. To this end we have labeled the peaks in the MP histograms in Figure 5 with the oligomeric state of the 2N/2SL7 subunits.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the Authors):
I find the science of the paper to be convincing and compellingly supported.
Thank you for this positive statement.
My primary complaints are with presentation or minor technical questions that, honestly, primarily arise due to my own ignorance and unfamiliarity with some of the techniques employed.
My primary issue is with the figures. I find, generally, the text in axes labels, ticks, and legends to be too small to comfortably read. This is particularly true in the CD spectra and
other data presented in Figures 1D, 2B, 4, 5, 6, and 8.
We agree and have increased the font size of all text and labels of the plots in Figure 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, and 8.
I also found the use of initialisms to be a bit overbearing and inconsistent. For example, the authors repeatedly switch between spelling out "nucleic acid" and the initialism "NA" (which is also never explicitly spelled out in the text). With the already substantial length of the text, my own personal opinion would be to suggest spelling out all initialisms in the interest of making the reading easier.
This is a valid criticism. To improve the readability, we have followed this advice and systematically spelled out “nucleic acid” instead of using “NA”. Similarly, we have now written out full-length instead of the abbreviation FL, and omitted the abbreviation IDR for intrinsically disordered regions, as well as VOC for variant of concern, and AF3 for AlphaFold.
Regarding the reference to mutants, we have now explained upfront the system of Latin and Greek nomenclature we consistently applied.
“We will adopt a nomenclature where the complete set of defining mutations of a variant will be referred to by its Greek letter, i.e., N:P13L/R203K/G204R/G214C is N<sub>l</sub>, and analogously the set of Omicron mutations N:P13L/Δ31-33/R203K/G204R are referred to as N<sub>ο</sub>; see Table 1”
I found the text to be verbose, bordering on overly so; the Introduction is more than two pages long. The section "Enhanced oligomerization of the leucine-rich sequence through cysteine mutations" has two long paragraphs of introduction before the present results are discussed, et cetera. An (admittedly, very rough) estimation of the length of the paper places it at ~9,000 -10,000 words long, and I think that the presentation might benefit from significant editing and
shortening.
We agree the manuscript is longer than would be desirable, and we generally prefer not to insert mini-introductions into Results sections. On the other hand, in order to make a solid contribution to understanding the big picture of fuzzy complexes in molecular evolution of RNA virus proteins it is indispensable to go into the details of RNP assembly and several of the interfaces. Therefore, we feel the length is in the range that it needs to be without losing clarity. In addition, other Reviewer suggestions to extend the discussion, for example, of limitations of VLP assays and the in vivo state of cysteines, conflict with significant shortening.
In the particular case of the cysteine mutations, cited by the Reviewer, we believe it is important to add detailed background on G215C, because the Results proceed in a comparison of the self-association mode between G215C and G214C. This is of significant interest in the present context not only for the independent introduction of interface-enhancing mutations highlighting the evolution of fuzzy complexes, but also because it illustrates the pleomorphic ability of RNPs.
Nonetheless, we have slightly shortened this text and merged the background into a single paragraph. More generally, we have critically reread the text to remove tangential sentences where possible and to make it more concise.
I have a few more specific comments.
In Figure 1A, I suggest explicitly labeling the location of the LRS, as it comes up repeatedly.
Yes, we thank the Reviewer for this suggestion and have introduced this label in Figure 1A.
In Figure 1B, the legend indicates that the red lines indicate "new inter-dimer interactions." However, these red lines are overlayed on a vertical stripe of red squiggles; it is unclear to me and not explicitly described in the legend what these squiggles are meant to illustrate.
We agree this background was confusing. As mentioned in our Response to Reviewer #1 we have replaced the structured background with a solid background and explained in the figure legend that these areas depict regions of self-association.
On lines 44-45, the authors state, "The IDRs amount to 45%, ..." 45% of what?
Thank you, this was unclear. We have now clarified “The IDRs amount to ≈45% of total residues”
In lines 244 - 246, the authors compare the sizes of complexes in reducing versus non- reducing conditions as measured by dynamic light scattering, stating, "However, dynamic light scattering (DLS) revealed the presence of N210-246:G214C complexes with hydrodynamic radii 244 ranging from 6 to 40 nm (in comparison to 1-2 nm for N210- 246:G215C(Zhao et al., 2022)) in reducing conditions, and slightly larger in non-reducing conditions (Supplementary Figure S4)." Using this single statistic seems to me to be a less-than-ideal way of characterizing what seems to me to be happening here. In Supplementary Figure 4, it appears to me that what is happening is that in non-reduced conditions, the sample is monodisperse, whereas in reducing conditions, the distribution becomes polydisperse/bimodal, with two clearly separate populations. I feel that this could use a more
thorough description rather than just stating the overall range of particle sizes.
Yes, the Reviewer is correct – it is indeed a good idea to be more precise here. To this end we have carried out cumulant analyses on the autocorrelation functions, as a time-honored method to quantify the polydispersity. Both samples are polydisperse, but more so in reducing conditions. We have now added “For N210-246:G214C a cumulant analysis results in radii of 8.8 nm and 10.6 nm and polydispersity indices of 0.40 and 0.35 for reducing and non-reducing conditions, respectively”
Finally, I have one remaining comment that is a result of my own inexperience with circular dichroism and interpreting the spectra. For me personally, I would appreciate a more thoroughdescription/illustration of the statistics involved in the CD spectra, but perhaps this is not necessary for people who are more familiar with interpreting these kinds of data. For example, in Figure 1D, it is not clear to me what the error bars/confidence intervals for the CD data look like. I see many squiggles, some of which the authors claim are significant (e.g., the differences between ~215 - 230 nm), and others are not worthy of comment. Let's say, for example, that I fit a smoothed spline through these data and then measure the magnitude of the fluctuations from that spline to define/quantify confidence intervals. What does that distribution look like? Or maybe the confidence intervals are so small that all squiggles are significant?
Thank you, this is a good question. As mentioned in the methods section, the CD spectra shown are averages of triplicate scans. Therefore, it is straightforward to extract the standard deviation at each wavelength from the three measurements (although a spline would probably work just as well). The values are what one would expect for the squiggles to be random noise. In the region 215 – 220 nm characteristic for helical secondary structure the standard deviations are small relative to the separation between curves, which indicates that the differences are highly significant. Naturally, the curves do overlap in other spectral regions, which would make a plot including the wavelength-dependent error bars or confidence bands too crowded. Therefore, we have kept the plot of the averaged triplicate scans, but have now provided the average standard deviations for all species in the figure legend and mentioned their significant separation:
“Triplicate scans yield average standard deviations of 0.13 (N), 0.17 (N+SL7), 0.16 (N<sub>l</sub>), and 0.21 (N<sub>l</sub> +SL7) 10<sup>3</sup> deg cm<sup>2</sup>/dmol, respectively, with non-overlapping confidence bands for the different species, for example, between 215-220 nm.”
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the Authors):
(1) The Discussion reiterates much of the background (mutational tolerance, fuzziness, SLiMs) already covered in the Introduction, diluting focus on the key new findings. The authors should consider shortening and refocusing the discussion on the main contributions in light of existing knowledge of viral assembly.
In the Introduction we have provided background on intrinsically disordered proteins in general and their mutational tolerance, as well as the concept of fuzzy complexes. The first several paragraphs of the Discussion have a different focus, which is protein binding interfaces between viral proteins (obviously key in fuzzy complexes), specifically their modulation and the remarkable de novo introduction of binding interfaces. We believe this deserves emphasis, since this highlights a novel aspect of fuzziness, for the mutant spectrum of RNA viruses to encode a range and of assembly stabilities and architectures.
To reduce redundancy between the end of the Introduction and the beginning of the Discussion, we have shortened the last paragraph of the Introduction and removed its preview of the conclusions, as described in the response to the next comment of the Reviewer (see below).
Unfortunately, the length of the Discussion is dictated in part also by the need to discuss methodological aspects, among them the limitations of VLP assays, and the redox state of the cysteine in the LRS mutants, which were important points recommended by other suggestions of the Reviewers. Similarly, we believe the discussion of other potential functions of Omicron N-arm mutations is warranted, as well as the background of the R203K/G204R double mutation that has attracted significant attention in the field due to its effects on phosphorylation and expression of truncated N species that also form RNPs. Our goal was to integrate the results by us and other laboratories regarding specific mutation effects into a comprehensive picture of molecular evolution of N, which we believe the framework of fuzzy complexes can provide.
(2) The Abstract and early Introduction set a broad stage (IDPs, fuzziness), but don't explicitly state the concrete hypotheses that the experiments test. Please add 2-3 sentences in the Introduction that enumerate testable hypotheses, e.g.:
(a) P13L creates a new N-arm interface that increases RNP stability.
(b) G214C/G215C strengthens LRS oligomerization to stabilize higher-order N assemblies.
We agree the introduction can be improved. However, it seems to us that it cannot be neatly framed in the hypothesis – answer dichotomy, without losing a lot of nuances and without requiring an even longer and more detailed introduction.
One of the main questions is to test whether the framework of fuzzy complexes can be applied to understand molecular evolution of N, and we feel the introduction is already flowing well towards this:
“ … In fuzzy complexes the total binding energy is distributed into multiple distinct ultra-weak interaction sites (Olsen et al., 2017). Similar to individual RNA virus proteins with loose or absent structure, maintaining disorder and a spatial distribution of low-energy interactions in the protein complexes may increase the tolerance for mutations and improve evolvability of protein complexes.\
The unprecedented worldwide sequencing effort of SARS-CoV-2 genomes during its rapid evolution in humans provides a unique opportunity to examine these concepts. ...”
To bring this to a more concrete set of questions in the end, we have shortened and rewritten the last paragraph in the Introduction:
“To examine how architecture and energetics of RNP assemblies can be impacted by N-protein mutations we study a panel of N-proteins derived from ancestral Wuhan-Hu-1 and different VOCs, including Alpha, Delta, Lambda, and Omicron (see Table 1), in biophysical experiments, VLP assays, and mutant virus. Specifically, we ask how the RNP size distribution and life-time is modulated by: (1) the novel binding interface created by the P13L mutation of Omicron; (2) enhancements of other weak self-association interfaces through G215C of Delta and G214C of Lambda; (3) the ubiquitous R203K/G204R double mutation of Alpha, Lambda, and Omicron. We also test whether the P13L mutation improves viral fitness, similar to G215C and R203K/G204R. The results are discussed in the framework of fuzzy complexes and molecular evolution of N in the course of viral adaptation to the human host. Understanding the salient features of the binding interfaces in viral assembly and their evolution expands our foundation for the design of therapeutics such as assembly inhibitors.”
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the previous reviews.
eLife Assessment:
Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive cancers without a cure. Glioblastoma cells are known to have high mitochondrial potential. This useful study demonstrates the critical role of the ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathway in regulating mitochondrial membrane potential and glioblastoma growth. Some assays are incomplete; further revision will improve the significance of this study.
For clarity, we propose revising the second sentence to: "It is well-established that certain cancer cells, such as glioblastoma cells, exhibit elevated mitochondrial membrane potential."
Reviewer #1 (Public Review):
Summary:
Cai et al have investigated the role of msiCAT-tailed mitochondrial proteins that frequently exist in glioblastoma stem cells. Overexpression of msiCAT-tailed mitochondrial ATP synthase F1 subunit alpha (ATP5) protein increases the mitochondrial membrane potential and blocks mitochondrial permeability transition pore formation/opening. These changes in mitochondrial properties provide resistance to staurosporine (STS)-induced apoptosis in GBM cells. Therefore, msiCAT-tailing can promote cell survival and migration, while genetic and pharmacological inhibition of msiCAT-tailing can prevent the overgrowth of GBM cells.
Strengths:
The CAT-tailing concept has not been explored in cancer settings. Therefore, the present provides new insights for widening the therapeutic avenue.
Your acknowledgment of our study's pioneering elements is greatly appreciated.
Weaknesses:
Although the paper does have strengths in principle, the weaknesses of the paper are that these strengths are not directly demonstrated. The conclusions of this paper are mostly well-supported by data, but some aspects of image acquisition and data analysis need to be clarified and extended.
We are grateful for your acknowledgment of our study’s innovative approach and its possible influence on cancer therapy. We sincerely appreciate your valuable feedback. In response, this updated manuscript presents substantial new findings that reinforce our central argument. Moreover, we have broadened our data analysis and interpretation, as well as refined our methodological descriptions.
Reviewer #2 (Public Review):
This work explores the connection between glioblastoma, mito-RQC, and msiCAT-tailing. They build upon previous work concluding that ATP5alpha is CAT-tailed and explore how CAT-tailing may affect cell physiology and sensitivity to chemotherapy. The authors conclude that when ATP5alpha is CAT-tailed, it either incorporates into the proton pump or aggregates and that these events dysregulate MPTP opening and mitochondrial membrane potential and that this regulates drug sensitivity. This work includes several intriguing and novel observations connecting cell physiology, RQC, and drug sensitivity. This is also the first time this reviewer has seen an investigation of how a CAT tail may specifically affect the function of a protein. However, some of the conclusions in this work are not well supported. This significantly weakens the work but can be addressed through further experiments or by weakening the text.
We appreciate the recognition of our study's novelty. To address your concerns about our conclusions, we have revised the manuscript. This revision includes new data and corrections of identified issues. Our detailed responses to your specific points are outlined below.
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations For The Authors):
(1) In Figure 1B, please replace the high-exposure blots of ATP5 and COX with representative results. The current results are difficult to interpret clearly. Additionally, it would be helpful if the author could explain the nature of the two different bands in NEMF and ANKZF1. Did the authors also examine other RQC factors and mitochondrial ETC proteins? I'm also curious to understand why CAT-tailing is specific to C-I30, ATP5, and COX-V, and why the authors did not show the significance of COX-V.
We appreciate your inquiry regarding the data. Additional attempts were made using new patient-derived samples; however, these results did not improve upon the existing ATP5⍺, (NDUS3)C-I30, and COX4 signals presented in the figure. This is possibly due to the fact that CAT-tail modified mitochondrial proteins represent only a small fraction of the total proteins in these cells. It is acknowledged that the small tails visible above the prominent main bands are not particularly distinct. To address this, the revised version includes updated images to better illustrate the differences. We believe the assertion that GBM/GSCs possess CAT-tailed proteins is substantiated by a combination of subsequent experimental findings. The figure (refer to new Fig. 1B) serves primarily as an introduction. It is important to note that the CAT-tailed ATP5⍺ plays a vital role in modulating mitochondrial potential and glioma phenotypes, a function which has been demonstrated through subsequent experiments.
It is acknowledged that the CAT-tail modification is not exclusive to the ATP5⍺protein. ATP5⍺ was selected as the primary focus of this study due to its prevalence in mitochondria and its specific involvement in cancer development, as noted by Chang YW et al. Future research will explore the possibility of CAT tails on other mitochondrial ETC proteins. Currently, NDUS3 (C-I30), ATP5⍺, and COX4 serve as examples confirming the existence of these modifications. It remains challenging to detect endogenous CAT-tailing, and bulk proteomics is not yet feasible for this purpose. COX4 is considered significant. We hypothesize that CAT-tailed COX4 may function similarly to the previously studied C-I30 (Wu Z, et al), potentially causing substantial mitochondrial proteostasis stress.
Concerning RQC proteins, our blotting analysis of GBM cell lines now includes additional RQC-related factors. The primary, more prominent bands (indicated by arrowheads) are, in our assessment, the intended bands for NEMF and ANKZF1. Subsequent blotting analyses showed only single bands for both ANKZF1 and NEMF, respectively. The additional, larger molecular weight band of NEMF, which was initially considered for property analysis (phosphorylation, ubiquitination, etc.), was not examined further as it did not appear in subsequent experiments (refer to new Fig. S1C).
References:
Chang YW, et al. Spatial and temporal dynamics of ATP synthase from mitochondria toward the cell surface. Communications biology. 2023;6(1).
Wu Z, et al. MISTERMINATE Mechanistically Links Mitochondrial Dysfunction With Proteostasis Failure. Molecular cell. 2019;75(4).
(2) In addition to Figure 1B, it would be interesting to explore CAT-tailed mETC proteins in cancer tissue samples.
This is an excellent point, and we appreciate the question. We conducted staining for ATP5⍺ and key RQC proteins in both tumor and normal mouse tissues. Notably, ATP5⍺ in GBM exhibited a greater tendency to form clustered punctate patterns compared to normal brain tissue, and not all of it co-localized with the mitochondrial marker TOM20 (refer to new Fig. S3C-E). Crucially, we observed a significant increase in NEMF expression within mouse xenograft tumor tissues, alongside a decrease in ANKZF1 expression (refer to new Fig. S1A, B). These findings align with our observations in human samples.
(3) Please knock down ATP5 in the patient's cells and check whether both the upper band and lower band of ATP5 have disappeared or not.
This control was essential and has been executed now. To validate the antibody's specificity, siRNA knockdown was performed. The simultaneous elimination of both upper and lower bands upon siRNA treatment (refer to new Fig. S2A) confirms they represent genuine signals recognized by the antibody.
(4) In Figure 1C and ID, add long exposure to spot aggregation and oligomer. Figure 1D, please add the blots where control and ATP5 are also shown in NHA and SF (similar to SVG and GSC827).
New data are included in the revised manuscript to address the queries. Specifically, the new Fig 1D now displays the full queue as requested, featuring blots for Control, ATP5α, AT3, and AT20. Our analysis reveals that AT20 aggregates exhibit higher expression and accumulation rates in GSC and SF cells.
Fig. 1C has been updated to include experimental groups treated with cycloheximide and sgNEMF. Our results show that sgNEMF effectively inhibits CAT-tailing in GBM cell lines, whereas cycloheximide has no impact. After consulting with the Reporter's original creator and optimizing expression conditions, we observed no significant aggregates with β-globin-non-stop protein, potentially due to the length of endogenous CAT-tail formation (as noted by Inada, 2020, in Cell Reports). Our analysis focused on the ratio of CAT-tailed (red box blots) and non-CAT-tailed proteins (green box blots). Comparing these ratios revealed that both anisomycin treatment and sgNEMF effectively hinder the CAT-tailing process, while cycloheximide has no effect.
(5) In Figure 1E, please double-check the results with the figure legend. ATP5A aggregated should be shown endogenously. The number of aggregates shown in the bar graph is not represented in micrographs. Please replace the images. For Figure 1E, to confirm the ATP5-specific aggregates, it would be better if the authors would show endogenous immunostaining of C-130 and Cox-IV.
Labels in Fig. 1E were corrected to reflect that the bar graph in Fig. 1F indicates the number of cells with aggregates, not the quantity of aggregates per cell. The presence
(6) Figure 3A. Please add representative images in the anisomycin sections. It is difficult to address the difference.
We appreciate your feedback. Upon re-examining the Calcein fluorescence intensity data in Fig. 3A, we believe the images accurately represent the statistical variations presented in Fig. 3B. To address your concerns more effectively, please specify which signals in Fig. 3A you find potentially misleading. We are prepared to revise or substitute those images accordingly.
(7) Figure 3D. If NEMF is overexpressed, is the CAT-tailing of ATP 5 reversed?
Thank you. Your prediction aligns with our findings. We've added data to the revised Fig. S6A, B, which demonstrates that both NEMF overexpression and ANKZF1 knockdown lead to elevated levels of CRC. This increase, however, was not statistically significant in GSC cells. A plausible explanation for this discrepancy is that the MPTP of GSC cells is already closed, thus any additional increase in CAT-tailing activity does not result in further amplification.
(8) Figure 3G. Why on the BN page are AT20 aggregates not the same as shown in Figure 2E?
We appreciate your inquiry regarding the ATP5⍺ blots, specifically those in the original Fig. 3G (left) and 2E (right). Careful observation of the ATP5⍺ band placement in these figures reveals a high degree of similarity. Notably, there are aggregates present at the top, and the diffuse signals extend downwards. Given that this is a gradient polyacrylamide native PAGE, the concentration diminishes towards the top. Consequently, the non-rigid nature of the Blue Native PAGE gel may lead to slight variations in the aggregate signals; however, the overall patterns are very much alike. To mitigate potential misinterpretations, we have rearranged the blot order in the new Fig. 3M.
(9) Figure 4D. The amount of aggregation mediated by AT20 is more compared to AT3. Why are there no such drastic effects observed between AT3 and AT20 in the Tunnel assay?
The previous Figure 4D presents the quantification of cell migration from the experiment depicted in Figure 4C. But this is a good point. TUNEL staining results are directly influenced by mitochondrial membrane potential and the state of mitochondrial permeability transition pores
(MPTP), not by the degree of protein aggregation. Our previous experiments showed comparable effects of AT3 and AT20 on mitochondria (Fig. 2E, 3K), which aligns with the expected similar outcomes on TUNEL staining. As for its biological nature, this could be very complicated. We hope to explore it in future studies.
(10) Figure 5C: The role of NEMF and ANKZF1 can be further clarified by conducting Annexin-PI assays using FACS. The inclusion of these additional data points will provide more robust evidence for CAT-tailing's role in cancer cells.
In response to your suggestion, we have incorporated additional data into the revised version.Using the Annexin-PI kit, we labeled apoptotic cells and detected them using flow cytometry (FACS). Our findings indicate that anisomycin pretreatment, NEMF knockdown (sgNEMF), and ANZKF1 upregulation (oeANKZF1) significantly increase the rate of STS-induced apoptosis compared to the control group (refer to new Fig. S9D-G).
(11) Figure 5F: STS is a known apoptosis inhibitor. Why it is not showing PARP cleavage? Also, cell death analysis would be more pronounced, if it could be shown at a later time point. What is the STS and Anisomycin at 24h or 48h time-point? Since PARP is cleaved, it would also be better if the authors could include caspase blots.
I guess what you meant to say here is "Staurosporine is a protein kinase inhibitor that can induce apoptosis in multiple mammalian cell lines." Our study observed PARP cleavage even in GSCs, which are typically more resistant to staurosporine-induced apoptosis (C-PARP in Fig. S9B). The ratio of C-PARP to total PARP increased. We selected a 180-minute treatment duration because longer treatments with STS + anisomycin led to a late stage of apoptosis and non-specific protein degradation (e.g., at 24 or 48 hours), making PARP comparisons less meaningful. Following your suggestion, we also examined caspase 3/7 activity in GSC cells treated with DMSO, CHX, and anisomycin. We found that anisomycin treatment also activated caspases (Fig. S9A).
(12) In Figure 5, the addition of an explanation, how CAT-tailing can induce cell death, would add more information such as BAX-BCL2 ratio, and cytochrome-c release from the mitochondria.
Thank you for your suggestion. In this study, we state that specific CAT-tails inhibit GSC cell death/apoptosis rather than inducing it. Therefore, we do not expect that examining BAX-BCL2 and mitochondrial cytochrome c release would offer additional insights.
(13) To confirm the STS resistance, it would be better if the author could do the experiments in the STS-resistant cell line and then perform the Anisomycin experiments.
Thank you. We should emphasize that our data primarily originates from GSC cells. These cells already exhibit STS-resistance when compared to the control cells (Fig. S8A-C).
(14) It would be more advantageous if the author could show ATP5 CATailed status under standard chemotherapy conditions in either cell lines or in vivo conditions.
This is an interesting question. It's worth exploring this question; however, GSC cells exhibit strong resistance to standard chemotherapy treatments like temozolomide (TMZ).
Additionally, we couldn't detect changes in CAT-tailed ATP5⍺ and thus did not include that data.
(15) In vivo (cancer mouse model or cancer fly model) data will add more weight to the story.
We appreciate your intriguing question. An effective approach would be to test the RQC pathway's function using the Drosophila Notch overexpression-induced brain tumor model. However, Khaket et al. have conducted similar studies, stating, "The RNAi of Clbn, VCP, and Listerin (Ltn), homologs of key components of the yeast RQC machinery, all attenuated NSC over-proliferation induced by Notch OE (Figs. 5A and S5A–D, G)." This data supports our theory, and we have incorporated it into the Discussion. While the mouse model more closely resembles the clinical setting, it is not covered by our current IACUC proposal. We intend to verify this hypothesis in a future study.
Reference:
Khaket TP, Rimal S, Wang X, Bhurtel S, Wu YC, Lu B. Ribosome stalling during c-myc translation presents actionable cancer cell vulnerability. PNAS Nexus. 2024 Aug 13;3(8):pgae321.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations For The Authors):
Figure 1B, C: To demonstrate that Globin, ATP5alpha, and C-130 are CAT-tailed, it is necessary to show that the high mobility band disappears after NEMF deletion or mutagenesis of the NFACT domain of NEMF. This can be done in a cell line. The anisomycin experiment is not convincing because the intensity of the bands drops and because no control is done to show that the effects are not due to translation inhibition (e.g. cycloheximide, which inhibits translation but not CAT tailing). Establishing ATP5alpha as a bonafide RQC substrate and CAT-tailed protein is critical to the relevance of the rest of the paper.
Thank you for suggesting this crucial control experiment. To confirm the observed signal is indeed a bona fide CAT-tail, it's essential to demonstrate that NEMF is necessary for the CAT-tailing process. We have incorporated data from NEMF knockdown (sgNEMF) and cycloheximide treatment into the revised manuscript. Our findings show that both sgNEMF and anisomycin treatment effectively inhibit the formation of CAT-tailing signals on the reporter protein (Fig. 1C). Similarly, NEMF knockdown in a GSC cell line also effectively eliminated CAT-tails on overexpressed ATP5⍺ (Fig. S2B).
In general, the text should be weakened to reflect that conclusions were largely gleaned from artificial CAT tails made of AT repeats rather than endogenously CAT-tailed ATP5alpha. CAT tails could have other sequences or be made of pure alanine, as has been suggested by some studies.
Thank you for your reminder. We have reviewed the recent studies by Khan et al. and Chang et al., and we found their analysis of CAT tail components to be highly insightful. We concur with your suggestion regarding the design of the CAT tail sequence. We aimed to design a tail that maintained stability and resisted rapid degradation, regardless of its length. In the revised version, we clarify that our conclusions are based on artificial CAT tails, specifically those composed of AT repeat sequences (p. 9). We acknowledge that the presence of other sequence components may lead to different outcomes (p. 19).
Reference:
Khan D, Vinayak AA, Sitron CS, Brandman O. Mechanochemical forces regulate the composition and fate of stalled nascent chains. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 14:2024.08.02.606406. Chang WD, Yoon MJ, Yeo KH, Choe YJ. Threonine-rich carboxyl-terminal extension drives aggregation of stalled polypeptides. Mol Cell. 2024 Nov 21;84(22):4334-4349.e7.
Throughout the work (e.g. 3B, C), anisomycin effects should be compared to those with cycloheximide to observe if the effects are specific to a CAT tail inhibitor rather than a translation inhibitor.
We agree that including cycloheximide control experiments is crucial. The revised version now incorporates new data, as depicted in Fig. S5A, B, illustrating alterations in the on/off state of MPTP following cycloheximide treatment. Furthermore, Fig. S6A, B present changes in Calcium Retention Capacity (CRC) under cycloheximide treatment. The consistency of results across these experiments, despite cycloheximide treatment, suggests that anisomycin's role is specifically as a CAT tail inhibitor, rather than a translation inhibitor.
Line 110, it is unclear what "short-tailed ATP5" is. Do you mean ATP5alpha-AT3? If so this needs to be introduced properly. Line 132: should say "may indicate accumulation of CAT-tailed protein" rather than "imply".
We acknowledge your points. We have clarified that the "short-tailed ATP5α" refers to ATP5α-AT3 and incorporated the requested changes into the revised manuscript.
Figure 1C: how big are those potential CAT-tails (need to be verified as mentioned earlier)?They look gigantic. Include a ladder.
In the revised Fig. 1D, molecular weight markers have been included to denote signal sizes. The aggregates in the previous Fig. 1C, also present in the control plasmid, are likely a result of signal overexposure. The CAT-tailed protein is observed just above the intended band in these blots. These aggregates have been re-presented in the updated figures, and their signal intensities quantified.
Line 170: "indicating that GBM cells have more capability to deal with protein aggregation". This logic is unclear. Please explain.
We appreciate your question and have thoroughly re-evaluated our conclusion. We offer several potential explanations for the data presented in Fig. 1D: (1) ATP5α-AT20 may demonstrate superior stability. (2) GSC (GBM) cells might lack adequate mechanisms to monitor protein accumulation. (3) GSC (GBM) cells could possess an increased adaptive capacity to the toxicity arising from protein accumulation. This discussion has been incorporated into the revised manuscript (lines 166-169).
Line 177: how do you know the endogenous ATP5alpha forms aggregates due to CAT-tailing? Need to measure in a NEMF hypomorph.
We understand your concern and have addressed it. Revised Fig. 3G, H demonstrates that a reduction in NEMF levels, achieved through sgNEMF in GSC cells, significantly diminishes ATP5α aggregation. This, in conjunction with the Anisomycin treatment data presented in revised Fig. 3E, F, confirms the substantial impact of the CAT-tailing process on this aggregation.
Line 218: really need a cycloheximide or NEMF hypomorph control to show this specific to CAT-tailing.
We have revised the manuscript to include data from sgNEMF and cycloheximide treatments, specifically Fig. 3G, H, and Fig. S5C, D, as detailed in our response above.
Lines 249,266, Figure 5A: The mentioned experiments would benefit from controls including an extension of ATP5alpha that was not alanine and threonine, perhaps a gly-ser linker, as well as an NEMF hypomorph.
We sincerely appreciate your insightful comments. In response, the revised manuscript now incorporates control data for ATP5α featuring a poly-glycine-serine (GS) tail. This data is specifically presented in Figs. S2E-G, S4E, S7A, D, E, and S8F, G. Our experimental findings consistently demonstrate that the overexpression of ATP5α, when modified with GS tails, had no discernible impact on protein aggregation, mitochondrial membrane potential, GSC cell mobility, or any other indicators assessed in our study.
Figure S5A should be part of the main figures and not in the supplement.
This has been moved to the main figure (Fig. 5C).
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
In this manuscript the authors examine the processing stages involved in perceptual decision-making using a new approach to analysing EEG data, combined with a critical stimulus manipulation. This new EEG analysis method enables single-trial estimates of the timing and amplitude of transient changes in EEG time-series recurrent across trials in a behavioural task. The authors find evidence for five events between stimulus onset and the response in a two-spatial-interval visual discrimination task. By analysing the timing and amplitude of these events in relation to behaviour and the stimulus manipulation, the authors interpret these events as related to separable processing stages for stimulus encoding (first two events), attention orientation (second event), motor planning (fourth event) and decision (deliberation, final event). This is largely consistent with previous findings from both event-related potentials (across trials) and single-trial estimates using decoding techniques and neural network approaches. However, by taking a data-driven approach (as opposed to theory-driven decoding analyses) a more nuanced picture emerges: there are several stimulus encoding steps which may contribute differently to behaviour, and decision processes extend beyond the planning of the motor response.
Strengths:
This work is not only important for the conceptual advance, but also in promoting this new analysis technique, which will likely prove useful in future research. For the broader picture, this work is an excellent example of the utility of neural measures for mental chronometry.
Weaknesses:
Though beyond the scope of this manuscript, these results should be considered within the broader decision-making literature, where task or domain-specific processes may not generalise (for example, in value-based decision-making).
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
From my reading, this study aimed to achieve two things:
(1) A neurally-informed account of how Pieron's and Fechner's laws can apply in concert at distinct processing levels.
(2) A comprehensive map in time and space of all neural events intervening between stimulus and response in an immediately-reported perceptual decision.
I believe that the authors achieved the first point, mainly owing to a clever contrast comparison paradigm, but with good help also from a new topographic parsing algorithm they created. With this, they found that the time intervening between an early initial sensory evoked potential and an "N2" type process associated with launching the decision process varies inversely with contrast according to Pieron's law. Meanwhile, the interval from that second event up to a neural event peaking just before response increases with contrast, fitting Fechner's law, and a very nice finding is that a diffusion model whose drift rates are scaled by Fechner's law, fit to RT, predicts the observed proportion of correct responses very well. These are all strengths of the study.
We thank the reviewer for their comments that added context to the events we detected in relation to previous findings. We also believe that the change in the HMP algorithm suggested by the reviewer improved the precision of our analyses and the manuscript. We respond to the reviewer’s specific comments below.
(1) The second, generally stated aim above is, in the opinion of this reviewer, unconvincing and ill-defined. Presumably, the full sequence of neural events is massively task-dependent, and surely it is more in number than just three. Even the sensory evoked potential typically observed for average ERPs, even for passive viewing, would include a series of 3 or more components - C1, P1, N1, etc. So are some events being missed? Perhaps the authors are identifying key events that impressively demarcate Pieron- and Fechner-adherent sections of the RT, but they might want to temper the claim that they are finding ALL events. In addition, the propensity for topographic parsing algorithms to potentially lump together distinct processes that partially co-evolve should be acknowledged.
We agree with the reviewer that the topographical solutions found by HMP will be dependent on the task and the quality and type of data. We address this point in the last section of the discussion (see also response to R3.5). We would also like to add that the events detected by HMP are, by construction, those that contribute to the RT and not necessarily all ERPs elicited by a stimulus.
In addition to the new last section of the discussion we also make these points clear in the revised manuscript at the discussion start:
“By modeling the recorded single-trial EEG signal between stimulus onset and response as a sequence of multivariate events with varying by-trial peak times, we aimed to detect recurrent events that contribute to the duration of the reaction time in the present perceptual decision-making task”.
Regarding the typical visual ERPs, in response to this comment but also comments R1.2, R1.3 and R2.1, we aimed for a more precise description of the topographies and thus reduced the width of the HMP expected events to 25ms. This ensures that we do not miss events shorter than the initial expectations of 50ms (see Appendix B of Weindel et al., 2024 and also response to R1.3). This new estimation provides evidence for at least two of the visual ERPs that, based on their timings and topographies (in relation with the spatial frequency of the stimulus), we interpret as the N40 and the P100 (see response to R1.5 for the justification of this categorization). We provide a description and justification of the interpretations in the result section “Five trial-recurrent sequential events occur in the EEG during decisions” and the discussion section “Visual encoding time”.
(2) To take a salient example, the last neural event seems to blend the centroparietal positivity with a more frontal midline negativity, some of which would capture the CNV and some motor-execution related components that are more tightly time-locked to, of course, the response. If the authors plotted the traditional single-electrode ERP at the frontal focus and centroparietal focus separately, they are likely to see very different dynamics and contrast- and SAT-dependency. What does this mean for the validity of the multivariate method? If two or more components are being lumped into one neural event, wouldn't it mean that properties of one (e.g., frontal burstiness at response) are being misattributed to the other (centroparietal signal that also peaks but less sharply at response)?
Using the new HMP parameterization described above we show that the reviewer's intuition was correct. Using an expected pattern duration of 25ms the last event in the original manuscript splits in two events. The before-last event, now referred to the lateralized readiness potential (LRP) presents a strong lateralization (Figure 3) with an increased negativity over the motor cortex contralateral to the right hand. The effect of contrast is mostly on the last event that we interpret as the CPP (Figure 5). Despite the improved precision of the topographies of the identified events, it is however to be noted that some components will overlap. If the LRP is generated when a certain amount of evidence is accumulated (e.g. that the CPP crosses a certain value) then a time-based topography will necessarily include that CPP activity in addition to the lateralized potential. We discuss this in the section “Motor execution” of the discussion:
“Adding the abrupt onset of this potential, we believe that this event is the start of motor execution, engaged after a certain amount of evidence. The evidence for this interpretation is manifest in the fact that the event's topography shares some activity with the CPP event that follows, an expected result if the LRP is triggered at a certain amount of evidence, indexed by the CPP”.
(3) Also related to the method, why must the neural events all be 50 ms wide, and what happens if that is changed? Is it realistic that these neural events would be the same duration on every trial, even if their duration was a free parameter? This might be reasonable for sensory and motor components, but unlikely for cognitive.
The HMP method is sensitive to the event's duration as shown in the manuscript about the method (Appendix B of Weindel et al., 2024). Nevertheless as long as the topography in the real data is longer than the expected one it shouldn't be missed (i.e. same goes for by-trial variations in the event width). For this reason we halved the expected event width of 50ms (introduced by the original HsMM-MVPA paper by Anderson and colleagues) in the revision. This new estimation with 25ms thus is much less likely to miss events as evidenced by the new visual and motor events. In the revised manuscript this is addressed at the start of the Results section:
“Contrary to previous applications (Anderson et al.,2016; Berberyan et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2018; Krause et al., 2024) we assumed that the multivariate pattern was represented by a 25ms half-sine as our previous research showed that a shorter expected pattern width increases the likelihood of detecting cognitive events (see Appendix B of Weindel et al., 2024)”.
Regarding the event width as a free parameter this is both technically and statistically difficult to implement as the amount of computing capacity, flexibility and trade-offs among the HMP parameters would, given the current implementation, render the model unfit for most computers and statistically unidentifiable.
(4) In general, I wonder about the analytic advantage of the parsing method - the paradigm itself is so well-designed that the story may be clear from standard average event-related potential analysis, and this might sidestep the doubts around whether the algorithm is correctly parsing all neural events.
Average ERP analysis suffers from an impossibility to differentiate between an effect of an experimental factor on the amplitude vs. on the timing of the underlying components (Luck, 2005). Furthermore the overlap of components across trials bluries the distinction between them. For both reasons we would not be able to reach the same level of certainty and precision using ERP analyses. Furthermore the relatively low number of trials per experimental cell (contrast level X SAT X participant = 6 trials) makes the analyses hard to perform on ERP which typically require more trials per modality. From the reviewer’s comment we understand that this point was not clear. We therefore discuss this in the revision, Section “Functional interpretation of the events” of the results:
“Nevertheless identifying neural dynamics on these ERPs centered on stimulus is complicated by the time variation of the underlying single-trial events (see probabilities displayed in Figure 3 for an illustration and Burle et al., 2008, for a discussion). The likely impact of contrast on both amplitude and time on the underlying single-trial event does not allow one to interpret the average ERP traces as showing an effect in one or the other dimension without strong assumptions (Luck, 2005)”.
(5) In particular, would the authors consider plotting CPP waveforms in the traditional way, across contrast levels? The elegant design is such that the C1 component (which has similar topography) will show up negative and early, giving way to the CPP, and these two components will show opposite amplitude variations (not just temporal intervals as is this paper's main focus), because the brighter the two gratings, the stronger the aggregate early sensory response but the weaker the decision evidence due to Fechner. I believe this would provide a simple, helpful corroborating analysis to back up the main functional interpretation in the paper.
We agree with the suggestion and have introduced the representation on top of Figure 5 for sets of three electrodes in the occipital, posterior and frontal regions. The new panels clearly show an inversion of the contrast effect dependent on the time and locus of the electrodes. We discuss this in Section “Functional interpretation of the events” of the results:
“This representation shows that there is an inversion of the contrast effect with higher contrasts having a higher amplitude on the electrodes associated with visual potentials in the first couple of deciseconds (left panel of Figure 5A) while parietal and frontal electrodes shows a higher amplitude for lower contrasts in later portions of the ERPs (middle and right panel of Figure 5A)”.
To us, this crucially shows that we cannot achieve the same decomposition using traditional ERP analyses. In these plots it appears that while, as described by the reviewer, there is an inversion, the timing and amplitude of the changes due to contrast can hardly be interpreted.
(6) The first component is picking up on the C1 component (which is negative for these stimulus locations), not a "P100". Please consult any visual evoked potential study (e.g., Luck, Hillyard, etc). It is unexpected that this does not vary in latency with contrast - see, for example. Gebodh et al (2017, Brain Topography) - and there is little discussion of this. Could it be that nonlinear trends were not correctly tested for?
We disagree with the reviewer on the interpretation of the ERP. The timing of the detected component is later than the one usually associated with a C1. Furthermore the central display does not create optimal conditions to detect a C1
We do agree that the topography raises the confusion but we believe that this is due to the spatial frequency of the stimulus that generates a high posterior positivity (see references in the following extract). The new HMP solution also now happens to show an effect of contrast on the P100 latencies, we believe this is due to the increased precision in the time location of the component. We discuss this in the “Visual encoding time” section of the discussion:
“The following event, the P100, is expressed around 70ms after the N40, its topography is congruent with reports for stimuli with low spatial frequencies as used in the current study (Kenemans et al., 2002, 2000; Proverbio et al., 1996). The timing of this P100 component is changed by the contrast of the stimulus in the direction expected by the Piéron law (Figure 4A)”.
(7) There is very little analysis or discussion of the second stage linked to attention orientation - what would the role of attention orientation be in this task? Is it spatial attention directed to the higher contrast grating (and if so, should it lateralise accordingly?), or is it more of an alerting function the authors have in mind here?
We agree that we were not specific enough on the interpretation of this attention stage. We now discuss our hypothesis in the section “Attention orientation” of the discussion:
“We do however observe an asymmetry in the topographical map Figure 3. This asymmetry might point to an attentional bias with participants (or at least some participants) allocating attention to one side over the other in the same way as the N2pc component (Luck and Hillyard, 1994, Luck et al., 1997). Based on this collection of observations, we conclude that this third event represents an attention orientation process. In line with the finding of Philiastides et al. (2006), this attention orientation event might also relate to the allocation of resources. Other designs varying the expected cognitive load or spatial attention could help in further interpreting the functional role of this third event”.
We would like to add that it is unlikely that the asymmetry we mention in the discussion cannot stem from the redirection towards higher contrast as the experimental design balanced the side of presentation. We therefore believe that this is a behavioral bias rather than a bias toward the highest contrast stimulus as suggested by the reviewer. We hope that, while more could be tested and discussed, this discussion is sufficient given the current manuscript's goal.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The authors decomposed response times into component processes and manipulated the duration of these processes in opposing directions by varying contrast, and overall by manipulating speed-accuracy tradeoffs. They identify different processes and their durations by identifying neural states in time and validate their functional significance by showing that their properties vary selectively as expected with the predicted effects of the contrast manipulation. They identify 3 processes: stimulus encoding, attention orienting, and decision. These map onto classical event-related potentials. The decision-making component matched the CPP, and its properties varied with contrast and predicted decision-accuracy, while also exhibiting a burst not characteristic of evidence accumulation.
Strengths:
The design of the experiment is remarkable and offers crucial insights. The analysis techniques are beyond state-of-the-art, and the analyses are well motivated and offer clear insights.
Weaknesses:
It is not clear to me that the results confirm that there are only 3 processes, since e.g., motor preparation and execution were not captured. While the authors discuss this, this is a clear weakness of the approach, as other components may also have been missed. It is also unclear to what extent topographies map onto processes, since, e.g., different combinations of sources can lead to the same scalp topography.
We thank the reviewer for their kind words and for the attention they brought on the question of the missing motor preparation event. In light of this comment (and also R1.1, R3.3) the revised manuscript uses a finer grained approach for the multivariate event detection. This preciser estimation comes from the use of a shorter expected pattern in which the initial expectation of a 50ms half-sine was halved, therefore ensuring that we do not miss events shorter than the initial expectations (see Appendix B of Weindel et al., 2024 and also response to R1.3). In the new solution the motor component that the reviewer expected is found as evidenced by the topography of the event, its lateralization and a time-to-response congruent with a response execution event. This is now described in the section “Motor execution” of the revised manuscript:
“The before last event, identified as the LRP, shows a strong hemispheric asymmetry congruent with a right hand response. The peak of this event is approximately 100 ms before the response which is congruent with reports that the LRP peaks at the onset of electromyographical activity in the effector muscle (Burle et al., 2004), typically happening 100ms before the response in such decision-making tasks (Weindel et al., 2021). Furthermore, while its peak time is dependent on contrast, its expression in the EEG is less clearly related to the contrast manipulation than the following CPP event”.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
In this manuscript, the authors examine the processing stages involved in perceptual decision-making using a new approach to analysing EEG data, combined with a critical stimulus manipulation. This new EEG analysis method enables single-trial estimates of the timing and amplitude of transient changes in EEG time-series, recurrent across trials in a behavioural task. The authors find evidence for three events between stimulus onset and the response in a two-spatial-interval visual discrimination task. By analysing the timing and amplitude of these events in relation to behaviour and the stimulus manipulation, the authors interpret these events as related to separable processing stages for stimulus encoding, attention orientation, and decision (deliberation). This is largely consistent with previous findings from both event-related potentials (across trials) and single-trial estimates using decoding techniques and neural network approaches.
Strengths:
This work is not only important for the conceptual advance, but also in promoting this new analysis technique, which will likely prove useful in future research. For the broader picture, this work is an excellent example of the utility of neural measures for mental chronometry.
We appreciate the very positive review and thank the reviewer for pointing out important weaknesses in our original manuscript and also providing resources to address them in the recommendations to authors. Below we comment on each identified weakness and how we addressed them.
Weaknesses:
(1) The manuscript would benefit from some conceptual clarifications, which are important for readers to understand this manuscript as a stand-alone work. This includes clearer definitions of Piéron's and Fechner's laws, and a fuller description of the EEG analysis technique.
We agree that the description of both laws were insufficient, we therefore added the following text in the last paragraph of the introduction:
“Piéron’s law predicts that the time to perceive the two stimuli (and thus the choice situation) should follow a negative power law with the stimulus intensity (Figure 1, green curve). In contradistinction, Fechner’s law states that the perceived difference between the two patches follows the logarithm of the absolute contrast of the two patches (Figure 1, yellow curve). As the task of our participants is to judge the contrast difference, Piéron’s law should predict the time at which the comparison starts (i.e. the stimuli become perceptible), while Fechner’s law should implement the comparison, and thus decision, difficulty”.
Regarding the EEG analysis technique we added a few elements at the start of the result:
“The hidden multivariate pattern model (HMP) implemented assumed that a task-related multivariate pattern event is represented by a half-sine whose timing varies from trial to trial based on a gamma distribution with a shape parameter of 2 and a scale, controlling the average latency of the event, free-to-vary per event (Weindel et al., 2024)”.
We also made the technique clearer at the start of the discussion:
“By modeling the recorded single-trial EEG signal between stimulus onset and response as a sequence of multivariate events with varying by-trial peak times, we aimed to detect recurrent events that contribute to the duration of the reaction time in the present perceptual decision-making task. In addition to the number of events, using this hidden multivariate pattern approach (Weindel et al., 2024) we estimated the trial-by-trial probability of each event’s peak, therefore accessing at which time sample each event was the most likely to occur”.
Additionally, we added a proper description in the method section (see the new first paragraph of the “Hidden multivariate pattern” subsection).
(2) The manuscript, broadly, but the introduction especially, may be improved by clearly delineating the multiple aims of this project: examining the processes for decision-making, obtaining single-trial estimates of meaningful EEG-events, and whether central parietal positivity reflects ramping activity or steps averaged across trials.
For the sake of clarity we removed the question of the ramping activity vs steps in the introduction and focused on the processes in decision-making and their single-trial measurement as this is the main topic of the paper. Furthermore the references provided by the reviewer allowed us to write a more comprehensive review of previous studies and how the current study is in line with those. These changes are mainly manifested in these new sentences:
“As an example Philiastides et al. (2006) used a classifier on the EEG activity of several conditions to show that the strength of an early EEG component was proportional to the strength of the stimulus while a later component was related to decision difficulty and behavioral performance (see also Salvador et al., 2022; Philiastides and Sajda, 2006). Furthermore the authors interpreted that a third EEG component was indicative of the resource allocated to the upcoming decision given the perceived decision difficulty. In their study, they showed that it is possible to use single-trial information to separate cognitive processes within decision-making. Nevertheless, their method requires a decoding approach, which requires separate classifiers for each component of interest and restrains the detection of the components to those with decodable discriminating features (e.g. stimuli with strong neural generators such as face stimuli, see Philiastides et al., 2006)”.
(3) A fuller discussion of the limitations of the work, in particular, the absence of motor contributions to reaction time, would also be appreciated.
As laid out in responses to comments R1.1 and R2 the new estimates now include evidence for a motor preparation component. We discuss this in the new “motor execution” paragraph in the discussion section. Additionally we discuss the limitation of the study and the method in the two last paragraphs of the discussion (in the new Section “Generalization and limitation”).
(4) At times, the novelty of the work is perhaps overstated. Rather, readers may appreciate a more comprehensive discussion of the distinctions between the current work and previous techniques to gauge single-trial estimates of decision-related activity, as well as previous findings concerning distinct processing stages in decision-making. Moreover, a discussion of how the events described in this study might generalise to different decision-making tasks in different contexts (for example, in auditory perception, or even value-based decision-making) would also be appreciated.
We agree that the original text could be read as overstating. In addition to the changes linked to R3.2 we also now discuss the link with the previous studies in the before-last paragraph of the discussion before the conclusion in the new “Generalization and limitations” section:
“The present study showed what cognitive processes are contributing to the reaction time and estimated single-trial times of these processes for this specific perceptual decision-making task. The identified processes and topographies ought to be dependent on the task and even the stimuli (e.g. sensory events will change with the sensory modality). More complex designs might generate a higher number of cognitive processes (e.g. memory retrieval from a cue, Anderson et al., 2016) and so could more natural stimuli which might trigger other processes in the EEG (e.g. appraisal vs. choice as shown by Frömer et al., 2024). Nevertheless, the observation of early sensory vs. late decision EEG components is likely to generalize across many stimuli and tasks as it has been observed in other designs and methods (Philiastides et al., 2006; Salvador et al., 2022). To these studies we add that we can evaluate the trial-level contribution, as already done for specific processes (e.g. Si et al., 2020; Sturm et al., 2016), for the collection of events detected in the current study”.
Reviewing Editor Comments:
As you will see, all three reviewers agree that the paper makes a valuable contribution and has many strengths. You will also see that they have provided a range of constructive comments highlighting potential issues with the interpretation of the outcomes of your signal decomposition method. In particular, all three reviewers point out that your results do not identify separate motor preparation signals, which we know must be operating on this type of task. The reviewers suggest further discussion of this issue and the potential limitations of your analysis approach, as well as suggesting some additional analyses that could be run to explore this further. While making these changes would undoubtedly enhance the paper and the final public reviews, I should note that my sense is that they are unlikely to change the reviewers' ratings of the significance of the findings and the strength of evidence in the final eLife assessment
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Abstract: "choice onset" is ill-defined and not the label most would give the start of the RT interval. Do you mean stimulus onset?
We replaced with "choice onset" with "stimulus onset" in the abstract
(2) Similarly "choice elements" in the introduction seem to refer to sensory attributes/objects being decided about?
We replaced "choice-elements" with "choice-relevant features of the stimuli"
(3) "how the RT emerges from these putative components" - it would be helpful to specify more what level of answer you're looking for, as one could simply answer "when they're done."
We replaced with "how the variability in RTs emerges from these putative components"
(4) Line 61-62: I'm not sure this is a fully correct characterisation of Frömer et al. It was not similar in invoking a step function - it did not invoke any particular mechanism or function, and in that respect does not compare well to Latimer et al. Also, I believe it was the overlap of stimulus-locked components, not response-locked, that they argued could falsely generate accumulator-like buildup in the response-locked ERP.
We indeed wrongly described Frömer et al. The sentence is now "In human EEG data, the classical observation of a slowly evolving centro-parietal positivity, scaling with evidence accumulation, was suggested to result from the overlap of time-varying stimulus-related activity in the response-locked event related potential"
(5) Line 78: Should this be single-trial *latency*?
This referred to location in time but we agree that the term is confusing and thus replaced it with latencies.
(6) The caption of Figure 1 should state what is meant by the y-axis "time"
We added the sentence "The y-axis refers the time predicted by each law given a contrast value (x-axis) and the chosen set of parameters." in the caption of Figure 1
(7) Line 107: Is this the correct description of Fechner's law? If the perceived difference follows the log of the physical difference, then a constant physical difference should mean a constant perceived difference. Perhaps a typo here.
This was indeed a typo we replaced the corresponding part of the sentence with "the perceived difference between the two patches follows the logarithm of the absolute contrast of the two patches"
(8) Line 128: By scale, do you mean magnitude/amplitude?
No, this refers to the parameter of a gamma distribution. To clarify we edited the sentence: "based on a gamma distribution with a shape parameter of 2 and a scale parameter, controlling the average latency of the event, free-to-vary per event"
(9) The caption of Figure 3 is insufficient to make sense of the top panel. What does the inter-event interval mean, and why is it important to show? What is the "response" event?
We agree that the top panel was insufficiently described. To keep the length of the paper short and because of the relatively low amount of information provided by these panels we replaced them for a figure only showing the average topographies as well as the asymmetry tests for each event.
(10) Figure 4: caption should say what the top vs bottom row represents (presumably, accuracy vs speed emphasis?), and what the individual dots represent, given the caption says these are "trial and participant averaged". A legend should be provided for the rightmost panels.
We agree and therefore edited Figure 4. The beginning of the caption mentioned by the reviewer now reads: “A) The panels represent the average duration between events for each contrast level, averaged across participants and trials (stimulus and response respectively as first and last events) for accuracy (top) and speed instructions (bottom).”. Additionally we added legends for the SAT instructions and the model fits.
(11) Line 189: argued for a decision-making role of what?
Stafford and Gurney (2004) proposed that Pieron’s law could reflect a non-linear transformation from sensory input to action outcomes, which they argued reflected a response mechanism. We (Van Maanen et al., 2012) specified this result by showing that a Bayesian Observer Model in which evidence for two alternative options was accumulated following Bayes Rule indeed predicted a power relation between the difference in sensory input of the two alternatives, and mean RT. However, the current data suggest that such an explanation cannot be the full story, as also noted by R3. To clarify this point we replaced the comment by the following sentence:
“Note that this observation is not necessarily incongruent with theoretical work that argued that Piéron’s law could also be a result of a response selection mechanism (Stafford and Gurney, 2004; Van Maanen et al., 2012; Palmer et al., 2005). It could be that differences in stimulus intensity between the two options also contribute to a Piéron-like relationship in the later intervals, that is convoluted with Fechner’s law (see Donkin and Van Maanen, 2014 for a similar argument). Unfortunately, our data do not allow us to discriminate between a pure logarithmic growth function and one that is mediated by a decreasing power function”.
(12) Table 2: There is an SAT effect even on the first interval, which is quite remarkable and could be discussed more - does this mean that the C1 component occurs earlier under speed pressure? This would be the first such finding.
The original event we qualified as a P100 was sensitive to SAT but the earliest event is now the N40 and isn’t statistically sensitive to speed pressure in this data. We believe that the fact that the P100 is still sensitive to SAT is not a surprise and therefore do not outline it.
(13) Line 221: "decrease of activation when contrast (and thus difficulty) increases" - is this shown somewhere in the paper?
The whole section for this analysis was rewritten (see comment below)
(14) I find the analysis of Figure 5 interesting, but the interpretation odd. What is found is that the peak of the decision signal aligns with the response, consistent with previous work, but the authors choose to interpret this as the decision signal "occurring as a short-lived burst." Where is the quantitative analysis of its duration across trials? It can at least be visually appraised in the surface plot, and this shows that the signal has a stimulus-locked onset and, apart from the slowest RTs, remains present and for the most part building, until response. What about this is burst-like? A peak is not a burst.
This was the residue of a previous version of the paper where an analysis reported that no evidence accumulation trace was found. But after proper simulations this analysis turned out to be false because of a poor statistical test. Thus we removed this paragraph in the revised manuscript and Figure 5 has now been extended to include surface plots for all the events.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
Overall, I really enjoyed reading this paper. However, in some places the approach is a bit opaque or the results are difficult to follow. As I read the paper, I noted:
Did you do a simple DDM, or did you do a collapsing bound for speed?
The fitted DDM was an adaptation of the proportional rate diffusion model. We make this clearer at the end of the introduction: "Given that Fechner’s law is expected to capture decision difficulty we connected this law to the classical diffusion decision models by replacing the rate of accumulation with Fechner’s law in the proportional rate diffusion model of Palmer et al.(2005).”
It is confusing that the order of intervals in the text doesn't match the order in the table. It might be better to say what events the interval is between rather than assuming that the reader reconstructs.
We agree and adapted the order in both the text and the table. The table is now also more explicit (e.g. RT instead of S-R)
Otherwise, I do wonder to what extent the method is able to differentiate processes that yield similar scalp topographies and find it a bit concerning that no motor component was identified.
We believe that the new version with the LRP/CPP is a demonstration that the method can handle similar topographies. The method can handle events with close topographies as long as they are separate in time, however if they are not sequential to one another the method cannot capture both events. We now discuss this, in relation with the C1/P100 overlap, in the discussion section “Visual encoding time”:
“Nevertheless this event, seemingly overlapping with the P100 even at the trial level (Figure 5C), cannot be recovered by the method we applied. The fact that the P100 was recovered instead of the C1 could indicate that only the timing of the P100 contributes to the RT (see Section 3 of Weindel et al., 2024)”.
And we more generally address the question of overlap in the new section “Generalization and limitation”.
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
Major Comments:
(1) If we agree on one thing, it is that motor processes contribute to response time. Line 364: "In the case of decision-making, these discrete neural events are visual encoding, attention-orientation, and decision commitment, and their latency make up the reaction time." Does the third event, "decision commitment", capture both central parietal positivity (decision deliberation) and motor components? If so, how can the authors attribute the effects to decision deliberation as opposed to motor preparation?
Thanks to the suggestions also in the public part. This main problem is now addressed as we do capture both a motor component and a decision commitment.
Line 351 suggests that the third event may contain two components.
This was indeed our initial, badly written, hypothesis. Nevertheless the new solution again addresses this problem.
The time series in Figure 6 shows an additional peak that is not evident in the simulated ramp of Appendix 1.
This was probably due to the overlap of both the CPP and the LRP. It is now much clearer that the CPP looks mostly like a ramp while the LRP looks much more like a burst-like/peaked activity. We make this clear in the “Decision event” paragraph of the discussion section:
“Regarding the build-up of this component, the CPP is seen as originating from single-trial ramping EEG activities but other work (Latimer et al., 2015; Zoltowski et al., 2019) have found support for a discrete event at the trial-level. The ERPs on the trial-by-trial centered event in Figure 5 show support for both accounts. As outlined above, the LRP is indeed a short burst-like activity but the build-up of the CPP between high vs low contrast diverges much earlier than its peak”.
Previous analyses (Weindel et al., 2024) found motor-related activity from central parietal topographies close to the response by comparing the difference in single-trial events on left- vs right-hand response trials. The authors suggest at line 315 that the use of only the right hand for responding prevented them from identifying a motor event.
The use of only the right hand should have made the event more identifiable because the topography would be consistent across trials (rather than inverting on left vs right hand response trials).
The reviewer is correct, in the original manuscript we didn’t test for lateralization, but the comment of the reviewer gave us the idea to explicitly test for the asymmetry (Figure 3). This test now clearly shows what would be expected for a motor event with a strong negativity over the left motor cortex.
The authors state on line 422 that the EEG data were truncated at the time of the response.
Could this have prevented the authors from identifying a motor event that might overlap with the timing of the response?
We thank the reviewer for this suggestion. This would have been a possibility but the problem is that adding samples after the response also adds the post-response processes (error monitoring, button release, stimulus disappearance, etc.). While increasing the samples after the response is definitely something that we need to inspect, we think that the separation we achieved in this revision doesn’t call for this supplementary analysis.
The largest effects of contrast on the third event amplitude appear around the peak as opposed to the ramp. If the peak is caused by the motor component, how does this affect the conclusions that this third event shows a decision-deliberation parietal processes as opposed to a motor process (a number of studies suggest a causal role for motor processes in decision-making e.g. Purcell et al., 2010 Psych Rev; Jun et al., 2021 Nat Neuro; Donner et al., 2009 Curr Bio).
This result now changed and it does look like the peak capturing most of the effect is no longer true. We do however think that there might be some link to theories of motor-related accumulation. We therefore added this to the discussion in the Motor execution section:
“Based on all these observations, it is therefore very likely that this LRP event signs the first passage of a two-step decision process as suggested by recent decision-making models (Servant et al., 2021; Verdonck et al., 2021; Balsdon et al., 2023)”.
I would suggest further investigation into the motor component (perhaps by extending the time window of analysed EEG to a few hundred ms after the response) and at least some discussion of the potential contribution of motor processes, in relation to the previous literature.
We believe that the absence of a motor component is sufficiently addressed in the revised manuscript and in the responses to the other comments.
(2) What do we learn from this work? Readers would appreciate more attention to previous findings and a clearer outline of how this work differs. Two points stand out, outlined below. I believe the authors can address these potential complaints in the introduction and discussion, and perhaps provide some clarification in the presentation of the results.
In the introduction, the authors state that "... to date, no study has been able to provide single-trial evidence of multiple EEG components involved in decision-making..." (line 64). Many readers would disagree with this. For example, Philiastides, Ratcliff, & Sadja (2006) use a single-trial analysis to unravel early and late EEG components relating to decision difficulty and accuracy (across different perceptual decisions), which could be related to the components in the current work. Other, network-based single-trial EEG analyses (e.g., Si et al., 2020, NeuroImage, Sturn et al., 2016 J Neurosci Methods) could also be related to the current component approach. Yet other approaches have used inverse encoding models to examine EEG components related to separable decision processes within trials (e.g., Salvador et al., 2022, Nat Comms). The results of the current work are consistent with this previous work - the two components from Philiastides et al., 2006 can be mapped onto the components in the current work, and Salvador et al., 2022 also uncover stimulus- and decision-deliberation related components.
We completely agree with the reviewer that the link to previous work was insufficient. We now include all references that the reviewer points out both in the introduction (see response R3.2) and in the discussion (see response R3.4). We wish to thank the reviewer for bringing these papers to our attention as they are important for the manuscript.
The authors relate their components to ERPs. This prompts the question of whether we would get the same results with ERP analyses (and, on the whole, the results of the current work are consistent with conclusions based on ERP analyses, with the exception of the missing motor component). It's nice that this analysis is single-trial, but many of the follow-up analyses are based on grouping by condition anyway. Even the single-trial analysis presented in Figure 4 could be obtained by median splits (given the hypotheses propose opposite directions of effects, except for the linear model).
We do not agree with the reviewer in the sense that classical ERP analyses would require much more data-points. The performance of the method is here to use the information shared across all contrast levels to be able to model the processing time of a single contrast level (6 trials per participant). Furthermore, as stated in the response to R1.4 and R1.5, the aim of the paper is to have the time of information processing components which cannot be achieved with classical ERPs without strong, and likely false, assumptions.
Medium Comments:
(1) The presentation of Piéron's law for the behavioural analysis is confusing. First, both laws should be clearly defined for readers who may be unfamiliar with this work. I found the proposal that Piéron's law predicts decreasing RT for increasing pedestal contrast in a contrast discrimination paradigm task surprising, especially given the last author's previous work. For example, Donkin and van Maanen (2014) write "However, the commonality ofPiéron's Law across so many paradigms has lead researchers (e.g., Stafford & Gurney, 2004; Van Maanen et al., 2012) to propose that Piéron's Law is unrelated to stimulus scaling, but is a result of the architecture of the response selection (or decision making) process." The pedestal contrast is unrelated to the difficulty of the contrast discrimination task (except for the consideration of Fechner's law). Instead, Piéron's law would apply to the subjective difference in contrast in this task, as opposed to the pedestal contrast. The EEG results are consistent with these intuitions about Piéron's law (or more generally, that contrast is accumulated over time, so a later EEG component for lower pedestal contrast makes sense): pedestal contrast should lead to faster detection, but not necessarily faster discrimination. Perhaps, given the complexity of the manuscript as a whole, the predictions for the behavioural results could be simplified?
We agree that the initial version was confusing. We now clarified the presentation of Piéron's law at the end of the introduction (see also response to R2).
Once Fechner's law is applied, decision difficulty increases with increasing contrast, so Piéron's law on the decision-relevant intensity (perceived difference in contrast) would also predict increasing RT with increasing pedestal contrast. It is unlikely that the data are of sufficient resolution to distinguish a log function from a power of a log function, but perhaps the claim on line 189 could be weakened (the EEG results demonstrate Piéron's law for detection, but do not provide evidence against Piéron's law in discrimination decisions).
This is an excellent observation, thank you for bringing it to our attention. Indeed, the data support the notion that Pieron’s law is related to detection, but do not rule out that it is also related to decision or discrimination. In earlier work, we (Donkin & Van Maanen, 2014) addressed this question as well, and reached a similar conclusion. After fitting evidence accumulation models to data, we found no linear relationship between drift rates and stimulus difficulty, as would have been the case if Pieron's law could be fully explained by the decision process (as -indirectly- argued by Stafford & Gurney, 2004; Van Maanen et al., 2012). The fact that we observed evidence for a non-linear relationship between drift rates and stimulus difficulty led us to the same conclusion, that Pieron’s law could be reflected in both discrimination and decision processes. We added the following comment to the discussion about the functional locus of Pieron's law to clarify this point:
“Note that this observation is not necessarily incongruent with theoretical work that argued that Piéron’s law could also be a result of a response selection mechanism (Stafford and Gurney, 2004; Van Maanen et al., 2012; Palmer et al., 2005). It could be that differences in stimulus intensity between the two options also contribute to a Piéron like relationship in the later intervals, that is convoluted with Fechner’s law (see Donkin and Van Maanen, 2014, for a similar argument). Unfortunately, our data do not allow us to discriminate between a pure logarithmic growth function and one that is mediated by a decreasing power function”.
(2) Appendix 1 shows that the event detection of the HMP method will also pick up on ramping activity. The description of the problem in the introduction is that event-like activity could look like ramping when averaged across trials. To address this problem, the authors should simulate events (with some reasonable dispersion in timing such that they look like ramping when averaged) and show that the HMP method would not pull out something that looked like ramping. In other words, the evidence for ramping in this work is not affected by the previously identified confounds.
We agree that this demonstration was necessary and thus added the suggested simulation to Appendix 1. As can be seen in the Figure 1 of the appendix, when we simulate a half-sine the average ERP based on the timing of the event looks like a half-sine.
(3) Some readers may be interested in a fuller discussion of the failure of the Fechner diffusion model in the speed condition.
We are unsure which failure the reviewer refers to but assumed it was in relation to the behavioral results and thus added:
It is unlikely that neither Piéron nor Fechner law impact the RT in the speed condition. Instead this result is likely due to the composite nature of the RT where both laws co-exist in the RT but cancel each other out due to their opposite prediction.
Minor Comments:
(1) "By-trial" is used throughout. Normally, it is "trial-by-trial" or "single-trial" or "trial-wise".
We replaced all occurrences of “by-trial” with the three terms suggested were appropriate.
(2) Line 22: "The sum of the times required for the completion of each of these precessing steps is the reaction time (RT)." The total time required. Processing.
Corrected for both.
(3) Line 26/27: "Despite being an almost two century old problem (von Helmholtz, 2021)." Perhaps the citation with the original year would make this point clearer.
We agree and replaced the citation.
(4) Line 73: "accounted by estimating". Accounted for by estimating.
Corrected.
(5) Line 77 "provides an estimation on the." Of the.
Corrected.
(6) Line 86: "The task of the participants was to answer which of two sinusoidal gratings." The picture looks like Gabor's? Is there a 2d Gaussian filter on top of the grating? Clarify in the methods, too.
We incorrectly described the stimuli as those were indeed just Gabor’s. This is now corrected both in the main text and the method section.
(7) Figure 1 legend: "The Fechner diffusion law" Fechner's law or your Fechner diffusion model?
Law was incorrect so we changed to model as suggested.
(8) Line 115: "further allows to connects the..." Allows connecting the.
Corrected.
(9) Line 123: "lower than 100 ms or higher than..." Faster/slower.
Corrected.
(10) Line 131: "To test what law." Which law.?
Corrected to model.
(11) Figure 2 legend: "Left: Mean RT (dot) and average fit (line) over trials and participants for each contrast level used." The fit is over trials and participants? Each dot is? Average trials for each contrast level in each participant?
This sentence was corrected to “Mean RT (dot) for each contrast level and averaged predictions of the individual fits (line) with Accuracy (Top) and Speed (Bottom) instructions.”.
(12) Line 231: "A comprehensive analysis of contrast effect on". The effect of contrast on.
This title was changed to “functional interpretation of the events”.
(13) Line 23: "the three HMP event with". Three HMP events.
The sentence no longer exists in the revised manuscript.
(14) Line 270: "Secondly, we computed the Pearson correlation coefficient between the contrast averaged proportion of correct." Pearson is for continuous variables. Proportion correct is not continuous. Use Spearman, Kendall, or compute d'.
The reviewer rightly pointed out our error, we corrected this by computing Spearman correlation.
(15) Line 377: "trial 𝑛 + 1 was randomly sampled from a uniform distribution between 0.5 and 1.25 seconds." It's just confusing why post-response activity in Figure 5 does look so consistent. Throughout methods: "model was fitted" should be "was fit", and line 448, "were split".
We do not have a specific hypothesis of why the post-response activity in the previous Figure 5 was so consistent. Maybe the Gaussian window (same as in other manuscripts with a similar figure, e.g. O’Connell et al. 2012) generated this consistency. We also corrected the errors mentioned in the methods.
(16) The linear mixed models paragraph is a bit confusing. Can it clearly state which data/ table is being referred to and then explain the model? "The general linear mixed model on proportion of correct responses was performed using a logit link. The linear mixed models were performed on the raw milliseconds scale for the interval durations and on the standardized values for the electrode match." We go directly from proportion correct to raw milliseconds...
The confusion was indeed due to the initial inclusion of a general linear mixed model on proportion correct which was removed as it was not very informative. The new revision should be clearer on the linear mixed models (see first sentence of subsection ‘linear mixed models' in the method section).
(17) A fuller description of the HMP model would be appreciated.
We agree that this was necessary and added the description of the HMP model in the corresponding method section “Hidden multivariate pattern” in addition to a more comprehensive presentation of HMP in the first paragraph of the Result and Discussion sections.
(18) Line 458: "Fechner's law (Fechner, 1860) states that the perceived difference (𝑝) between the two patches follows the logarithm of the difference in physical intensity between..." ratio of physical intensity.
Corrected.
(19) P is defined in equations 2 and 4. I would include the beta in equation 4, like in equation 2, then remove the beta from equations 3 and 5 (makes it more readable). I would also just include the delta in equation 2, state that in this case, c1 = c+delta/2 or whatever.
This indeed makes the equation more readable so we applied the suggestions for equations 2, 3, 4 and 5. The delta was not added in equation 2 but instead in the text that follows:
“Where 𝐶1 = 𝐶0 + 𝛿, again with a modality and individual specific adjustment slope (𝛽).”
(20) The appendix suggests comparing the amplitudes with those in Figure 3, but the colour bar legend is missing, so the reader can only assume the same scale is used?
We added the color bar as it was indeed missing. Note though that the previous version displayed the estimation for the simulated data while this plot in the revised manuscript shows the solution on real data obtained after downsampling the data (and therefore look for a larger pattern as in the main text). We believe that this representation is more useful given that the solution for the downsampled data is no longer the same as the one in the main text (due to the difference in pattern width).
survey data showing sex differences in political values.
The Political Parties are Gender Sex Based now,
I like the idea of a Man get's a vote, if he get's married he get's two, and if he has over 3+ children then has three votes. Get divorced, only gets one now
ECU Digital Tools Checklist.pdf
The checklist feels too extensive for what we would ask a student to do. Suggest pairing it back alot or sticking with the 3 S style of short evaluation. Just Part B comparison for example.
Santé Mentale et Addictions : De l'Intime au Populationnel
Ce document de synthèse analyse les thèmes centraux de la leçon inaugurale de Maria Melchior, épidémiologiste et titulaire de la chaire Santé Publique 2025-2026 au Collège de France.
La santé mentale, désignée grande cause nationale pour 2025 et 2026, est présentée comme un défi majeur qui nécessite une double approche : une compréhension empathique de la souffrance intime et une analyse rigoureuse des dynamiques populationnelles.
L'épidémiologie offre un regard distancié mais essentiel pour quantifier l'ampleur du phénomène, identifier les facteurs de risque et éclairer les politiques publiques.
Les données révèlent une prévalence élevée en France : un adulte sur dix souffre de dépression ou d'anxiété, et une part significative de la population, y compris les jeunes, est touchée par des conduites addictives (tabac, alcool, cannabis, mais aussi jeux et internet).
Un constat central est celui des inégalités sociales "massives" qui se manifestent dès l'enfance, creusant un fossé entre les populations défavorisées, plus à risque et ayant moins accès aux soins, et les plus privilégiées.
L'étude de la santé mentale se heurte à des défis de taille, notamment une forte stigmatisation persistante dans la société et des difficultés métrologiques dues à l'absence de marqueurs biologiques objectifs.
La stratégie de santé publique la plus efficace, selon le "paradoxe de la prévention" de Geoffrey Rose, ne consiste pas uniquement à cibler les individus les plus à risque, mais à améliorer la santé mentale de l'ensemble de la population en agissant sur les déterminants sociaux.
Le concept d' "universalisme proportionné" affine cette approche en combinant des actions universelles avec un soutien renforcé pour les groupes les plus vulnérables.
En conclusion, l'amélioration de la santé mentale collective passe par des interventions qui dépassent le système de soins pour s'attaquer aux racines du mal-être : l'isolement, les inégalités sociales, et les conditions de vie et de travail.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
L'analyse de la santé mentale exige une articulation constante entre la souffrance individuelle et les dynamiques collectives. L'épidémiologie, bien que centrée sur l'étude des populations, ne peut ignorer la dimension subjective et intime du mal-être psychique.
Maria Melchior insiste sur la nécessité de ne jamais oublier que "derrière les concepts, les théories et les chiffres, il y a de vraies personnes et des histoires singulières".
Cette prise de conscience, issue d'une expérience personnelle durant ses études de psychologie, souligne que toute démarche de recherche sur la santé mentale doit conserver une forme d'empathie et s'interroger sur le vécu des personnes concernées.
S'intéresser à la santé mentale, même à grande échelle, requiert d'imaginer une personne réelle et ce qui se passe en elle.
L'épidémiologie se distingue par sa démarche observationnelle et intégrative.
Elle ne se limite pas aux mécanismes biologiques, mais englobe une large gamme de facteurs de risque : psychologiques, médicaux, comportementaux, sociaux et économiques.
• Objectif : Identifier les facteurs qui augmentent ou diminuent le risque de troubles psychiques et d'addictions à l'échelle d'une population.
• Méthode : Mettre en place des enquêtes de grande ampleur pour dégager des tendances concernant les variations de risque dans le temps, l'espace et entre les sous-groupes.
• Finalité : Passer de situations particulières à des points communs pour "monter en généralité" et identifier les forces qui régissent les comportements humains. Les chiffres produits peuvent ainsi éclairer les politiques publiques et, en retour, aider à mieux saisir des situations individuelles.
Les grandes enquêtes épidémiologiques menées en France, notamment par Santé publique France et l'Observatoire français des drogues et des tendances addictives (OFDT), permettent de dresser un tableau précis de la prévalence des troubles psychiques et des addictions.
Population Cible
Trouble / Addiction
Statistique Clé et Source
Adultes
Épisode dépressif caractérisé
1 personne sur 10 (Baromètre SPF, 2021)
États anxieux
1 personne sur 10 (Baromètre SPF, 2021)
Consommation d'alcool à risque
Plus d'1 personne sur 5
Consommation de cannabis (année)
1 personne sur 10
Tabagisme quotidien
1 personne sur 4 (taux en baisse)
Toute population
Addiction comportementale (jeux d'argent)
1 personne sur 10 a un comportement problématique (OFDT, 2023)
Adolescents
Risque de dépression (modéré à sévère)
14 % des collégiens, 15 % des lycéens
(17 ans)
Usage excessif des réseaux sociaux
1 jeune sur 5 (ESCAPADE, 2017)
(17 ans)
Jeux d'argent et de hasard (année)
1/3 des jeunes de 17 ans, bien qu'interdit aux mineurs (ESCAPADE)
Enfants
Trouble probable de la santé mentale
13 % des enfants (Étude Enabee, 2002)
Les addictions comportementales, notamment liées à l'usage d'internet (réseaux sociaux, jeux vidéo) et aux jeux d'argent en ligne, sont un phénomène en hausse, particulièrement chez les jeunes.
L'épidémiologie permet d'identifier des groupes plus vulnérables et des facteurs de risque spécifiques.
• Différences de genre : Les filles et les femmes présentent des niveaux plus élevés de dépression et d'anxiété, tandis que les garçons et les hommes sont plus touchés par les troubles du comportement, l'hyperactivité/inattention et les conduites addictives.
• Inégalités sociales : Qualifiées de "massives", elles apparaissent dès l'enfance et se creusent avec le temps. Les enfants issus des familles et des quartiers les plus défavorisés ont les risques les plus élevés tout en ayant l'accès aux soins le plus faible.
Un rapport de la Cour des comptes de 2023 illustre cette disparité : le recours aux soins en pédopsychiatrie est deux fois plus élevé à Paris qu'en Seine-Saint-Denis.
• Facteurs environnementaux : De nouvelles recherches explorent l'impact de facteurs comme l'absence d'espaces verts ou l'exposition aux nuisances sonores sur la santé mentale.
Étudier la santé mentale présente des obstacles uniques, tant sur le plan social qu'éthique et méthodologique.
Les troubles psychiques continuent de faire peur et d'être associés à des représentations négatives.
• Dangerosité perçue : 74 % des personnes interrogées en 2014 estimaient que les "malades mentaux" sont dangereux.
• Discrimination : Dans un sondage de 2023, 80 % des personnes estiment qu'avoir un trouble psychique réduit les opportunités de trouver un emploi ou un logement, et 63 % pensent que les personnes concernées sont moins bien traitées dans le système éducatif ou au travail.
La nature intime de la santé mentale suscite des questionnements éthiques fréquents dans la recherche.
La crainte principale est que poser des questions sur la souffrance psychique, et notamment sur les pensées suicidaires, pourrait inciter à un passage à l'acte.
Cependant, la science invalide cette crainte :
"De méta-analyses [...] montrent qu'interroger des personnes [...] sur leurs pensées ou sur leurs intentions suicidaires non seulement n'entraîne pas de passage à l'acte mais n'est pas non plus perçu de manière négative et pourrait même parfois être associé à une légère diminution des comportements suicidaires."
L'étude de cohorte Tempo, qui suit plus de 1000 personnes depuis l'enfance jusqu'à l'âge adulte, illustre la faisabilité et la richesse de la recherche longitudinale en santé mentale.
• Originalité : C'est l'une des rares études au monde à disposer de données sur trois générations (les participants, leurs parents via la cohorte Gazel, et bientôt leurs propres enfants), permettant d'étudier la transmission intergénérationnelle.
• Résultats clés :
◦ Le trouble de l'hyperactivité/inattention (TDAH) de l'enfance persiste sur près de 30 ans et est associé à des conduites addictives, des difficultés scolaires et un risque de chômage accru.
◦ La consommation de cannabis à l'adolescence a des effets délétères sur le parcours scolaire et professionnel 20 ans plus tard.
◦ La consommation ponctuelle importante d'alcool à l'adolescence prédit un trouble de l'usage à l'âge adulte dans 25 % des cas.
L'un des plus grands défis de l'épidémiologie psychiatrique est la mesure des troubles.
Contrairement à de nombreuses maladies, il n'existe pas de test biologique (sanguin, cérébral) pour diagnostiquer un trouble psychique.
L'évaluation repose entièrement sur la parole et le comportement rapportés par les personnes, ce qui introduit une part d'incertitude.
Pour standardiser l'évaluation, des classifications ont été développées.
• Historique : Les premières nosographies (Pinel, Kraepelin) se concentraient sur les pathologies les plus sévères observées en asile.
• Le tournant du DSM : La nécessité d'évaluer les conscrits américains lors des guerres mondiales a accéléré le développement de manuels standardisés.
Une révolution a eu lieu dans les années 1970 sous l'égide de Robert Spitzer : le Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) est passé d'une approche basée sur les causes psychanalytiques (difficiles à observer) à une définition basée sur des symptômes observables et leurs répercussions sur la vie des personnes.
• Conséquence : Cette approche a rendu possible la création de questionnaires standardisés, pierre angulaire de l'épidémiologie psychiatrique moderne.
Selon la réflexion du philosophe Georges Canguilhem, un état n'est pas pathologique simplement parce qu'il est statistiquement rare ou jugé négativement par la société (l'exemple de l'homosexualité, autrefois listée comme un trouble mental, en est une illustration frappante).
La définition moderne d'un état pathologique se centre sur la souffrance psychique exprimée par la personne et l'impact négatif des symptômes sur sa vie.
La santé publique considère que les caractéristiques d'une population influencent en retour la santé de chaque individu qui la compose.
• Le Paradoxe de Geoffrey Rose : Les maladies et leurs facteurs de risque se distribuent sur un continuum dans la population.
Par conséquent, la stratégie de prévention la plus efficace ne consiste pas à cibler uniquement les quelques individus à très haut risque, mais à décaler légèrement la distribution de l'ensemble de la population.
Autrement dit, une petite amélioration de la santé mentale de tous a un impact collectif plus grand qu'une grande amélioration pour quelques-uns.
• L'Universalisme Proportionné de Michael Marmot : Cette approche moderne combine la vision populationnelle de Rose avec une attention particulière pour les plus vulnérables.
Il s'agit de mettre en place des actions universelles bénéfiques à tous, tout en modulant l'intensité de l'aide en fonction des besoins. Le programme Improva de promotion de la santé mentale dans les collèges en est un exemple.
Le fardeau sociétal le plus lourd n'est pas le fait des cas les plus sévères (qui sont peu nombreux), mais de la masse de personnes présentant des symptômes intermédiaires ou "infracliniques".
Même sans correspondre à un diagnostic formel, ces symptômes causent de la souffrance et altèrent significativement la qualité de vie, la capacité à travailler ou à nouer des liens.
Pour améliorer la santé mentale de la population, il est impératif d'agir sur ses déterminants, qui se situent en grande partie en dehors du système de santé.
• Agir sur les déterminants sociaux : Suivant les travaux d'Émile Durkheim sur l'isolement et de Lisa Berkman sur les réseaux sociaux, il est crucial d'améliorer la densité et la qualité des liens relationnels.
Cela passe par une action sur leurs causes profondes : les inégalités sociales, les conditions de travail, l'accès au logement et les politiques de protection des familles.
• La Grande Cause Nationale 2025-2026 : Cet engagement politique vise à améliorer les perceptions collectives des troubles psychiques pour faciliter l'accès aux soins et réduire la stigmatisation.
• Améliorer la littératie en santé mentale : La diffusion à grande échelle des connaissances issues de la recherche épidémiologique est fondamentale pour que chacun puisse mieux reconnaître les signes de mal-être (chez soi ou chez les autres) et accepter les personnes qui souffrent.
After gaining control of the fabled wealth of the Delhi Sultans, Timur stripped the city of not only gold and jewels, but of architects, masons, and other artisans whom he took back to Samarkand to build monuments.
This is interesting that Timur stripped the city of all jewels, gold, masons, etc. I feel like this is a huge act to do.
Document d'information : Enjeux et Perspectives de la Transition Climatique et Énergétique
Ce document synthétise les analyses et les perspectives issues de la Journée du Climat organisée à Le Mans Université, dix ans après les Accords de Paris.
Il met en lumière une réalité complexe : si des progrès notables ont été accomplis, les grands objectifs climatiques mondiaux demeurent hors d'atteinte.
Les émissions de CO2 continuent d'augmenter à l'échelle planétaire, et la consommation d'énergies fossiles atteint des niveaux records, principalement en raison de la croissance des marchés asiatiques.
Dans ce contexte, la France représente un cas singulier, avec un mix électrique déjà largement décarboné grâce au nucléaire et aux énergies renouvelables.
Cependant, le pays fait face à un paradoxe majeur : alors que la consommation réelle d'électricité est en baisse depuis 2017, la politique énergétique nationale prévoit une augmentation massive de la capacité de production. Cette divergence crée un risque de surproduction, de perturbation du marché et de tensions sur le réseau électrique et le parc nucléaire.
La transition énergétique induit également de nouvelles dépendances stratégiques, notamment vis-à-vis des minéraux critiques pour les batteries, les panneaux solaires et les éoliennes, dont le raffinage est massivement contrôlé par la Chine.
La technologie des batteries, pilier de la décarbonation des transports et du stockage des énergies renouvelables, est au cœur de ces enjeux.
L'Europe peine à établir une chaîne de valeur souveraine, comme en témoigne l'échec de projets d'envergure.
Des innovations de rupture, telles que les batteries sodium-ion développées en France, et l'intégration de diagnostics avancés ("batteries intelligentes") offrent des perspectives prometteuses pour améliorer la durabilité et la performance.
Enfin, l'efficacité de la transition repose sur son ancrage territorial.
Les stratégies doivent intégrer les services écosystémiques (comme le carbone bleu), encourager l'implication citoyenne (via les communautés énergétiques) et repenser la gouvernance.
Les approches descendantes, qu'il s'agisse de réglementations européennes ou des négociations climatiques mondiales (COP), montrent leurs limites en peinant à intégrer les réalités et les aspirations locales, soulignant l'impératif d'une concertation plus juste et inclusive.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
La transition énergétique constitue le défi central de la lutte contre le changement climatique.
L'analyse présentée par Marc Fontecave, Professeur au Collège de France, dresse un tableau lucide de la situation, soulignant les écarts entre les ambitions affichées et les dynamiques réelles.
La première observation est sans appel : les objectifs fixés lors des Accords de Paris ne seront pas atteints.
• Objectifs manqués : L'ambition de limiter le réchauffement à 1,5°C d'ici 2100 et d'atteindre la neutralité carbone en 2050 est désormais considérée comme "relativement inatteignable".
• Hausse des émissions : Les émissions mondiales de CO2 continuent leur progression.
Le rythme d'augmentation en 2024 est comparable à celui des dix années précédentes. Cette hausse est principalement tirée par les marchés asiatiques en croissance rapide, notamment l'Inde.
• Dépendance fossile record : Loin de diminuer, la consommation mondiale de charbon, de pétrole et de gaz naturel n'a jamais été aussi élevée.
Les projections indiquent une augmentation continue des capacités mondiales de charbon et une demande record pour le pétrole en 2025.
• Un fossé persistant : Un écart se creuse entre les connaissances scientifiques, les déclarations politiques et les actions concrètes.
Bien que l'Europe et la France voient leurs émissions territoriales diminuer, ce chiffre doit être nuancé.
Pour la France, une part importante de cette baisse est attribuée à une désindustrialisation continue.
L'empreinte carbone du pays, qui inclut les émissions liées aux importations, ne baisse pratiquement pas.
La France se distingue par une situation énergétique particulière qui en fait un cas d'étude à part.
• Forte électrification : Avec 25-27 % d'électricité dans sa consommation énergétique totale, la France est l'un des pays les plus électrifiés au monde.
• Électricité très décarbonée : La production électrique française est à 95 % bas-carbone, ce qui place la dépendance du pays aux énergies fossiles juste en dessous de 60 %, une performance bien meilleure que la moyenne mondiale.
• Facture fossile : Cette dépendance représente néanmoins une facture considérable, s'élevant en moyenne à 60 milliards d'euros par an pour l'importation d'hydrocarbures.
Les trois piliers de la transition énergétique pour la France sont :
1. La diminution de la consommation : Tous les scénarios, y compris la feuille de route gouvernementale, prévoient une baisse drastique de la consommation d'énergie, de 1500 TWh actuellement à moins de 1000 TWh.
2. L'électrification des usages : Pour sortir des fossiles, il est nécessaire d'électrifier massivement les transports (véhicules électriques), le chauffage (pompes à chaleur) et l'industrie (fours électriques, hydrogène vert).
L'électrification directe est privilégiée pour son efficacité énergétique supérieure.
3. Le recours au carbone et à la chaleur non fossiles : Pour les usages non électrifiables, des alternatives comme la biomasse (bois, biocarburants), la géothermie et les biogaz sont nécessaires, bien qu'elles présentent des limites (gisements, compétition avec l'alimentaire, empreinte carbone).
L'analyse de la production et de la consommation électrique en France révèle une divergence préoccupante.
État des lieux de la production électrique française (Données 2024)
Indicateur
Valeur
Commentaire
Production totale
~540 TWh
La France est le premier pays exportateur d'électricité en Europe.
Part du nucléaire
~360 TWh
Socle du mix, assurant près de 70 % de la production.
Production bas-carbone
95 %
Niveau le plus élevé depuis 1950.
Part des fossiles
3,6 %
Niveau le plus bas depuis 1950.
Intensité carbone
21 g CO2/kWh
Parmi les plus basses du monde (vs. ~360 g CO2/kWh en Allemagne).
La politique nucléaire a connu un changement majeur, passant d'un projet de fermeture de réacteurs à la décision d'en construire 14 nouveaux (6 confirmés, 8 en option).
La capacité des réacteurs français à moduler leur production ("pilotabilité") est un atout stratégique pour équilibrer le réseau.
Le paradoxe identifié est le suivant :
• Une consommation en baisse : Contrairement aux projections, la consommation d'électricité en France diminue depuis 2017 pour atteindre en 2024 son niveau de 2004.
Cette baisse s'explique par l'efficacité énergétique, les prix élevés, la sobriété, la désindustrialisation et une électrification des usages plus lente que prévu.
• Une production planifiée en forte hausse : La feuille de route du gouvernement, basée sur des scénarios de consommation désormais obsolètes (projections RTE 2021/2023), prévoit une augmentation de la production de près de 200 TWh, principalement via l'éolien et le solaire.
• Les risques associés : Cette décorrélation pourrait mener à une surproduction structurelle, perturbant gravement le marché, nécessitant une modulation excessive et techniquement risquée du parc nucléaire, et créant des tensions sur les réseaux électriques.
De nouveaux scénarios de consommation revus à la baisse par RTE sont attendus pour corriger cette trajectoire.
La transition énergétique, si elle réduit la dépendance aux fossiles, en crée de nouvelles.
• Dépendance aux minéraux : La production de batteries, d'éoliennes et de panneaux solaires nécessite une quantité croissante de ressources minérales (graphite, lithium, cobalt, cuivre, etc.).
Le raffinage de ces matériaux est très largement dominé par la Chine, créant une nouvelle dépendance géopolitique.
• Maturité technologique : De nombreuses technologies clés ne sont pas encore matures et nécessitent des efforts de recherche et d'innovation considérables.
Cela inclut la production d'hydrogène vert, le recyclage des matériaux, l'amélioration des rendements photovoltaïques, le développement de mines responsables, la décarbonation de l'industrie lourde (acier), la valorisation de la biomasse, le nucléaire de 4ème génération, la modernisation des réseaux et le stockage d'énergie.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Les batteries sont au cœur de la transition, essentielles pour la mobilité électrique et pour stabiliser les réseaux face à l'intermittence des énergies renouvelables.
La conférence de Jean-Marie Tarascon, Professeur au Collège de France, a mis en évidence les avancées, les défis et les innovations de ce secteur stratégique.
Le stockage électrochimique est en passe de devenir la forme dominante de stockage d'énergie, dépassant le stockage hydroélectrique.
• Marchés en plein essor : La demande est tirée par trois secteurs majeurs : le véhicule électrique (50 % des ventes mondiales prévues en 2030), le stockage stationnaire pour les énergies renouvelables, et les drones.
• Les Gigafactories : Pour répondre à cette demande, des usines de très grande capacité se construisent dans le monde.
L'Europe, avec plus de 20 projets dont 6 en France, tente d'acquérir sa souveraineté, visant 19 % de la production mondiale en 2029.
• Le manque de chaîne de valeur : L'Europe reste massivement dépendante, important 98 % des machines d'assemblage et une part similaire des matériaux.
L'échec du projet suédois Northvolt, qui visait une intégration verticale complète sans maîtriser toute la chaîne de valeur, illustre cette fragilité. La proposition de créer un "Airbus des batteries" pour fédérer les compétences se heurte aux réticences des acteurs à collaborer.
La recherche scientifique est la clé pour surmonter les dépendances et améliorer les performances.
• Du NMC au LFP : Dans le lithium-ion, la technologie dominante des véhicules électriques évolue.
Les matériaux NMC (Nickel-Manganèse-Cobalt) à haute densité énergétique cèdent du terrain aux matériaux LFP (Lithium-Fer-Phosphate), qui sont moins chers, plus sûrs et ne contiennent pas de cobalt.
Cependant, la production de LFP est contrôlée à 88 % par la Chine.
• La technologie Sodium-ion : Portée en France par la start-up Tiamat, cette technologie représente une alternative stratégique.
Le sodium est 10 000 fois plus abondant que le lithium.
Bien que moins denses en énergie, les batteries sodium-ion offrent une puissance supérieure, une durée de vie exceptionnelle (jusqu'à 17 000 cycles) et un coût potentiellement plus faible.
Elles sont idéales pour le stockage stationnaire (ex: data centers) et la mobilité légère.
• Vers le tout-solide et les batteries intelligentes :
La recherche s'oriente vers les batteries "tout-solide", qui remplacent l'électrolyte liquide par un solide pour plus de sécurité et de densité énergétique, bien que des défis d'interface persistent.
Une autre innovation majeure est l'intégration de capteurs (fibres optiques) au cœur des batteries pour en suivre l'état de santé en temps réel (température, pression, chimie).
Ce "passeport de santé" permettra d'optimiser leur usage, de faciliter leur seconde vie et de développer des systèmes d'auto-réparation.
La durabilité des batteries est un enjeu aussi important que leur performance.
• Pression sur les ressources :
Un véhicule électrique utilise six fois plus de minéraux qu'un véhicule thermique.
La demande en lithium, cobalt et nickel pourrait dépasser la production d'ici 2030.
L'exploitation de nouvelles ressources, y compris en Europe (comme le lithium en France), et surtout le développement du recyclage ("mine urbaine") sont impératifs.
• Réglementation européenne : L'UE met en place un cadre strict imposant la déclaration de l'empreinte carbone, des taux de matériaux recyclés obligatoires (dès 2030) et un passeport électronique pour chaque batterie.
• Recherche sur le recyclage : Les méthodes actuelles (pyrométallurgie, hydrométallurgie) sont énergivores.
L'un des objectifs de la recherche est de concevoir des batteries "de type Lego", facilement démontables pour un recyclage ciblé de leurs composants.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
La réussite de la transition climatique ne peut être décrétée d'en haut ; elle doit s'incarner dans les territoires, en tenant compte de leurs spécificités géographiques, sociales et économiques.
Les approches locales varient considérablement, reflétant la diversité des enjeux.
• Plans Climat-Air-Énergie Territoriaux (PCAET) : L'analyse des PCAET dans l'Ouest de la France montre un foisonnement d'initiatives.
Si l'atténuation (mitigation) est un axe commun, les notions d'adaptation et de résilience sont traitées de manière inégale, la résilience étant plus prégnante dans les territoires littoraux directement menacés.
• Rôle des écosystèmes : Les écosystèmes locaux sont des alliés pour la neutralité carbone.
Les zones humides littorales, par exemple, stockent massivement du carbone ("carbone bleu") tout en fournissant d'autres services essentiels comme la protection contre les inondations.
• Controverses du "Rewilding" : Les stratégies de restauration, comme le réensauvagement, peuvent générer des conflits.
Laisser des écosystèmes évoluer librement ou réintroduire de grands animaux se heurte aux paysages culturels et agricoles européens, créant des tensions sur les usages et des chocs de valeurs.
Le succès de telles approches dépend fondamentalement de l'inclusion et de la concertation avec les populations locales.
L'implication des citoyens est un levier puissant pour accélérer la transition.
• Communautés énergétiques citoyennes : Des collectifs de citoyens émergent pour produire et consommer localement de l'énergie renouvelable.
Ces initiatives favorisent l'appropriation locale des enjeux, contribuent à la justice énergétique et permettent de lutter contre la précarité.
L'Ouest de la France est une région particulièrement dynamique, accueillant près d'un quart des projets citoyens nationaux.
• Décarboner les mobilités : Le secteur des transports représente 31 % des émissions de CO2 en France, les trajets domicile-travail en voiture comptant pour une part significative (13 % du total national).
Comprendre les facteurs (individuels, contextuels, normes sociales) qui influencent le choix du mode de transport est essentiel pour concevoir des politiques publiques efficaces favorisant les mobilités douces.
L'articulation entre les décisions locales, nationales et internationales reste un point de friction majeur.
• Approches descendantes : Des réglementations comme celle de l'UE sur la déforestation importée, bien qu'intentionnées, peuvent être perçues comme unilatérales et impérialistes par les pays producteurs, qui se tournent vers d'autres marchés moins regardants.
De même, dans certains pays comme Haïti, les plans climatiques sont souvent impulsés par des acteurs internationaux et déconnectés des réalités du terrain.
• Le défi des COP : Les négociations climatiques mondiales, comme la COP30 au Brésil, peinent à intégrer de manière authentique la voix des populations locales et des peuples autochtones.
Leurs préoccupations sont souvent diluées dans un langage diplomatique visant le consensus, ce qui conduit à une forme de décision à deux vitesses et pousse les groupes non entendus à s'auto-organiser en marge des processus officiels.
L'enjeu est de traduire les aspirations des territoires en politiques internationales concrètes et justes.
Note: This response was posted by the corresponding author to Review Commons. The content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
We are grateful to the reviewers for their thoughtful and constructive evaluations of our manuscript. Their comments helped us clarify key aspects of the study and strengthen both the presentation and interpretation of our findings. The central goal of this work is to dissect how the opposing activities of GATA4 and CTCF coordinate chromatin topology and transcriptional timing during human cardiomyogenesis. The reviewers’ feedback has allowed us to refine this message and better contextualize our results within the broader framework of chromatin regulation and cardiac development.
In response to the reviews, in our preliminary revision we have already implemented substantial improvements to the manuscript, including additional analyses, clearer data visualization, and revisions to the text to avoid overinterpretation. These refinements enhance the robustness of our conclusions without altering the overall scope of the study. A small number of additional analyses and experiments are ongoing and will be added to the full revision, as detailed below.
We believe that the revised manuscript, together with the planned updates, fully addresses the reviewers’ concerns and substantially strengthens the contribution of this work to the field.
Reviewer 1 – Point 1:
In the datasets you are examining, what are the relative percentages in each of the four groups relating compartmentalization change to expression change (A→B, expression up; A→B, down; B→A, up; B→A, down)?
We quantified compartment–expression relationships using Hi-C and bulk RNA-seq from H9 ESCs and CMs. The percentages for each category are shown below and incorporated into updated Figure S2H.
Group
Downregulated in CM
Upregulated in CM
A-to-A
11.92%
8.44%
A-to-B
18.20%
2.79%
B-to-A
7.96%
18.07%
B-to-B
14.36%
6.44%
A chi-squared test comparing observed vs. expected distributions (based on gene density across bins) confirmed a strong association between compartment dynamics and transcriptional behavior. B-to-A genes are significantly enriched among genes upregulated in CMs, while A-to-B genes are enriched among those downregulated (updated Figure S2H).
We next assessed with GSEA how these gene classes respond to GATA4 and CTCF knockdown. In 2D CMs, GATA4 knockdown reduces expression of CM-upregulated B-to-A genes and increases expression of CM-downregulated A-to-B genes, whereas CTCF knockdown produces the opposite pattern (updated Figure 2F).
Applying the same analysis to cardioid bulk RNA-seq (updated Figure 4E) revealed the strongest effects in SHF-RV organoids, consistent with monolayer data. In SHF-A organoids, only GATA4 knockdown had a measurable impact on CM-upregulated B-to-A and CM-downregulated A-to-B genes. Because the subsets of CM-downregulated B-to-A and CM-upregulated A-to-B genes were very small and showed no consistent trends, Figure 4 focuses on the two informative categories only. The full classification is provided in Reviewer Figure 1 below.
(The figure cannot be rendered in this text-only format)
Reviewer Figure 1. GSEA for CM-upregulated B-to-A and CM-downregulated A-to-B genes. p-values by Adaptive Monte-Carlo Permutation test.
Reviewer 1 – Point 2
This phrase in the abstract is imprecise: ‘whereas premature CTCF depletion accelerates yet confounds cardiomyocyte maturation.’
The abstract has been revised to: “whereas premature CTCF depletion accelerates yet alters cardiomyocyte maturation.” (lines 29-30).
Reviewer 1 – Point 3
Regarding this statement: "Disruption of [3D chromatin architecture] has been linked to genetic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) caused by lamin A/C mutations8,9, and mutations in chromatin regulators are strongly enriched in de novo congenital heart defects (CHD)10, underscoring their pathogenic relevance11." The first studies to implicate chromatin structural changes in heart disease, including the role of CTCF in that process, were PMID: 28802249, a model of acquired, rather than genetic, disease.
We added the following sentence to the paragraph introducing CTCF: “Moreover, depletion of CTCF in the adult cardiomyocytes leads to heart failure28,29.” (line 72)
Reviewer 1 – Point 4
Can you quantify this statement: ‘the compartment switch coincided with progressive reduction of promoter–gene body interactions’?
We quantified promoter–gene body contacts by calculating the area under the curve (AUC) of the virtual 4C signal derived from H9 Hi-C data across differentiation. As a result of this analysis we added the following sentence: “Quantitatively, interactions between the TTN promoter and its gene body decreased by ~55% from the pluripotent stage to day 80 cardiomyocytes.” (lines 89-91).
Reviewer 1 – Point 5
Regarding this statement: "six regions became less accessible in CMs, correlating with ChIP-seq signal for the ubiquitous architectural protein CTCF." I don't see 6 ATAC peaks in either TTN trace in Figure 1A.
We corrected the text as it follows: “TTN experienced clear changes in chromatin accessibility during CM differentiation: ATAC-seq identified two CM-specific peaks that correlated with ChIP-seq signal for the cardiac pioneer TF GATA4 at the two promoters, one driving full length titin and the other the shorter cronos isoform. In contrast, two regions became less accessible in CMs, correlating with two of the six ChIP-seq peaks for the ubiquitous architectural protein CTCF” (lines 93-97). We attribute the differences between ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq profiles to methodological sensitivity and/or biological variability between datasets generated in different laboratories and cell batches.
Reviewer 1 – Point 6
Western blots need molecular weight markers.
We edited the relevant panels accordingly (updated Figures 1E and 2B).
Reviewer 1 – Point 7
Regarding this statement: "The decrease in CTCF protein levels may explain its selective detachment from TTN during cardiomyogenesis." At face value, these findings suggest the opposite: i.e. that a massive downregulation of CTCF at protein level should affect its binding across the genome, which is not tested and is hard to evaluate between ChIP-seq studies from different groups and from different developmental timeframes.
We revised the text to avoid implying selective detachment and performed a genome-wide analysis of CTCF occupancy using ENCODE ChIP-seq datasets generated by the same laboratory with matched protocols in hESCs and hESC-derived CMs. This analysis shows that 43.2% of CTCF sites present in ESCs are lost in CMs, whereas only 5.7% are gained, confirming a broad reduction in CTCF binding during differentiation. These results are now included in__ updated Figure 1B__.
Reviewer 1 – Point 8a
A couple thoughts on the FISH experiments in Figure 2. A claim of 'impaired B-A transition' would be more convincing if you show, by FISH, that the relative distance of TTN from lamin B increases with differentiation.
Although prior work from us and others has established that TTN transitions from the nuclear periphery in hESCs to a more internal position during cardiomyogenesis (Poleshko et al. 2017; Bertero et al. 2019a), we are reproducing this trajectory in WTC11 hiPSCs as part of the FISH experiments for the full revision.
__Reviewer 1 – Point 8b __
In the [FISH] images: are you showing a total projection of all z planes? One assumes the quantitation is relative to a 3D reconstruction in which the lamin B signal is restricted to the periphery. Have you shown this? __
Quantification was performed on full 3D reconstructions from Z-stacks, as detailed in the Methods (lines 721-727). While the original submission displayed maximum-intensity projections, updated Figure 2D and Figure S2E now show representative single optical sections, which more clearly highlight the spatial relationship between the TTN locus and the nuclear lamina.
Reviewer 1 – Point 8c
Lastly, these data are very interesting and important, provoking reexamination of your interpretation of the results in Figure 1. Figure 1 was interpreted to show that less CTCF binding led to decreased lamina (and thus B compartment) association during development. Figure 2 shows that depleting CTCF does not change association of TTN with lamina.
Our interpretation is that by day 25 of hiPSC-CM differentiation the TTN locus may have reached its maximal radial repositioning even in control cells, limiting the ability to detect earlier effects of CTCF depletion. To test whether CTCF knockdown accelerates lamina detachment at earlier stages, we are repeating the FISH analysis for the inducible CTCF knockdown line at multiple time points during differentiation.
Reviewer 1 – Point 9
A thought about this statement: "Altogether, these results suggest that GATA4 and CTCF function as positive and negative regulators of B-to-A compartment switching, likely acting through global and local chromatin remodeling, respectively." GATA4 induces TTN expression and its knockdown prevents TTN expression-the evidence that GATA4 affects compartmentalization is unclear. By activating the gene, GATA4 may shift TTN to B classification.
Our current data do not allow us to disentangle whether GATA4-driven transcriptional activation precedes or follows the B-to-A compartment shift. We have therefore removed the mechanistic speculation from this sentence to avoid overinterpretation. Nevertheless, the analyses in updated Figure 2F, discussed in the response to Reviewer 1 - Point 1, show that GATA4 knockdown preferentially reduces expression of CM-upregulated B-to-A genes, while CTCF knockdown has the opposite effect, supporting the conclusion that both factors influence the transcriptional programs associated with B-to-A transitions.
Reviewer 1 – Point 10
__I'm not sure what I am looking at in Figure 3C. Are those traces integration of interactions over a defined window? "Each [mutant is] clearly different from WT" is not obvious from the presentation. The histograms are plotting AUC of what? Interactions of those peaks with the mutated region? I genuinely appreciate how laborious this experiment must have been and encourage you to explain better what you are showing. __
We revised the main text to avoid overstating the differences (“clearly” “in a similar manner”, line 192) and expanded the l__egends of updated Figures 3C–D__ to clarify what is being shown: “(C) 4C-seq in hiPSCs using the promoter-proximal region of TTN as viewpoint. The top panel shows raw interaction profiles. The lower panels plot pairwise differences between conditions to reveal subtle changes. A schematic indicating the 4C viewpoint is included for clarity. Right inset: zoom of the CBS4–5 region. Mean of n = 3 cultures. (D) AUC of the differential 4C-seq signal for defined intervals (panel C). p-values by one-sample t-test against μ = 0.”. We also added a visual cue in updated Figure 3C indicating the 4C viewpoint to facilitate interpretation.
Reviewer 1 – Point 11
Again acknowledging how challenging these experiments are: when you mutant a locus, you change CTCF binding but you also change the DNA. Thus, attributing the changes in interactions to presence/absence of CTCF binding is difficult, because the DNA substrate itself has changed. Perhaps you are presenting all of this as a negative result, given the modest effect on transcription, which is as important as a positive result, given the assumptions usually made about such things. But the results are not clearly described and your interpretation seems to go between implying the structural change causative and being agnostic.
We recognize that deleting a genomic region can affect both CTCF binding and the DNA substrate itself. For this reason, we implemented two parallel genome-editing strategies:
(1) a straightforward Cas9-mediated deletion of ~100 bp centered on each CBS, and
(2) a more precise HDR approach replacing only the 20 bp core CTCF motif.
Because the HDR strategy succeeded, all downstream analyses were carried out on these minimal edits, which substantially limit disruption of other transcription factor motifs and reduce the likelihood of sequence-dependent polymer effects unrelated to CTCF.
Nevertheless, to avoid implying unwarranted causality in the absence of more conclusive evidence, we added a paragraph to the Discussion outlining these limitations, including the sentence: “Our study also reflects general challenges in separating chromatin-architectural and transcriptional mechanisms. Although the CBS edits were restricted to the core CTCF motifs, additional sequence-dependent effects cannot be fully excluded, and we therefore interpret the resulting changes as consistent with—but not exclusively due to—loss of CTCF binding.” (lines 365-368)
Reviewer 1 - Point 12.
Figure 4C: since you have RNA-seq data, a much more objective way to present these data would be to show all data (again, A-B, up; A-B, down; B-A, up; B-A, down) and the effects of CTCF or GATA4. Regardless, you can still focus on the cardiac specific genes. But my guess is if you examine all genes, the pattern you show in panel C will not be present in the majority of cases. Furthermore, if this hypothesis is wrong, such an analysis will allow you to identify other genes affected by the mechanisms you describe and your analysis will test whether these mechanisms are in fact conserved at different loci.
As outlined in our response to Point 1, we extended the analysis to all genes undergoing compartment changes and incorporated this into the cardioid RNA-seq dataset. This revealed a clear and consistent relationship between GATA4 or CTCF knockdown and the expression of B-to-A and A-to-B gene classes (updated Figure 4E).
Reviewer 2 - Point 1.1
1. CTCF regulation at TTN locus:
(1) Figure 1A: The claim of the authors about convergent CTCF sites and transcriptional activation of TTN is quite simplistic. This claim is only valid when we know where cohesin is loaded. If cohesin is loaded at then intragenic GATA4 binding site, then the only important CTCF sites is at the promoter of TTN. I suggest that the authors read few more publications which may help the authors to better understand how cohesin and CTCF team up to regulate transcription, such as Hsieh et al., Nature Genetics, 2022; Liu et al., Nature Genetics, 2021; Rinzema et al., Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 2022.
__Suggestion: The authors should add cohesin (RAD21/SMC1A) and NIPBL ChIP-seq for better interpretation. __
In line with the reviewer’s insightful suggestion, we integrated cohesin ChIP-seq data into updated Figure 1A. Specifically, we added a RAD21 ChIP-seq track from hESCs, which provides direct evidence of cohesin occupancy across the TTN locus. RAD21 binding closely parallels CTCF binding at five sites within the gene body, supporting a model in which promoter-proximal CTCF anchors cohesin to stabilize repressive loops at this locus. This analysis substantially strengthens the mechanistic framework and is consistent with the studies recommended by the reviewer, which we have now cited (lines 68 and 104).
Reviewer 2 - Point 1.2. (2) Figure 3B: If delta2CBS only has heterozygenous deletion of CBS6, why we would expect the binding will be weaken to 50%. However, the CTCF binding is reduced to around 1/10 in the ChIP-qPCR. How do the authors explain this?
Sequencing of the Δ2CBS line shows that one CBS6 allele carries the intended EcoRI replacement, while the second allele contains a 2-bp deletion within the core CTCF motif (Figure S3C). Remarkably, this small deletion is sufficient to abolish CTCF binding, resulting in complete loss of occupancy at CBS6 despite heterozygosity. We clarified this in the text as follows: “CTCF ChIP-qPCR in hiPSCs confirmed complete loss of CTCF binding at the targeted sites, including CBS6 in the Δ2CBS line, indicating that the 2-bp deletion sufficed to disrupt CTCF binding while occupancy at other CBSs remained unaffected.” (lines 187–189).
Reviewer 2 - Point 1.3a (3) Figure 3C: There are two problems with the 4C experiments: (a) The changes are really mild. In fact, none of the p-values in Figure 3D are significant.
The effect of deleting CBS1 is indeed modest, consistent with reports that individual CTCF binding sites often show functional redundancy (i.e., Rodríguez-Carballo et al. 2017; Barutcu et al. 2018; Kang et al. 2021). Nevertheless, our 4C-seq experiments have reproducibly shown the same directional trend across biological replicates. To increase statistical power and more rigorously assess the robustness of this effect, we are generating additional 4C replicates as part of the full revision.
Reviewer 2 - Point 1.3b [In the 4C experiments] (b) The authors should also consider a model that CTCF directly serves as a repressor. In this way, 3D genome may not be involved. B-A switch is simply caused by the activation of the locus.
We now explicitly acknowledge this possibility in the Discussion. The revised text states: “Moreover, our data cannot unambiguously separate CTCF’s architectural role from potential direct repressive activity. Both mechanisms could contribute to the observed effects, and our findings likely reflect the combined influence of CTCF on chromatin topology and gene regulation.” (lines 368–371).
Reviewer 2 - Point 2.1a 2. __(CTCF) detachment: The authors mentioned few times "detachment". In the context of this manuscript, the authors indicate detachment from nuclear lamina. However, the authors haven't provide convincing evidence about this. __
In the two instances where we used the term “detachment,” we intended it to refer exclusively to reduced CTCF binding to DNA, not to lamina repositioning. To avoid ambiguity, we have replaced “detachment” with “reduced binding” in both locations (lines 123 and 329). We do not use this term to describe TTN–lamina positioning.
Reviewer 2 - Point 2.1b (1) Figure 1D: I doubt whether such changes of CTCF protein abundance will lead to LAD detachment. Suggest the authors read van Schaik et al., Genome Biology, 2022. With the full depletion of CTCF, the effects on LADs are still very restricted.
We agree that the observed correlation between reduced CTCF levels and the relocation of TTN away from a LAD does not establish causality. As outlined in our response to Reviewer 1 – Point 8c, we are performing additional FISH experiments at earlier differentiation stages in the CTCF inducible knockdown line to directly assess whether partial CTCF depletion is sufficient to alter the timing of TTN–lamina separation.
Reviewer 2 - Point 2.2 (2) Figure 2D: Lamin B1 should be mostly at nuclear periphery. I have few questions: (1) is the antibody specific? (2) do these cells carry mutation in LMNB1 gene? (3) is the staining actually LMNA?
As also clarified in response to Reviewer 1 – Point 8b, the original images displayed maximum-intensity projections of Z-stacks, which obscured the peripheral distribution of LMNB1. We have updated Figure 2D and Figure S2E to show representative individual optical sections, which more clearly display the expected peripheral LMNB1 signal. We also confirm that the antibody used is specific for LMNB1 and previously validated (Bertero et al. 2019b), and that the WTC11-derived lines used in this study carry no mutation in LMNB1.
Reviewer 2 - Point 3
3. Opposite functions of GATA4 and CTCF: These data in Figure 5E-H argues the opposite role of GATA4 and CTCF in transcriptional regulation. Would it be that CTCF KD just affected cell proliferation, which is actually known for many cell types, rather than affect CM differentiation process? If this is the reason, inversed correlation between CTCF KD and GATA4 KD in Figure 4D could also be explained by opposite effects on cell cycle.
We directly evaluated this possibility. In FHF–LV cardioids, cell cycle profiling in Figure 6C and Figure S6C (now S7C) showed that CTCF knockdown does not alter the distribution of CMs across G1/S/G2–M phases, in contrast to the marked increase in proliferation observed with GATA4 knockdown.
Because this comment referred specifically to the SHF data, we also analyzed mitotic gene expression in the SHF–RV bulk RNA-seq dataset using GSEA. CTCF knockdown did not significantly enrich any cell cycle–related gene sets, whereas GATA4 knockdown produced a strong enrichment for mitotic cell cycle terms, in line with FHF-LV data (Reviewer Figure 2).
These results are summarized in updated Figure S5C, reporting also the results of the broader GSEA analysis, and together indicate that the transcriptional divergence between CTCF and GATA4 knockdown is not simply explained by opposing effects on proliferation.
(The figure cannot be rendered in this text-only format)
Reviewer Figure 2. GSEA for mitotic cell cycle in SHF-RV after inducible knockdown of CTCF (left) or GATA4 (right). p-values by Adaptive Monte-Carlo Permutation test.
Reviewer 2 - Point 4 4. In discussion, the authors suggested that CTCF is a local chromatin remodeller. In my view, association with local chromatin compaction doesn't qualify CTCF as a chromatin remodeler. To my knowledge, CTCF does not have an enzymatic domain, then how does it remodel chromatin?
Our intended meaning was that CTCF shapes 3D chromatin architecture through its role in organizing intergenic looping, not that it remodels chromatin enzymatically. To avoid confusion, we have removed the original sentence from the Discussion.
Reviewer 2 - Point 5. 5. Some conclusions are drawn based on insignificant p-values, e.g. Figure 2F, Figure 3D, etc. The authors should be careful about their conclusion, and tone down their statement for the observations have borderline significance.
The conclusions based on bulk RNA-seq have been revised in response to Reviewer 1 – Point 1 (updated Figure 2F). By subsetting B-to-A and A-to-B genes according to their expression dynamics, this analysis now yields clearer and statistically significant differences between conditions.
Regarding the 4C-seq data, as acknowledged in Reviewer 2 – Point 3a, the observed effects are modest. We are generating additional biological replicates to increase statistical power. In the meantime, we have adjusted the text to avoid overstating these findings. The revised manuscript now states: “While the difference did not reach significance, these trends suggest …” (lines 199–200).
Reviewer 2 - Minor comment 1. Minor comments: 1. Figure 1A: (1) I suggest to label two promoters in the gene model. It's unclear in the figure in the current version; (2) I was a bit confused with the way how the authors labeled CTCF directionality. I thought there are a lot of promoters. Why didn't they use triangles?
We updated Figure 1A to label both TTN promoters and indicate their orientation. For CTCF sites, we now clearly display the motif direction and core binding region as determined by FIMO analysis of the CTCF ChIP-seq peaks, improving consistency and interpretability.
Reviewer 2 - Minor comment 2. 2. Figure 2C: I think the drastical reduction of titin-mEGFP levels is only due to the way how the authors analyze their FACS data. Can the author quantify on median fluorescence intensity?
The gating strategy for titin-mEGFP⁺ cells was defined using a reporter-negative control, and cells lacking TNNT2 expression showed no detectable titin-mEGFP signal, confirming the specificity of the gate. To complement this analysis, we also quantified the median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of titin-mEGFP⁺ cells. The MFI analysis corroborates the original findings, showing a significant decrease in GATA4 knockdown and an increase in CTCF knockdown (updated Figure S2D).
__Reviewer 2 - Minor comment 3. 3. Figure S2G: P value should be -log10, I assume. Please label it accurately. __
We appreciate the reviewer pointing out this labeling error. In the revised manuscript, this panel has been removed to accommodate the updated compartment–expression analysis now presented in updated Figure 2H (see response to Reviewer 1 – Point 1), and the issue is no longer applicable.
References
Barutcu AR, Maass PG, Lewandowski JP, Weiner CL, Rinn JL. 2018. A TAD boundary is preserved upon deletion of the CTCF-rich Firre locus. Nat Commun 9: 1444.
Bertero A, Fields PA, Ramani V, Bonora G, Yardımcı GG, Reinecke H, Pabon L, Noble WS, Shendure J, Murry CE. 2019a. Dynamics of genome reorganization during human cardiogenesis reveal an RBM20-dependent splicing factory. Nature communications 10: 1538.
Bertero A, Fields PA, Smith AS, Leonard A, Beussman K, Sniadecki NJ, Kim D-H, Tse H-F, Pabon L, Shendure J, et al. 2019b. Chromatin compartment dynamics in a haploinsufficient model of cardiac laminopathy. Journal of Cell Biology 218: 2919–44.
Kang J, Kim YW, Park S, Kang Y, Kim A. 2021. Multiple CTCF sites cooperate with each other to maintain a TAD for enhancer–promoter interaction in the β-globin locus. The FASEB Journal 35: e21768.
Poleshko A, Shah PP, Gupta M, Babu A, Morley MP, Manderfield LJ, Ifkovits JL, Calderon D, Aghajanian H, Sierra-Pagán JE, et al. 2017. Genome-Nuclear Lamina Interactions Regulate Cardiac Stem Cell Lineage Restriction. Cell 171: 573–587.
Rodríguez-Carballo E, Lopez-Delisle L, Zhan Y, Fabre PJ, Beccari L, El-Idrissi I, Huynh THN, Ozadam H, Dekker J, Duboule D. 2017. The HoxD cluster is a dynamic and resilient TAD boundary controlling the segregation of antagonistic regulatory landscapes. Genes Dev 31: 2264–2281.
Note: This preprint has been reviewed by subject experts for Review Commons. Content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
Becca et al. characterized the functions of GATA4 and CTCF in the context of cardiomyogenesis. The authors aim to establish a link between 3D genome changes (A/B compartment and long-range chromatin interactions) and activation of cardiac specific genes such as TTN. They showed opposite effects of GATA4 and CTCF in regulating these genes as well as phenotypical traits. I have the following suggestions and questions:
Major comments:
(1) Figure 1A: The claim of the authors about convergent CTCF sites and transcriptional activation of TTN is quite simplistic. This claim is only valid when we know where cohesin is loaded. If cohesin is loaded at then intragenic GATA4 binding site, then the only important CTCF sites is at the promoter of TTN. I suggest that the authors read few more publications which may help the authors to better understand how cohesin and CTCF team up to regulate transcription, such as Hsieh et al., Nature Genetics, 2022; Liu et al., Nature Genetics, 2021; Rinzema et al., Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 2022.
Suggestion: The authors should add cohesin (RAD21/SMC1A) and NIPBL ChIP-seq for better interpretation. (2) Figure 3B: If delta2CBS only has heterozygenous deletion of CBS6, why we would expect the binding will be weaken to 50%. However, the CTCF binding is reduced to around 1/10 in the ChIP-qPCR. How do the authors explain this?
(3) Figure 3C: There are two problems with the 4C experiments: (a) The changes are really mild. In fact, none of the p-values in Figure 3D are significant; (b) The authors should also consider a model that CTCF directly serves as a repressor. In this way, 3D genome may not be involved. B-A switch is simply caused by the activation of the locus. 2. (CTCF) detachment: The authors mentioned few times "detachment". In the context of this manuscript, the authors indicate detachment from nuclear lamina. However, the authors haven't provide convincing evidence about this.
(1) Figure 1D: I doubt whether such changes of CTCF protein abundance will lead to LAD detachment. Suggest the authors read van Schaik et al., Genome Biology, 2022. With the full depletion of CTCF, the effects on LADs are still very restricted.
(2) Figure 2D: Lamin B1 should be mostly at nuclear periphery. I have few questions: (1) is the antibody specific? (2) do these cells carry mutation in LMNB1 gene? (3) is the staining actually LMNA? 3. Opposite functions of GATA4 and CTCF: These data in Figure 5E-H argues the opposite role of GATA4 and CTCF in transcriptional regulation. Would it be that CTCF KD just affected cell proliferation, which is actually known for many cell types, rather than affect CM differentiation process? If this is the reason, inversed correlation between CTCF KD and GATA4 KD in Figure 4D could also be explained by opposite effects on cell cycle. 4. In discussion, the authors suggested that CTCF is a local chromatin remodeller. In my view, association with local chromatin compaction doesn't qualify CTCF as a chromatin remodeler. To my knowledge, CTCF does not have an enzymatic domain, then how does it remodel chromatin? 5. Some conclusions are drawn based on insignificant p-values, e.g. Figure 2F, Figure 3D, etc. The authors should be careful about their conclusion, and tone down their statement for the observations have borderline significance.
Minor comments:
Strengths and limitations:
I feel that single-cell analysis and functional analysis of GATA4 and CTCF using cardiac organoid model are elegant. However, the weak part of the manuscript is the link between 3D genome and activation of TTN. I also think the authors should include more possible explanations for the interpretation of some genome organization data (CTCF site deletion, 4C, etc).
Advance: The study does provide useful information to understand transcriptional regulation during cardiac lineage specification. The link between 3D genome and cardiac lineage specification is conceptually nice but needs more data to support.
Audience: developmental biologists who is interested in heart development and molecular biologists with specific interests in gene regulation.
proporcionalidade
Fonte: Os princípios da razoabilidade e da proporcionalidade no Direito Constitucional Luís Roberto Barroso
As one of the community and public health nursing Specialists competences is the community empowerment [3], there is a great management opportunity for primary health care leaders to ensure that these specialists are allocated to public health units
de vijf groepen van Porter
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
The authors report the results of a tDCS brain stimulation study (verum vs sham stimulation of left DLPFC; between-subjects) in 46 participants, using an intense stimulation protocol over 2 weeks, combined with an experience-sampling approach, plus follow-up measures after 6 months.
Strengths:
The authors are studying a relevant and interesting research question using an intriguing design, following participants quite intensely over time and even at a follow-up time point. The use of an experience-sampling approach is another strength of the work.
Weaknesses:
There are quite a few weaknesses, some related to the actual study and some more strongly related to the reporting about the study in the manuscript. The concerns are listed roughly in the order in which they appear in the manuscript.
(1) In the introduction, the authors present procrastination nearly as if it were the most relevant and problematic issue there is in psychology. Surely, procrastination is a relevant and study-worthy topic, but that is also true if it is presented in more modest (and appropriate) terms. The manuscript mentions that procrastination is a main cause of psychopathology and bodily disease. These claims could possibly be described as 'sensationalized'. Also, the studies to support these claims seem to report associations, not causal mechanisms, as is implied in the manuscript.
(2) It is laudable that the study was pre-registered; however, the cited OSF repository cannot be accessed and therefore, the OSF materials cannot be used to (a) check the preregistration or to (b) fill in the gaps and uncertainties about the exact analyses the authors conducted (this is important because the description of the analyses is insufficiently detailed and it is often unclear how they analyzed the data).
(3) Related to the previous point: I find it impossible to check the analyses with respect to their appropriateness because too little detail and/or explanation is given. Therefore, I find it impossible to evaluate whether the conclusions are valid and warranted.
(4) Why is a medium effect size chosen for the a priori power analysis? Is it reasonable to assume a medium effect size? This should be discussed/motivated. Related: 18 participants for a medium effect size in a between-subjects design strikes me as implausibly low; even for a within-subjects design, it would appear low (but perhaps I am just not fully understanding the details of the power analysis).
(5) It remains somewhat ambiguous whether the sham group had the same number of stimulation sessions as the verum stimulation group; please clarify: Did both groups come in the same number of times into the lab? I.e., were all procedures identical except whether the stimulation was verum or sham?
(6) The TDM analysis and hyperbolic discounting approach were unclear to me; this needs to be described in more detail, otherwise it cannot be evaluated.
(7) Coming back to the point about the statistical analyses not being described in enough detail: One important example of this is the inclusion of random slopes in their mixed-effects model which is unclear. This is highly relevant as omission of random slopes has been repeatedly shown that it can lead to extremely inflated Type 1 errors (e.g., inflating Type 1 errors by a factor of then, e.g., a significant p value of .05 might be obtained when the true p value is .5). Thus, if indeed random slopes have been omitted, then it is possible that significant effects are significant only due to inflated Type 1 error. Without more information about the models, this cannot be ruled out.
(8) Related to the previous point: The authors report, for example, on the first results page, line 420, an F-test as F(1, 269). This means the test has 269 residual degrees of freedom despite a sample size of about 50 participants. This likely suggests that relevant random slopes for this test were omitted, meaning that this statistical test likely suffers from inflated Type 1 error, and the reported p-value < .001 might be severely inflated. If that is the case, each observation was treated as independent instead of accounting for the nestedness of data within participants. The authors should check this carefully for this and all other statistical tests using mixed-effects models.
(9) Many of the statistical procedures seem quite complex and hard to follow. If the results are indeed so robust as they are presented to be, would it make sense to use simpler analysis approaches (perhaps in addition to the complex ones) that are easier for the average reader to understand and comprehend?
(10) As was noted by an earlier reviewer, the paper reports nearly exclusively about the role of the left DLPFC, while there is also work that demonstrates the role of the right DLPFC in self-control. A more balanced presentation of the relevant scientific literature would be desirable.
(11) Active stimulation reduced procrastination, reduced task aversiveness, and increased the outcome value. If I am not mistaken, the authors claim based on these results that the brain stimulation effect operates via self-control, but - unless I missed it - the authors do not have any direct evidence (such as measures or specific task measures) that actually capture self-control. Thus, that self-control is involved seems speculation, but there is no empirical evidence for this; or am I mistaken about this? If that is indeed correct, I think it needs to be made explicit that it is an untested assumption (which might be very plausible, but it is still in the current study not empirically tested) that self-control plays any role in the reported results.
(12) Figures 3F and 3H show that procrastination rates in the active modulation group go to 0 in all participants by sessions 6 and 7. This seems surprising and, to be honest, rather unlikely that there is absolutely no individual variation in this group anymore. In any case, this is quite extraordinary and should be explicitly discussed, if this is indeed correct: What might be the reasons that this is such an extreme pattern? Just a random fluctuation? Are the results robust if these extreme cells are ignored? The authors remove other cells in their design due to unusual patterns, so perhaps the same should be done here, at least as a robustness check.
(13) The supplemental materials, unfortunately, do not give more information, which would be needed to understand the analyses the authors actually conducted. I had hoped I would find the missing information there, but it's not there.
In sum, the reported/cited/discussed literature gives the impression of being incomplete/selectively reported; the analyses are not reported sufficiently transparently/fully to evaluate whether they are appropriate and thus whether the results are trustworthy or not. At least some of the patterns in the results seem highly unlikely (0 procrastination in the verum group in the last 2 observation periods), and the sample size seems very small for a between-subjects design.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
Chen and colleagues conducted a cross-sectional longitudinal study, administering high-definition transcranial direct stimulation targeting the left DLPFC to examine the effect of HD-tDCS on real-world procrastination behavior. They find that seven sessions of active neuromodulation to the left DLPFC elicited greater modulation of procrastination measures (e.g., task-execution willingness, procrastination rates, task aversiveness, outcome value) relative to sham. They report that tDCS effects on task-execution willingness and procrastination are mediated by task outcome value and claim that this neuromodulatory intervention reduces procrastination rates quantified by their task. Although the study addresses an interesting question regarding the role of DLPFC on procrastination, concerns about the validity of the procrastination moderate enthusiasm for the study and limit the interpretability of the mechanism underlying the reported findings.
Strengths:
(1) This is a well-designed protocol with rigorous administration of high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation across multiple sessions. The approach is solid and aims to address an important question regarding the putative role of DLPFC in modulating chronic procrastination behavior.
(2) The quantification of task aversiveness through AUC metrics is a clever approach to account for the temporal dynamics of task aversiveness, which is notoriously difficult to quantify.
Weaknesses:
(1) The lack of specificity surrounding the "real-world measures" of procrastination is problematic and undermines the strength of the evidence surrounding the DLPFC effects on procrastination behavior. It would be helpful to detail what "real-world tasks" individuals reported, which would inform the efficacy of the intervention on procrastination performance across the diversity of tasks. It is also unclear when and how tasks were reported using the ESM procedure. Providing greater detail of these measures overall would enhance the paper's impact.
(2) Additionally, it is unclear whether the reported effects could be due to differential reporting of tasks (e.g., it could be that participants learned across sessions to report more achievable or less aversive task goals, rather than stimulation of DLPFC reducing procrastination per se). It would be helpful to demonstrate whether these self-reported tasks are consistent across sessions and similar in difficulty within each participant, which would strengthen the claims regarding the intervention.
(3) It would be helpful to show evidence that the procrastination measures are valid and consistent, and detail how each of these measures was quantified and differed across sessions and by intervention. For instance, while the AUC metric is an innovative way to quantify the temporal dynamics of task-aversiveness, it was unclear how the timepoints were collected relative to the task deadline. It would be helpful to include greater detail on how these self-reported tasks and deadlines were determined and collected, which would clarify how these procrastination measures were quantified and varied across time.
(4) There are strong claims about the multi-session neuromodulation alleviating chronic procrastination, which should be moderated, given the concerns regarding how procrastination was quantified. It would also be helpful to clarify whether DLPFC stimulation modulates subjective measures of procrastination, or alternatively, whether these effects could be driven by improved working memory or attention to the reported tasks. In general, more work is needed to clarify whether the targeted mechanisms are specific to procrastination and/or to rule out alternative explanations.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
This manuscript explores whether high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) of the left DLPFC can reduce real-world procrastination, as predicted by the Temporal Decision Model (TDM). The research question is interesting, and the topic - neuromodulation of self-regulatory behavior - is timely.
However, the study also suffers from a limited sample size, and sometimes it was difficult to follow the statistics.
The preregistration and ecological design (ESM) are commendable, but I was not able the find the preregistration, as reported in the paper.
Overall, the paper requires substantial clarification and tightening.
Author response:
Reviewer #1:
(1) We fully thank you to point out the risks of sensationalizing ramification of procrastination on psychopathology, and would rewrite the Introduction section by adding balanced evidence and overall toning down such inappropriate claims meanwhile.
(2) Thank you to raise this crucial question. We are sorry for this fundamental technical issue to preregistration. This occurs from a seriously technical hurdle. The OSF has banned my OSF account, as it claimed to detect “suspicious user’s activities” in my account. This causes no accesses to all materials that already deposited in this OSF account, including this preregistration. We have contacted OSF team, but received no valid technical solution. We reckon that this may be mistaken by my affiliation changes to Third Military Medical University of People’s Liberation Army (PLA). To tackle with this technical issue, we shall upload preregistration in a new repository soon.
(3) This is a back-to-back study to conceptually probe into whether strengthening left DLPFC can mitigate procrastination via reducing task aversiveness or weighting outcome value. Thus, the current study selected a medium effect size in aprior by following the previous one (Xu et al., 2023). This effect size is calculated by the new tool called “Power Contours” (Baker et al., 2021), which weights statistical power by increasing within-subject repeated measures. As you kindly pointed out, we shall clarify effect size calculation in the revised manuscript.
(4) Yes, both groups come in the same number of times into the lab for tDCS stimulation, except to the type (active vs sham).
(5) We shall add full details for clarifying TDM and hyperbolic discounting modeling.
(6) Thank you to raise this very crucial statistical question. We shall double-check whether multiple sessions are modeled as random slopes, and would like to reanalysis it in case which those random slopes are omitted.
(7) Thank you. We have no intentions of confusing you by adding those complicated statistics, but indeed enrich understanding of how we can interpret those findings.
(8) Yes, as mentioned above, we shall add balanced evidence to clarify both left and right DLPFC may function to self-control capability in the Introduction section.
(9) Yes, this is a conceptual hypothesis --- actively stimulating left DLPFC could improve self-control functions. Thank you for this very nuanced but crucial insight, and we could explicitly clarify the nature of our conclusions.
(10) Yes, we ensure that all the participants successfully completed their tasks before deadline at session 6 and 7, and the procrastination rates have been all decreased to 0. Personally speaking, this is somewhat surprise to us as well, but we affirmed this case. For a portion of participants included in the active group, we have received written letters of thanks from them. Thus, this is surprise but exciting finding. Furthermore, thank you for this helpful suggestion, and we would like to do this robustness check by iteratively removing each session, to obviate the statistical biases from an extreme pattern.
(11) Yep, we fully agree with you to add full details in the main text rather in Supplemental materials, and would like to do so in the first round of revision.
Reviewer #2:
(1) Thank you for this very crucial suggestion. We are sorry for this case that much details are omitted to comply with editorial requirement at Nature Human Behaviour (last submission). We do apologize to confuse you as those ambiguous descriptions, and would like to clearly clarify how we measure participants’ procrastination in the real-world tasks. In brief, we asked participant to report a real task that would really happen in the tomorrow and its deadline is also no more than tomorrow. When tomorrow comes, we used ESM to require participant reporting real task completion rate (0-100%) at five time points before the deadline. The five time points are determined by a hyperbolic discounting model (see how and why we set those five time points in the full author’s response letter later). When participant reports the real task completion rate (0-100%) at a given time point, she/he is required to provide a photo to prove its authenticity. The dependent variable --- real-world procrastination rates --- is thus calculated as 100% subtracts the task completion rate (0-100%) when the deadline meets. That is to say, if participant reports task has been fully completed before or when deadline meets, his/her real-world procrastination rate is 100% - 100% = 0%; if reporting task has been completed 60% when deadline meets, the real-world procrastination rate is determined as 100% - 60% = 40%. Do not worry for spurious reporting, we asked all the participants to provide photo verifying the real task completion rate. This is merely a short instance. We shall show the full details in the formal author response letter later.
(2) This is a very meaningful point. We agree with you for this case that participants may learn how to complete this experiment task swiftly rather benefit from neuromodulation. This speculation makes sense, but is compromised by experimental control and empirical observations. Firstly, we do not say “You must complete this task” or “The task completion is associated with bonus/rewards you may get” for participants, which indicates no motivations to do so. Then, the measures to task completion rate are not yet fully based on self-reporting, and we mandate them to provide photos for verification. Thus, this controls the marked risks of spurious reporting. Lastly, all the participants, including ones in either active or sham group, received all the same treatments, excepting “real simulation” and “sham simulation” protocol. Results demonstrated the significant amelioration in the active group rather sham one, indicating no significant “placebo” or “task learning” side effect.
(3) Thank you. As you kindly suggested, we would like to add huge details for those measures in the revised manuscript. While this is a great idea, we did not collect procrastination scores from scales after neuromodulation, and would like to warrant this point into the Limitation section.
(4) Yep, this is a conceptual hypothesis --- actively stimulating left DLPFC could improve self-control functions. We cannot rule out possibilities of amplifying working memory, attention or other cognitive components from this neuromodulation protocol. We fully agree with you for this helpful recommendation --- we would like tone down those claims regarding the roles of DLPFC on self-control, and explicitly warrant that this mechanism may be specialized to the procrastination.
Reviewer #3:
(1) Thank you for taking valuable time to review our manuscript. Yep, limited sample size should warrant cautions to draw a solid conclusion. We would like to claim it into the limitation section. Also, we have streamlined and tightened statistic section by removing complicated and redundancy statistical models.
(2) As mentioned above, we are sorry for this fundamental technical issue to preregistration. This occurs from a seriously technical hurdle. The OSF has banned my OSF account, as it claimed to detect “suspicious user’s activities” in my account. This causes no accesses to all materials that already deposited in this OSF account, including this preregistration. We have contacted OSF team, but received no valid technical solution. We reckon that this may be mistaken by my affiliation changes to Third Military Medical University of People’s Liberation Army (PLA). To tackle with this technical issue, we shall upload preregistration in a new repository soon.
(3) Yep, thank you for this very helpful suggestion. As you kindly indicated, we would like to clarify measures, analyses, methods, and protocols, as well as tighten the whole manuscript.
References
Baker, D. H., Vilidaite, G., Lygo, F. A., Smith, A. K., Flack, T. R., Gouws, A. D., & Andrews, T. J. (2021). Power contours: Optimising sample size and precision in experimental psychology and human neuroscience. Psychological methods, 26(3), 295–314. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000337
Xu, T., Zhang, S., Zhou, F., & Feng, T. (2023). Stimulation of left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex enhances willingness for task completion by amplifying task outcome value. Journal of experimental psychology. General, 152(4), 1122-1133. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001312
Again, we wholeheartedly appreciate all of those very helpful and insightful comments, with each one to contribute substantially for the quality of this manuscript. Notably, those response we presented above are merely provisional and initial. We shall revise our manuscript following those suggestions, one-by-one, along with a full-length response letter.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
In this review article, the authors discuss the whole-brain activity changes induced by brain stimulation. They review the literature on how these activity changes depend on the cognitive state of the brain and divide the results by the scale of the change being induced, from microscale changes across small groups of neurons, up to macroscale changes across the entire brain. Finally, they describe attempts to model these changes using computational models.
Strengths:
The review provides an overview of the results within this subfield of neuroscience, and the authors are able to discuss a lot of prior results. The framing of the changes in neuronal activity in terms of computational changes is also a helpful approach.
Weaknesses:
However, the authors are not able to contextualize these results within a single framework, i.e. explaining from first principles how different aspects of stimulus-induced changes interact to generate functional changes in the brain, and how different changes - at distinct spatiotemporal scales - combine to form larger effects. This is a significant weakness in generating a review of the literature, since the authors do not provide a cohesive conceptual framework on which to frame the results. Similarly, the authors do not explain how their different computational models fit together, and how one can get a singular computational understanding of the distinct mechanisms of brain activity changes due to stimulation under different brain states, by combining the results derived from each separate model.
Major Comments:
(1) The authors have written this review as if it were intended for an audience who is already familiar with the topics. For example, they introduce concepts like complexity, spiral vs planar waves, without much explanation.
(2) Regarding complexity, the authors present a quantification termed PCI. However, in the associated box, they state that PCI could be implemented in a number of different ways, using analogous metrics (which are, nonetheless, not identical). Yet the authors simply claim that all these metrics are sufficiently similar to be grouped together as "PCI". The authors do not provide much intuition about this, and they also don't present any other potential quantifications. This makes any interpretation of their results strongly dependent on your understanding of the concept of PCI. It would be helpful to present some other, analogous metric to demonstrate that the results that the authors are focusing on are not somehow tied to the specific computational structure of the PCI metric.
(3) The authors divide the review into sections organized by the spatial extent of the effects that they are exploring (e.g. from microscale to macroscale). However, they don't bring together these insights into a cohesive structure - for example, by providing potential explanations of the macroscale effects by using the microscale changes.
(4) The authors completely ignore any aspect of cell-type specificity in their review, despite the known importance of specific cell types at the microcircuit scale. This makes it difficult to map their results onto the true biological system.
(5) The authors introduce several different computational models, such as the Hopf model, the AdEx model, and the MPR model. However, they do not provide the reader with a conceptual understanding of the structure of each of these models (except through potentially more complex terminology, e.g. the Hopf model is a "phenomenological Stuart-Landau nonlinear oscillator"). Additionally, though they present the results of each simulation, they don't provide the reader with intuition about how these models compare against each other, and how best to interpret results derived from each model.
(6) In several cases, the authors make statements that they appear to believe to be completely straightforward (and require no justification), but that do not appear so to the reader. For example, they mention: "In wakefulness and REM sleep, ..., the membrane potential is depolarized and close to the spike threshold, which explains why neurons respond more reliably and with less response variability compared with slow-wave sleep". However, this statement is not obvious to the reader and requires explanation (for example, in a system that is close to balance, bringing cells closer to the firing threshold can result in increased response jitter).
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
In the paper, the authors review literature on synchronous activity, its relationship to brain state, and the multi-scale mechanisms underlying it.
Strengths:
The overall strength of the paper is the wide range of information reviewed, and the diversity of perspectives/approaches it brings together.
Weaknesses:
However, this strength is also the source of its major weaknesses - namely, that the overall structure lacks clarity, and there are inconsistencies throughout. Overall, in the opinion of this reviewer, the manuscript reads as disorganized and incomplete. Major and minor points are delineated below.
Major points:
(1) Most of the text in many figures was too small to read.
(2) Terminology is inconsistent throughout the manuscript. What is the difference between slow oscillations and delta waves? Sometimes the term slow waves is used instead. For sleep state, sometimes the term SWS is used, sometimes non-REM. Similarly, "spindle activity" is not defined, but simply stated as if the reader knows. This brings up two issues: (a) the manuscript should be clearer and more consistent about its terminology, and (b) it's unclear who is the intended readership of the review - is it a pedagogical review for people outside the field of sleep and slow oscillations, or is it meant to be a consensus statement for readers who are already in the field in which a pressing concern has been addressed? It seems part way between these two, and as a result, is ineffective at either goal.
(3) I suggest the authors look again at the overall structure and flow of the review... many sections feel redundant, and it's unclear how they fit together into a single review.
(4) There are many speculative statements in the review that are not justified or explained sufficiently for the reader. For example: "While highly regular slow waves in vivo suggest a single mechanism of generation, namely local cortical circuits, irregular cycles are compatible with a larger role of subcortical nuclei, ..."; "The involvement of different cortical areas and subcortical nuclei can form the basis of these different roles in memory.". For these statements, I assume the relationship between slow wave statistics, subcortical nuclei, and memory either has been written about before, and then should be cited and summarized, or is a novel claim of the authors, which then should be explained and defended rather than stated. There are other similar examples, and I suggest the authors go through the manuscript and make sure that it's clear what is a novel claim of the authors vs a cited claim, and make sure that both are sufficiently justified for the reader.
(5) An especially notable example can be found in the section on the role of the thalamus, where the authors state that they "hold that slow oscillations are fundamentally cortical". However, this section is far too short, and very little evidence is provided to back up this claim. Please review the ways in which the thalamus modulates, and, e.g., ways in which up-down is similar/different without the thalamus.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
In this review article, the authors discuss the correlated dynamical states associated with distinct cognitive states, including those associated with anesthesia and sleep. They present evidence that these states are primarily cortically generated, and demonstrate the properties of these dynamical states at different levels, from the microscale dynamics in individual neurons to the macroscale dynamics across the brain.
Strengths:
Multiple groups have been adding to this field over the past decades, and therefore, a review of this literature is very helpful. This review collates a large amount of the literature within this field into a single document, which should make it a valuable resource within this area of neuroscience.
Weaknesses:
Unfortunately, this review does not seem to be a balanced viewpoint of the field in question. Although there are a lot of authors in the review, it feels as if they are from a common school of thought. The authors provide only a single perspective on these dynamical states, focusing on the perspective of wave-like electrical dynamics across the cortex. Their perspective is embedded in methods such as EEG and LFP recordings. This makes the work hard to interpret outside of the field in which the authors reside. Indeed, the review seems intended for a more specialized audience.
In addition, the article reads more like a catalog of prior studies as opposed to a true synthesis across the large volume of data in this field that highlights links across multiple sources. Hence, it does not seem to provide a novel way of understanding the dynamics involved in cognitive state transitions.
We have included more details on these general comments below:
Major Comments:
(1) The authors have written this review as if it were intended for an audience who is already familiar with these topics. They do not define many of the terms that they introduce within the review, including concepts like complexity, metastability, and oscillations that are fundamental to the concepts that the authors are introducing. Though these may seem like first principles concepts to the authors, they often introduce assumptions that may be unfamiliar to the general reader. For example, are slow wave oscillations periodic? A naïve reader may assume that oscillations - characterized by their frequency - should be somewhat periodic, but that is often not the case. For a journal with a general biological science readership, it would be particularly helpful for each of these terms to be formally defined and characterized.
(2) It would be helpful for the authors to reframe their work in different perspectives and to incorporate all the literature on the dynamics of cortical brain states, and not simply the work that is most familiar to them. As one example, the authors do not discuss cell-type-specific changes in brain state during anesthesia and in altered states of consciousness (including dissociative states and hallucinatory states). There is recent work in this vein (Suzuki and Larkum, 2020; Vesuna et al, 2020; Bharioke, Munz et al, 2023), and yet the authors do not discuss these papers.
(3) Given the authors' clear, extensive knowledge of their field, it would also be extremely helpful for the authors to reframe fundamental concepts in terms of neuronal population activity, trajectory analyses, etc. This would enable a more general audience to better understand their work.
(4) The authors have one section focused on thalamic contributions to cortical wave-like activity. This is a cursory treatment of a subject that is quite controversial in the field. It would be helpful if the authors could provide a more balanced consideration of all the evidence regarding potential thalamocortical interactions and their role in wave-like activity.
(5) The authors present many computational models and describe the results of simulations with these different models. However, this doesn't provide the reader with intuition about what each model adds or removes from the true biological picture. It would be helpful for the authors to provide some intuition about the assumptions and constraints that underlie each model.
(6) The authors state that "The main mechanism [of slow oscillatory dynamics] consists of a combination of two ingredients: the recurrent connectivity, which maintains the excitability in the network, and adaptation, an activity-dependent fatigue variable that provides inhibitory feedback". They make this statement as a fact, yet they don't provide much justification for it. Additionally, it's not clear that any other possible combination of ingredients would be able to produce slow oscillatory dynamics.
(7) The authors often define one concept in terms of other equally complex concepts. For example: "EIA (excitatory-inhibitory with adaptation) cortical circuits then display the typical slow-fast dynamics of relaxation oscillators". The reader would need an explanation of slow-fast dynamics and relaxation oscillators to understand this line, neither of which is provided in the text.
(8) When discussing sleep, the authors do not discuss REM sleep, focusing on slow-wave non-REM sleep. It would be helpful if the authors could at least frame the full sleep cycle and discuss why they are focusing on one part of it.
(9) The authors introduce the concept of sleep spindles without any explanation.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This report demonstrates that the gene expression output of the Wnt pathway, when controlled precisely by a synthetic light-based input, depends substantially on the frequency of stimulation. The particular frequency-dependent trend that is observed - anti-resonance, a suppression of target gene expression at intermediate frequencies given a constant duty cycle - is a novel aspect that has not been clearly shown before for this or other signaling pathways. The paper provides both clear experimental evidence of the phenomenon with engineered cellular systems and a model-based analysis of how the pairing of rate constants in pathway activation/deactivation could result in such a trend.
Strengths:
This report couples in vitro experimental data with an abstracted mathematical model. Both of these approaches appear to be technically sound and to provide consistent and strong support for the main conclusion. The experimental data are particularly clear, and the demonstration that Brachyury expression is subject to anti-resonance in ESCs is particularly compelling. The modeling approach is reasonably scaled for the system at the level of detail that is needed in this case, and the hidden variable analysis provides some insight into how the anti-resonance works.
Weaknesses:
(1) The anti-resonance phenomenon has not been demonstrated using physiological Wnt ligands; however, I view this as only a minor weakness for an initial report of the phenomenon. The potential significance of the phenomenon for Wnt outweighs the amount of effort it would take to carry the demonstration further - testing different frequencies/duty cycles at the level of ligand stimulus using microfluidics could get quite involved, and would likely take quite some time. Adding some more discussion about how the time scales of ligand-receptor binding could play into the reduced model would further ameliorate this issue.
We thank the reviewer for this comment and the interesting suggestion to test the anti-resonance phenomenon with microfluidics. We agree that combining physiological Wnt ligands with microfluidic stimulation would go beyond the scope of this current study, though it is an interesting extension. One advantage of the optogenetic setup, as mentioned in the discussion, is that the Wnt stimulus can be turned off sharply. This allows us to test the output from perfectly square wave input profiles; in microfluidics, washing the sticky ligand off the cells might “smear” the effective input profile cells respond to.
We show in Supplement Fig. 6, that our reduced model matches the experimental data and that we would expect the antiresonance phenomenon as long as 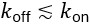 (see Fig. 4). Practically, a smeared input profile implies an effective reduction of 𝑘<sub>off</sub>, which means that the phenomenon would be visible with microfluidics (provided the minimum is deep enough, see Fig. 4). However, this should still be considered with caution, as the antiresonance would then appear because the cells essentially receive a smeared out or continuous pulse in the high frequency limit, rather than cells responding to a square wave in a specific way.
(see Fig. 4). Practically, a smeared input profile implies an effective reduction of 𝑘<sub>off</sub>, which means that the phenomenon would be visible with microfluidics (provided the minimum is deep enough, see Fig. 4). However, this should still be considered with caution, as the antiresonance would then appear because the cells essentially receive a smeared out or continuous pulse in the high frequency limit, rather than cells responding to a square wave in a specific way.
(2) While the model is fully consistent with the data, it has not been validated using experimental manipulations to establish that the mechanisms of the cell system and the model are the same. There may be some ways to make such modifications, for example, using a proteasome inhibitor. An alternative would be to more explicitly mention the need to validate the model's mechanism with experiments.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable and constructive comment. We agree that future experimental perturbations that directly modulate pathway activation and reset kinetics—such as proteasome inhibition, targeted degradation of pathway components, or engineered changes in receptor turnover—would provide an important validation of the model’s mechanistic interpretation. In the present study, our primary goal was to establish the existence and quantitative features of anti-resonance in the Wnt pathway and to identify the minimal set of timescale relationships that can explain it. We view the proposed experimental validations as exciting next steps that extend beyond the scope of the current work, and we are grateful to the reviewer for emphasizing their importance. We now mention this explicitly in the discussion of our manuscript.
(3) I think the manuscript misses an opportunity to discuss the potential of the phenomenon in other pathways. The hedgehog pathway, for example, involves GSK3-mediated partial proteolysis of a transcription factor, which could conceivably be subject to similar behaviors, and there are certainly other examples as well.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out an opportunity to emphasize the possibility of this phenomenon in other pathways. The minimal model indicates that anti-resonance emerges whenever a rapid activating process is paired with a slower deactivating/reset process. Beyond Hedgehog/Gli processing, candidate circuits include: NF-κB (rapid IκBα phosphorylation/degradation vs slower IκBα resynthesis), ERK (fast phosphorylation bursts vs slower transcriptional negative feedback such as DUSPs), Notch (fast γ-secretase NICD release vs slower NICD turnover and feedback), BMP/TGF-β–SMAD (fast R-SMAD phosphorylation vs slower receptor trafficking/SMAD7 feedback), and Hippo/YAP (rapid cytoplasmic sequestration vs slower transcriptional feedback). Each contains the same timescale separation that should create a frequency ‘stop-band,’ predicting suppressed gene expression or fate transitions at intermediate stimulation frequencies. We have updated the manuscript’s discussion to mention the Hedgehog connection with the following added sentence in the discussion: Analogous band-stop filtering should arise in other developmental circuits that couple a fast ‘ON’ step to slower deactivation or negative feedback. In Hedgehog, for example, PKA/CK1/GSK3-mediated partial proteolysis of Gli with slower recovery of full-length Gli creates the same fast-activation/slow-reset motif our hidden-variable model predicts will yield anti-resonance, and Wnt–Hedgehog crosstalk through the shared kinase GSK3 suggests such frequency selectivity could occur in other developmental signaling pathways.
We also added an additional sentence regarding different activation and deactivation timescales in other pathways.
(4) Some aspects of the modeling and hidden variable analysis are not optimally presented in the main text, although when considered together with the Supplemental Data, there are no significant deficiencies.
We have addressed the model choices and analysis now more clearly in the main manuscript and also referred to the Supplemental Data more directly.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
By combining optogenetics with theoretical modelling, the authors identify an anti-resonance behavior in the WnT signaling pathway. This behavior is manifested as a minimal response at a certain stimulation frequency. Using an abstracted hidden variable model, the authors explain their findings by a competition of timescales. Furthermore, they experimentally show that this anti-resonance influences the cell fate decision involved in human gastrulation.
Strengths:
(1) This interdisciplinary study combines precise optogenetic manipulation with advanced modelling.
(2) The results are directly tested in two different systems: HEK293T cells and H9 human embryonic stem cells.
(3) The model is implemented based on previous literature and has two levels of detail: i) a detailed biochemical model and ii) an abstract model with a hidden parameter.
Weaknesses:
(1) While the experiments provide both single-cell data and population data, the model only considers population data.
We thank the reviewer for correctly pointing out that the single-cell measurements would in principle allow us to incorporate the cell-to-cell heterogeneity into the model. In this study, we sought to identify a minimal quantitative model of the Wnt pathway that could explain anti-resonance through competing time scales. We believe that, for our purposes, focusing on population data allowed us to keep the complexity of the model to a minimum to increase its explanatory value. We agree with the reviewer that considering single-cell trajectories is an interesting direction for further work.
(2) Although the model captures the experimental data for TopFlash very well, the beta-Cat curves (Figure 2B) are only described qualitatively. This discrepancy is not discussed.
Indeed, our model fits to mean β-catenin expressions are more qualitative than for TopFlash. The fit for β-catenin was tricky, as expression of β-catenin is typically low and closer to the detectable limits than TopFlash. These experimental constraints mean that the variation between individual signal trajectories is higher for β-catenin compared to the light-off condition than for TopFlash. Therefore, we strove to obtain a qualitative rather than a quantitative fit to the mean expression profile in β-catenin. The current model fit is well within the standard deviation of variation. Given the observed heterogeneity and the fact that we take the parameters from literature (which ensures that the order of magnitude of parameters is in a sensible range), we believe that the model fits are reasonable. We now mention this explicitly in the text.
Overall Assessment:
The authors convincingly identified an anti-resonance behavior in a signaling pathway that is involved in cell fate decisions. The focus on a dynamic signal and the identification of such a behavior is important. I believe that the model approach of abstracting a complicated pathway with a hidden variable is an important tool to obtain an intuitive understanding of complicated dependencies in biology. Such a combination of precise ontogenetic manipulation with effective models will provide a new perspective on causal dependencies in signaling pathways and should not be limited only to the system that the authors study.
We thank both reviewers for the positive assessment of our manuscript.
Recommendations for the authors:
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
There are several points that deserve more discussion, as noted above in the review.
(1) It would be worthwhile to consider whether a relatively simple experiment with a proteasome inhibitor or similar pharmacological manipulation could provide useful validation data for the model.
We address this point above in the weaknesses section from reviewer 1.
(2) The figure legend for S5C should clarify whether the values plotted are at a particular fixed time point, or (more likely) at a certain time following the second pulse, which would be variable.
We have modified the figure caption to clarify that the values plotted are at a fixed time point in the simulation (t\=48 hrs). We chose this timepoint sufficiently long after the second pulse to ensure that there are no residual dynamical effects. We thank the reviewer for noting this.
(3) As noted in the Sci Score document, various aspects of the resource reporter should be improved, such as including RRIDs, etc.
We are sending out our plasmids to AddGene; versions for Python and Matlab are listed in our methods section.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
I mostly have suggestions to improve the clarity of the presentation.
(1) Not all symbols in the equations given in the main text are explained. This is rather annoying, because either you present them and explain what they are or you don't show them and refer to the supplements. For example, d_0 or c_o or \bar{b} or n or K are not explained.
We have now more clearly presented the parameters in the main text and added signposts to the Methods section.
(2) Overall, it is often not clear what data in the figures are redundant, although the authors referred to them in the text. For example, in Figure 2c, a curve for 24 hours is shown and referred back to Figure 1D. However, in Figure 1D there is no curve for 24 hours. Is the data from Supplementary Figure 1 H and K also in the main text?
We thank the referee for pointing out these redundancies. We have now included the 24hr line in Figure 1D and are now only showing the unsmoothed data, also in the main text of the manuscript. To clarify supplemental figures, we have now removed S1H and S1K since all they showed was the unsmoothed version of the data. The remaining plots in Supplementary Figure 1 are normalized differently from what we show in Figure 1 to demonstrate our choice of normalization is not the reason for the observed optogenetic response.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1:
(1) The authors state that more is known about glial reactivation than cell-cycle re-entry. They are confusing many points here. More gene networks that require cell-cycle re-entry are known. Some of the genes listed for "reactivation" are, in fact, required for cell cycle re-entry/proliferation. And the authors confuse gliosis vs glial reactivation.
We thank the reviewer for this important and constructive comment. We fully agree that clearly distinguishing between the concepts of glial reactivation, glial proliferation, gliosis, and neurogenesis is essential to avoid conceptual confusion in our study.
Injury-induced retinal regeneration in zebrafish:
Glial reactivation refers to the initial response of quiescent Müller glia (MG) to injury, characterized by morphological changes and upregulation of reactive markers (e.g., gfap, ascl1a, lin28a) and activation of signaling pathways such as Notch, Jak/Stat, and Wnt (Lahne et al., 2020; Pollak et al., 2013; Sifuentes et al., 2016; Yao et al., 2016).
Glial proliferation refers to the clonal expansion of these MG-derived progenitor cells, which undergo rapid cell-cycle re-entry and amplify to generate sufficient progenitors for regeneration (Iribarne and Hyde, 2022; Lee et al., 2024; Wan and Goldman, 2016)
Gliosis vs neurogenesis represents a divergent fate decision following proliferation. In zebrafish, MG-derived progenitor cells differentiate into retinal neurons that can replace those damaged or lost due to retinal injury. In contrast, mammalian MG tend to undergo an initial gliotic surge and rapidly revert to a quiescent state, exhibiting gliosis and glial scarring (Thomas et al., 2016; Yin et al., 2024). Thus, we totally agreed that gliosis cannot be confused with glial reactivation because glial reactivation is the very first step of glial injury responses, whereas gliogensis is the very last glial response to the injury.
We agree with the reviewer that many genes typically described as “reactivation markers” (e.g., ascl1a, lin28a, sox2, mycb, mych) are also essential regulators of cell-cycle re-entry (Gorsuch et al., 2017; Hamon et al., 2019; Lee et al., 2024; Lourenço et al., 2021; Pollak et al., 2013; Thomas et al., 2016). Because the glial reactivation is a leading event for glial proliferation, the regulators of glial reactivation are expected to be responsible for glial proliferation as well.
In our study, we focused on the states preceding glial proliferation to understand the mechanism underlying injury-induced glial cell-cycle re-entry. We defined these transitional states and the subsequent proliferative MG states based on single-cell RNA-seq trajectory analysis. (revised lines: 41-58)
(2) A major weakness of the approach is testing cone ablation and regeneration in early larval animals. For example, cones are ablated starting the day that they are born. MG that are responding are also very young, less than 48 hrs old. It is also unclear whether the immune response of microglia is a mature response. All of these assays would be of higher significance if they were performed in the context of a mature, fully differentiated, adult retina. All analysis in the paper is negatively affected by this biological variable.
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point regarding the developmental stage of the retina in our model system. We have carefully considered this concern and now provide additional clarification and justification, as follows:
(1) The glial responses in larval and adult retina:
Previous studies have demonstrated that injury-induced glial responses are largely conserved in larval and adult zebrafish retina, including reactive gliosis marked by gfap upregulation and proliferation(Meyers et al., 2012; Sarich et al., 2025). In our study, G/R cones were ablated beginning at 5 dpf using metronidazole (MTZ), and we observed robust induction of PCNA⁺ MG in the inner nuclear layer, consistent with injury-induced proliferation (Figure 1E). These findings align with previous studies showing that key features of MG regenerative responses are conserved across larval and adult stages.
(2) The microglial responses in larval and adult retina:
Retinal microglia functionally mature at 5 dpf in the zebrafish retina (Mazzolini et al., 2020; Svahn et al., 2013), and prior studies have demonstrated that microglia in larval and adult zebrafish exhibit similar responses to injury, including migration, morphological activation, and phagocytosis(Nagashima and Hitchcock, 2021; White et al., 2017). In our experiments using Tg(mpeg1: GFP) larvae, we observed clear microglial recruitment to the outer nuclear layer (ONL) following cone ablation (Figure 1E and Figure 1-figure supplement 1A), supporting the functional competence of larval microglia in injury-induced immune responses
(3) The contribution using larval animals to study the regeneration program:
We agree that regeneration studies in the adult retina can provide important biological insights, particularly in a fully differentiated tissue environment. Accordingly, we have acknowledged this limitation in our revised manuscript “limitations of this study” section (revised lines 534-540: “1. Our study focuses on larval zebrafish, in which the core features of MG and immune responses are conserved compared to the adult. However, we acknowledge that the adult retina—with its fully matured differentiated retina and immune response—provides irreplaceable biological insight. Nevertheless, larval models offer a powerful platform to uncover conserved regenerative mechanisms and serve as a valuable complement for identifying age-dependent differences in MG-mediated regeneration.”) and have stated our intention to extend future analyses to adult zebrafish, especially to explore age-dependent differences in redox signaling and MG proliferation. At the same time, we believe that the larval model offers unique advantages for uncovering fundamental, conserved mechanisms of regeneration and enables characterization of age-dependent regulatory differences. Thus, our study in larval animals serves as a complementary and informative platform for understanding both the conserved and developmental stage-specific features of injury-induced regeneration.
(4) Related to the above point, the clonal analysis of cxcl18b+ MG is complicated by the fact that new MG are still being born in the CMZ (as are new cones for that matter).
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point regarding potential contributions from CMZ-derived progenitors to the lineage-traced cxcl18b⁺ MG clones. To address this concern, we have implemented evidence to rule out a CMZ origin for the clones analyzed:
Spatial restriction of clones: All clones included in our analysis were located exclusively within the central and dorsal retina, as shown in Figure 2H. From the spatial distribution of reactive MG populations across the retina, we observed a patterned organization in which the vast majority of proliferating MG arose from local mature MG–derived progenitors, rather than from peripheral CMZ-derived progenitors. However, we acknowledge that we cannot entirely exclude the possibility that CMZ-derived progenitors contribute to injury-induced MG proliferation, particularly in the peripheral retina.
We have clarified this point in the revised Methods section (revised lines 756–762: “Clone analysis of cxcl18b<sup>+</sup> lineage-traced MG was restricted to cells located in the central and dorsal region of the zebrafish retina after G/R cone ablation in Figure 2, Figure 6, and their figure supplement. This spatial restriction strongly suggests that the proliferative MG originate from local mature MG, although we cannot completely rule out the possibility that CMZ-derived progenitors contribute to the generation of proliferative MG in the peripheral retina.”) and updated the corresponding figure legends.
(4) A near identical study was already done by Hoang et al., 2020, in adult zebrafish, a more relevant biological timepoint. Did the authors check this published RNA-seq database for their gene(s) of interest?
We thank the reviewer for pointing out the relevance of the study by Hoang et al., 2020, which characterized the transcriptional dynamics of MG reactivation in the adult zebrafish retina. We agree that comparisons with their single-cell RNA-seq dataset are important to confirm the conservation of our findings in larval vs adult zebrafish.
To this end, we examined the adult zebrafish MG dataset reported by Hoang et al., and confirmed that cxcl18b is also present and enriched in their analysis, particularly in activated MG populations under various injury paradigms:
(1) cxcl18b is listed as a differentially expressed gene (DEG) in Supplementary Table ST2, enriched in GFP⁺ MG following injury. It is also significantly upregulated in both NMDA-induced and light damage conditions, as shown in Supplementary Table ST3.
(2) In Supplementary Table ST5, cxcl18b is identified as a classifier of activated MG, with classification power scores of 0.552 (NMDA), 0.632 (light damage), and 0.574 (TNFα + γ-secretase inhibitor treatment), indicating its consistent expression across multiple injury models.
(3). In their pseudotime analysis (Figure 4C and Supplementary Table ST8), cxcl18b is specifically expressed in Module 5, which is expressed earlier along the trajectory than ascl1a. This temporal pattern of cxcl18b preceding ascl1a expression is consistent with our trajectory analysis in larval MG (Figure 1H), further supporting its role as an early marker of the transitional state before proliferation.
These findings underscore the robustness and biological relevance of cxcl18b as a conserved marker of injury-responsive MG in both larval and adult zebrafish. Our data expand upon the prior work by specifically characterizing a cxcl18b-defined transitional MG state preceding cell-cycle re-entry, thereby offering additional insights into the temporal staging of MG activation during regeneration.
(5) KD of cxcl18b did not affect MG proliferation or any other defined outcome. And yet the authors continually state such phrases as "microglia-mediated inflammation is critical for activating the cxcl18b-defined transitional states that drive MG proliferation." This is false. Cxcl18b does not drive MG proliferation at all.
We thank the reviewer for raising this concern. We agree with the reviewer and have revised this statement as "These findings suggest that microglia-mediated inflammation may contribute to the activation of cxcl18b-defined transitional states that precede MG proliferation, although a causal relationship remains to be established." (revised lines 251-253).
(6) A technical concern is that intravitreal injections are not routinely performed in larval fish.
We appreciate the reviewer’s technical concern regarding the use of intravitreal injections in larval zebrafish. In our study, we performed intraocular injection according to previously established methods (Alvarez et al., 2009; Giannaccini et al., 2018; Rosa et al., 2023). This approach involves carefully delivering a small volume of viral suspension into the intraocular space by a glass micropipette. To address this concern, we will revise the Materials and Methods section to clearly describe the injection procedure and will cite the relevant references accordingly.
Reviewer #2:
(1) The authors note a peak of PCNA+ Muller glia at 72 hours post injury. This is somewhat surprising as the MG would be expected to generate progenitor cells that would continue proliferating and stain with PCNA. Indeed, only a handful of PCNA+ cells are seen in the INL/ONL layer in Figure 1E2 with few clusters of progenitors present. It would be helpful to stain with a Muller glia marker to confirm these PCNA+ cells are Muller glia. It's also curious that almost all the PCNA+ cells are in the dorsal retina, even though G/R cone loss extends across both dorsal and ventral retina. Is this typical for cone ablation models in larval zebrafish?
We thank the reviewer for their insightful comment regarding the spatial distribution and identity of PCNA⁺ cells following injury.
In our study, we observed that the injury-induced proliferating cells (PCNA⁺) were predominantly located in the central and dorsal regions of the retina at 72 hours post-injury (hpi) (Figure 1E). To verify the identity of these proliferating cells, we performed additional immunostaining using BLBP, and confirmed that the majority of PCNA⁺ cells also express BLBP (Figure 1–figure supplement 1B in our revised Data), these results supporting their MG origin.
The regional bias of MG proliferation towards the central and dorsal retina is consistent with previous findings. Notably, (Krylov et al., 2023) demonstrated that MG exhibit region-specific heterogeneity in their regenerative responses to photoreceptor ablation. Their study identified proliferative MG subpopulations predominantly in the central (fgf24-expressing) and dorsal (efnb2a-expressing) domains, whereas ventral MG showed limited proliferative capacity (Krylov et al., 2023). These observations provide a plausible explanation for the spatially restricted PCNA⁺ MG population observed in our model following cone ablation.
(2) In Line 148: What is meant by "most original MG states" in this context? Original meaning novel? Or original meaning the earliest state MG adopted following injury? The language here is confusing.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out the ambiguous phrasing in our original manuscript. The term “most original MG states” was imprecise and misleading, as it could be interpreted as referring to the quiescent state of MG. In our context, we intended to describe the earliest transitional states in MG respond to injury, as they begin to exit quiescence and enter reactive characteristics. These early transitional MG populations co-express quiescent markers such as cx43 and early reactive markers gfap, as shown in Figure 1H.
To avoid confusion and improve conceptual clarity, we have revised the manuscript by replacing “most original MG states” with “early transitional MG state” (revised line 154) and have added a clearer explanation in the corresponding Results section to define this population more accurately.
(3) Perhaps provide a better image in Figure 2A of the cxcl18b at 48 hpi and 72 hpi. The current images appear virtually identical, with very little cxcl18b expression observed, especially compared to the 24 hpi. This is in contrast to the Tg(cxcl18b:GFP) transgenic line shown in Figure 2D, which indicates either much higher expression in proliferating cells at 48 hpi or the stability of GFP protein. Can the authors provide guidance on the accurate temporal expression of cxcl18b? Does expression peak rapidly at 24 hpi and then rapidly decline or is there persistence of expression to 48-72 hpi?
We appreciate the reviewer’s careful observation regarding the apparent similarity of cxcl18b expression at 48 hpi and 72 hpi in the in situ hybridization (ISH) images (Figure 2A), and the differences compared to the Tg(cxcl18b: GFP) reporter line shown in Figure 2D.
(1) The similarity of ISH images at the 48 hpi and 72 hpi (Figure 2A):
The cxcl18b mRNA signal peaked at 24 hpi, suggesting a rapid transcriptional response after retina injury. By 48 hpi, cxcl18b expression had already declined substantially, and by 72 hpi, the signal was further reduced to near-background levels. This temporal expression pattern explains why the ISH images at 48 hpi and 72 hpi appear nearly identical and much weaker compared to 24 hpi.
(2) The discrepancy between ISH and GFP reporter signal (Figure 2D):
The Tg(cxcl18b: GFP) reporter line shows persistent GFP expression beyond the transcriptional window of cxcl18b mRNA. This may be due to the prolonged stay of GFP protein, which remains detectable even after the endogenous transcription of cxcl18b has diminished. This explanation is also noted in the manuscript (revised lines 198–200). As a result, GFP⁺ MG cells are still visible at 48–72 hpi, and some of them co-label with PCNA.
These findings are consistent with our Pseudotime analysis based on scRNA-seq data (Figure 1H), which shows that cxcl18b expression precedes the induction of proliferative markers such as pcna and ascl1a.
(4) Line 198: The establishment of the Tg(cxcl18b:Cre-vhmc:mcherry::ef1a:loxP-dsRed-loxP-EGFP::lws2:nfsb-mCherry) is considerable but the nomenclature doesn't properly fit. Is the mCherry fused with Cre and driven by the cxcl18b promoter? What is the vhmc component? Finally, while this may provide the ability to clonally track cxcl18b-expressing MG, it does not address the prior question of what is the actual temporal expression of cxcl18b? If anything, this only addresses whether proliferating MG expressed cxcl18b at some point in their history, but does not indicate that cxcl18b expression co-exists in proliferating cells. The most convincing evidence is in Supplemental Figure 2B.
The "vmhc" component refers to the ventricular myosin heavy chain promoter, commonly used to label atrial cardiomyocytes (Jin et al., 2009). We cloned the vmhc upstream region containing its promoter and fusing with mCherry for selection during transgenic fish line construction.
Clone analysis using the Tg(cxcl18b: Cre-vmhc: mCherry::ef1a: loxP-DsRed-loxP-EGFP::lws2: nfsb-mCherry) further indicates that cxcl18b-defined the transitional state is the essential routing for MG proliferation. We have clarified in the revised text that this lineage tracing indicates a “history of injury-induced cxcl18b expression” rather than its ongoing expression during proliferation (revised line 205).
(5) Line 203: The data shown in Figure 2F do not indicate that these MG are cxcl18b+. Rather, the data are consistent with the interpretation that these MG expressed Cre at some prior stage and now express GFP from the ef1a promoter rather than DsRed. Whether these MG continue to express cxcl18b at the time these fish were collected is not addressed by these data. It is not accurate to conclude that these cells are cxcl18b+.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out this important issue. We agreed that the GFP<sup>+</sup> MG shown in Figure 2F represents cells that have previously expressed cxcl18b and thus belong to the cxcl18b-expressing cell lineage, but this does not indicate that they continue to express cxcl18b at the time of sample collection. Performing clonal analysis using the Cre-loxp system, the GFP signal reflects historical cxcl18b promoter activity rather than ongoing transcription. We have revised the relevant sentence in our manuscript to clarify this point and now refer to these GFP<sup>+</sup> cells as "cxcl18b lineage-traced MG" rather than "cxcl18b<sup>+</sup> MG" to avoid any misinterpretation (revised line 207).
(6) Line 213: The statement that proliferative MG mostly originated from cxcl18b+ MG transitional states is a conclusion that does appear fully supported by the data. Whether those MG continue to express cxcl18b remains unanswered by the data in Figure 2 and would likely be inconsistent with the single-cell data in Figure 1.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable comment. We agree that the original statement on Line 213 regarding the lineage relationship between cxcl18b⁺ transitional MG and proliferative MG required clarification.
(1) The cxcl18b expression dynamics:
Our single-cell RNA-seq and ISH analyses consistently show that cxcl18b expression peaks as early as 24 hpi and declines rapidly, with significantly reduced expression by 48 and 72 hpi. These findings suggest that cxcl18b marks an early transitional MG state, rather than being maintained in proliferative MG. Indeed, in our scRNA-seq pseudotime trajectory analysis (Figure 1H), cxcl18b expression is highest in early transitional MG clusters (Clusters 1) and downregulated as cells progress toward proliferative states (Clusters 3/6), supporting a model in which cxcl18b is downregulated before cell-cycle re-entry.
(2) Prolonged stability of GFP protein:
The GFP signal observed in Tg(cxcl18b: GFP) retinas at 72 hpi may be because of the prolonged stability of GFP protein, rather than sustained cxcl18b transcription. The actual expression dynamics of cxcl18b are more directly reflected by our in situ hybridization and single-cell RNA-seq data, both showing a rapid decline after its early peak at 24 hpi. This explanation is also noted in the manuscript (revised lines 196–197).
(7) Line 246: The use of Dexamethasone to block inflammation is a widely used approach. However, dexamethasone is a broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory molecule that works through glucocorticoid signaling that may involve more than microglia. The observation that microglia recruitment and cxcl18a expression are both reduced is correlative but does not prove causation. Thus, the data are not sufficient to conclude that microglia-mediated inflammation is critical for activating cxcl18b expression. Indeed, data in Figure 1 indicate that cxcl18b expression occurs prior to microglia migration to the ONL.
We thank the reviewer for this thoughtful and important comment. We fully acknowledge that dexamethasone is a broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory agent that acts via glucocorticoid receptor signaling and may influence multiple immune and non-immune pathways beyond microglia.
In our study, dexamethasone treatment led to a reduction in both microglial recruitment and the number of cxcl18b<sup>+</sup> MG at 72 hpi, suggesting a potential association between inflammation and cxcl18b activation. However, we agree that this observation remains correlative and is not sufficient to establish a direct link between microglia activity and cxcl18b induction. Our time-course analysis indicates that cxcl18b expression peaks at 24 hpi, preceding robust microglial accumulation in the ONL, further highlighting the need to clarify the temporal dynamics and cellular sources of inflammatory cues.
To address this question more conclusively, selective ablation of microglia during cone injury would be necessary. However, implementing such an approach would require a complex intersection of three transgenic lines—Tg(mpeg1: nfsB-mCherry) for microglia ablation, Tg(lws2: nfsB-mCherry) for cone ablation, and Tg(cxcl18b: GFP) for reporting—posing substantial genetic and experimental challenges.
We have revised the Results section accordingly to state: “These findings suggest that microglia-mediated inflammation may contribute to the activation of cxcl18b-defined transitional states that precede MG proliferation, although a causal relationship remains to be established.” (revised lines 251–253). We also added a new paragraph in the “Result: Clonal analysis reveals injury-induced MG proliferation via cxcl18b-defined transitional states associated with inflammation” as “While dexamethasone suppressed both microglial recruitment and cxcl18b<sup>+</sup> MG generation, its broad anti-inflammatory action precludes definitive conclusions about microglial causality. Dissecting this relationship would require concurrent ablation of microglia and cone photoreceptors using a triple-transgenic strategy, which is beyond the scope of the current study. Targeted approaches will be necessary to resolve the specific role of microglia in initiating cxcl18b expression.” (revised lines 251–258) to explicitly acknowledge this limitation and the need for future studies using microglia-specific ablation models to resolve the mechanism.
(8) Could the authors clarify the basis of investigating NO signaling, given the relative expression of the genes by either cxcl18b+ MG or uninjured MG? Based on the expression illustrated in Supplemental Figure 4A, there is almost no expression of nos1 or nos2b in any MG. The authors are encouraged to revisit the earlier single-cell data sets to identify those cells that express components of NO signaling to determine the source(s) of NO that could be impacting the Muller glia.
We thank the reviewer for raising these important points.
Nitric oxide (NO) signaling has been implicated in the regeneration of multiple zebrafish tissues, including the heart (Rochon et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2024), spinal cord (Bradley et al., 2010), and fin (Matrone et al., 2021). Based on these findings, we hypothesized that NO signaling might also contribute to retinal regeneration.
As described in the manuscript, we compiled a redox-related gene list and systematically screened their roles in injury-induced MG proliferation using CRISPR-Cas9-mediated gene disruption. Among the candidates, disruption of nos genes significantly reduced the number of PCNA<sup>+</sup> MG cells following G/R cone ablation (Figure 4), prompting us to further investigate the role of NO signaling.
(9) Line 319-320: this sentence appears to be missing text as "while no influenced across the nos mutants and gsnor mutants" does not make sense.
We appreciate the reviewer’s observation and agree that the original sentence was unclear. We have revised the sentence in the manuscript as follows:
“In contrast, no significant change in MG proliferation was observed in nos1, nos2a, or gsnor mutants compared to wild type (Figures 4F–4I)” (revised lines 326-328).
(10) Line 326-328: The text should be rewritten as the current meaning would suggest there was no significant loss of photoreceptors in the nos2b mutants. That is incorrect. Rather, there was no significant difference between WT and the nos2b mutants in the number of photoreceptors lost at 72 hpi following MTZ treatment. Both groups lost photoreceptors, but the number lost in nos2b hets and homozygotes was the same as WT.
We agree with the suggestion and have revised our manuscript. We have revised the sentence in the manuscript as follows:
“We observed no significant difference in the loss of cone photoreceptor at 72 hpi between nos2b mutants and WT, indicating that the reduced MG proliferation observed in nos2b mutants is independent of the injury (WT: 45 ± 8 remaining cones, n = 24; nos2b⁺/⁻: 49 ± 12, n = 20; nos2b⁻/⁻: 46 ± 9, n = 20; mean ± SEM) (Figure 4K).” (revised lines 331-335).
(11) There is concern over the inconsistencies with some of the data. In Figure 4, Supplement 1A, the single-cell data found virtually no expression of nos2b in either uninjured MG or cxcl18b+ MG. In contrast, the authors find nos2b expression by RT-PCR in the cxcl18b:GFP+ MG. The in situ expression of nos2b in Figure 5 - Supplement 1 is not persuasive. The red puncta are seen in a single cxcl18b:GFP+ cell but also in the plexiform layer and is other non cxcl18b:GFP+ cells.
We appreciate the concern regarding the apparent inconsistencies in nos2b expression across different datasets. We provide the following explanations:
(1) Low expression of nos2b in scRNA-seq data:
We propose a potential explanation: Nitric oxide (NO) signaling is known to exert its biological functions in a dose-dependent manner and is tightly regulated post-transcriptionally, especially in inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (Bogdan, 2001; Nathan and Xie, 1994; Thomas et al., 2008). Thus, even modest changes in nos2b expression may exert meaningful biological effects without producing strong transcriptional signals detectable by scRNA-seq, which could fall below the detection threshold of scRNA-seq methods. Supporting this idea, our functional assay (Figure 4J) reveals a clear concentration-dependent effect of NO on MG proliferation, consistent with the biological relevance of Nos2b activity despite its low transcript abundance.
(2) Regarding the in situ hybridization data:
We used both commercially available in situ hybridization probes from (HCR<sup>TM</sup>) and RNAscope<sup>TM</sup> (data not shown) to detect nos2b transcripts. While the nos2b signal was observed in other retinal cell types, including cells in the plexiform layer, our primary study was focused on examining its expression within the cxcl18b<sup>+</sup> MG lineage.
(3) Regarding RT-PCR detection of nos2b in cxcl18b: GFP<sup>+</sup> MG:
To enhance detection sensitivity, we enriched cxcl18b: GFP<sup>+</sup> MG by FACS at 72 hpi and performed cDNA amplification before RT-PCR. This approach allowed the detection of low-abundance transcripts such as nos2b. It is also important to note that RT-PCR reflects fold changes in expression compared to MG to other retina cell type. The subtle but biologically upregulated of nos2b expression may not be readily captured by in situ hybridization or scRNA-seq.
(12) Line 356 - there is a disagreement over the interpretation of the current data. The statement that nos2b was specifically expressed in cxcl18b+ transitional MG states is not entirely accurate. This conclusion is based on expression of GFP from a cxcl18b promoter, which may reflect persistence of the GFP protein and not evidence of cxcl18b expression. Even assuming that the nos2b in situ hybridization and RT-PCR data are correct, the data would indicate that nos2b is expressed in proliferating MG that are derived from the cxcl18b+ transitional states. The single-cell trajectory analysis in Figure 2 indicates that cxcl18b is not co-expressed with PCNA. Furthermore, the single-cell data in Figure 4, Supplement 1, indicates no expression of nos2b in cxcl18b+ MG. The authors need to reconcile these seemingly contradictory pieces of data.
We thank the reviewer for this thoughtful and important comment. We agree that clarification is needed to accurately interpret the relationship between cxcl18b, nos2b, and MG proliferation, particularly considering the different temporal and technical contexts of our datasets.
(1) Lineage labeling and interpretation of GFP expression:
We acknowledge that in the Tg(cxcl18b: Cre-vhmc: mcherry::ef1a: loxP-dsRed-loxP-EGFP::lws2: nfsb-mCherry) line, GFP expression reflects historical activity of the cxcl18b promoter, rather than ongoing transcription. This GFP signal, due to its prolonged stay, may persist beyond the time window of endogenous cxcl18b expression. Accordingly, we have revised the manuscript to replace “cxcl18b⁺ MG” with “cxcl18b⁺ lineage-traced MG” throughout the relevant sections to prevent potential misinterpretation.
(2) Functional experiments support a lineage relationship between cxcl18b⁺ states and nos2b activity:
To further investigate the regulatory relationship between cxcl18b and nos2b, we conducted NO scavenging experiments using C-PTIO in the Tg(cxcl18b: GFP) background. We observed that the generation of cxcl18b: GFP⁺ MG after injury was not affected by NO depletion, indicating that cxcl18b activation precedes NO signaling (data not shown). However, PCNA⁺ MG was significantly reduced under the same treatment, suggesting that NO signaling is not required for cxcl18b⁺ transitional state formation, but is necessary for proliferation. Together with our MG-specific nos2b knockout data, these results support a model in which nos2b-derived NO acts downstream of the cxcl18b⁺ transitional state to promote MG cell-cycle re-entry.
(3) The scRNA-seq data with nos2b expression:
We agree with the reviewer that our scRNA-seq dataset shows minimal overlap between cxcl18b and pcna expression, which is consistent with our interpretation that cxcl18b expression marks a transitional phase before cell-cycle entry. Furthermore, nos2b transcripts were not robustly detected in cxcl18b⁺ MG clusters in our scRNA dataset. This discrepancy may be caused by technical limitations of scRNA-seq in capturing low-abundance or transient transcripts such as nos2b, as discussed in response to comment #11.
(13) The data in Figure 7 are interesting and suggest a link between NO signaling and notch activity. The use of the C-PTIO NO scavenger is not specific to MG, which limits the conclusions related to autocrine NO signaling in cxcl18b+ MG.
We acknowledge that the use of C-PTIO cannot distinguish between NO signaling within MG and paracrine effects from other retinal cells. Currently, technical limitations prevent MG-specific NO depletion. We have discussed this limitation accordingly in our revised “Limitations of this study” section (revised lines 540-545: “2. While our data suggest that injury-induced NO suppresses Notch signaling activation and promotes MG proliferation, the use of a general NO scavenger (C-PTIO) does not allow us to determine whether this regulation occurs in an autocrine or paracrine manner. The specific role of NO signaling within cxcl18b⁺ MG requires further validation using MG-specific NO depletion.”)
(14) Line 446-448. As mentioned before, the data do not support a causative link between microglia recruitment and cxcl18b induction. More specifically, dexamethasone is a broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory drug that blocks microglia activation and recruitment. Critically, the authors demonstrate that expression of cxcl18b occurs prior to microglia recruitment (see Figure 1, Supplement 1). Thus, the statement that cxcl18b induction depends on microglia recruitment is not accurate.
We thank the reviewer for reiterating this important point. We fully agree that the current data do not support a direct causal relationship between microglia recruitment and cxcl18b induction. As also addressed in our response to Comment 7, dexamethasone, as a broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory agent, cannot distinguish microglia-specific effects from those of other immune components. We have revised the text in revised lines 251–258 to clarify that microglia-mediated inflammation is associated with—but not required for—activation of cxcl18b-defined transitional MG states.
Reference:
Bogdan, C. (2001). Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nature immunology 2, 907-916.
Bradley, S., Tossell, K., Lockley, R., and McDearmid, J.R. (2010). Nitric oxide synthase regulates morphogenesis of zebrafish spinal cord motoneurons. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 30, 16818-16831.
Gorsuch, R.A., Lahne, M., Yarka, C.E., Petravick, M.E., Li, J., and Hyde, D.R. (2017). Sox2 regulates Müller glia reprogramming and proliferation in the regenerating zebrafish retina via Lin28 and Ascl1a. Experimental eye research 161, 174-192.
Hamon, A., García-García, D., Ail, D., Bitard, J., Chesneau, A., Dalkara, D., Locker, M., Roger, J.E., and Perron, M. (2019). Linking YAP to Müller Glia Quiescence Exit in the Degenerative Retina. Cell reports 27, 1712-1725.e1716.
Iribarne, M., and Hyde, D.R. (2022). Different inflammation responses modulate Müller glia proliferation in the acute or chronically damaged zebrafish retina. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 10, 892271.
Jin, D., Ni, T.T., Hou, J., Rellinger, E., and Zhong, T.P. (2009). Promoter analysis of ventricular myosin heavy chain (vmhc) in zebrafish embryos. Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists 238, 1760-1767.
Krylov, A., Yu, S., Veen, K., Newton, A., Ye, A., Qin, H., He, J., and Jusuf, P.R. (2023). Heterogeneity in quiescent Müller glia in the uninjured zebrafish retina drive differential responses following photoreceptor ablation. Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 16, 1087136.
Lahne, M., Nagashima, M., Hyde, D.R., and Hitchcock, P.F. (2020). Reprogramming Müller Glia to Regenerate Retinal Neurons. Annual review of vision science 6, 171-193.
Lee, M.S., Jui, J., Sahu, A., and Goldman, D. (2024). Mycb and Mych stimulate Müller glial cell reprogramming and proliferation in the uninjured and injured zebrafish retina. Development (Cambridge, England) 151.
Lourenço, R., Brandão, A.S., Borbinha, J., Gorgulho, R., and Jacinto, A. (2021). Yap Regulates Müller Glia Reprogramming in Damaged Zebrafish Retinas. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 9, 667796.
Matrone, G., Jung, S.Y., Choi, J.M., Jain, A., Leung, H.E., Rajapakshe, K., Coarfa, C., Rodor, J., Denvir, M.A., Baker, A.H., et al. (2021). Nuclear S-nitrosylation impacts tissue regeneration in zebrafish. Nat Commun 12, 6282.
Mazzolini, J., Le Clerc, S., Morisse, G., Coulonges, C., Kuil, L.E., van Ham, T.J., Zagury, J.F., and Sieger, D. (2020). Gene expression profiling reveals a conserved microglia signature in larval zebrafish. Glia 68, 298-315.
Meyers, J.R., Hu, L., Moses, A., Kaboli, K., Papandrea, A., and Raymond, P.A. (2012). β-catenin/Wnt signaling controls progenitor fate in the developing and regenerating zebrafish retina. Neural development 7, 30.
Nagashima, M., and Hitchcock, P.F. (2021). Inflammation Regulates the Multi-Step Process of Retinal Regeneration in Zebrafish. Cells 10.
Nathan, C., and Xie, Q.W. (1994). Nitric oxide synthases: roles, tolls, and controls. Cell 78, 915-918.
Pollak, J., Wilken, M.S., Ueki, Y., Cox, K.E., Sullivan, J.M., Taylor, R.J., Levine, E.M., and Reh, T.A. (2013). ASCL1 reprograms mouse Muller glia into neurogenic retinal progenitors. Development (Cambridge, England) 140, 2619-2631.
Rochon, E.R., Missinato, M.A., Xue, J., Tejero, J., Tsang, M., Gladwin, M.T., and Corti, P. (2020). Nitrite Improves Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish. Antioxidants & redox signaling 32, 363-377.
Sarich, S.C., Sreevidya, V.S., Udvadia, A.J., Svoboda, K.R., and Gutzman, J.H. (2025). The transcription factor Jun is necessary for optic nerve regeneration in larval zebrafish. PloS one 20, e0313534.
Sifuentes, C.J., Kim, J.W., Swaroop, A., and Raymond, P.A. (2016). Rapid, Dynamic Activation of Müller Glial Stem Cell Responses in Zebrafish. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 57, 5148-5160.
Svahn, A.J., Graeber, M.B., Ellett, F., Lieschke, G.J., Rinkwitz, S., Bennett, M.R., and Becker, T.S. (2013). Development of ramified microglia from early macrophages in the zebrafish optic tectum. Developmental neurobiology 73, 60-71.
Thomas, D.D., Ridnour, L.A., Isenberg, J.S., Flores-Santana, W., Switzer, C.H., Donzelli, S., Hussain, P., Vecoli, C., Paolocci, N., Ambs, S., et al. (2008). The chemical biology of nitric oxide: implications in cellular signaling. Free radical biology & medicine 45, 18-31.
Thomas, J.L., Ranski, A.H., Morgan, G.W., and Thummel, R. (2016). Reactive gliosis in the adult zebrafish retina. Experimental eye research 143, 98-109.
Wan, J., and Goldman, D. (2016). Retina regeneration in zebrafish. Current opinion in genetics & development 40, 41-47.
White, D.T., Sengupta, S., Saxena, M.T., Xu, Q., Hanes, J., Ding, D., Ji, H., and Mumm, J.S. (2017). Immunomodulation-accelerated neuronal regeneration following selective rod photoreceptor cell ablation in the zebrafish retina. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114, E3719-e3728.
Yao, K., Qiu, S., Tian, L., Snider, W.D., Flannery, J.G., Schaffer, D.V., and Chen, B. (2016). Wnt Regulates Proliferation and Neurogenic Potential of Müller Glial Cells via a Lin28/let-7 miRNA-Dependent Pathway in Adult Mammalian Retinas. Cell reports 17, 165-178.
Yin, Z., Kang, J., Xu, H., Huo, S., and Xu, H. (2024). Recent progress of principal techniques used in the study of Müller glia reprogramming in mice. Cell regeneration (London, England) 13, 30.
Yu, C., Li, X., Ma, J., Liang, S., Zhao, Y., Li, Q., and Zhang, R. (2024). Spatiotemporal modulation of nitric oxide and Notch signaling by hemodynamic-responsive Trpv4 is essential for ventricle regeneration. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 81, 60.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Lai and Doe address the integration of spatial information with temporal patterning and genes that specify cell fate. They identify the Forkhead transcription factor Fd4 as a lineage-restricted cell fate regulator that bridges transient spatial transcription factors to terminal selector genes in the developing Drosophila ventral nerve cord. The experimental evidence convincingly demonstrates that Fd4 is both necessary for late-born NB7-1 neurons, but also sufficient to transform other neural stem cell lineages toward the NB7-1 identity. This work addresses an important question that will be of interest to developmental neurobiologists: How can cell identities defined by initial transient developmental cues be maintained in the progeny cells, even if the molecular mechanism remains to be investigated? In addition, the study proposes a broader concept of lineage identity genes that could be utilized in other lineages and regions in the Drosophila nervous system and in other species.
Strengths:
While the spatial factors patterning the neuroepithelium to define the neuroblast lineages in the Drosophila ventral nerve cord are known, these factors are sometimes absent or not required during neurogenesis. In the current work, Lai and Doe identified Fd4 in the NB7-1 lineage that bridges this gap and explains how NB7-1 neurons are specified after Engrailed (En) and Vnd cease their expression. They show that Fd4 is transiently co-expressed with En and Vnd and is present in all nascent NB7-1 progenies. They further demonstrate that Fd4 is required for later-born NB7-1 progenies and sufficient for the induction of NB7-1 markers (Eve and Dbx) while repressing markers of other lineages when force-expressed in neural progenitors, e.g., in the NB5-6 lineage and in the NB7-3 lineage. They also demonstrate that, when Fd4 is ectopically expressed in NB7-3 and NB5-6 lineages, this leads to the ectopic generation of dorsal muscle-innervating neurons. The inclusion of functional validation using axon projections demonstrates that the transformed neurons acquire appropriate NB7-1 characteristics beyond just molecular markers. Quantitative analyses are thorough and well-presented for all experiments.
Weaknesses:
(1) While Fd4 is required and sufficient for several later-born NB7-1 progeny features, a comparison between early-born (Hb/Eve) and later-born (Run/Eve) appears missing for pan-progenitor gain of Fd4 (with sca-Gal4; Figure 4) and for the NB7-3 lineage (Figure 6). Having a quantification for both could make it clearer whether Fd4 preferentially induces later-born neurons or is sufficient for NB7-1 features without temporal restriction.
(2) Fd4 and Fd5 are shown to be partially redundant, as Fd4 loss of function alone does not alter the number of Eve+ and Dbx+ neurons. This information is critical and should be included in Figure 3.
(3) Several observations suggest that lineage identity maintenance involves both Fd4-dependent and Fd4-independent mechanisms. In particular, the fact that fd4-Gal4 reporter remains active in fd4/fd5 mutants even after Vnd and En disappear indicates that Fd4's own expression, a key feature of NB7-1 identity, is maintained independently of Fd4 protein. This raises questions about what proportion of lineage identity features require Fd4 versus other maintenance mechanisms, which deserves discussion.
(4) Similarly, while gain of Fd4 induces NB7-1 lineage markers and dorsal muscle innervation in NB5-6 and NB7-3 lineages, drivers for the two lineages remain active despite the loss of molecular markers, indicating some regulatory elements retain activity consistent with their original lineage identity. It is therefore important to understand the degree of functional conversion in the gain-of-function experiments. Sparse labeling of Fd4 overexpressing NB5-6 and NB7-3 progenies, as was done in Seroka and Doe (2019), would be an option.
(5) The less-penetrant induction of Dbx+ neurons in NB5-6 with Fd4-overexpression is interesting. It might be worth the authors discussing whether it is an Fd4 feature or an NB5-6 feature by examining Dbx+ neuron number in NB7-3 with Fd4-overexpression.
(6) It is logical to hypothesize that spatial factors specify early-born neurons directly, so only late-born neurons require Fd4, but it was not tested. The model would be strengthened by examining whether Fd4-Gal4-driven Vnd rescues the generation of later-born neurons in fd4/fd5 mutants.
(7) It is mentioned that Fd5 is not sufficient for the NB7-1 lineage identity. The observation is intriguing in how similar regulators serve distinct roles, but the data are not shown. The analysis in Figure 4 should be performed for Fd5 as supplemental information.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
The goal of the work is to establish the linkage between the spatial transcription factors (STFs) that function transiently to establish the identities of the individual NBs and the terminal selector genes (typically homeodomain genes) that appear in the newborn post-mitotic neurons. How is the identity of the NB maintained and carried forward after the spatial genes have faded away? Focusing on a single neuroblast (NB 7-1), the authors present evidence that the fork-head transcription factor, fd4, provides a bridge linking the transient spatial cues that initially specified neuroblast identity with the terminal selector genes that establish and maintain the identity of the stem cell's progeny.
The study is systematic, concise, and takes full advantage of 40+ years of work on the molecular players that establish neuronal identities in the Drosophila CNS. In the embryonic VNC, fd4 is expressed only in the NB 7-1 and its lineage. They show that Fd4 appears in the NB while the latter is still expressing the Spatial Transcription Factors and continues after the expression of the latter fades out. Fd4 is maintained through the early life of the neuronal progeny but then declines as the neurons turn on their terminal selector genes. Hence, fd4 expression is compatible with it being a bridging factor between the two sets of genes.
Experimental support for the "bridging" role of Fd4 comes from a set of loss-of-function and gain-of-function manipulations. The loss of function of Fd4, and the partially redundant gene Fd5, from lineage 7-1 does not affect the size of the lineage, but terminal markers of late-born neuronal phenotypes, like Eve and Dbx, are reduced or missing. By contrast, ectopic expression of fd4, but not fd5, results in ectopic expression of the terminal markers eve and Dbx throughout diverse VNC lineages.
A detailed test of fd4's expression was then carried out using lineages 7-3 and 5-6, two well-characterized lineages in Drosophila. Lineage 7-3 is much smaller than 7-1 and continues to be so when subjected to fd4 misexpression. However, under the influence of ectopic Fd4 expression, the lineage 7-3 neurons lost their expected serotonin and corazonin expression and showed Eve expression as well as motoneuron phenotypes that partially mimic the U motoneurons of lineage 7-1.
Ectopic expression of Fd4 also produced changes in the 5-6 lineage. Expression of apterous, a feature of lineage 5-6, was suppressed, and expression of the 7-1 marker, Eve, was evident. Dbx expression was also evident in the transformed 5-6 lineages, but extremely restricted as compared to a normal 7-1 lineage. Considering the partial redundancy of fd4 and fd5, it would have been interesting to express both genes in the 5-6 lineage. The anatomical changes that are exhibited by motoneurons in response to Fd4 expression confirm that these cells do, indeed, show a shift in their cellular identity.
Author response:
Reviewer #1 (Public Review):
Lai and Doe address the integration of spatial information with temporal patterning and genes that specify cell fate. They identify the Forkhead transcription factor Fd4 as a lineage-restricted cell fate regulator that bridges transient spatial transcription factors to terminal selector genes in the developing Drosophila ventral nerve cord. The experimental evidence convincingly demonstrates that Fd4 is both necessary for lateborn NB7-1 neurons, but also sufficient to transform other neural stem cell lineages toward the NB7-1 identity. This work addresses an important question that will be of interest to developmental neurobiologists: How can cell identities defined by initial transient developmental cues be maintained in the progeny cells, even if the molecular mechanism remains to be investigated? In addition, the study proposes a broader concept of lineage identity genes that could be utilized in other lineages and regions in the Drosophila nervous system and in other species.
Thanks for the accurate summary and positive comments!
While the spatial factors patterning the neuroepithelium to define the neuroblast lineages in the Drosophila ventral nerve cord are known, these factors are sometimes absent or not required during neurogenesis. In the current work, Lai and Doe identified Fd4 in the NB7-1 lineage that bridges this gap and explains how NB7-1 neurons are specified after Engrailed (En) and Vnd cease their expression. They show that Fd4 is transiently co-expressed with En and Vnd and is present in all nascent NB7-1 progenies. They further demonstrate that Fd4 is required for later-born NB7-1 progenies and sufficient for the induction of NB7-1 markers (Eve and Dbx) while repressing markers of other lineages when force-expressed in neural progenitors, e.g., in the NB56 lineage and in the NB7-3 lineage. They also demonstrate that, when Fd4 is ectopically expressed in NB7-3 and NB5-6 lineages, this leads to the ectopic generation of dorsal muscle-innervating neurons. The inclusion of functional validation using axon projections demonstrates that the transformed neurons acquire appropriate NB7-1 characteristics beyond just molecular markers. Quantitative analyses are thorough and well-presented for all experiments.
Thanks for the positive comments!
(1) While Fd4 is required and sufficient for several later-born NB7-1 progeny features, a comparison between early-born (Hb/Eve) and later-born (Run/Eve) appears missing for pan-progenitor gain of Fd4 (with sca-Gal4; Figure 4) and for the NB7-3 lineage (Figure 6). Having a quantification for both could make it clearer whether Fd4 preferentially induces later-born neurons or is sufficient for NB7-1 features without temporal restriction.
We quantified the percentage of Hb+ and Runt+ cells among Eve+ cells with sca-gal4, and the results are shown in Figure 4-figure supplement 1. We found that the proportion of early-born cells is slightly reduced but the proportion of later-born cells remain similar. Interestingly, we also found a subset of Eve+ cells with a mixed fate (Hb+Runt+) but the reason remains unclear.
(2) Fd4 and Fd5 are shown to be partially redundant, as Fd4 loss of function alone does not alter the number of Eve+ and Dbx+ neurons. This information is critical and should be included in Figure 3.
Because every hemisegment in an fd4 single mutant is normal, we just added it as the following text: “In fd4 mutants, we observe no change in the number of Eve+ neurons or Dbx+ neurons (n=40 hemisegments).”
(3) Several observations suggest that lineage identity maintenance involves both Fd4dependent and Fd4-independent mechanisms. In particular, the fact that fd4-Gal4 reporter remains active in fd4/fd5 mutants even after Vnd and En disappear indicates that Fd4's own expression, a key feature of NB7-1 identity, is maintained independently of Fd4 protein. This raises questions about what proportion of lineage identity features require Fd4 versus other maintenance mechanisms, which deserves discussion.
We agree, thanks for raising this point. We add the following text to the Discussion. “Interestingly, the fd4 fd5 mutant maintains expression of fd4:gal4, suggesting that the fd4/fd5 locus may have established a chromatin state that allows “permanent” expression in the absence of Vnd, En, and Fd4/Fd5 proteins.”
(4) Similarly, while gain of Fd4 induces NB7-1 lineage markers and dorsal muscle innervation in NB5-6 and NB7-3 lineages, drivers for the two lineages remain active despite the loss of molecular markers, indicating some regulatory elements retain activity consistent with their original lineage identity. It is therefore important to understand the degree of functional conversion in the gain-of-function experiments. Sparse labeling of Fd4 overexpressing NB5-6 and NB7-3 progenies, as was done in Seroka and Doe (2019), would be an option.
We agree it is interesting that the NB7-3 and NB5-6 drivers remain on following Fd4 misexpression. To explore this, we used sca-gal4 to overexpress Fd4 and observed that Lbe expression persisted while Eg was largely repressed (see Author response image 1 below). The results show that Lbe and Eg respond differently to Fd4. A non-mutually exclusive possibility is that the continued expression of lbe-Gal4 UAS-GFP or eg-Gal4 UAS-GFP may be due to the lengthy perdurance of both Gal4 and GFP.
Author response image 1.
(5) The less-penetrant induction of Dbx+ neurons in NB5-6 with Fd4-overexpression is interesting. It might be worth the authors discussing whether it is an Fd4 feature or an NB56 feature by examining Dbx+ neuron number in NB7-3 with Fd4-overexpression.
In the NB7-3 lineages misexpressing Fd4, only 5 lineages generated Dbx+ cells (0.1±0.4, n=64 hemisegments), suggesting that the low penetrance of Dbx+ induction is an intrinsic feature of Fd4 rather than lineage context. We have added this information in the results section.
(6) It is logical to hypothesize that spatial factors specify early-born neurons directly, so only late-born neurons require Fd4, but it was not tested. The model would be strengthened by examining whether Fd4-Gal4-driven Vnd rescues the generation of laterborn neurons in fd4/fd5 mutants.
When we used en-gal4 driver to express UAS-vnd in the fd4/fd5 mutant background, we found an average 7.4±2.2 Eve+ cells per hemisegment (n=36), significantly higher than fd4/fd5 mutant alone (3.9±0.8 cells, n=52, p=2.6x10<sup.-11</sup>) (Figure 3J). In addition, 0.2±0.5 Eve+ cells were ectopic Hb+ (excluding U1/U2), indicating that Vnd-En integration is sufficient to generate both early-born and late-born Eve+ cells in the fd4/fd5 mutants. We have added the results to the text.
(7) It is mentioned that Fd5 is not sufficient for the NB7-1 lineage identity. The observation is intriguing in how similar regulators serve distinct roles, but the data are not shown. The analysis in Figure 4 should be performed for Fd5 as supplemental information.
Thanks for the suggestion. Because the results are exactly the same as the wild type, we don’t think it is necessary to provide an additional images or analysis as supplemental information.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Via a detailed expression analysis, they find that Fd4 is selectively expressed in embryonic NB7-1 and newly born neurons within this lineage. They also undertake a comprehensive genetic analysis to provide evidence that fd4 is necessary and sufficient for the identity of NB7-1 progeny.
Thanks for the accurate summary!
The analysis is both careful and rigorous, and the findings are of interest to developmental neurobiologists interested in molecular mechanisms underlying the generation of neuronal diversity. Great care was taken to make the figures clear and accessible. This work takes great advantage of years of painstaking descriptive work that has mapped embryonic neuroblast lineages in Drosophila.
Thanks for the positive comments!
The argument that Fd4 is necessary for NB7-1 lineage identity is based on a Fd4/Fd5 double mutant. Loss of fd4 alone did not alter the number of NB7-1-derived Eve+ or Dbx+ neurons. The authors clearly demonstrate redundancy between fd4 and fd5, and the fact that the LOF analysis is based on a double mutant should be better woven through the text.
The authors generated an Fd5 mutant. I assume that Fd5 single mutants do not display NB7-1 lineage defects, but this is not stated. The focus on Fd4 over Fd5 is based on its highly specific expression profile and the dramatic misexpression phenotypes. But the LOF analysis demonstrates redundancy, and the conclusions in the abstract and through the results should reflect the existence of Fd5 in the conclusions of this manuscript.
We agree, and have added new text to clarify the single mutant phenotypes (there are none) and the double mutant phenotype (loss of NB7-1 molecular and morphological features. The following text is added to the manuscript: “Not surprisingly, we found that fd4 single mutants or fd5 single mutants had no phenotype (Eve+ neurons were all normal). Thus, to assess their roles, we generated a fd4 and fd5 double mutant. Because many Eve+ and Dbx+ cells are generated outside of NB7-1 lineage, it was also essential to identify the Eve+ or Dbx+ cells within NB7-1 lineage in wild type and fd4 mutant embryos. To achieve this, we replaced the open reading frame of fd4 with gal4 (called fd4-gal4) (see Methods); this stock simultaneously knocked out both fd4 and fd5 (called fd4/fd5 mutant hereafter) while specifically labeling the NB7-1 lineage. For the remainder of this paper we use the fd4/fd5 double mutant to assay for loss of function phenotypes.”
It is notable that Fd4 overexpression can rewire motor circuits. This analysis adds another dimension to the changes in transcription factor expression and, importantly, demonstrates functional consequences. Could the authors test whether U4 and U5 motor axon targeting changes in the fd4/fd5 double mutant? To strengthen claims regarding the importance of fd4/fd5 for lineage identity, it would help to address terminal features of U motorneuron identity in the LOF condition.
Thanks for raising this important point. We examined the axon targeting on body wall muscles in both wild type and in fd4/fd5 mutant background and added the results in Figure 3-figure supplement 2. We found that the axon targeting in the late-born neuron region (LL1) is significantly reduced, suggesting that the loss of late-born neurons in fd4/fd5 mutant leads to the absence of innervation of corresponding muscle targets.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
The goal of the work is to establish the linkage between the spatial transcription factors (STFs) that function transiently to establish the identities of the individual NBs and the terminal selector genes (typically homeodomain genes) that appear in the newborn postmitotic neurons. How is the identity of the NB maintained and carried forward after the spatial genes have faded away? Focusing on a single neuroblast (NB 7-1), the authors present evidence that the fork-head transcription factor, fd4, provides a bridge linking the transient spatial cues that initially specified neuroblast identity with the terminal selector genes that establish and maintain the identity of the stem cell's progeny.
Thanks for the positive comments!
The study is systematic, concise, and takes full advantage of 40+ years of work on the molecular players that establish neuronal identities in the Drosophila CNS. In the embryonic VNC, fd4 is expressed only in the NB 7-1 and its lineage. They show that Fd4 appears in the NB while the latter is still expressing the Spatial Transcription Factors and continues after the expression of the latter fades out. Fd4 is maintained through the early life of the neuronal progeny but then declines as the neurons turn on their terminal selector genes. Hence, fd4 expression is compatible with it being a bridging factor between the two sets of genes.
Thanks for the accurate summary!
Experimental support for the "bridging" role of Fd4 comes from a set of loss-of-function and gain-of-function manipulations. The loss of function of Fd4, and the partially redundant gene Fd5, from lineage 7-1 does not aoect the size of the lineage, but terminal markers of late-born neuronal phenotypes, like Eve and Dbx, are reduced or missing. By contrast, ectopic expression of fd4, but not fd5, results in ectopic expression of the terminal markers eve and Dbx throughout diverse VNC lineages.
Thanks for the accurate summary!
A detailed test of fd4's expression was then carried out using lineages 7-3 and 5-6, two well-characterized lineages in Drosophila. Lineage 7-3 is much smaller than 7-1 and continues to be so when subjected to fd4 misexpression. However, under the influence of ectopic Fd4 expression, the lineage 7-3 neurons lost their expected serotonin and corazonin expression and showed Eve expression as well as motoneuron phenotypes that partially mimic the U motoneurons of lineage 7-1.
Thanks for the positive comments!
Ectopic expression of Fd4 also produced changes in the 5-6 lineage. Expression of apterous, a feature of lineage 5-6, was suppressed, and expression of the 7-1 marker, Eve, was evident. Dbx expression was also evident in the transformed 5-6 lineages, but extremely restricted as compared to a normal 7-1 lineage. Considering the partial redundancy of fd4 and fd5, it would have been interesting to express both genes in the 5-6 lineage. The anatomical changes that are exhibited by motoneurons in response to Fd4 expression confirm that these cells do, indeed, show a shift in their cellular identity.
We appreciate the positive comments. We agree double misexpression of Fd4 and Fd5 might give a stronger phenotype (as the reviewer says) but the lack of this experiment does not change the conclusions that Fd4 can promote NB7-1 molecular and morphological aspects at the expense of NB5-6 molecular markers.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
The study by Yadav et al. describes a new setup to quantify a number of aggression and mating behaviors in Drosophila melanogaster. The investigation of these behaviors requires the analysis of large number of videos to identify each kind of behavior displayed by a fly. Several approaches to automatize this process have been published before, but each of them has their limitations. The authors set out to develop a new setup that includes a very low-cost, easy to acquire hardware and open-source machine-learning classifiers to identify and quantify the behavior.
Strengths:
(1) The study demonstrates that their cheap, simple, and easy to obtain hardware works just as well as custom-made, specialized hardware for analyzing aggression and mating behavior. This enables the setup to be used in a wide range of settings, from research with limited resources to classroom teaching.
(2) The authors used previously published software to train new classifiers for detecting a range of behaviors related to aggression and mating and make them freely available. The classifiers are very positively benchmarked against a manually acquired ground-truth as well as existing algorithms.
(3) The study demonstrates the applicability of the setup (hardware and classifiers) to common methods in the field by confirming a number of expected phenotypes with their setup.
Taken together, this work can greatly facilitate research of aggression and mating in Drosophila. The combination of low-cost, off-the-shelf hardware and open-source, robust software enables researchers with very little funding or technical expertise to contribute to the scientific process, and also allows large-scale experiments, for example, in classroom teaching with many students, or for systematic screenings.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
The study introduces an open-source, cost-effective method for automating the quantification of male social behaviors in Drosophila melanogaster. It combines machine-learning-based behavioral classifiers developed using JAABA (Janelia Automatic Animal Behavior Annotator) with inexpensive hardware constructed from off-the-shelf components. This approach addresses the limitations of existing methods, which often require expensive hardware and specialized setups. The authors demonstrate that their new "DANCE" classifiers accurately identify aggression (lunges) and courtship behaviors (wing extension, following, circling, attempted copulation, and copulation), closely matching manually annotated groundtruth data. Furthermore, DANCE classifiers outperform existing rule-based methods in accuracy. Finally, the study shows that DANCE classifiers perform as well when used with low-cost experimental hardware as with standard experimental setups across multiple paradigms, including RNAi knockdown of the neuropeptide Dsk and optogenetic silencing of dopaminergic neurons.
The authors make creative use of existing resources and technology to develop an inexpensive, flexible, and robust experimental tool for the quantitative analysis of Drosophila behavior. A key strength of this work is the thorough benchmarking of both the behavioral classifiers and the experimental hardware against existing methods. In particular, the direct comparison of their low-cost experimental system with established systems across different experimental paradigms is compelling.
While JAABA-based classifiers have been previously used to analyze aggression and courtship (Tao et al., J. Neurosci., 2024; Sten et al., Cell, 2023; Chiu et al., Cell, 2021; Isshi et al., eLife, 2020; Duistermars et al., Neuron, 2018), the demonstration that they work as well without expensive experimental hardware opens the door to more low-cost systems for quantitative behavior analysis.
We thank the reviewer for their positive assessment and constructive suggestions. We have cited these additional JAABA studies in the Introduction. We clarified that several prior JAABA-based classifiers were developed using specialized machinevision cameras or custom setups, and that in some cases the original code and classifiers were not made publicly available, which limits reproducibility and wider adoption. To address this, we explicitly note in the revised manuscript that DANCE was developed with accessibility in mind.
Although the study provides a detailed evaluation of DANCE classifier performance, its conclusions would be strengthened by a more comprehensive analysis. The authors assess classifier accuracy using a bout-level comparison rather than a frame-level analysis, as employed in previous studies (Kabra et al., Nat Methods, 2013). They define a true positive as any instance where a DANCE-detected bout overlaps with a manually annotated ground-truth bout by at least one frame. This criterion may inflate true positive rates and underestimate false positives, particularly for longer-duration courtship behaviors. For example, a 15-second DANCE-classified wing extension bout that overlaps with ground truth for only one frame would still be considered a true positive. A frame-level analysis performance would help address this possibility.
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point. Our original use of bout-level analysis followed existing literature (Duistermars et al., 2018; Ishii et al., 2020; Chiu et al., 2021; Tao et al., 2024; Hindmarsh Sten et al., 2025). While our lunge classifier already operates at the frame level, we have now performed additional frame-level evaluations for the duration based courtship classifiers. These analyses revealed only minor differences in precision, recall, and F1 scores compared with the original bout-level approach (see new Figure 5—Figure Supplement 3). Details of this analysis are now included in the Materials and Methods.
In summary, this work provides a practical and accessible approach to quantifying Drosophila behavior, reducing the economic barriers to the study of the neural and molecular mechanisms underlying social behavior.
We thank the reviewer for their encouraging comments and for recognizing the accessibility and practical value of our approach. We appreciate the constructive suggestions, which have helped strengthen the manuscript.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript addresses the development of a low-cost behavioural setup and standardised open-source high-performing classifiers for aggression and courtship behaviour. It does so by using readily available laboratory equipment and previously developed software packages. By comparing the performance of the setup and the classifiers to previously developed ones, this study shows the classifier's overperformance and the reliability of the low-cost setup in recapitulating previously described effects of different manipulations on aggression and courtship.
Strengths:
The newly developed classifiers for lunges, wing extension, attempted copulation, copulation, following, and circling, perform better than available previously developed ones. The behavioural setup developed is low cost and reliably allows analysis of both aggression and courtship behaviour, validated through social experience manipulation (social isolation), gene knock (Dsk in Dilp2 neurons) and neuronal inactivation (dopaminergic neurons) known to affect courtship and aggression.
We thank the reviewer for the clear summary of our work and for highlighting its strengths. We appreciate these positive comments and suggestions, which have helped improve the clarity of the manuscript.
Weaknesses:
Aggression encompasses multiple defined behaviours, yet only lunges were analysed. Moreover, the CADABRA software to which DANCE was compared analyses further aggression behaviours, making their comparisons incomplete. In addition, though DANCE performs better than CADABRA and Divider in classifying lunges in the behavioural setup tested, it did not yield very high recall and F1 scores.
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point. We focused on lunges because they are widely used as a standard proxy for male aggression across multiple laboratories (Agrawal et al., 2020; Asahina et al., 2014; Chiu et al., 2021; Chowdhury et al., 2021; Dierick et al., 2007; Hoyer et al., 2008; Jung et al., 2020; Nilsen et al., 2004; Watanabe et al., 2017). As noted in the Discussion, our study also provides a template for the future development of additional aggression classifiers (fencing, wing flick, tussle, chase, female headbutt) and courtship classifiers (tapping, licking, rejection), which can be trained and shared through the same DANCE framework. Developing and validating these was beyond the scope of the present work.
To address the concern regarding precision, recall, and F1 scores, we performed additional analyses across all training videos and compiled these results in the new Figure 2—Figure Supplement 2. Our earlier lunge classifier had performance metrics obtained after training on a total of 11 videos. Our analysis shows performance metrics for classifiers trained on four independent datasets (Videos 8– 11). We found that the classifier trained on nine videos provided the best balance of precision, recall, and F1 (78.73%, 73.07%, and 75.79%, respectively), which was slightly better than the earlier classifier. We therefore updated the main figure, text, and Materials and Methods to use this version and uploaded the corresponding classifier and training details to the GitHub repository.
DANCE is of limited use for neuronal circuit-level enquiries, since mechanisms for intensity and temporally controlled optogenetic manipulations, which are nowadays possible with open-source software and low-cost hardware, were not embedded in its development.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable point. The primary aim of DANCE is to provide an accessible, modular, and low-cost behavioural recording and analysis platform. It was designed so that users can readily integrate additional components such as optogenetic control when needed. As a proof of concept, we implemented optogenetic silencing of dopaminergic neurons using the DANCE hardware and confirmed that this manipulation increased aggression (Figure 7R).
To facilitate adoption, we now provide schematic diagrams, LED control code, and instructions on our GitHub page and setup photographs in the manuscript (see new Figure 7—Figure Supplement 1). The released code allows programmable timing and intensity control, enabling users to reproduce temporally precise optogenetic protocols or extend the system for other stimulation paradigms.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
The preprint by Yadav et al. describes a new setup to quantify a number of aggression and mating behaviors in Drosophila melanogaster. The investigation of these behaviors requires the analysis of a large number of videos to identify each kind of behavior displayed by a fly. Several approaches to automatize this process have been published before, but each of them has its limitations. The authors set out to develop a new setup that includes very low-cost, easy-to-acquire hardware and open-source machine-learning classifiers to identify and quantify the behavior.
Strengths:
(1) The study demonstrates that their cheap, simple, and easy-to-obtain hardware works just as well as custom-made, specialized hardware for analyzing aggression and mating behavior. This enables the setup to be used in a wide range of settings, from research with limited resources to classroom teaching.
(2) The authors used previously published software to train new classifiers for detecting a range of behaviors related to aggression and mating and to make them freely available. The classifiers are very positively benchmarked against a manually acquired ground truth as well as existing algorithms.
(3) The study demonstrates the applicability of the setup (hardware and classifiers) to common methods in the field by confirming a number of expected phenotypes with their setup.
We thank the reviewer for the positive assessment of our work and for highlighting its strengths. We appreciate these encouraging comments and suggestions, which have helped improve the clarity and presentation of the manuscript.
Weaknesses:
(1) When measuring the performance of the duration-based classifiers, the authors count any bout of behavior as true positive if it overlaps with a ground-truth positive for only 1 frame - despite the minimal duration of a bout is 10 frames, and most bouts are much longer. That way, true positives could contain cases that are almost totally wrong as long there was an overlap of a single frame. For the mating behaviors that are classified in ongoing bouts, I think performance should be evaluated based on the % of correctly classified frames, not bouts.
We thank the reviewer for raising this concern. In response to this point, and to Reviewer #1’s similar comment, we performed a frame-level evaluation of all duration-based courtship classifiers. The analysis revealed only minor differences compared with the original bout-level metrics (see new Figure 5—Figure Supplement 3), confirming the robustness of our classifiers. We have also added a description of this analysis in the Materials and Methods section.
(2) In the methods part, only one of the pre-existing algorithms (MateBook), is described. Given that the comparison with those algorithms is a so central part of the manuscript, each of them should be briefly explained and the settings used in this study should be described.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful suggestion. In the revised manuscript, we expanded the Materials and Methods to include concise descriptions and parameter settings for all pre-existing algorithms used for comparison. This includes dedicated subsections for CADABRA and the Divider assay, with explicit reference to their rulebased or geometric features. For MateBook, we specified the persistence filters used and the adjustments made for fair benchmarking. These changes ensure transparency and reproducibility.
Taken together, this work can greatly facilitate research on aggression and mating in Drosophila. The combination of low-cost, off-the-shelf hardware and open-source, robust software enables researchers with very little funding or technical expertise to contribute to the scientific process and also allows large-scale experiments, for example in classroom teaching with many students, or for systematic screenings.
We thank the reviewer for the encouraging comments and for recognizing the accessibility and broad applicability of DANCE. We believe these revisions have further strengthened the manuscript.
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
The following comments highlight areas where additional context, clarification, or further analysis could strengthen the manuscript. I hope these suggestions will be useful in refining your work.
(1) Lines 71-73: The authors state that Ctrax "leads to frequent identity switches among tracked flies, which is not the case while using FlyTracker." However, Ctrax was specifically designed to minimize identity errors, and Kabra et al. (2013) reported a low frequency of such errors-approximately one per five fly-hours in 10-fly videos. In contrast, Caltech FlyTracker does not correct identity errors automatically, requiring manual corrections, as noted in the Methods section of this study. If this is not an oversight, please provide further context to clarify this distinction.
We thank the reviewer for raising this clarification. As reported by Bentzur et al. (2021), when groups of flies were tracked simultaneously, Ctrax often generated multiple identities for the same individual, sometimes producing more trajectories than the actual number of flies. To prevent ambiguity, we revised the text to read: “While both Ctrax and FlyTracker (Eyjolfsdottir et al., 2014) may produce identity switches, when groups of flies were tracked simultaneously, Ctrax led to inaccuracies that required manual correction using specialized algorithms such as FixTrax (Bentzur et al., 2021).” We also quantified FlyTracker identity-switch rates in our datasets and report them in new Supplementary File 5, confirming that such events were rare (< 2% of tracked intervals). We believe, this updated version provides the necessary context and ensures accuracy in describing each tracker’s limitations.
(2) Line 85: Providing additional context on how this study builds on previous work using JAABA-based classifiers for fly social behavior and comparing these classifiers to rule-based methods would more accurately situate it within the field. The authors state that "recently, a few JAABA-based classifiers have been developed for measuring aggression and courtship" and cite four related studies. However, this statement seems to underrepresent the use of JAABA-based classifiers for quantifying fly social behavior, which has become common in the field. Several additional studies (as noted in the public review) have developed JAABA-based classifiers for scoring aggression or courtship. Furthermore, other studies have compared the performance of JAABA-based classifiers with rule-based classifiers like CADABRA (e.g., Chowdhury et al., Comm Biology 2021; Leng et al., PlosOne 2020; Kabra et al., Nat Methods 2013). Mentioning the similar findings in those studies and your own helps strengthen the conclusion that machine-learning-based classifiers outperform rule-based classifiers in several experimental contexts.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful suggestion. We have revised the Introduction to include additional references to studies that applied JAABA-based classifiers for aggression and courtship and made textual edits to reflect this. We further noted that, unlike several previous studies, all DANCE classifiers and analysis code are publicly available.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Suggestions for improved or additional experiments, data or analyses: As mentioned in the description of the effect of optogenetic inactivation of dopaminergic neurons, in the conclusion and also reported in the literature, there are other important identified aggression behaviours, such as fencing, wing flick, tussle, and chase. Similarly, for courtship, tapping and licking have also been defined. This study, as opposed to proposed future studies, would benefit from creating opensource classifiers for these established behaviours, which are important for the analysis of aggression and courtship.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable suggestion. As clarified in the Discussion, this manuscript intentionally focuses on six core, well-validated aggression and courtship behaviors to demonstrate DANCE’s modularity and reproducibility. Developing additional classifiers such as fencing, wing flick, tussle, chase, tapping, and licking would require extensive annotation and validation beyond the present scope. To address this point, we explicitly note in the revised text that the DANCE pipeline is readily extendable, allowing the community to build new classifiers within the same framework.
In terms of observer bias assessment for ground-truthing in courtship, this was only presented for circling and it would be beneficial to have encompassed all behaviours analysed.
We thank the reviewer for this suggestion. Observer-bias comparisons for all six classifiers are presented in Figure 2—Figure Supplement 1 (panels A–F). We clarified in the Results that annotations from two independent evaluators were compared for all classifiers, with no significant differences observed, confirming their robustness.
Finally, intensity and temporal optogenetic control are important for neuronal circuit analysis of underlying behaviour. The authors could embed this aspect in DANCE by integrating control of the green light LED strip used in this study using, for example, the open-source visual reactive programming software Bonsai (Lopes et al., 2015) and open-source electronics platform Arduino. This is an important and valuable addition in line with maintaining low cost.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable suggestion. DANCE was designed to be modular, allowing integration of temporal optogenetic control. To support immediate adoption, we now provide Arduino LED control code, setup schematics, and photographs (new Figure 7—Figure Supplement 1) along with step-by-step instructions on our GitHub page. We also note that Bonsai and Arduino frameworks are compatible with DANCE, enabling future extensions for closed-loop or behaviortriggered stimulation.
(2) Minor corrections to the text and figures:
Figure Supplement 1 refers only to Figure 2, yet panels D-F refer to the behaviour circling in courtship and therefore should be assigned to the respective figure.
Thanks, we have corrected this.
In lines 315-316, the cumbersome task of fluon coating for aggression assays seems to be ubiquitous across assays which is not the case, and therefore the sentence should include the word 'some'.
Thanks, we have edited this.
The cost of the phone and/or tablet should be included in the DANCE setup costs, as presumably these devices will be dedicated to the behavioural studies, for consistency purposes.
We thank the reviewer for this comment. We intentionally did not include smartphones or tablets in the setup cost because, in our experiments, these devices were not dedicated exclusively to DANCE but were repurposed from routine personal use. Our aim was to leverage readily available consumer electronics so that their cost does not become a barrier to adoption. We confirmed that commonly available Android phones capable of 30 fps at 1080p in H.264 format, as well as tablets or phones running a simple white-screen light app, are sufficient for reliable behavior classification and illumination. Since these devices can be returned to regular use after recordings, including their cost in the setup would not accurately reflect the intended accessibility of DANCE. For consistency, we now clarify in the Materials and Methods that such devices should be placed in airplane mode during recordings.
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) For my taste, the authors put too much emphasis on the point that their method outperforms existing methods. I understand the value in comparing to published methods and it is of course fully justified to state the advantages of the new method. But the whole preprint is set up as a competition with the old algorithms, and the conclusion that the new classifier is better is repeated in each figure caption and after each paragraph of the results. This competitive mindset also extends to the selection of which results are presented as main figures and which as supplements - all cases in which the previous methods actually perform well are only presented in the supplement. I think this is simply unnecessary as the authors' results speak for themselves, and do not need the continuous competitive comparison.
We thank the reviewer for this thoughtful suggestion. Our intention was to benchmark DANCE rigorously against existing methods, not to frame the study competitively. We agree that repeated emphasis on relative performance was unnecessary. In the revised version, we streamlined figure captions and text throughout the manuscript to balance comparisons and removed redundant phrasing. Instances where other methods performed well are now presented with equal clarity to maintain a neutral and informative tone.
(2) When describing the DANCE hardware, as a reader I would find it interesting to also read about potential issues that the authors encountered. For example, how difficult is it to handle the materials without breaking or deforming them, which could affect the behavioral assays? How critical is it to use specific blister packs - the availability of which will likely vary strongly between countries? Did the authors try different sizes, and products? Such information, even as a supplement, could be very helpful for the widespread use of the hardware.
We thank the reviewer for this important point. To address this, we conducted additional tests comparing DANCE arenas of different diameters (new Figure 7— Figure Supplement 3A–C and new Figure 7—Figure Supplement 4A–L). We also consulted colleagues in multiple countries and verified that the blister packs used in our assays are readily available. The Materials and Methods now include practical handling notes: blister foils can be reused ~30–40 times for aggression assays and ~10–15 times for courtship assays before deformation. We also describe how to prevent agar surface damage during assembly and how to wash and dry the arenas for optimal reusability.
(3) I find the arrows pointing to several videos in a number of figures rather distracting and redundant, and suggest omitting them.
Thanks, we have omitted these arrows from all relevant figures and clarified the figure legends to enhance readability.
(4) P8, line 169 ff: this is a very long sentence that should be separated into several sentences.
We have rewritten this as follows: “DANCE scores remained comparable to groundtruth scores across all categories, whereas CADABRA and Divider underestimated the lunge counts (Figure 2B–E). Correlation analysis revealed a strong relationship between DANCE and ground-truth scores (Figure 2F, Supplementary File 2). In comparison, CADABRA and the Divider assay classifier showed a weaker correlation (Figure 2G-H, Supplementary File 2).”
(5) P10, line 216: please explain, here and in the methods, how these behavioral indices are calculated. I did not find this information anywhere in the paper.
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out. We now define the behavioral index explicitly in Materials and Methods: “For each assay, a behavioral index was calculated as the proportion of frames in which the male engaged in the specified behavior. This was obtained by dividing the total number of frames annotated for that behavior by the total number of frames in the recording.”
(6) P11, line 253: I don't understand the modifications to MateBook regarding attempted copulations, neither in the results nor the methods section. I would ask the authors to explain more explicitly what was done.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful suggestion. We have re-written several parts of the Materials and methods to clarify these details and streamline the text. To train the attempted copulation classifier, we combined datasets from assays with mated and decapitated virgin females, using manual annotations as ground truth. We also adapted MateBook’s persistence filters (Ribeiro et al., 2018) and defined thresholds explicitly: mounting lasting >45 s (>1350 frames at 30 fps) was defined as copulation, whereas abdominal curling without mounting, or mounting lasting 0.33– 45 s, was defined as attempted copulation.
(7) Figure 7F: this is the only case with a significant difference between the two setups. What explanations do the authors have for the discrepancy?
We thank the reviewer for raising this point. After repeating the experiments, we no longer found a significant difference between the setups. Figure 7 and its legend have been updated to reflect these results.
(8) Figure 2 - Supplement 1: I do not understand why the boxes for Observer 1 have different colors in different figures. Does this have a meaning?
Thanks for pointing this out. The color differences had no intended meaning, and we have corrected the figure for consistency across panels.
(9) P22, line 517ff: It would be interesting to know how frequently identity switches occurred. For large-scale, automatic behavioral screenings that step could be a crucial bottleneck.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable suggestion. We analyzed identity switches using the FlyTracker “Visualizer” package, which flags frames with possible overlaps or jumps. Flagged intervals were manually verified, and we report these data in new Supplementary File 5. Identity switch rates were very low: 0.66% for high-resolution recordings and 1.9% for smartphone DANCE videos in the most challenging decapitated-virgin dataset. These findings demonstrate robust tracking performance under both setups.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Biomolecular condensates are an essential part of cellular homeostatic regulation. In this manuscript, the authors develop a theoretical framework for the phase separation of membrane-bound proteins. They show the effect of non-dilute surface binding and phase separation on tight junction protein organization.
Strengths:
It is an important study, considering that the phase separation of membrane-bound molecules is taking the center stage of signaling, spanning from immune signaling to cell-cell adhesion. A theoretical framework will help biologists to quantitatively interpret their findings.
Weaknesses:
Understandably, the authors used one system to test their theory (ZO-1). However, to establish a theoretical framework, this is sufficient.
We acknowledge this limitation. While we agree that additional systems would strengthen the generality of our theory, we note that the focus of this work is to introduce and validate a theoretical framework. As the reviewer notes, this is sufficient for establishing the framework. Nonetheless, we are open to further collaborations or future studies to test the model with other systems.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The authors present a clear expansion of biophysical (thermodynamic) theory regarding the binding of proteins to membrane-bound receptors, accounting for higher local concentration effects of the protein. To partially test the expanded theory, the authors perform in vitro experiments on the binding of ZO1 proteins to Claudin2 C-terminal receptors anchored to a supported lipid bilayer, and capture the effects that surface phase separation of ZO1 has on its adsorption to the membrane.
Strengths:
(1) The derived theoretical framework is consistent and largely well-explained.
(2) The experimental and numerical methodologies are transparent.
(3) The comparison between the best parameterized non-dilute theory is in reasonable agreement with experiments.
Weaknesses:
(1) In the theoretical section, what has previously been known, compared to which equations are new, should be made more clear.
We have revised the theory section to clearly distinguish previously established formulations from novel contributions following equation (4), which is .
(2) Some assumptions in the model are made purely for convenience and without sufficient accompanying physical justification. E.g., the authors should justify, on physical grounds, why binding rate effects are/could be larger than the other fluxes.
For our problem, binding is relevant together with diffusive transport in each phase. Each process is accompanied by kinetic coefficients that we estimate for the experimental system. For the considered biological systems (and related ones), it is difficult to determine whether other fluxes (see, e.g., Eq. 8(e)) have relaxed or not. We note that their effects are, of course, included in the kinetic model applied to the coarsening of ZO1 surface condensates as boundary conditions. But we cannot exclude that the corresponding kinetic coefficient in the actual biological system is large enough such that, e.g., Eq. (9e) does not vanish to zero “quasi-statically”. We have now added a sentence to the outlook highlighting the relevance of testing those flux-force relationships in biological systems.
(3) I feel that further mechanistic explanation as to why bulk phase separation widens the regime of surface phase separation is warranted.
We have discussed the mechanistic explanation related to bulk protein interaction strength in the manuscript in the section: “Effects of binding affinity and interactions on surface phase separation”. We explained how the bulk interaction parameter affects the binding equilibrium.
(4) The major advantage of the non-dilute theory as compared with a best parameterized dilute (or homogenous) theory requires further clarification/evidence with respect to capturing the experimental data.
We thank reviewer for this helpful question. To address this point, we have added new paragraphs in the conclusion section, which explicitly discuss the necessity of employing the non-dilute theory for interpreting the experimental data.
(5) Discrete (particle-based) molecular modelling could help to delineate the quantitative improvements that the non-dilute theory has over the previous state-of-the-art. Also, this could help test theoretical statements regarding the roles of bulk-phase separation, which were not explored experimentally.
We appreciate the suggestion and agree that such modeling would be valuable. However, this is beyond the scope of the current study.
(6) Discussion of the caveats and limitations of the theory and modelling is missing from the text.
We sincerely appreciate the reviewer’s helpful comment. We have added a discussion in the conclusion section outlining the caveats and limitations of our modeling approach.
Reviewing Editor Comments:
Upon discussing with the reviewers, we feel that this manuscript could significantly be improved if testing the model with a different model system (beyond ZO1/tight junctions), in which case we foresee that we could enhance the strength of evidence from "compelling" to "exceptional". But of course, this is up to the authors to go for it or not, the paper is already very good.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Lines 132-134: Re-word, the use of "complex" is confusing.
We have rephrased the sentence for clarity. The revised version reads: ṽ<sub>_𝑃𝑅</sub>_ are the molecular volume and area of the protein-receptor complex ѵ<sub>𝑃𝑅</sub>, respectively”, and the changes have been in the revised manuscript.
(2) Line 154 use of ""\nu"" for volume and area could be avoided for better clarity.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful suggestion. We have removed the statement involving ""\nu"" as these quantities have already been defined in the preceding context.
(3) Line 158 the total "Helmholtz" free energy F...
We have added the word "Helmholtz" to the sentence.
(4) Line 160 typo "In specific,..."
We carefully checked this sentence but could not identify a typo.
(5) For equation 5 explain the physical origins of each term, or provide a reference if this equation is explained elsewhere.
Thank you very much for your valuable suggestions. We have carefully rephrased Equation (5) and added a paragraph immediately afterward to provide a detailed explanation of its physical meaning.
(6) Derivation on lines 163-174 is poorly written. Make the logical flow between the equations clearer.
We greatly appreciate your insightful suggestions. Equation (6) has been carefully revised for clarity, and the explanation has been rewritten to ensure better readability. All modifications are Done.
(7) Define bold "t" in Equation 6.
The variable “t” has been explicitly defined in the context for clarity.
(8) In equations. 7b-7c the nablas (gradients) should be the 2D versions.
We have updated the gradient operators in Equations (7b) and (7c) [Eq. (9) in revised manuscript] to their 2D forms for consistency.
(9) Line 190, avoid referring to the future Equation 14, and state in words what is meant by "thermodynamic equilibrium".
We have added the explanation of “thermodynamic equilibrium” and remove the reference to equation accordingly.
(10) In Equation 11 you don't explain what you are doing ( which is a perturbation around the minimum of the free energy).
We have revised the paragraph before equation (11) [Eq. (13) in revised manuscript] to clarify that the expression represents a perturbation around the minimum of the free energy.
(11) In Equation 12, doesn't this also depend on how you have written equation 6 (not just equation 5).
Eq. (12) [Eq. (14) in revised manuscript] is derived directly from the variation of the total free energy F. In contrast, Eq. (6) contains the time derivative of free energies that were not written in their final form. In the revised version, we have now given the conjugate forces and fluxes in Eqs. (7) and (8) for clarity.
(12) Line 206 specify the threshold of local concentration (or provide a reference).
We have specified the threshold of local concentration in the revised text, and the corresponding statement has been highlighted.
(13) Line 223 is the deviation from ideality captured in a pair-wise fashion? I presume it does not account for N many-body interactions?
Yes, our model is formulated within a mean-field framework that incorporates pairwise (second order) interaction coefficients. For example, 𝜒<sub>𝑃𝑅 -𝑅</sub> characterizes the interaction between the complex 𝑃𝑅 and the free receptor 𝑅, 𝜒<sub>𝑅 -L</sub> the interaction between free receptor 𝑅 and free lipid 𝐿, 𝜒<sub>𝑃𝑅-𝐿</sub> the interaction between complex 𝑃𝑅and free lipid 𝐿. We have stressed this choice of free energy in the revised manuscript.
(14) Line 274, how do the authors know the secondary effects (of which they should mention a few) do not significantly impact the observed behaviour?
We sincerely thank the reviewer for the helpful comment. First, the parameters 𝜒<sub>𝑅 -L</sub> and 𝜒<sub>𝑃𝑅 -𝑅</sub> are not essential based on the experimental observations. For more information, please see our revised paragraph on the choice of the specific parameter values, which has been in the following Eq. (21).
(15) It's not clear how Figures 3 b and c are generated with reference to which parameters are changed to investigate with/without bulk phase separation.
To improve clarity, we have revised Figure 3 to display the corresponding parameter values directly in each panel. Figures 3b and 3c were generated by computing the surface binding curves (as shown in Fig. 2) for each binding affinity 𝜔<sub>𝑃𝑅</sub> and membrane-complex interaction strength 𝜒<sub>𝑃𝑅-𝐿</sub>, under different bulk interaction strengths chi, to compare the cases with and without bulk phase separation.
(16) The jump between theory and the "Mechanism in ..." section is too much. The authors should include the biological context of tight junctions and ZO1 in the main introduction.
We appreciate the reviewer’s suggestion. Following this comment, we have added an extended discussion in the main introduction to provide the necessary biological context of tight junctions and ZO1. In addition, we inserted new bridging paragraphs between the theoretical section and the section “Mechanism in tight junction formation” to create a smoother transition from theory to experiments. These revisions help to better connect the theoretical framework with the biological phenomena discussed in the later section.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Disclaimer: While I am familiar with the CFS method and the CFS literature, I am not familiar with primate research or two-photon calcium imaging. Additionally, I may be biased regarding unconscious processing under CFS, as I have extensively investigated this area but have found no compelling evidence in favor of unconscious processing under CFS.
This manuscript reports the results of a nonhuman-primate study (N=2 behaving macaque monkeys) investigating V1 responses under continuous flash suppression (CFS). The results show that CFS substantially suppressed V1 orientation responses, albeit slightly differently in the two monkeys. The authors conclude that CFS-suppressed orientation information "may not suffice for high-level visual and cognitive processing" (abstract).
The manuscript is clearly written and well-organized. The conclusions are supported by the data and analyses presented (but see disclaimer). However, I believe that the manuscript would benefit from a more detailed discussion of the different results observed for monkeys A and B (i.e., inter-individual differences), and how exactly the observed results are related to findings of higher-order cognitive processing under CFS, on the one hand, and the "dorsal-ventral CFS hypothesis", on the other hand.
Major Comments:
(1) Some references are imprecise. For example, l.53: "Nevertheless, two fMRI studies reported that V1 activity is either unaffected or only weakly affected (Watanabe et al., 2011; Yuval-Greenberg & Heeger, 2013)". "To the best of my understanding, the second study reaches a conclusion that is entirely opposite to that of the first, specifically that for low-contrast, invisible stimuli, stimulus-evoked fMRI BOLD activity in the early visual cortex (V1-V3) is statistically indistinguishable from activity observed during stimulus-absent (mask-only) trials. Therefore, high-level unconscious processing under CFS should not be possible if Yuval-Greenberg & Heeger are correct. The two studies contradict each other; they do not imply the same thing.
(2) Line 354: "The flashing masker was a circular white noise pattern with a diameter of 1.89{degree sign}{degree sign}, a contrast of 0.5, and a flickering rate of 10 Hz. The white noise consisted of randomly generated black and white blocks (0.07 × 0.07 each)." Why did the authors choose a white noise stimulus as the CFS mask? It has previously been shown that the depth of suppression engendered by CFS depends jointly on the spatiotemporal composition of the CFS and the stimulus it is competing with (Yang & Blake, 2012). For example, Hesselmann et al. (2016) compared Mondrian versus random dot masks using the probe detection technique (see Supplementary Figure S4 in the reference below) and found only a poor masking performance of the random dot masks.
Yang, E., & Blake, R. (2012). Deconstructing continuous flash suppression. Journal of Vision, 12(3), 8. https://doi.org/10.1167/12.3.8
Hesselmann, G., Darcy, N., Ludwig, K., & Sterzer, P. (2016). Priming in a shape task but not in a category task under continuous flash suppression. Journal of Vision, 16, 1-17.
(3) Related to my previous point: I guess we do not know whether the monkeys saw the CF-suppressed grating stimuli or not? Therefore, could it be that the differences between monkey A and B are due to a different individual visibility of the suppressed stimuli? Interocular suppression has been shown to be extremely variable between participants (see reference below). This inter-individual variability may, in fact, be one of the reasons why the CFS literature is so heterogeneous in terms of unconscious cognitive processing: due to the variability in interocular suppression, a significant amount of data is often excluded prior to analysis, leading to statistical inconsistencies. Moreover, the authors' main conclusion (lines 305-307) builds on the assumption that the stimuli were rendered invisible, but isn't this speculation without a measure of awareness?
Yamashiro, H., Yamamoto, H., Mano, H., Umeda, M., Higuchi, T., & Saiki, J. (2014). Activity in early visual areas predicts interindividual differences in binocular rivalry dynamics. Journal of Neurophysiology, 111(6), 1190-1202. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00509.2013
(4) The authors refer to the "tool priming" CFS studies by Almeida et al. (l.33, l.280, and elsewhere) and Sakuraba et al. (l.284). A thorough critique of this line of research can be found here:
Hesselmann, G., Darcy, N., Rothkirch, M., & Sterzer, P. (2018). Investigating Masked Priming Along the "Vision-for-Perception" and "Vision-for-Action" Dimensions of Unconscious Processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology. General. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000420
This line of research ("dorsal-ventral CFS hypothesis") has inspired a significant body of behavioral and fMRI/EEG studies (see reference for a review below). The manuscript would benefit from a brief paragraph in the discussion section that addresses how the observed results contribute to this area of research.
Ludwig, K., & Hesselmann, G. (2015). Weighing the evidence for a dorsal processing bias under continuous flash suppression. Consciousness and Cognition, 35, 251-259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2014.12.010
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
In this study, Tang, Yu & colleagues investigate the impact of continuous flash suppression (CFS) on the responses of V1 neurons using 2-photon calcium imaging. The report that CFS substantially suppressed V1 orientation responses. This suppression happens in a graded fashion depending on the binocular preference of the neuron: neurons preferring the eye that was presented with the marker stimuli were most suppressed, while the neurons preferring the eye to which the grating stimuli were presented were least suppressed. The binocular neuron exhibited an intermediate level of suppression.
Strengths:
The imaging techniques are cutting-edge, and the imaging results are convincing and consistent across animals.
Weaknesses:
I am not totally convinced by the conclusions that the authors draw based on their machine learning models.
Author response:
Reviewer #2
We respectfully disagree with Reviewer 2’s critiques, upon which the eLife assessment of “incomplete evidence” is primarily based. We believe these critiques do not accurately reflect our study and are rooted in a misinterpretation of the evidence. Consequently, we suggest that the conclusion of “incomplete evidence” is not warranted.
On the basis of Reviewer 2’s critiques, the eLife assessment states: “However, the evidence presented is incomplete and, in particular, does not distinguish whether this suppression is due to reduced contrast or due to masking.” We emphasize that the suppression we observed is a consequence of interocular masking, not contrast reduction. Reviewer 2 cites Yuval-Greenberg and Heeger (2013), which proposes that during CFS, the mask reduces the gain of neural responses in V1 in a manner analogous to reducing stimulus contrast. We agree that both CFS masking and contrast reduction can decrease signal-to-noise ratio and thereby reduce visibility. However, in our paradigm, the physical stimulus contrast was held constant, while suppression was induced by interocular competition under CFS. This is a fundamentally different mechanism from lowering stimulus contrast. Our results therefore reflect genuine masking-induced suppression, rather than the effect of physical contrast reduction.
Furthermore, Reviewer 2 cited Yuval-Greenberg and Heeger’s discussion that null results can arise from insufficient data, and suggested that this applies to our study. This main critique from Reviewer 2 is misplaced for two reasons: First, our main result is not a null effect. A null effect would mean that CFS masking had no impact on population orientation responses. Instead, we observed significant suppression, including abolished tuning in some conditions, which clearly indicates a strong effect of masking. Second, our findings are based on large neural populations recorded using two-photon calcium imaging, providing extensive sampling and high statistical power. Thus, concerns about “insufficient data” do not apply to our study.
Finally, we used machine learning approaches to examine the effects of CFS masking on orientation discrimination and recognition, providing new insight into the long-standing debate over whether the brain can perform high-level cognitive processing under CFS. Although it is, to some extent, a matter of personal judgment whether our work represents a theoretical advance, Reviewer 2 made no comment, positive or negative, on this major component of our study while forming his/her judgment. (In response to Reviewer 3’s main concern about the suitability of SVMs, we now performed a multi-way classification analysis, which yielded results largely consistent with those obtained using the SVM approach in the original manuscript, confirming the robustness of our mechine learning results.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the previous reviews
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
In this study, participants completed two different tasks. A perceptual choice task in which they compared the sizes of pairs of items and a value-different task in which they identified the higher value option among pairs of items with the two tasks involving the same stimuli. Based on previous fMRI research, the authors sought to determine whether the superior frontal sulcus (SFS) is involved in both perceptual and value-based decisions or just one or the other. Initial fMRI analyses were devised to isolate brain regions that were activated for both types of choices and also regions that were unique to each. Transcranial magnetic stimulation was applied to the SFS in between fMRI sessions and it was found to lead to a significant decrease in accuracy and RT on the perceptual choice task but only a decrease in RT on the value-different task. Hierarchical drift diffusion modelling of the data indicated that the TMS had led to a lowering of decision boundaries in the perceptual task and a lower of nondecision times on the value-based task. Additional analyses show that SFS covaries with model derived estimates of cumulative evidence, that this relationship is weakened by TMS.
Strengths:
The paper has many strengths, including the rigorous multi-pronged approach of causal manipulation, fMRI and computational modelling, which offers a fresh perspective on the neural drivers of decision making. Some additional strengths include the careful paradigm design, which ensured that the two types of tasks were matched for their perceptual content while orthogonalizing trial-to-trial variations in choice difficulty. The paper also lays out a number of specific hypotheses at the outset regarding the behavioural outcomes that are tied to decision model parameters and well justified.
We thank the reviewer for their thoughtful summary of the study and for highlighting these strengths. We are pleased that the multi-pronged approach combining causal manipulation, fMRI, and hierarchical drift–diffusion modelling, as well as the careful matching of perceptual content across the two tasks, came across clearly. We also appreciate the reviewer’s positive remarks on the specificity of our a priori hypotheses and their links to decision-model parameters. In revising the manuscript, we have aimed to further streamline the presentation of these hypotheses and to more explicitly connect the behavioural predictions, model parameters, and neural readouts throughout the Results and Discussion sections.
Weaknesses:
In my previous comments (1.3.1 and 1.3.2) I noted that key results could be potentially explained by cTBS leading to faster perceptual decision making in both the perceptual and value-based tasks. The authors responded that if this were the case then we would expect either a reduction in NDT in both tasks or a reduction in decision boundaries in both tasks (whereas they observed a lowering of boundaries in the perceptual task and a shortening of NDT in the value task). I disagree with this statement. First, it is important to note that the perceptual decision that must be completed before the value-based choice process can even be initiated (i.e. the identification of the two stimuli) is no less trivial than that involved in the perceptual choice task (comparison of stimulus size). Given that the perceptual choice must be completed before the value comparison can begin, it would be expected that the model would capture any variations in RT due to the perceptual choice in the NDT parameter and not as the authors suggest in the bound or drift rate parameters since they are designed to account for the strength and final quantity of value evidence specifically. If, in fact, cTBS causes a general lowering of decision boundaries for perceptual decisions (and hence speeding of RTs) then it would be predicted that this would manifest as a short NDT in the value task model, which is what the authors see.
We thank the reviewer for raising these points and for the helpful clarification. We agree that, in principle, the architecture of the value-based task can be conceived as involving an upstream perceptual process that must be completed, to some degree, before value comparison can proceed. Under such a multistage framework, it is indeed possible that cTBS-induced changes in a perceptual decision stage could manifest as a reduction in boundary separation in the pure perceptual task, while the same perturbation appears as a shortening of non-decision time (NDT) when fitting a single-stage DDM to the value task. In this sense, our earlier statement that a “general speeding effect” would necessarily produce identical parameter changes (either NDT or boundaries) in both tasks was too strong, and we are grateful to the reviewer for pointing this out.
At the same time, this alternative explanation remains fully compatible with our central claim that the left SFS plays a perceptual rather than value-based role. We agree with the reviewer that there must be a stimulus-related circuit (in visual and parietal regions) that encodes the physical attributes of the options, and that this upstream processing can influence both tasks. However, a large body of work suggests that left SFS is not part of this primary identification circuitry, but rather contributes specifically to the accumulation and comparison of sensory evidence (e.g., Heekeren et al., 2004, 2006), downstream from areas such as FFA, PPA, or MT/V5 that encode stimulus identity. In other words, stimulus identification (forming a representation of “what is where”) is anatomically and functionally distinct from the accumulation of evidence toward a perceptual decision. Within this framework, the reviewer’s proposal that cTBS speeds “perceptual decisions” across tasks can be understood as targeting precisely the evidence-accumulation stage we ascribe to SFS, with the value-comparison stage proper likely implemented in other regions (e.g., vmPFC and connected valuation circuitry).
We therefore do not rely solely on the dissociation between boundary changes in the perceptual task and NDT changes in the value task as decisive evidence against a “general speeding” account. Instead, our interpretation is based on the convergence of behavioural, model-based, and neural results. First, in the perceptual task, cTBS to left SFS leads to a selective reduction in decision boundary and a concomitant change in trialwise BOLD activity within the stimulated region that covaries with perceptual choice behaviour and with the latent decision variable inferred from the HDDM. Second, in the value task, cTBS does not affect value sensitivity or accuracy, nor does it alter value-related drift or boundary parameters; the only robust HDDM effect is a modest shortening of NDT. Third, critically, left SFS BOLD activity is modulated by perceptual evidence and by cTBS in the perceptual task, but we observe no evidence that SFS activity encodes value evidence or shows value-related cTBS neuronal effects in the value task.
Taken together, these findings indicate that the left SFS serves a causal role in the accumulation of perceptual evidence and in the setting of the choice criterion for perceptual decisions. The reviewer’s suggestion that cTBS may induce a general speeding of perceptual processes that also influences the value task is compatible with this conclusion, in the sense that any contribution of SFS to the value task is best understood as acting via a perceptual component that is upstream of value comparison, rather than via the value accumulation process itself. We have clarified this point in the Discussion of the revised manuscript and now explicitly acknowledge that our DDM dissociation alone does not exclude a general perceptual speeding account, but that the combination of task-specific neural effects in SFS, preserved value-based choice behaviour, and the absence of value-related BOLD changes in SFS strongly support a primarily perceptual role for this region.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The authors set out to test whether a TMS-induced reduction in excitability of the left Superior Frontal Sulcus influenced evidence integration in perceptual and value-based decisions. They directly compared behaviour-including fits to a computational decision process model---and fMRI pre and post TMS in one of each type of decision-making task. Their goal was to test domain-specific theories of the prefrontal cortex by examining whether the proposed role of the SFS in evidence integration was selective for perceptual but not value-based evidence.
Strengths:
The paper presents multiple credible sources of evidence for the role of the left SFS in perceptual decision making, finding similar mechanisms to prior literature and a nuanced discussion of where they diverge from prior findings. The value-based and perceptual decision-making tasks were carefully matched in terms of stimulus display and motor response, making their comparison credible.
We thank the reviewer for their clear summary of our aims and approach, and for highlighting these strengths. We are pleased that the convergence between causal TMS, fMRI, and hierarchical modelling comes across as providing credible evidence for the role of left SFS in perceptual decision-making, and that our attempt to link these results to the existing literature is seen as appropriately nuanced. We also appreciate the reviewer’s positive assessment of the task design, in particular the close matching of perceptual content and motor output across perceptual and value-based decisions, which was central to our goal of testing domain-specific theories of prefrontal function. In revising the manuscript, we have further clarified these design choices and their rationale, and we have streamlined the exposition of how the hypotheses, model parameters, and neural readouts are connected across the two decision domains.
Weaknesses:
I was confused about the model specification in terms of the relationship between evidence level and drift rate. While the methods (and e.g. supplementary figure 3) specify a linear relationship between evidence level and drift rate, suggesting, unless I misunderstood, that only a single drift rate parameter (kappa) is fit. However, the drift rate parameter estimates in the supplementary tables (and response to reviewers) do not scale linearly with evidence level.
We thank the reviewer for raising this point and appreciate the opportunity to clarify the model specification. In our hierarchical DDM, we did not fit separate, free drift parameters for each evidence level. As shown in Supplementary Fig. 3, the drift on each trial is specified as
where 𝐸<sub>𝑐,𝑠,𝑖</sub> the trial-wise evidence (difference in size or value) and κ<sub>𝑐,𝑠</sub> is a single drift-scaling parameter per condition and session. Thus, the linear dependence of drift on evidence is implemented at the trial level via 𝜅; we do not estimate independent 𝛿 parameters for each evidence level.
In Supplementary Tables 8 and 9 we report, for descriptive purposes, the posterior means of 𝛿 conditional on each evidence bin (levels 1–4), alongside the corresponding decision boundary and nondecision time summaries. These values are therefore derived quantities that reflect the combination of (i) the single κ<sub>𝑐,𝑠</sub> parameter, (ii) the empirical distribution of continuous evidence values 𝐸 within each bin, and (iii) hierarchical pooling across subjects and sessions. Consequently, they are expected to increase monotonically with evidence level—as they do in our data—but not to lie exactly on a straight line in the discrete level index, because the underlying evidence bins are not equally spaced in physical units and because of between-subject variability and posterior uncertainty.
We will revise the text and table captions to make clear that the evidence-level entries are descriptive summaries of 𝛿 implied by the 𝜅×𝐸 formulation, rather than independently estimated drift parameters, in order to avoid this confusion.
-The fit quality for the value-based decision task is not as good as that for the PDM, and this would be worth commenting on in the paper.
We agree that the HDDM fit for the value-based task is somewhat weaker than for the perceptual task. This is reflected in the somewhat higher DIC values for VDM compared with PDM and in slightly broader posterior-predictive distributions (Supplementary Tables 8–11 and Supplementary Figs. 11–16). We believe this difference primarily reflects the greater intrinsic variability of subjective value-based choices (e.g. trial-to-trial fluctuations in preferences, satiety, or attention), coupled with our decision to use the same relatively simple DDM architecture for both tasks to allow a principled cross-task comparison. Importantly, posterior-predictive checks show that, for VDM as well, the model adequately reproduces both accuracy and full RT distributions at the group and subject level (Supplementary Figs. 11–16), indicating that the fit quality is sufficient for our purposes. In the revised manuscript we now explicitly note that the model captures PDM behaviour more tightly than VDM and that this may reduce sensitivity to very small cTBS effects on value-based decision parameters, even though no systematic effects are evident in our data. Crucially, our central conclusion—that left SFS plays a domain-specific role in setting the decision boundary for perceptual evidence—relies on the robust behavioural, computational, and neural effects observed in PDM and does not depend on assuming a perfect model fit for VDM.
- Supplementary Figure 3 specifies the distribution for kappa hyper-parameter twice.
We thank the reviewer for spotting this typo. We have revised Supplementary Figure 3 legend.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Age-related synaptic dysfunction can have detrimental effects on cognitive and locomotor function. Additionally, aging makes the nervous system vulnerable to late-onset neurodegenerative diseases. This manuscript by Marques et al. seeks to profile the cell surface proteomes of glia to uncover signaling pathways that are implicated in age-related neurodegeneration. They compared the glial cell-surface proteomes in the central brain of young (day 5) and old (day 50) flies, and identified the most up- and down-regulated proteins during the aging process. 48 genes were selected for analysis in a lifespan screen, and interestingly, most sex-specific phenotypes. Among these, adult-specific pan-glial DIP-β overexpression (OE) significantly increased the lifespan of both males and females and improved their motor control ability. To investigate the effect of DIP-β in the aging brain, Marques et al. performed snRNA-seq on 50-day-old Drosophila brains with or without DIP-β OE in glia. Cortex and ensheathing glia showed the most differentially expressed genes. Computational analysis revealed that glial DIP-β OE increased cell-cell communication, particularly with neurons and fat cells.
Strengths:
(1) State-of-the-art methodology to reveal the cell surface proteomes of glia in young and old flies.
(2) Rigorous analyses to identify differentially expressed proteins.
(3) Examination of up- and down-regulated candidates and identification of glial-expressed mediators that impact fly lifespan.
(4) Intriguing sex-specific glial genes that regulate life span.
(5) Follow-up RNA-seq analysis to examine cellular transcriptomes upon overexpression of an identified candidate (DIP-β).
(6) A compelling dataset for the community that should generate extensive interest and spawn many projects.
Weaknesses:
(1) DIP-β OE using flySAM:
a) These flies showed a larger increase in lifespan compared to using UAS-DIP-β (Figure 2 C, D). Do the authors think that flySAM is a more efficient way of OE than UAS? Also, the UAS construct would be specific to one DIP-β isoform, while flySAM would likely express all isoforms. Could this also contribute to the phenotypes observed?
b) The Glial-GS>DIP-β flySAM flies without RU-486 have significantly shorter lifespans (Figure 2C) than their UAS-DIP-β counterparts. flySAM is lethal when expressed under the control of tubulin-GAL4 (Jia et al. 2018), likely due tothe toxicity of such high levels of overexpression. Is it possible that a larger increase in lifespan is due to the already reduced viability of these flies?
c) Statistics: It is stated in the Methods that "statistical methods used are described in the figure legend of each relevant panel." However, there is no description of the statistics or sample sizes used in Figure 2.
(2) Figure 3: The authors use a glial GeneSwitch (GS) to knock down and overexpress candidate genes. In Figure 3A, they look at glial-GS>UAS-GFP with and without RU. Without RU, there is no GFP expression, as expected. With RU, there is GFP expression. It is expected that all cell body GFP signal should colocalize with a glial nuclear marker (Repo). However, there is some signal that does not appear to be glia. Also, many glia do not express GFP, suggesting the glial GS driver does not label all glia. This could impact which glia are being targeted in several experiments.
(3) It is interesting that sex-specific lifespan effects were observed in the candidate screen.
a) The authors should provide a discussion about these sex-specific differences and their thoughts about why these were observed.
b) The authors should also provide information regarding the sex of the flies used in the glial cell surface proteome study.
c) Also, beyond the scope of this study, examining sex-specific glial proteomes could reveal additional insights into age-related pathways affecting males and females differentially.
(4) The behavioral assay used in this study (climbing) tests locomotion driven by motor neurons. The proteomic analysis was performed with the central adult brain, which does not include the nerve cord, where motor neurons reside. While likely beyond the scope of this study, it would be informative to test other behaviors, including learning, circadian rhythms, etc.
(5) It is surprising that overexpressing a CAM in glia has such a broad impact on the transcriptomes of so many different cell types. Could this be due to DIP-β OE maintaining the brain in a "younger" state and indirectly influencing the transcriptomes? Instead of DIP-β OE in glia directly influencing cell-cell interactions? Can the authors comment on this?
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
This manuscript presents an ambitious and technically innovative study that combines in situ cell-surface proteomics, functional genetic screening, and single-nucleus RNA sequencing to uncover glial factors that influence aging in Drosophila. The authors identify DIP-β as a glial protein whose overexpression extends lifespan and report intriguing sex-specific differences in lifespan outcomes. Overall, the study is conceptually compelling and offers a valuable dataset that will be of considerable interest to researchers studying glia-neuron communication, aging biology, and proteomic profiling in vivo.
The in-situ proteomic labeling approach represents a notable methodological advance. If validated more extensively, it has the potential to become a widely used resource for probing glial aging mechanisms. The use of an inducible glial GeneSwitch driver is another strength, enabling the authors to carefully separate aging-relevant effects from developmental confounds. These technical choices meaningfully elevate the rigor of the study and support its central conclusions. The discovery of new candidate genes from the proteomics pipeline, including DIP-β, is intriguing and opens new avenues for understanding glial contributions to organismal lifespan. The observation of sex-specific lifespan effects is particularly interesting and warrants further exploration; the study sets the stage for future work in this direction.
At the same time, several areas would benefit from clarification or additional analysis to fully support the manuscript's claims:
(1) The manuscript frequently refers to "improved" or "increased" cell-cell communication following DIP-β overexpression, but the meaning of this term remains somewhat vague. Because the current analysis relies largely on transcriptomic predictions, it would be helpful to define precisely what metric is being used, e.g., increased numbers of predicted ligand-receptor interactions, enrichment of specific signaling pathways, or altered expression of communication-related components. Strengthening the mechanistic link between DIP-β, cell-cell communication, and lifespan extension, potentially through targeted validation of specific glial interactions, would substantially reinforce the interpretation.
(2) The lifespan screen is central to the paper, and clearer visualization and contextualization of these results would significantly improve the manuscript's impact. For example, Figure 3D is challenging to interpret in its current form. More explicit presentation of which manipulations extend lifespan in each sex, along with effect sizes and significance values, would provide clarity. Including positive controls for lifespan extension would also help contextualize the magnitude of the observed effects. The reported effects of DIP-β, while promising, are modest relative to baseline effects of RU feeding, and a discussion of this would help appropriately calibrate the conclusions.
(3) Several figures would benefit from improved labeling or more detailed legends. For instance, the meaning of "N" and "C" in Figure 1D is unclear; Figure 3A should clarify that Repo is a glial marker; and Figure 5C appears to have truncated labels. Reordering certain panels (e.g., moving control data in Figure 4A-B) may also improve narrative flow. These refinements would greatly aid reader comprehension.
(4) A few claims would be strengthened by more specific references or acknowledgment of alternative interpretations. Examples include the phenoxy-radical labeling radius, the impact of H₂O₂ exposure, and the specificity of neutravidin. Additionally, downregulation of synapse-related GO terms may reflect age-related transcriptional changes rather than impaired glia-neuron communication per se, and this possibility should be recognized. The term "unbiased" to describe the screen may also be reconsidered, given the preselection of candidate genes.
(5) Clarifying the rationale for focusing on central brain glia over optic-lobe glia would be useful.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
Razlan and colleagues provide a detailed anatomical characterization of lamina I projection neurons in the mouse spinal cord that are densely innervated by primary afferents activated by cooling of the skin. The authors, building on their previous anatomical work, validate a Trpm8-Flp mouse line, show synaptic contacts between Trpm8⁺ boutons and projection neurons at the ultrastructural level, and demonstrate at the physiological level that these neurons specifically respond to cooling stimuli. Next, by taking advantage of their previous transcriptomic analysis of ALS neurons, they identify calbindin as a marker for cold-activated lamina I projection neurons and map their ascending projections to the rostral lateral parabrachial area, caudal periaqueductal gray, and ventral posterolateral thalamus, well-known thermosensory and thermoregulatory centers. Altogether, these findings provide strong anatomical and functional evidence for a direct line of transmission from Trpm8⁺ sensory afferents through Calb1⁺ lamina I neurons to key supraspinal centers controlling perception of cold and thermoregulatory responses.
Strengths:
The combination of mouse genetics, electron microscopy, ex vivo physiology, and viral tracing provides convincing evidence for a direct cold pathway. The work validates the Trpm8-Flp line by extensive anatomical and molecular characterization. Integration with previous transcriptomic and anatomical data neatly links the cold-selective lamina I neurons to a molecularly defined cluster of ALS neurons, strengthening the bridge between molecular identity, anatomy, and physiological function.
Weaknesses:
While anatomical evidence for direct synaptic connectivity between Trpm8+ afferents and lamina I projection neurons is compelling, a physiological demonstration of strict monosynaptic transmission is not shown. The conclusion that these inputs are exclusively monosynaptic should be toned down. Similarly, the statement that "Lamina I ALS neurons that are surrounded by Trpm8 afferents are cold-selective" should also be toned down as only a few neurons have been tested and it cannot be excluded that other neurons with similar characteristics may be polymodal.
Climate sensitivity is the most basic issue. Juel Charnie. The Charnie sensitivity refers to the case in which ice sheets on Greenland and Antarctica are fixed. Charie's estimate had a huge uncertainty from 1.5 to 4.5 degrees
for - definition - Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity (ECS) - The global average surface temperature increase when CO2 levels double from pre-industrial levels, allowing all climate feedbacks (like ice melt, water vapor, clouds) to fully manifest. - climate crisis - Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity - huge range - 1.5 to 4.5 deg Celsius - IPCC estimates 3 deg C
[B6SJL-Tg(APPSwFlLon,PSEN1*M146L* L286V)6799Vas/Mmjax] purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME), an NIH funded strain repository, and was donated to the MMRRC
DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-7483320/v1
Resource: Mutant Mouse Regional Resource Center (RRID:SCR_002953)
Curator: @AleksanderDrozdz
SciCrunch record: RRID:SCR_002953
LE-Tg(Chat-Cre)5.1DeisRRRC
DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.113885
Resource: (RRRC Cat# 00658,RRID:RRRC_00658)
Curator: @bandrow
SciCrunch record: RRID:RRRC_00658
MMRRC_034843
DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-7686971/v1
Resource: RRID:MMRRC_034843-JAX
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:MMRRC_034843-JAX
for - James Hansen - youtube - The truth about global warming
Transcript
2:47 We do not have to wait 10 years to conclude that we have reached 1.5 Degrees of warming. Satelllite data shows that earth is strongly out of energy balance.
3:09 An important factor is that IPCC's best estimate of climate sensitivity is a substantial underestimate. I will show that tomorrow in several independent ways.
3:28 Climate sensitivity is probably between 4 and 5 degrees Celcius for doubled CO2 rather than 3 degrees
4:28 What we witness now is scientific reticence on steroids, perhaps because IPCC was granted the position of supreme authority
4:43 But in science, supreme authority is not granted to anyone. Galileo proved that.
4:55 An example of expert herd mentality is the response to our global warming acceleration paper which Annie was coauthor on. The next day, these experts condemned our paper in the media.
5:26 Not one of them discussed the physics in our paper or explained what was wrong. Instead there were ad hominem remarks.
5:51 What could the media do They dropped the paper.
, the deeply colonial nature of catego-rizing Indigenous people often goes unacknowledged. Simply adding Two-Spirit to the list of LGBTQ fails to fully account for the underlying systems ofpower and knowledge that continue to shape possibilities for solidarity be-tween queer and Indigenous communities.
I feel like the authors capture the idea of this perfectly. In colonialism, we see that there is a need for everything to be categorized and defined. For example, in Western culture, a lot of clothes are put into categories of "masculine" and "feminine." This reminded me of the idea of Western epistemology vs Indigenous epistemology that we learned about in class. During week 3, we learned that often times Western knowledge is fixed, whereas Indigenous epistemology is alive and always changing (Bos 2025). I think categorizing things is deeply rooted in colonialism, and it adds to the dichotomous view of gender and sexuality that we see in everyday life through norms, societal views, etc.
/hyperpost/~/indyweb/📓/20/25/11/3/setup/-/indy0wiki.pad/index.html
secret.link: setup-indy0wiki.pad
HyperPost Presentation setup via IPFS Desktop on ThinkPad still experimental but got it to work
with confidence
Before you get into your about section, I would list out the 3 options you want to steer people towards and specifically call out (one 1:1 offer, your best-selling low-ticket resource, yoru membership, and your checklist freebie). Then have a button underneath to 'Check out all my offers' (linking to your work with me page).
and Italy, Khrushchev (with Castro’s agreement) began an,initially, secret placement of Soviet missiles in Cuba.The Russian buildup was detected by U–2 flights,while the Russians rushed to construct the supporting in-frastructure for the missiles, bombers, and defending SA-2 surface-to-air missile sites and MiG fighters. Russianmerchant ships bound for Cuba were scrutinized for sus-pected weapons systems. Eventually there was clear evi-dence that intermediate and medium-range missilelaunch pads hade been constructed despite Khrushchev’sassertion that no construction was ongoing—only themovement of agricultural machinery to aid in moderniz-ing the Cuban agrarian sector.Bromley then follows a timeline illustrating moves andcountermoves by the two key players. US aircraft conductedreconnaissance over Cuba. Strategic Air Command dis-persed its forces and maintained armed, airborne B–52s inanticipation of possible nuclear strikes. Soviet submarinesreached their stations off the US Atlantic coast and in theCaribbean, while the US Navy aggressively tracked them.Soviet anti-ship missiles were activated in Cuba. Kennedydeclared a blockade (quarantine) of Cuba (an act of war?).The Soviets, on October 27, 1962, shot down a US U–2, po-tentially pushing the crisis to the brink. A few days later aSoviet submarine crew, unsure of whether or not they werealready at war, came far too close to launching a nucleartorpedo at threatening US Navy surface vessels.The Cuban Missile Crisis was the single most unnerv-ing crisis of many during that era, one complicated by achain of often unanticipated events. It might sound like ahighly imaginative Cold War novel, but it did happen, asthis monograph makes very clear.A complicating sideshow was the need for each side torein in its own players. The Pentagon’s JCS wanted to in-vade Cuba. Submariners were ready to employ nuclear tor-pedoes. US destroyer commanders were itching to depthcharge Soviet submarines. Somehow, both direct and indi-rect exchanges between the two sides managed to end thecrisis.These monographs very effectively revisit Cold Warmoments of incredible consequence. For those of us whohave firsthand memories, reading the two volumes broughtthem all back. For readers with no firsthand knowledge,Bromley has provided an easy-to-follow account of whathappened, the impacts, and how we escaped a nuclear war.Without a question, these are very good reference materi-als and well worth the time to read.John Cirafici, Milford DEA6M2/3 Zero-sen; New Guinea and the Solomons1942 & Operation RO-GO 1943; Japanese Air PowerTackles the Bougainville Landings. Both by MichaelJohn Claringbould. Oxford UK: Osprey, 2023. Maps. Tables.Diagrams. Illustrations. Photographs. Appendices. Bibliog-raphy. Index. Pp. 80 and 96. Cost: $23.00 and $25.00 pa-perback. ISBN: 978-1-4728-5749-1 and 978-1-4728-5557-2-1In these two books, Michael Claringbould take thereader to the South Pacific at the time when the Japanesejuggernaut was stopped, and the allies began to take theinitiative in the theater. The A6M2/3 plays a leading rolein both books. Claringbould is an accomplished writer andan even better researcher, using his Japanese languageskills to bring new anecdotes and lessons to a well-knownstory. He frequently drops Japanese terms and phrasesthroughout his writing (ofttimes, it seems more to establishhis bona fides than to enlighten the reader).A6M2/3 Zero-sen is most effective when it provides auniquely detailed picture of the life of a Japanese aviatordeployed to a forward area. By mid-1942, the Japanesesupply chain was already stretched and under increasingpressure, so daily life and operations were harsh by anystandard. Claringbould’s research seems to have found aunique supply of anecdotes. He does not hesitate to callother writers to task for their failures to do the same, e.g.,criticizing Martin Caiden for his sterilization of the 1957Saburo Sakai biography Samurai for being an unrecogniz-able version of the original Japanese publication.This book abandoned the usual color profiles in favorof color schematics of air engagements. While eye-catching,the two-dimensional diagrams were more confusing thanhelpful. In his previous publications, Claringbould alsomakes clear that he believes regional geography and cli-mate are unappreciated factors that had significant tacti-cal and strategic impact.The A6M2/3 fighters were the heart of his story. Thebook shows that Japanese fighters were capable of domi-nating opposition when in the hands of skilled pilots. Inthe hands of novices, however, engagements with P–39s,F4Fs, and P–40s were more of an even match—and Japan-ese aircraft losses were much harder to replace. Pilots wereirreplaceable. Claringbould notes that, while the upgradeof the A6M2 to the A6M3 standard was significant, theSakae radial had reached the end of its evolution. Melzerstates in Wings for the Rising Sun that the Sakae radialdesign was a direct outgrowth of the Pratt & Whitney-Mit-subishi partnership. Once the war ended that partnership,Mitsubishi hit a technological dead end.Operation RO-GO 1943 moves the clock forward sixmonths as the Japanese struggled to regain the theaterinitiative. In doing so, Claringbould shows the results ofthe Japanese inability to both effectively redress the Zero-sen’s shortcomings and replace the loss of skilled aviators.He again beats the drum of geography and climate as op-erational factors that impacted the Japanese more thanthe allies. What began as a Japanese offensive strokequickly turned into a defensive battle to protect Truk andRabaul with demoralized and ill-equipped Japanese Army149������JOURNAL OF THE AFHF/ SPRING 2024
alksjdf
Baker also describes the successes and failures ofmany supersonic designs, including the Tu–22, T–4, Tu–160, and the Tu–144 supersonic passenger aircraft. Theseprovided lessons learned that will ultimately lead to thenext generation of Russian aircraft.This book is eminently readable and enjoyable. It pro-vides a wealth of detailed knowledge and inside stories onthe politics and technological development of weapons sys-tems in the Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia. There aremany high-quality photographs and layouts. It is a worthyreference book for historians and technologists alike andis definitely worth the readFrank Willingham, NASM docentPigs, Missiles and the CIA Volume One: Havana,Miami, Washington and the Bay of Pigs, 1959-1961& Volume Two: Kennedy. Khrushchev, Castro andthe Cuban Missile Crisis. By Linda Rios Bromley. War-wick UK: Helion & Co, 2021 and 2023. Photographs. Illus-trations. Maps. Notes. Bibliography, Pp. 62 and 92. $21.00each. ISBN: 978-1-91-437714-3 and 978-1-91-507075-3The 1961 Bay of Pigs fiasco was the precursor to thefar more ominous Cuban Missile Crisis just a year later.The latter event brought the USSR and US closer thanever to a mutually annihilating thermonuclear war. Be-cause this country should never again precipitate a crisisof that magnitude, it is essential to understand the eventsleading up to it. Volume 1 revisits one critical portion ofthat equation by examining CIA activities as it preparedto conduct an attack on Cuba itself.That the CIA pursued operations against the sover-eignty of other countries independent of congressionaloversight and known to only a handful of people is disturb-ing. It orchestrated the overthrow of legitimately electedgovernments in Iran and Guatemala and interfered in thepolitical process in other countries, such as Italy. It was nota reach to pursue the overthrow of the Castro government.Additionally, the State Department justified official rejec-tion of Castroite Cuba’s legitimacy by identifying it as aSoviet client posing a threat to the western hemisphere.Bromley summarizes Cuban history from the revolu-tion against Spain to Castro’s overthrow of the Batista gov-ernment. Why did the US strongly reject Castro’s reforms?Recall that clandestine operations to overthrow the Iraniangovernment in 1953 were in response to its nationalizationof foreign oil interests. Highly successful CIA operationsthere created a sense of confidence for future clandestineoperations. The Agency acted in 1954 to overthrow theGuatemala government on behalf of US commercial inter-ests. When Castro nationalized the huge land holdings ofUS sugar corporations and oil refineries, the CIA focusedon overthrowing the Cuban regime. Efforts to recruit pilots,aircraft, soldiers, equipment, and ships and establish basesfor a planned attack on Cuba are described in thisoverview.Very senior Pentagon officers were asked to assess theplan and said it had only a fair chance of success—and onlywith absolute air superiority. Choosing the Bay of Pigs areafor the invasion only increased the possibility of failure.President Kennedy’s closest advisors told him the plan wasdeeply flawed and would probably fail. As landings com-menced, Kennedy wavered in his support causing furtherconfusion leading to catastrophe—not his finest hour.The final section provides a play-by-play description of theinvasion, failure to support the troops on the ground, andthe final abandonment of the brigade. The poorly plannedand supported invasion wasn’t the end of crises forKennedy. Khrushchev soon humiliated him at the ViennaSummit followed by the Berlin Wall.Volume Two seamlessly picks up the story with anoverview of the two superpowers’ confrontational relation-ship. Cuba, rightfully fearing a US invasion, played only asecondary role at that point. To counterbalance America’splacing of nuclear intermediate-range missiles in Turkey
;laksdf
the imperative to respect black noise—the shrieks, the moans, the non-sense, and the opacity, which are always in excess of legibility and of the law and which hintat and embody aspirations that are wildly utopian, derelict to capitalism, and antithetical toits attendant discourse of Man.3
This passage speaks directly to what we studied under theories of the flesh. When Hartman writes about the “imperative to respect black noise—the shrieks, the moans, the non-sense, and the opacity,” she invokes the idea that the flesh carries forms of knowledge that cannot be translated into the language of the archive or the law (Moraga and Anzaldúa, 2022). Hartman’s insistence on “noise” directly challenges the logic of capitalism as the author states. In class, we discussed Silvia Federici’s work on capital accumulation where, broadly, capitalism emerges through the transformation of people into laboring bodies, units of value, and property (Federici, 2018). However, respecting the “noise” wouldn't allow for that. The shrieks, moans, and non-sense that Hartman describes cannot be translated into value or productivity. Moreover, respecting the pain experienced and humanizing the affected would make it more difficult to justify that exploitation.
I hoped toilluminate the contested character of history, narrative, event, and fact, to topple the hierar-chy of discourse, and to engulf authorized speech in the clash of voices. The outcome of thismethod is a “recombinant narrative,” which “loops the strands” of incommensurate accountsand which weaves present, past, and future in retelling the girl’s story and in narrating thetime of slavery as our present.3
Hartman describes her method as an effort to “topple the hierarchy of discourse” a hierarchy built by colonial, patriarchal, and Western epistemologies. This method "...which weaves past, present, and future..." is tied to the Indigenous epistemologies we learned about in class, regarding conceptions of time as non-linear and relational, something lived with, not simply looked back upon. By "...narrating the time of slavery as our present" Hartman engages in a decolonial act, another concept we learned about in class, with this nonlinear and interconnected approach with time.
Endogenous GFP tagging did not yield clear results likely due to low protein expression
It looks like there's at least one putative UPRE upstream of FMP52 (425 bases upstream of the ATG, 5'-TACGTGT-3')! I'm curious if you tried looking at endogenous Fmp52-GFP with t-2-hex or other ER stress-inducing treatment, as it may get upregulated and be more visible than in unstressed conditions? This would be consistent with your pFMP52-luciferase results.
The lowest 2% to 3% of students, when viewed according to IQ scores, receive the bulk of services, personnel, and funding to facilitate their education (Winner, 1996). Students with IQs ranging in the top 2% to 3% often experience very little in the way of services and supplementary aides (Winner, 1996).
This disparity shocked me at first but then when I reflected on my own experiences, I couldn't recall a time where I saw a gifted or talented student receive services.
Note: This response was posted by the corresponding author to Review Commons. The content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
Reviewer #1
First, the authors have not convincingly shown that skin cells, or more specifically skin ECs, are a major source of circulating G-CSF in the psoriasis model as stated in the title and abstract. The data in Figure 4 show selective upregulation of Csf3 gene in skin ECs and their ability to secrete G-CSF upon IMQ treatment in vitro. However, the provided data do not address to what degree the skin EC-derived G-CSF contributes to the elevated level of circulating G-CSF. Additional experiments to selectively deplete G-CSF in skin ECs, or at least in skin cells of the affected site, are warranted to support the authors' claim. Does intradermal injection of G-CSF neutralizing antibody into the psoriatic skin reduce circulating levels of G-CSF?
Author's response:
Thank you for reviewer's comment. We agree with the Reviewer#1 that it is important to directly block G-CSF to the skin via intradermal injection and measure the G-CSF level in the serum afterwards. Therefore, we will perform intradermal injection of IgG-isotype or anti-G-CSF antibody into the IMQ-induced psoriatic mice.
Another concern is insufficient demonstration of G-CSF-mediated emergency granulopoiesis in the psoriasis model. All data in Figure 5 were obtained from experiments with only n=3, and adding more replicates, in particular to those in Figure 5B, which show quite some variation in MPP numbers, is recommended. The relatively small reduction of BM granulocyte numbers (Figure 5C) compared to greater depletion of circulating granulocytes (Figure S5A) raises the possibility that it is the mobilization effect rather than granulopoiesis-stimulating effect that skin-derived G-CSF exerts to promote supply of circulating neutrophils that eventually infiltrate into the affected skin. This could also explain the negligible effect of IL-1blockade (Figure S4), which selectively shut off myelopoiesis-stimulating effect of IL-1 (Pietras et al. Nat Cell Biol 2016, PMID: 27111842). Are the HSPCs in the psoriasis model more cycling? Do they show myeloid-skewed differentiation when cultured ex vivo or upon transplantation?
Author's response: Thank you for these critical comments. We agree to do the following experiments to address them:
1) HSPCs quantification in Figure 5 especially the MPPs will be added with more replicates.
2) We will assess cycling status of HSPCs by flow cytometric analysis of Ki67and Propidium Iodide to characterize G0, G1 and G2/M cell cycle phase.
3) To test myeloid-skewed differentiation, Lin- c-Kit+ Sca-1+ cells containing HSPCs will be isolated from bone marrow of Vas/IMQ-treated mice and transplanted into lethally irradiated syngeneic mice.
The authors' claim that skin-derived G-CSF "induces" neutrophil infiltration warrants further clarification. Alternative explanation is that the upregulated neutrophil-attracting chemokines (Figure S1D) could induce infiltration, whereas G-CSF increase the number of neutrophils to circulate in the vessels near the psoriatic skin. This notion seems supported elsewhere (Moos et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2019, PMID: 30684554). Can the infiltration be inhibited by systemically injecting neutralizing antibody of their receptor, CXCR2?
Author's response: The manuscript focuses on the skin-derived G-CSF function as a long-distance signal for emergency granulopoiesis in the bone marrow upon psoriasis, not the chemoattractant property of it. The sentence of interest is "We found that upon psoriasis induction, skin-resident endothelial cells are activated to produce G-CSF which activates emergency granulopoiesis in bone marrow and induces cutaneous infiltration and accumulation of neutrophil that are functionally inflammatory." in line 28-30. In agreement with point #2 from Reviewer#2, the fact that neutrophil recruitment factors (CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL5) were upregulated in psoriatic skin (Figure S1D), suggesting a CXCL-mediated neutrophil recruitment. The sentence of concern need to be changed to "We found that upon psoriasis induction, skin-resident endothelial cells are activated to produce G-CSF which activates emergency granulopoiesis in bone marrow, leading to cutaneous accumulation of neutrophil that are functionally inflammatory.". This revised sentence has omitted the proposal that G-CSF directly dictates neutrophils mobilization to the skin, which is not the key message of the study. Therefore, we found that the CXCR2 (CXCLs receptor) blockade experiment may be of the benefit of future studies.
It remains unclear how skin-derived G-CSF accumulates pathogenic neutrophils. The authors state "pathogenic granulopoiesis," but are the circulating neutrophils in the psoriatic mice already "pathogenic" or do they acquire pathogenic phenotype after cutaneous infiltration? Additional RNA-seq to compare circulating and infiltrated neutrophils would answer this question.
Author's response: We appreciate this valuable comment. We will perform RNA-seq with the peripheral blood-circulating neutrophils (CD45+ CD11b+ Ly6G+ Ly6Cmid) versus skin-infiltrating neutrophils from both Vas/IMQ mice.
In addition, how the accumulated pathogenic neutrophils exacerbate the psoriatic changes remains obscure. Although the authors have attempted to correlate Il17a gene expression in infiltrated neutrophils with psoriatic skin changes, the data do not address to what degree it contributes to cutaneous IL-17A protein levels. The data that cutaneous neutrophil depletion leads to subtle decrease in skin IL-17A expression (Figure 2H) rather supports alternative possibilities. For instance, as indicated elsewhere, IL-17A cutaneous tone could be enhanced by neutrophil-mediated augmentation of Th17 or gamma/delta T cell function (Lambert et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2019, PMID: 30528823). Does neutrophil depletion or G-CSF neutralization alter cell numbers or function of cutaneous Th17 and gamma/delta T cells?
Author's response: Thank you for this insightful comment. To better understand the relative contribution of neutrophils to the cutaneous IL-17A tone in the psoriatic skin, we will perform flowcytometric analysis of Th17 and gamma/delta T cells which are widely known as the major source of IL-17 in psoriatic skin of IMQ-induced mice following injection of isotype-matched or anti-Ly6G antibody.
Finally, as the above conclusions rely solely on the IMQ-induced acute psoriasis model, it would be informative if they could be derived from another psoriasis model. IMQ is known to induce unintended systemic inflammation due to grooming-associated ingestion (Gangwar et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2022, PMID: 34953514), and "pathological crosstalk between skin and BM in psoriatic inflammation" could be strengthened by an intradermal injection model.
Author's response: We appreciate the reviewer for bringing this important point. Regarding the systemic inflammation upon psoriasis, the above-cited study reported increased IFN-B expression in the intestines of IMQ-ingested animal (Grine L et al. Sci Rep. 2016, PMID: 26818707 in Gangwar et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2022, PMID: 34953514). We examined several pro-inflammatory cytokines including IFN-b, IFN-g, and IL-6 and in contrast, found no systemic increase in all these cytokines, except for IFN-g downregulation (Explanation Figure 1), which suggests no evidence of grooming-associated ingestion.
We also examined the Csf3 expression across several distinctively located tissues which showed a selective upregulation in the skin (Figure 4C), suggesting a skin-restricted perturbation. In addition, one study showed that IMQ-ingestion didn't alter number of gut injury-associated CXCR3+ macrophages nor did it aggravate skin inflammation (Pinget et al. Cell Reports. 2022, PMID: 35977500). Together, these findings support that IMQ-induced psoriasis by topical cutaneous application used in our study elicit a local inflammation but not systemic inflammation.
The authors, however, realize that testing alternative psoriasis model such as intradermal injection of IL-23 (Chan et al. J Exp Med. 2006, PMID: 17074928) will strengthen the skin-local insults within the psoriasis model employed, and should be tested in the future.
Minor comments
Figure 1E shows multiple elongated Ly6G+ structures in d0-2 control and d0 IMQ skins that do not appear to be neutrophils.
Author's response: We appreciate the Reviewer#1 pointing this issue. As mentioned by the Reviewer#1, the elongated structures detected in the intravital microscopy are not neutrophils, but autofluorescence from the skin bulge regions (Wun et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2005, PMID: 15816847). We have eliminated these unspecific signals from the transformation and quantification (Figure 1F, S1G, and S1H). We will also add an explanatory sentence in Materials and Methods section "Of note, the fluorescent signal with elongated structures resembling hair bulge were autofluorescence and thus removed from further analysis." to be more precise about our methods.
In Figure 2C, the bottom GSEA seems to be showing type II IFN response, not type I IFN, according to the text.
Author's response: Thank you for the comment, we will correct this misspelling.
Author's response: We appreciate that Reviewer#1 bring up this point. We examined the kinetics of the bone marrow cellularity and GMPs across 4 days of psoriasis induction in mice. The bone marrow cell number was lowered along that span with lowermost count at 2 days. Consistent to the BM-cellularity, the GMP number was also lowered about one-third in the first 2 days of psoriasis. This kinetic is consistent with the previous report showing a rapid reduction of GMPs in the bone marrow within 2 days following systemic G-CSF administration driven emergency granulopoiesis (Hirai et al. Nat. Immunol. 2006, PMID: 16751774). From 2 days to 4 days, the GMP number rapidly increased to slightly above basal number (Explanation Figure 2). This timely coordinated expansion suggests a significant supply of GMPs from the differentiating upstream myeloid progenitors (Figure 3B).
When the psoriatic mice with elevated G-CSF is injected with anti-G-CSF or IgG-isotype antibody, the bone marrow cellularity and GMP numbers at 4 days were (Explanation Figure 3). Firstly, as psoriasis reduced bone marrow cellularity (Explanation Figure 2), the unchanged number after anti-G-CSF injection indicates that administration of 10µg/day for 4 days does not significantly affect mobilization of psoriatic bone marrow cells. Secondly, the similar GMP numbers at 4 days psoriasis is plausibly due to snapshot analysis when it has already in the numerical recovery period (Explanation Figure 2). Importantly, the notion that anti-G-CSF injection to psoriatic mice reduced granulocytes in the bone marrow, peripheral blood, and skin suggesting G-CSF as a key mediator in psoriatic driven emergency granulopoiesis on top of unlikely case of ineffective anti-G-CSF treatment.
Taken together, these data suggest a G-CSF mediated emergency granulopoiesis occurrence in the IMQ-induced psoriasis. We will put these data into a revised Figure.
In Figures 6B, in which cluster of human skin cells IL-17A expression would be enriched?
Author's response: Thank you for this important point. The IL-17A expression is found in the T-cell cluster (Explanation Figure 4). We also expected to see IL-17A contribution from other cell subset(s), in particular neutrophil. However, due to the fragile nature of neutrophils and thereby, technical difficulty to get their sequencing reads, this dataset (GSE173706) doesn't contain neutrophils, but rather monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells among the myeloid subset (Explanation Figure 5). With this, it leaves open the question on what potential contribution of IL-17A produced by neutrophils is in human psoriasis (Reich et al. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, PMID: 25828362).
Figure 1E shows multiple elongated Ly6G+ structures in d0-2 control and d0 IMQ skins that do not appear to be neutrophils.
Author's response: We appreciate the Reviewer#1 pointing this issue. As mentioned by the Reviewer#1, the elongated structures detected in the intravital microscopy are not neutrophils, but autofluorescence from the skin bulge regions (Wun et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2005, PMID: 15816847). We have eliminated these unspecific signals from the transformation and quantification (Figure 1F, S1G, and S1H). We will also add an explanatory sentence in Materials and Methods section "Of note, the fluorescent signal with elongated structures resembling hair bulge were autofluorescence and thus removed from further analysis." to be more precise about our methods.
In Figure 2C, the bottom GSEA seems to be showing type II IFN response, not type I IFN, according to the text.
Author's response: Thank you for the comment, we will correct this misspelling.
Reviewer#2
Interpretation of neutrophil transcriptomic changes (Figure 2)
The RNA-seq analysis reveals substantial downregulation of several canonical pro inflammatory pathways in neutrophils from psoriatic skin, including IL-6, IL-1, and type II interferon signaling. The authors should discuss the functional relevance of this unexpected transcriptional repression. For example, does this indicate a shift toward specialized effector functions rather than classical cytokine responsiveness? More importantly, the most striking transcriptional change is the upregulation of NADPH oxidase-related genes (e.g., Nox1, Nox3, Nox4, Enox2). This suggests an oxidative stress-driven pathogenic mechanism, potentially more relevant than IL-17A production. Yet this aspect is not explored in the manuscript. Assessing ROS levels or oxidative neutrophil effector functions in this model would considerably strengthen the mechanistic link. Conversely, although IL-17A is upregulated in neutrophils, neutrophil depletion reduces total Il17a expression in skin only partially. This indicates that neutrophils are unlikely to be the dominant IL-17A source in the lesion. The authors' focus on neutrophil-derived IL 17A therefore seems overstated. A more rigorous assessment-e.g., conditional deletion of Il17a specifically in neutrophils-would be required to establish its true contribution. Taken together, the data suggest that oxidative programs, rather than IL-17A production, may represent the principal pathogenic axis downstream of neutrophils, and this deserves deeper discussion.
Author's response: Thank you for raising this valuable views. We have agreed to address these critical points by the following approaches:
1) To address the changes in NADPH oxidase-related gene signature, we will measure ROS production in the neutrophils from skin and peripheral blood with DHR123.
2) Responding to the IL17A contribution by neutrophils, we will flow cytometrically assess the Th17 and gamma/delta T cell population in the skin of psoriatic mice treated with anti-Ly6G or isotype-matched antibody as was suggested by Reviewer#1.
3) We will discuss downregulation of the canonical pro inflammatory and IL-17 pathways in the psoriatic neutrophils in the discussion.
Human data reanalysis (Figure 6):
The re-analysis of bulk and single-cell RNA-seq datasets is valuable but incomplete. Several mechanistically relevant questions could be addressed with the available data:
2.1. GM-CSF (CSF2) is also strongly upregulated in psoriatic lesions (bulk RNA-seq). It would be informative to determine whether endothelial cells also express CSF2 in the scRNA-seq dataset, as this would suggest coordinated regulation of myeloid-supporting cytokines.
2.2. Myeloid cell subsets should be examined more closely. A comparison of human myeloid transcriptomes with the mouse neutrophil RNA-seq would clarify whether similar IL-17A-related or NADPH oxidase-related signatures occur in human disease. In particular, which cell types express IL17A in human lesions?
2.3. Chemokine production should be attributed to specific cell types. Bulk RNA-seq confirms strong induction of CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL5, but the scRNA-seq dataset allows determining whether these chemokines originate from endothelial cells or other stromal/immune populations. This information is important for defining whether endothelial cells coordinate both neutrophil recruitment and granulopoiesis.
Addressing these points would make the human-mouse comparison substantially stronger.
Author's response: Thank you for pointing these important issues. By reanalyzing the dataset, we found several points regarding the comments, as follows:
2.1) CSF2 is expressed by T-cell cluster in the human skin dataset (Explanation Figure 4), in agreement with previous murine study (Hartwig et al. Cell Reports. 2018, PMID: 30590032). We will add this data in the revised manuscript.
2.2) In line with point#10 from Reviewer#1, the dataset clearly shows T-cell cluster as the main IL17A source (Explanation Figure 4 above). The dataset, however, doesn't contain phenotypic neutrophils (CEACAM (CD66b) and PGLYRP1) but monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (Explanation Figure 5 above). This loss was probably due to a technical limitation given the difficulty in capturing sequencing reads from fragile neutrophils. Therefore, it is no longer possible to reanalyze IL-17 expression in the absence of neutrophils in the datapool.
2.3) Reanalysis of CXCLs in the human scRNAseq dataset (GSE173706) clarified their secretion dynamics and cellular sources under normal and psoriatic condition. In normal skin, all examined cell subsets show only low CXCLs expression. In contrast, psoriatic skin exhibits significant CXCLs upregulation with distinct cell subsets clearly showing dramatic upregulation, potentially being the major CXCLs source. CXCL1 is markedly upregulated in fibroblasts, myeloid cells, and melanocyte and nerve cells. CXCL2 is strikingly upregulated to myeloid cells, while CXCL5 is hugely increased in fibroblasts, myeloid cells, and mast cells (Explanation Figure 7). Taken together, these results suggest that CXCLs upregulation in the psoriatic skin is coordinatively executed by both stromal and immune compartments. Of note, the endothelial cells show minimal changes in CXCLs expression, even downregulate CXCL2 in psoriasis, indicating that they are unlikely to be the major contributor to CXCL-mediated neutrophil recruitment.
**Referees cross-commenting**
I agree with Reviewer 1 that the contribution of EC-derived G-CSF to circulating G-CSF levels and to emergency myelopoiesis requires additional genetic or neutralization experiments to be fully established.
Author's response: We appreciate that Reviewer#2 raised this key point. In addition to examining the serum G-CSF upon intradermal anti-G-CSF administration in point#1 from Reviewer#1 above, we will also examine the emergency myelopoiesis signs in vivo.
Minor points
Line 319: the text likely refers to Figure S4, not S3.
Author's response: Thank you, we will correct the nomenclature.
Line 338: "psoriatic" is misspelled.
Author's response: Thank you, we will change this to "psoriatic".
Reviewer #3
- Place the work in the context of the existing literature (provide references, where appropriate).
Psoriasis is extensively studied, a good recent reference- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2024.101306
Author's response: Thank you for Reviewer#3's suggestion. The referenced study highlights the current paradigm that largely focus on skin-restricted mechanism and overlook potential cross-organ interaction in the psoriasis inflammation. Our findings provide a new insight into the skin-bone marrow crosstalk in the disease context. In addition, the suggested reference underscores the key roles of diverse innate immune cells including neutrophils, eosinophils, dendritic cells, etc. which is fundamental for our study and might also guide future exploration of additional innate cell subsets beyond neutrophils. We will therefore include the mentioned reference to our revised manuscript.
- Do you have suggestions that would help the authors improve the presentation of their data and conclusions?
It is all good. May add graphical-abstract.
Author's response: Thank you for the reviewer's input, we agree that a graphical-abstract will help the readers more clearly grasp the key messages of our manuscript. We will include it in the revised manuscript.
Major comments:
- Should the authors qualify some of their claims as preliminary or speculative, or remove them altogether?
No. It is very solid.
Author's response: We appreciate the reviewer's view that the claims in our paper are solid.
- Would additional experiments be essential to support the claims of the paper? Request additional experiments only where necessary for the paper as it is, and do not ask authors to open new lines of experimentation.
Such a discovery clearly opens many options, and it is fascinating to suggest additional experiments for future studies. It is a complete study, best to publish as-is and let many to read and proceed with this new concept.
Author's response: We thank the reviewer for noting that the current experimental evidence is complete that no additional experiments are necessary at this stage. We agree that the discovery opens prospective directions for future studies.
- Are the suggested experiments realistic in terms of time and resources? It would help if you could add an estimated cost and time investment for substantial experiments.
N/A - I suggest no additional experiments at this point. Get it published and see how many will follow this new direction!
Author's response: We thank the reviewer for recognizing that the experimental data has been sufficient to be a foundation for the future research.
- Are the data and the methods presented in such a way that they can be reproduced?
Yes.
Author's response: We thank the reviewer for recognizing that our methods are reproducible.
- Are the experiments adequately replicated, and is the statistical analysis adequate?
Yes. The data are of very high quality.
Author's response: We are grateful that the reviewer view our replication strategy and statistical analysis are of a high quality.
Minor comments:
- Specific experimental issues that are easily addressable.
None. It is good as-is. One may always suggest minor things- but this one is better published so many laboratories may rush for this new direction. I think it will be interesting studying some long-term impacts, and changes not only of neutrophils but also of other innate cells, such as DCs, Macrophages, and Eosinophils - so it is best to let laboratories that focus on these cells know of the discovery and pursue independent studies.
Author's response: We appreciate the reviewer's assessment that our paper is already well set for the community to explore the newly proposed direction.
- Are the text and figures clear and accurate?
Yes.
Author's response: We thank the reviewer's evaluation. We have ensured that the text and figures in our manuscript are clear and accurate. Once again, we thank the reviewer for the encouraging and constructive appraisal. We are pleased that the reviewer find the manuscript has already been strong and suitable for publication.
Note: This preprint has been reviewed by subject experts for Review Commons. Content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
Summary:
Provide a short summary of the findings and key conclusions (including methodology and model system(s) where appropriate).
Study titled: "Skin-derived G-CSF activates pathological granulopoiesis upon psoriasis" by Kosasih and Takizawa. Paper show establishment of psoriasis model in C57BL/6 mice. They focus on neutrophils infiltration following the Imiquimod cream induction. Importantly, authors show that the induction of psoriasis in the skin cause a robust enhancement of granulopoiesis in the bone marrow. Mechanistically, G-CSF is produced in the skin, especially by endothelial cells. Blocking of G-CSF gained clear inhibition of psoriatic pathology. They further add human data showing that patient with psoriasis have more neutrophils and more G-CSF in their skin endothelial cells.
Parts of the study are simply in line with previous knowledge (e.g.- neutrophils infiltration into psoriatic skin, IL17a). authors show some data that largely confirm the model used. Major discovery: skin endothelial cells are secreting G-CSF that induce granulopoiesis in the bone-marrow. This is a conceptual advancement of this study: psoriatic skin not only recruit neutrophils from the blood, but also enhance the generation of new neutrophils in the bone-marrow. That a major- psoriasis at the level of the model used must not be considered as a confined-pathology. It affect systematically, and might also benefit new systemic treatments. There are plenty of follow-up experiments to pursue now, so it is critical to publish this finding and let many laboratories to know of this new direction. I expect this study to attract high interest and many citations.
Major comments:
Yes. The study has excellent data, with good quantification, and very solid support for the discovery and interpretations. - Should the authors qualify some of their claims as preliminary or speculative, or remove them altogether?
No. It is very solid. - Would additional experiments be essential to support the claims of the paper? Request additional experiments only where necessary for the paper as it is, and do not ask authors to open new lines of experimentation.
Such a discovery clearly opens many options, and it is fascinating to suggest additional experiments for future studies. It is a complete study, best to publish as-is and let many to read and proceed with this new concept. - Are the suggested experiments realistic in terms of time and resources? It would help if you could add an estimated cost and time investment for substantial experiments.
N/A - I suggest no additional experiments at this point. Get it published and see how many will follow this new direction! - Are the data and the methods presented in such a way that they can be reproduced?
Yes. - Are the experiments adequately replicated, and is the statistical analysis adequate?
Yes. The data are of very high quality.
Minor comments:
None. It is good as-is. One may always suggest minor things- but this one is better published so many laboratories may rush for this new direction. I think it will be interesting studying some long-term impacts, and changes not only of neutrophils but also of other innate cells, such as DCs, Macrophages, and Eosinophils - so it is best to let laboratories that focus on these cells know of the discovery and pursue independent studies. - Are prior studies referenced appropriately?
Yes. I may suggest adding a recent review by Park and Jung, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2024.101306 to cover current concepts of innate immunity in psoriasis. - Are the text and figures clear and accurate?
Yes. - Do you have suggestions that would help the authors improve the presentation of their data and conclusions?
It is all good. May add graphical-abstract.
Conceptual advancement - discovery of a major impact of psoriasis on bone-marrow granulopoiesis. Explicit finding of endothelial-cells G-CSF as a major communication moiety.
Neutrophil recruitment and IL17A are well established. G-CSF of endothelial cells brings the conceptual advancement- psoriasis at the level induced by IMQ develops local pathology, but is tightly linked to systemic changes. The impact on bone-marrow granulopoiesis may have many implications. So far, it was largely considered that chronic inflammation may affect hematopoiesis, but this study reveals an acute and specific communication between skin and bone marrow. The neutrophils are not only recruited from blood- they are made anew, so the disease is enhanced significantly! This discovery led to a novel basic understanding and suggests novel therapeutic options. - State what audience might be interested in and influenced by the reported findings.
Dermatologist, immunologist, haematologist - this one goes for a broad audience. - Define your field of expertise with a few keywords to help the authors contextualize your point of view. Indicate if there are any parts of the paper that you do not have sufficient expertise to evaluate.
Immunology and hematology. I am not an expert of dermatology.
Note: This preprint has been reviewed by subject experts for Review Commons. Content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
Summary:
A role of neutrophils in psoriasis pathogenesis has been highlighted by several past studies; however, how the neutrophils are recruited to the affected skin has not been fully understood. The work by Kosasih et al. tackles a relevant question and has investigated the effect of psoriatic skin inflammation on BM myelopoiesis. Using an IMQ-induced acute psoriasis mouse model, the authors derive 3 major conclusions: (1) skin ECs secrete G-CSF into circulation in response to psoriatic stress, (2) skin EC-derived G-CSF stimulates emergency granulopoiesis, and (3) skin EC-derived G-CSF induces infiltration and accumulation of pathogenic neutrophils in the affected skin. The authors provide many pieces of interesting data, but most of them remain correlative and insufficient to support the conclusions. Many of the experiments were performed in a small number of samples or mice (mostly with n=3), leaving the story still preliminary.
Major comments:
Minor comments:
Although quite a few studies have reported various examples of emergency myelopoiesis (Swann et al. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024, PMID: 38467802), there is limited evidence on its occurrence and involvement in locally restricted disease, such as periodontitis (Li et al. Cell 2022, PMID: 35483374; 35483374). As an HSC biologist, I see this study is conceptually interesting as it could extend the above concept to psoriasis, a non-infectious, local inflammatory disease in the skin, and describes a potential causal link between skin-derived G-CSF and emergency myelopoiesis. That said, as detailed in the first section, the conclusions, especially that related to emergency myelopoiesis driven by skin-derived G-CSF, need to be more convincingly supported before taking its value. The findings offer additional understanding of how psoriasis is developed in concert with aberrant hematopoiesis and will be relevant to those working in the field of dermatology, immunology, and hematology.
Evapotranspiration from the surface (land and oceans) accounts for 80 W m super negative two of the surface-absorbed radiation. This is transferred to the atmosphere. How does this compare to other processes transferring energy to the atmosphere?
Evapotransipiration is a similar value of incoming SR directly absorbed by the atmopheres, nearly 5x that transferred by sesnisble heat and 22% ofrom surface emitted LW radiation
Therefore, the global average solar radiation arriving at the top of the atmosphere is one-quarter of the solar constant.
Global average of SR at the top of the atmosphere is 1/4 solar constant
The energy budget can be determined at different timescales but is usually averaged over one or more years to account for seasonal effects. This is known as the steady-state condition. It does not mean that the atmosphere is unchanging, but that these variations average out and it is not in a rapid transition to a different state.
Energy budget is determined at steady state across one or more years to account for seasonal affects
Energy is always conserved. Considering the Earth’s environment as a whole, this means that the energy that goes in must either come back out or be stored in it. The energy going in is almost all from absorbed solar (short-wave) radiation, and energy going out is almost all infrared (long-wave) terrestrial radiation. As you saw in the previous study session, just under a third of solar radiation is reflected or scattered back to space, and about a third of what is left is absorbed by the atmosphere. This leaves the planet’s surface to absorb roughly half of the total radiation incident at the top of the atmosphere, predominantly in the visible region.
Energy coming in is mostly absorbed by SW RD Energy out is infrared LW TR 1/3 SR is refelceted back, and 1/3 of whats left is absrobed by the atmospehre, so half of total radiation incident is absrobed at hte top of the atmophere in the visible region
A particularly important window in the atmospheric absorption spectrum is found at infrared wavelengths from roughly 8 mu m to 15 mu m , where there is relatively low absorption by air, except just below 10 mu m due to ozone. This is also the region where the radiation emitted by Earth is high. Transparency in this region of the spectrum is what allows the land to cool rapidly on a cloudless night, as most of the energy being emitted from Earth’s surface is being lost to space. This window can be ‘closed’ if clouds are present, since they absorb and scatter radiation over a wider range of wavelengths than clear air.
Another important window is at infrared WL ~8-15um, where there's low air absorption, expect just below 10 um due to ozon. This is where the radiation emitted by Earth is high and transparency in this region allows land to cool on cloudless nights as energy emited by earth is lost to space, the window is closed if clouds are present as they absrob and scatter radiation
The atmosphere is, however, a relatively good absorber of long-wave (infrared) radiation, due principally to carbon dioxide and water vapour, and these gases absorb much of the long-wave radiation emitted by the Earth. Because the atmosphere is largely transparent to short-wave (solar) radiation but absorbs more long-wave radiation, the atmosphere is heated from the ground up. Water vapour, which is more concentrated near the Earth’s surface, absorbs about 60% of the radiation emitted by the Earth and is the gas mainly responsible for warm temperatures in the lower troposphere. As you move further away from the surface, the temperature drops, as we saw in Study session 2.1.2. The fact that the atmosphere receives most of its energy from the Earth’s surface, rather than directly from the Sun, is critical for driving weather processes.
Atmosphere is very good at absorbing long wave infrared radiation due to carbon dioxide & water vapur Because the atmosphere is mostly transpoarent to short wave radiation, but it does absorb long wave, it heats from the group up. Water vapour, espeically at the earths surface, absorbs 60% of radiation emited by earth and is the gas mainly respoinble for warmer temps inteh lower troposphere Becase the atmosphere gets most of its energy from the surface and not directly the sun it is critical for driving weather processes.
There are two important regions of the spectrum where the atmosphere is relatively transparent: the visible region and part of the radio region. The fact that humans have evolved to see in the visible region and have developed technology that uses radio wavelengths to communicate long distances is of course no coincidence. These regions are known as ‘windows’ because electromagnetic radiation of these wavelengths can pass through the air without much absorption (the regions in Figure 2.1.17(b) where total absorption and scattering is near zero). Because the atmosphere is largely transparent to visible radiation, most of this energy reaches the Earth’s surface, and it does not have a role in heating the atmosphere.
The visible and radio regions are important parts of the pectrum where the atmosphere is pretty transparent Radio & visible regions are known as windows because these wavelenghts can pass through the air without being absrobs Because the atmosphere is mostly tarnsparent to visible radiation most of it reaches the surface and doesn't warm the atmopshere.
The gases that are important for the absorption of incoming solar radiation are water vapour, oxygen and ozone. Although nitrogen is the main constituent of the atmosphere, it is a poor absorber of solar radiation. Water vapour is the dominant gas, absorbing and scattering radiation across many regions of the spectrum. Oxygen and ozone are very effective at absorbing short-wavelength, high-energy radiation, such that very little radiation less than 0.3 mm reaches the Earth’s surface. Recall that the temperature profile of the atmosphere (Figure 2.1.8) shows warming in the stratosphere, between about 10 and 50 km altitude, which is due to the absorption of ultraviolet radiation in this region. This will be covered in more detail in Part 4 of the block.
Water vapour, oxygen and ozone are important to absorbing solar radiation Nitrogen is a poor absorber of SR Water vapour is the dominate gas which absorbs & scatters radiation across many regions of the specturm. Oxygen & Ozon are v. effective absorbing sWL, high energy radiation, less that 0.3mm reaches the earths surfaces
In Figure 2.1.17 the absorption features of gases are smoothed for clarity and are actually comprised of numerous extremely fine lines, which merge into the larger features seen on the curve. The peaks in a gas’s absorption spectrum correspond to specific vibrational and rotational transitions of its molecules. Each transition occurs at a characteristic energy and therefore at a specific wavelength (or frequency) of electromagnetic radiation.
The image is curved but is actually lots of little lines
Peaks in gas absorption spectrum correspond to specific vibrational and rotational transitions of its molecules, with each occuring at a characteristic energy and specific WL of EMR
The gases in the Earth’s atmosphere are selective absorbers, and emitters, of radiation. About 20% of the radiation that arrives at the top of the atmosphere is absorbed, with this absorption occurring in different regions and wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum due to the properties of the different gases present.
Gases in the atmosphere are selective, 20% of radiation that arrives at the top is abosrobed, occuring at differen regions & wavelenghts due to the properties of the gases present
Note: This response was posted by the corresponding author to Review Commons. The content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
Reviewer #1 (Evidence, reproducibility and clarity (Required)):
Summary The manuscript by Aarts et al. explores the role of GRHL2 as a regulator of the progesterone receptor (PR) in breast cancer cells. The authors show that GRHL2 and PR interact in a hormone-independent manner and based on genomic analyses, propose that they co-regulate target genes via chromatin looping. To support this model, the study integrates both newly generated and previously published datasets, including ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN, RNA-seq, and chromatin interaction assays, in breast cancer cell models (T47DS and T47D).
Major comments: R1.1 Novelty of GRHL2 in steroid receptor biology The role of GRHL2 as a co-regulator of steroid hormone receptors has previously been described for ER (J Endocr Soc. 2021;5(Suppl 1):A819) and AR (Cancer Res. 2017;77:3417-3430). In the ER study, the authors also employed a GRHL2 ΔTAD T47D cell model. Therefore, while this manuscript extends GRHL2 involvement to PR, the contribution appears incremental rather than conceptual.
We are fully aware of the previously described role of GRHL2 as a co-regulator of steroid hormone receptors, particularly ER and AR. As acknowledged in our introduction (lines 104-108), we explicitly state: "Grainyhead-like 2 (GRHL2) has recently emerged as a potential pioneer factor in hormone receptor-positive cancers, including breast cancer21. However, nearly all studies to date have focused on GRHL2 in the context of ER and estrogen signaling, leaving its role in PR- and progesterone-mediated regulation unexplored22-26".
As for the specific publications that the reviewer refers to: The first refers to an abstract from an annual meeting of the Endocrine Society. As we have been unable to assess the original data underpinning the abstract - including the mentioned GRHL2 DTAD model - we prefer not to cite this particular reference. We do cite other work by the same authors (Reese et al. 2022, our ref. 25). We also cite the AR study mentioned by the reviewer (our ref. 55) in our discussion. As such, we think we do give credit to prior work done in this area.
By characterizing GRHL2 as a co-regulator of the progesterone receptor (PR), we expand on the current understanding of GRHL2 as a common transcriptional regulator within the broader context of steroid hormone receptor biology. Given that ER and PR are frequently co-expressed and active within the same breast cancer cells, our findings raise the important possibility that GRHL2 may actively coordinate or modulate the balance between ER- and PR-driven transcriptional programs, as postulated in the discussion paragraph.
Importantly, we also functionally link PR/GRHL2-bound enhancers to their target genes (Fig5), providing novel insights into the downstream regulatory networks influenced by this interaction. These results not only offer a deeper mechanistic understanding of PR signaling in breast cancer but also lay the groundwork for future comparative analyses between GRHL2's role in ER-, AR-, and PR-mediated gene regulation.
As such, we respectfully suggest that our work offers more than an incremental advance in our knowledge and understanding of GRHL2 and steroid hormone receptor biology.
R1.2 Mechanistic depth The study provides limited mechanistic insight into how GRHL2 functions as a PR co-regulator. Key mechanistic questions remain unaddressed, such as whether GRHL2 modulates PR activation, the sequential recruitment of co-activators/co-repressors, engages chromatin remodelers, or alters PR DNA-binding dynamics. Incorporating these analyses would considerably strengthen the mechanistic conclusions.
Although our RNA-seq data demonstrate that GRHL2 modulates the expression of PR target genes, and our CUT&RUN experiments show that GRHL2 chromatin binding is reshaped upon R5020 exposure, we acknowledge that we have not further dissected the molecular mechanisms by which GRHL2 functions as a PR co-regulator.
We did consider several follow-up experiments to address this, including PR CUT&RUN in GRHL2 knockdown cells, CUT&RUN for known co-activators such as KMT2C/D and P300, as well as functional studies involving GRHL2 TAD and DBD mutants. However, due to technical and logistical challenges, we were unable to carry out these experiments within the timeframe of this study.
That said, we fully recognize that such approaches would provide deeper mechanistic insight into the interplay between PR and GRHL2. We have therefore explicitly acknowledged this limitation in our limitations of the study section (line 502-507) and mention this as an important avenue for future investigation.
R1.3 Definition of GRHL2-PR regulatory regions (Figure 2) The 6,335 loci defined as GRHL2-PR co-regulatory regions are derived from a PR ChIP-seq performed in the presence of hormone and a GRHL2 ChIP-seq performed in its absence. This approach raises doubts about whether GRHL2 and PR actually co-occupy these regions under ligand stimulation. GRHL2 ChIP-seq experiments in both hormone-treated and untreated conditions are necessary to provide stronger support for this conclusion.
Although bulk ChIP-seq cannot definitively demonstrate simultaneous binding of PR and GRHL2 at the same genomic regions, we agree that the ChIP-seq experiments we present do not provide a definitive answer on if GRHL2 and PR co-occupy these regions under ligand stimulation. As a first step to address this, we performed CUT&RUN experiments for both GRHL2 and PR under untreated and R5020-treated conditions. These experiments revealed a subset of overlapping PR and GRHL2 binding sites (approximately {plus minus}5% of the identified PR peaks under ligand stimulation).
We specifically chose CUT&RUN to minimize artifacts from crosslinking and sonication, thereby reducing background and enabling the mapping of high-confidence direct DNA-binding events: Given that a fraction of GRHL2 physically interacts with PR (Fig1D), it is possible that ChIP-seq detects indirect binding of GRHL2 at PR-bound sites and vice versa. CUT&RUN, by contrast, allows us to identify direct binding sites with higher confidence.
Nonetheless, although outside the scope of the current manuscript, we agree that a dedicated GRHL2 ChIP with and without ligand stimulation would provide additional insight, and we have accordingly added this suggestion to the discussion (line 502-507).
R1.4 Cell model considerations The manuscript relies heavily on the T47DS subclone, which expresses markedly higher PR levels than parental T47D cells (Aarts et al., J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2023; Kalkhoven et al., Int J Cancer 1995). This raises concerns about physiological relevance. Key findings, including co-IP and qPCR-ChIP experiments, should be validated in additional breast cancer models such as parental T47D, BT474, and MCF-7 cells to generalize the conclusions. Furthermore, data obtained from T47D (PR ChIP-seq, HiChIP, CTCF and Rad21 ChIP-seq) and T47DS (RNA-seq, CUT&RUN) are combined along the manuscript. Given the substantial differences in PR expression between these cell lines, this approach is problematic and should be reconsidered.
We agree that physiological relevance is important to consider. Here, all existing model systems have some limitations. In our experience, it is technically challenging to robustly measure gene expression changes in parental T47D cells (or MCF7 cells, for that matter) in response to progesterone stimulation (Aarts et al., J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2023). As we set out to integrate PR and GRHL2 binding to downstream target gene induction, we therefore opted for the most progesterone responsive model system (T47DS cells). We agree that observations made in T47D and T47DS cells should not be overinterpreted and require further validation. We have now explicitly acknowledged this and added it to the discussion (line 507-509).
As for the reviewer's suggestion to use MCF7 cells: apart from its suboptimal PR-responsiveness, this cell line is also known to harbor GRHL2 amplification, resulting in elevated GRHL2 levels (Reese et al., Endocrinology2019). By that line of reasoning, the use of MCF7 cells would also introduce concerns about physiological relevance. That being said, and as noted in the discussion (line 390-391), the study by Mohammed et al. which identified GRHL2 as a PR interactor using RIME, was performed in both MCF7 and T47D cells. This further supports the notion that the PR-GRHL2 interaction is not limited to a single cell line.
R1.5 CUT&RUN vs ChIP-seq data The CUT&RUN experiments identify fewer than 10% of the PR binding sites reported in the ChIP-seq datasets. This discrepancy likely results from methodological differences (e.g., absence of crosslinking, potential loss of weaker binding events). The overlap of only 158 sites between PR and GRHL2 under hormone treatment (Figure 3B) provides limited support for the proposed model and should be interpreted with greater caution.
We acknowledge the discrepancy between the number of binding sites between ChIP-seq and CUT&RUN. Indeed, methodological differences likely contribute to the differences in PR binding sites reported between the ChIP-seq and CUT&RUN datasets. As the reviewer correctly notes, the absence of crosslinking and sonication in CUT&RUN reduces detection of weaker binding events. However, it also reduces the detection of indirect binding events which could increase the reported number of peaks in ChIPseq data (e.g. the common presence of "shadow peaks").
As also discussed in our response to R1.3, we deliberately chose the CUT&RUN approach to enable the identification of high-confidence direct DNA-binding events. Since GRHL2 physically interacts with PR, ChIP-seq could potentially capture indirect binding of GRHL2 at PR-bound sites, and vice versa. By contrast, CUT&RUN primarily captures direct DNA-protein interactions, offering a more specific binding profile. Thus, while the number of CUT&RUN binding sites is much smaller than previously reported by ChIP-seq, we are confident that they represent true, direct binding events.
We would also like to emphasize that the model presented in figure 6 does not represent a generic or random gene, but rather a specific gene that is co-regulated by both GRHL2 and PR. In this specific case, regulation is proposed to occur via looping interactions from either individual TF-bound sites (e.g., PR-only or GRHL2-only) or shared GRHL2/PR sites. We do not propose that only shared sites are functionally relevant, nor do we assume that GRHL2 and PR must both be directly bound to DNA at these shared sites. Therefore, overlapping sites identified by ChIP-seq-potentially reflecting indirect binding events-could indeed be missed by CUT&RUN, yet still contribute to gene regulation. To clarify this, we have revised the main text (line 331-334) and the legend of Figure 6 to explicitly state that the model refers to a gene with established co-regulation by both GRHL2 and PR.
R1.6 Gene expression analyses (Figure 4) The RNA-seq analysis after 24 hours of hormone treatment likely captures indirect or secondary effects rather than the direct PR-GRHL2 regulatory program. Including earlier time points (e.g., 4-hour induction) in the analysis would better capture primary transcriptional responses. The criteria used to define PR-GRHL2 co-regulated genes are not convincing and may not reflect the regulatory interactions proposed in the model. Strong basal expression changes in GRHL2-depleted cells suggest that much of the transcriptional response is PR-independent, conflicting with the model (Figure 6). A more straightforward approach would be to define hormone-regulated genes in shControl cells and then examine their response in GRHL2-depleted cells. Finally, integrating chromatin accessibility and histone modification datasets (e.g., ATAC-seq, H3K27ac ChIP-seq) would help establish whether PR-GRHL2-bound regions correspond to active enhancers, providing stronger functional support for the proposed regulatory model.
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out. We now recognize that our criteria for selecting PR/GRHL2 co-regulated genes were not clearly described. To address this, we have revised our approach as per the reviewer's suggestion: we first identified early and sustained PR target genes based on their response at 4 and 24 hours of induction and subsequently overlaid this list with the gene expression changes observed in GRHL2-depleted cells. This revised approach reduced the amount of PR-responsive, GRHL2 regulated target genes from 549 to 298 (46% reduction). We consequently updated all following analyses, resulting in revised figures 4 and 5 and supplementary figures 2,3 and 4. As a result of this revised approach, the number of genes that are transcriptionally regulated by GRHL2 and PR (RNAseq data) that also harbor a PR loop anchor at or near their TSS after 30 minutes of progesterone stimulation (PR HiChIP data) dropped from 114 to 79 (30% reduction). We thank the reviewer for suggesting this more straightforward approach and want to emphasize that our overall conclusions remain unaltered.
As above in our response to R1.3, we want to emphasize that the model presented in figure 6 does not depict a generic or randomly chosen gene, but a gene that is specifically co-regulated by both GRHL2 and PR. We also want to emphasize that the majority of GRHL2's transcriptional activity is PR-independent. This is consistent with the limited fraction of GRHL2 that co-immunoprecipitated with PR (Figure 1D), and with the well-established roles of GRHL2 beyond steroid receptor signaling. In fact, the overall importance of GRHL2 for cell viability in T47D(S) cells is underscored by our inability to generate a full knockout (multiple failed attempts of CRISPR/Cas mediated GRHL2 deletion in T47D(S) and MCF7 cells), and by the strong selection we observed against high-level GRHL2 knockdown using shRNA.
As for the reviewer's suggestion to assess whether GRHL2/PR co-bound regions correspond to active enhancers by integrating H3K27ac and ATAC-seq data: We have re-analyzed publicly available H3K27ac and ATAC-seq datasets from T47D cells (references 42 and 43). These analyses are now added to figure 2 (F and G). The H3K27Ac profile suggests that GRHL2-PR overlapping sites indeed correspond to more active enhancers (Figure 2F), with a proposed role for GRHL2 since siGRHL2 affects the accessibility of these sites (Figure 2G).
Minor comments Page 19: The statement that "PR and GRHL2 trigger extensive chromatin reorganization" is not experimentally supported. ATAC-seq would be an appropriate method to test this directly.
We agree with the reviewer and have removed this sentence, as it does not contribute meaningfully to the flow of the manuscript.
Prior literature on GRHL2 as a steroid receptor co-regulator should be discussed more thoroughly.
We now added additional literature on GRHL2 as a steroid hormone receptor co-regulator in the discussion (line 397-401) and we cite the papers suggested by R1 in R1.1 (references 25 and 54).
Reviewer #1 (Significance (Required)):
The identification of novel PR co-regulators is an important objective, as the mechanistic basis of PR signaling in breast cancer remains incompletely understood. The main strength of this study lies in highlighting GRHL2 as a factor influencing PR genomic binding and transcriptional regulation, thereby expanding the repertoire of regulators implicated in PR biology.
That said, the novelty is limited, given the established roles of GRHL2 in ER and AR regulation. Mechanistic insight is underdeveloped, and the reliance on an engineered T47DS model with supra-physiological PR levels reduces the general impact. Without validation in physiologically relevant breast cancer models and clearer separation of direct versus indirect effects, the overall advance remains modest.
The manuscript will be of interest to a specialized audience in the fields of nuclear receptor signaling, breast cancer genomics, and transcriptional regulation. Broader appeal, including translational or clinical relevance, is limited in its current form.
We have addressed all of these points in our response above and agree that with our implemented changes, this study should reach (and appeal to) an audience interested in transcriptional regulation, chromatin biology, hormone receptor signaling and breast cancer.
Reviewer #2 (Evidence, reproducibility and clarity (Required)):
The authors present a study investigating the role of GRHL2 in hormone receptor signaling. Previous research has primarily focused on GRHL2 interaction with estrogen receptor (ER) and androgen receptor (AR). In breast cancer, GRHL2 has been extensively studied in relation to ER, while its potential involvement with the progesterone receptor (PR) remains largely unexplored. This is the rationale of this study to investigate the relation between PR and GRHL2. The authors demonstrate an interaction between GRHL2 and PR and further explore this relationship at the level of genomic binding sites. They also perform GRHL2 knockdown experiments to identify target genes and link these transcriptional changes back to GRHL2-PR chromatin occupancy. However, several conceptual and technical aspects of the study require clarification to fully support the authors' conclusions.
R2.1 Given the high sequence similarity among GRHL family members, this raises questions about the specificity of the antibody used for GRHL2 RIME. The authors should address whether the antibody cross-reacts with GRHL1 or GRHL3. For example, GRHL1 shows a higher log fold change than GRHL2 in the RIME data.
Indeed, GRHL1, GRHL2, and GRHL3 are structurally related. They share a similar domain organization and are all {plus minus}70kDa in size. Sequence similarity is primarily confined to the DNA-binding domain, with GRHL2 and GRHL3 showing 81% similarity in this region, and GRHL1 showing 63% similarity to GRHL2/3 (Ming, Nucleic Acids Res 2018).
The antibody used, sourced from the Human Protein Atlas, is widely used in the field. It targets an epitope within the transactivation domain (TAD) of GRHL2-a region with relatively low sequence similarity to the corresponding domains in GRHL1 and GRHL3.
We assessed the specificity of the antibody using western blotting (Supplementary Figure 2A) in T47DS wild-type and GRHL2 knockdown cells. As expected, GRHL2 protein levels were reduced in the knockdown cells providing convincing evidence that the antibody recognizes GRHL2. The remaining signal in shGRHL2 knockdown cells could either be due to remaining GRHL2 protein or due to the antibody detecting GRHL1/3. Furthermore, the observed high log-fold enrichment of GRHL1 in our RIME may reflect known heterodimer formation between GRHL1 and GRHL2, rather dan antibody cross-reactivity. As such, we cannot formally rule out cross-reactivity and have mentioned this in the limitations section (line 497-501).
R2.2 In addition, in RIME experiments, one would typically expect the bait protein to be among the most highly enriched proteins compared to control samples. If this is not the case, it raises questions about the efficiency of the pulldown, antibody specificity, or potential technical issues. The authors should comment on the enrichment level of the bait protein in their data to reassure readers about the quality of the experiment.
We agree with the reviewer that this information is crucial for assessing the quality of the experiment. We have therefore added the enrichment levels (log₂ fold change of IgG control over pulldown) to the methods section (line 592).
As the reviewer notes, GRHL2 was not among the top enriched proteins in our dataset. This is due to unexpectedly high background binding of GRHL2 to the IgG control antibody/beads, for which we currently have no explanation. As a result, although we detected many unique GRHL2 peptides, observed high sequence coverage (>70%), and GRHL2 ranked among the highest in both iBAQ and LFQ values, its relative enrichment was reduced due to the elevated background. During our RIME optimization, Coomassie blue staining of input and IP samples revealed a band at the expected molecular weight of GRHL2 in the pull down samples that was absent in the IgG control (see figure 1 for the reviewer below, 4 right lanes), supporting the conclusion that GRHL2 is specifically enriched in our GRHL2 RIME samples. Combined with enrichment of some of the expected interacting proteins (e.g. KMT2C and KMT2D), we are convinced that the experiment of sufficient quality to support our conclusions.
Figure 1 for reviewer: Coomassie blue staining of input and IP GRHL2 and IgG RIME samples. NT = non-treated, T = treated.
R2.3 The authors report log2 fold changes calculated using iBAQ values for the bait versus IgG control pulldown. While iBAQ provides an estimate of protein abundance within samples, it is not specifically designed for quantitative comparison between samples without appropriate normalization. It would be helpful to clarify the normalization strategy applied and consider using LFQ intensities.
We understand the reviewer's concern. Due to the high background observed in the IgG control sample (see R2.2), the LFQ-based normalization did not accurately reflect the enrichment of GRHL2, which was clearly supported by other parameters such as the number of unique peptides (see rebuttal Table 1). After discussions with our Mass Spectrometry facility, we decided to consider the iBAQ values-which reflect the absolute protein abundance within each sample-as a valid and informative measure of enrichment. In the context of elevated background levels, iBAQ provides an alternative and reliable metric for assessing protein enrichment and was therefore used for our interactor analysis.
Unique peptides
IBAQ GRHL2
IBAQ IgG
LFQ GRHL2
LFQ IgG
GRHL2
52
1753400.00
155355.67
5948666.67
3085700.00
GRHL1
23
56988.33
199.03
334373.33
847.23
*Table 1. Unique peptide, IBAQ and LFQ values of the GRHL2 and IgG pulldowns for GRHL2 and GRHL1 *
R2.4 Other studies have reported PR RIME, which could be a valuable source to investigate whether GRHL proteins were detected.
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out. We are aware of the PR RIME, generated by Mohammed et al., which we refer to in the discussion (lines 390-391). This study indeed identified GRHL2 as a PR-interacting protein in MCF7 and T47D cells. Although they do not mention this interaction in the text, the interaction is clearly indicated in one of the figures from their paper, which supports our findings. To our knowledge, no other PR RIME datasets in MCF7 or T47D cells have been published to date.
R2.5 In line 137, the term "protein score" is mentioned. Could the authors please clarify what this means and how it was calculated.
We agree that this point was not clearly explained in the original text. The scores presented reflect the MaxQuant protein identification confidence, specifically the sum of peptide-level scores (from Andromeda), which indicates the relative confidence in protein detection. We have now added this clarification to line 137 and to the legend of Figure 1.
R2.6 In line 140-141. The fact that GRHL2 interacts with chromatin remodelers does not by itself prove that GRHL2 acts as a pioneer factor or chromatin modulator. Demonstrating pioneer function typically requires direct evidence of chromatin opening or binding to closed chromatin regions (e.g., ATAC-seq, nucleosome occupancy assays). I recommend revising this statement or providing supporting evidence.
We agree that the fact that GRHL2 interacts with chromatin remodelers does not by itself prove that GRHL2 acts as a pioneer factor or chromatin modulator. However, a previous study (Jacobs et al, Nature genetics, 2018) has shown directly that the GRHL family members (including GRHL2) have pioneering function and regulate the accessibility of enhancers. We adapted line 140-141 to state this more clearly. In addition, our newly added data in Figure 2G also support the fact that GRHL2 has a role in regulating chromatin accessibility in T47D cells.
R2.7 The pulldown Western blot lacks an IgG control in panel D.
This is correct. As the co-IP in Figure 1D served as a validation of the RIME and was specifically aimed at determining the effect of hormone treatment on the observed PR/GRHL2 interaction, we did not perform this control given the scale of the experiment. However, during RIME optimization, we performed GRHL2 staining of the IgG controls by western blot, shown in figure 2 for the reviewer below. As stated above, some background GRHL2 signal was observed in the IgG samples, but a clear enrichment is seen in the GRHL2 IP.
Taken together, we believe that the well-controlled RIME, combined with the co-IP presented, provides strong evidence that the observed signal reflects a genuine GRHL-PR interaction.
Figure 2 for reviewer: WB of input and IP GRHL2 and IgG RIME samples stained for GRHL2. NT = non-treated, T = treated
R2.8 Depending on the journal and target audience, it may be helpful to briefly explain what R5020 is at its first mention (line 146).
Thank you. We have adapted this accordingly.
R2.9 The authors state that three technical replicates were performed for each experimental condition. It would be helpful to clarify the expected level of overlap between biological replicates of RIME experiments. This clarification is necessary, especially given the focus on uniquely enriched proteins in untreated versus treated cells, and the observation that some identified proteins in specific conditions are not chromatin-associated. Replicates or validations would strengthen the findings.
We use the term technical rather than biological replicates because for cell lines, defining true biological replicates is challenging, as most variability arises from experimental rather than biological differences. To introduce some variation, we split our T47DS cells into three parallel dishes 5 days prior to starting the treatment. We purposely did this, to minimize to minimize the likelihood that proteins identified as uniquely enriched are artifacts. Each of the three technical replicates comes from one of these three parallel splits (so equal passage numbers but propagated in parallel dishes for 5 days before the start of the experiment).
To generate the three technical replicates for our RIME, we plated cells from the parallel grown splits. Treatments for the three replicates were performed per replicate. Samples were crosslinked, harvested and lysed for subsequent RIME analysis, the three replicates were processed in parallel, for technical and logistical reasons. To clarify the experimental setup, we have updated the methods section accordingly (lines 566-568).
As for the detection of non-chromatin-associated proteins: We cannot rule out that these are artifacts, as they may arise from residual cytosolic lysate during nuclear extraction. Alternatively, they could reflect a more dynamic subcellular localization of these proteins than currently annotated or appreciated.
R2.10 The volcano plot for the RIME experiment appears to show three distinct clusters of proteins on the right, which is unusual for this type of analysis. The presence of these apparent groupings may suggest an artifact from the data processing, such as imputation. Can the authors clarify the origin of these groupings? If it is due to imputation or missing values, I recommend applying a stricter threshold, such as requiring detection in all three replicates (3/3) to improve the robustness of the enrichment analysis and increase confidence in the identified interactors.
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out. As suggested, we re-evaluated the imputation and applied a stricter threshold, requiring detection in all three replicates. Indeed, the separate clusters were due to missing values, therefore we now revised the imputation method by imputing values based on the normal distribution. Using this revised analysis, we identify 2352 GRHL2 interactors instead of 1140, but the number of interacting proteins annotated as transcription factors or chromatin-associated/modifying proteins was still 103. Figure 1B, 1E, and Supplementary Figure 4A have been updated accordingly. We also revised the methods section to reflect this change. We think this suggestion has improved our analysis of the data and we thank the reviewer for pointing this out.
R2.11 The statement that "PR and GRHL2 frequently overlap" may be overstated given that only ~700 overlapping sites are reported (cut&run).
We have replaced "frequently overlap" by "can overlap" (line 229-230).
R2.12 The model in Figure 6 suggests limited chromatin occupancy of PR and GRHL2 in hormone-depleted conditions, consistent with the known requirement of ligand for stable PR-DNA binding. However, Figure 1 shows no major difference in GRHL2-PR interaction between untreated and hormone-treated cells. This raises questions about where and how this interaction occurs in the absence of hormone. Since PR binding to chromatin is typically minimal without ligand, can the authors clarify this given that RIME data reflect chromatin-bound interactions.
Indeed, the model in figure 6 suggests limited chromatin occupancy of PR and GRHL2 under hormone-depleted conditions. It is, however, important to note that the locus shown represents a gene regulated by both PR and GRHL2 - and not just any gene. We recognize that this was not sufficiently clear in the original version, and we have now clarified this in both the main text (line 331-334) and the figure legend.
We propose that PR and GRHL2 bind or become enriched at enhancer sites associated with their target genes upon ligand stimulation. This is consistent with the known requirement of ligand for stable PR-DNA binding and with our observation that PR/GRHL2 overlapping peaks are detected only in the ligand-treated condition of the CUT&RUN experiment. Given the broader role of GRHL2, it also binds chromatin independently of progesterone and the progesterone receptor, which is why we included-but did not focus on-GRHL2-only binding events in our model.
We would also like to clarify that, although RIME includes a nuclear enrichment step that enriches for chromatin-associated proteins, the pulldown is performed on nuclear lysates. Therefore, it captures both chromatin-bound protein complexes and freely soluble nuclear complexes, which unfortunately cannot be distinguished. GRHL2 is well established as a nuclear protein (Zeng et al., Cancers 2024; Riethdorf et al., International Journal of Cancer 2015), and although PR is classically described as translocating to the nucleus upon hormone stimulation, several studies-including our own-have shown that PR is continuously present in the nucleus (Aarts et al., J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2023; Frigo et al., Essays Biochem. 2021).
We therefore propose that PR and GRHL2 may already interact in the nucleus without directly binding to chromatin. Given our observation that GRHL2 binding sites on the chromatin are redistributed upon R5020 mediated signaling activation, we hypothesize that such pre-formed PR-GRHL2 nuclear complexes may assist the rapid recruitment of GRHL2 to progesterone-responsive chromatin regions.
We have expanded the discussion to include a dedicated section addressing this point (line 376-388).
R2.13 It would be of interest to assess the overlap between the proteins identified in the RIME experiment and the motif analysis results.
In the discussion section of our original manuscript, we highlighted some overlapping proteins in the RIME and motif analysis, including STAT6 and FOXA1. However, we had not yet systematically analyzed overlap in both analyses. To address this, we now compared all enriched motifs (so not only the top 5 as displayed in our figures) under GRHL2, PR, and GRHL2/PR shared sites from both the CUT&RUN and ChIP-seq datasets with the proteins identified as GRHL2 interactors in our RIME. Although we identified numerous GRHL2-associated proteins, relatively few of them were transcription factors whose binding motifs were also enriched under GRHL2 peaks.
In our revised manuscript we have added a section in the discussion highlighting our systematic overlap of the results of our RIME experiment and the motif enrichment of the ChIP-seq and CUT&RUN analysis (line 415-436).
R2.14 The authors chose CUT&RUN to assess chromatin binding of PR and GRHL2. Given that RIME is also based on chromatin immunoprecipitation - ChIP protocol, it would be helpful to clarify why CUT&RUN was selected over ChIP-seq for the DNA-binding assays. What is the overlap with published data?
As also mentioned in our response to R1.3 and R1.5, we deliberately chose the CUT&RUN approach to minimize artifacts introduced by crosslinking and sonication, thereby reducing background and allowing the identification of high-confidence, direct DNA-binding events. Since GRHL2 physically interacts with PR, ChIP-seq could potentially capture indirect binding of GRHL2 at PR-bound sites (and vice versa). In contrast, CUT&RUN primarily detects direct DNA-protein interactions, providing a more specific and accurate binding profile. Additionally, CUT&RUN serves as an independent validation method for data obtained using ChIP-like protocols.
Since CUT&RUN, similar to ChIP, can show limited reproducibility (Nordin et al., Nucleic Acids Research, 2024), and to our knowledge few PR CUT&RUN and no GRHL2 CUT&RUN datasets are currently available, it is challenging to directly compare our data with published datasets. Nevertheless, studies performing PR or ER CUT&RUN (Gillis et al., Cancer Research, 2024; Reese et al., Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2022) report a comparable number of peaks-in the same range of thousands-as observed in our data. This suggests that a single CUT&RUN experiment in general may detect fewer events than a single ChIP-seq experiment, but that the peaks that are found are likely to reflect direct binding events.
Reviewer #2 (Significance (Required)):
General Assessment: This study investigates the role of the transcription factor GRHL2 in modulating PR function, using RIME and CUT&RUN to explore protein-protein and protein-chromatin interactions. GRHL2 have been implicated in epithelial biology and transcriptional regulation and interaction with steroid hormone receptors has been reported. This study extends the field by showing a functional link between GRHL2 and PR, which has implications for understanding hormone-dependent gene regulation.
The research will primarily interest a specialized audience in transcriptional regulation, chromatin biology, and hormone receptor signaling.
Key words for this reviewer: chromatin biology, transcription factor function, epigenomics, and proteomics.
We agree that with our implemented changes, this study should reach (and appeal to) an audience interested in transcriptional regulation, chromatin biology, hormone receptor signaling and breast cancer.
Reviewer #3 (Evidence, reproducibility and clarity (Required)):
This study explores the important transcriptional coordination role of Grainyhead-like 2 (GRHL2) on the transcriptional regulatory function of progesterone receptor (PR). In this paper, the authors start with their recruitment characteristics, take into account their regulatory effects on downstream genes and their effects on the occurrence and development of breast cancer, and further clarify the coordination between them in three-dimensional space. The interaction between GRHL2 and PR, and the subsequent important influence on the co-regulated genes by GRHL2 and PR are analyzed. The overall framework of this study is mainly by RNA seq and CUT-TAG analysis, the molecular mechanism underlying the association between GRHL2 and PR and regulation function of two proteins in breast cancer is not clearly clarified. Some details need to be further improved:
Major comments: R3.1 For Fig.1D, the molecular weight of each protein should be marked in the diagram, and the expression of GRHL2 in the input group should be supplemented.
We apologize for not including molecular weights in our initial submission. We are not entirely clear what the reviewer means with their statement that "the expression of GRHL2 in the input group should be supplemented". The blot depicted in Figure 1D shows both the input signal and the IP. For the reviewer's information, the full Western blot is depicted below.
Figure 3 for reviewer: Full WBs of input and IP GRHL2 samples stained for GRHL2 or PR. NT = non-treated, T = treated
R3.2 In Fig.2B and Fig 5C, it should be describe well whether GRHL2 recruitment is in the absence or presence of R5020? How about the co-occupancy of PR and GRHL2 region, Promoter or enhancer region? It would be better to show histone marks such as H3K27ac and H3K4me1 to annotate the enhancer region.
As also stated in our response to R1.3, we acknowledge that the ChIP-seq experiments cannot definitively determine whether GRHL2 and PR co-occupy genomic regions under ligand-stimulated conditions, since the GRHL2 dataset was generated in the absence of progesterone stimulation (as indicated in lines 167-169). To clarify this, we have now specified this detail in the legend of figure 2 by noting "untreated GRHL2 ChIP." To directly assess GRHL2 chromatin binding under progesterone-stimulated conditions, we performed CUT&RUN experiments for both GRHL2 and PR under untreated and R5020-treated conditions. These experiments revealed a subset of overlapping PR and GRHL2 binding sites (approximately 5% of all identified PR peaks.
In our original manuscript, we performed genomic annotation of the GRHL2, PR, and GRHL2/PR overlapping peaks (Figure 2E) and found that most of these sites were located in intergenic regions, where enhancers are typically found, with ~20% located in promoter regions. We appreciate the reviewer's suggestion to further overlap the ChIP-seq peaks with histone marks such as H3K27ac and H3K4me1. We have now incorporated publicly available ATAC-seq and H3K27ac ChIP datasets in our revised manuscript (as also suggested by Reviewer 1) and find that shared GRHL2/PR sites are indeed located in active enhancer regions marked by H3K27ac (see Figure 2F). Additionally, as expected, we find that GRHL2/PR overlapping sites are enriched at open chromatin (Figure 2G).
R3.3 What is the biological function analysis by KEGG or GO analysis for the overlapping genes from VN plots of RNA-seq with CUT-TAG peaks. The genes co-regulated by GRH2L and PR are further determined.
For us, it is not entirely clear what reviewer 3 is asking here, but we can explain the following: as it is challenging to integrate HiChIP with CUT&RUN, due to the fundamentally different nature of the two techniques, we chose not to directly assign genes to CUT&RUN peaks. However, we did carefully link the GRHL2, PR, and GRHL2/PR ChIP-seq peaks to their target genes by integrating chromatin looping data from a PR HiChIP analysis. The result from this analysis is depicted in Figure 4B.
As suggested by this reviewer, we also performed a GO-term analysis on the 79 genes that are regulated by both GRHL2 and PR (we now have 79 genes after the re-analysis as suggested in R1.6). The corresponding results are provided for the reviewer in figure 3 of this rebuttal (below). As this additional analysis does not provide further biological insight beyond what is already presented in Figure 4C, we decided to not include this figure in the manuscript.
Figure 4 for reviewer: GO-term analysis on the 79 GRHL2-PR co-regulated genes that are transcriptionally regulated by GRHL2 and PR and that also harbor a PR HiChIP loop anchor at or near their TSS
R3.4 Western blotting should be performed to determine the protein levels of downstream genes co-regulated genes by GRH2L and PR in the absence or presence of R5020.
We agree that determining the response of co-regulated is important. Therefore, in Figure 4D, we present three representative examples of genes that are directly co-regulated by GRHL2 and PR-specifically, genes that are differentially expressed after 4 hours of R5020 exposure. Although protein levels of the targets are of functional importance, GRHL2 and PR are of transcription factors whose immediate effects are primarily exerted at the level of gene transcription. Therefore, in our opinion, changes in mRNA abundance provide the most direct and mechanistically relevant readout of their regulatory activity.
R3.5 The author mentioned that this study positions that GRHL2 acts as a crucial modulator of steroid hormone receptor function, while the authors do not provide the evidences that how does GRHL2 regulate PR-mediated transactivation, and how about these two proteins subcellular distribution in breast cancer cells.
We agree that while our RNA-seq data demonstrate that GRHL2 modulates the expression of PR target genes, and our CUT&RUN experiments show that GRHL2 chromatin binding is reshaped upon R5020 exposure, we have not yet further dissected the molecular mechanism by which GRHL2 functions as a PR co-regulator.
As also mentioned in our response to R1.2, we did consider several follow-up experiments to address this, including PR CUT&RUN in GRHL2 knockdown cells, CUT&RUN for known co-activators such as KMT2C/D and P300, as well as functional studies involving GRHL2 TAD and DBD mutants. However, due to technical and logistical challenges, we were unable to carry out these experiments within the timeframe of this study.
That said, we fully recognize that such approaches would provide deeper mechanistic insight into the interplay between PR and GRHL2. We have therefore explicitly acknowledged this limitation in our limitations of the study section (lines 502-507) and consider it an important avenue for future investigation.
Regarding the subcellular distribution in breast cancer cells: As also mentioned in our response to R2.12, GRHL2 is well established as a nuclear protein (Zeng et al., Cancers 2024; Riethdorf et al., International Journal of Cancer 2015), and although PR is classically described as translocating to the nucleus upon hormone stimulation, several studies-including our own-have shown that PR is continuously present in the nucleus (Aarts et al., J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2023; Frigo et al., Essays Biochem. 2021). Thus, both proteins mostly reside in the nucleus in breast (cancer) cells both in the absence and presence of hormone stimulation, but dynamic subcellular shuttling is likely to occur.
Minor comments: Please describe in more detail the relationship between PR and GRHL2 binding independent of the hormone in the discussion section.
As also mentioned in our response to R2.12, we have expanded the discussion to include a dedicated section addressing this point (lines 376-388).
Reviewer #3 (Significance (Required)):
Advance: Compare the study to existing published knowledge, it fills a gap. The authors provide RNA seq and CUT-TAG sequence analysis to show the recruitment of GRHL2 and PR and the co-regulated genes in the absence or presence of progesterone.
Audience: breast surgery will be interested, and the audiences will cover clinical and basic research.
My expertise is focused on the epigenetic modulation of steroid hormone receptors in the related cancers, such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, and endometrial carcinoma.
We agree that with our implemented changes, this study should reach (and appeal to) an audience interested in transcriptional regulation, chromatin biology, hormone receptor signaling and breast cancer.
Note: This preprint has been reviewed by subject experts for Review Commons. Content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
This study explores the important transcriptional coordination role of Grainyhead-like 2 (GRHL2) on the transcriptional regulatory function of progesterone receptor (PR). In this paper, the authors start with their recruitment characteristics, take into account their regulatory effects on downstream genes and their effects on the occurrence and development of breast cancer, and further clarify the coordination between them in three-dimensional space. The interaction between GRHL2 and PR, and the subsequent important influence on the co-regulated genes by GRHL2 and PR are analyzed. The overall framework of this study is mainly by RNA seq and CUT-TAG analysis, the molecular mechanism underlying the association between GRHL2 and PR and regulation function of two proteins in breast cancer is not clearly clarified. Some details need to be further improved:
Major comments:
Minor comments:
Please describe in more detail the relationship between PR and GRHL2 binding independent of the hormone in the discussion section.
Advance: Compare the study to existing published knowledge, it fills a gap. The authors provide RNA seq and CUT-TAG sequence analysis to show the recruitment of GRHL2 and PR and the co-regulated genes in the absence or presence of progesterone.
Audience: breast surgery will be interested, and the audiences will cover clinical and basic research.
My expertise is focused on the epigenetic modulation of steroid hormone receptors in the related cancers, such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, and endometrial carcinoma.
Note: This preprint has been reviewed by subject experts for Review Commons. Content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
The authors present a study investigating the role of GRHL2 in hormone receptor signaling. Previous research has primarily focused on GRHL2 interaction with estrogen receptor (ER) and androgen receptor (AR). In breast cancer, GRHL2 has been extensively studied in relation to ER, while its potential involvement with the progesterone receptor (PR) remains largely unexplored. This is the rational of this study to investigate the relation between PR and GRHL2. The authors demonstrate an interaction between GRHL2 and PR and further explore this relationship at the level of genomic binding sites. They also perform GRHL2 knockdown experiments to identify target genes and link these transcriptional changes back to GRHL2-PR chromatin occupancy. However, several conceptual and technical aspects of the study require clarification to fully support the authors' conclusions.
General Assessment:
This study investigates the role of the transcription factor GRHL2 in modulating PR function, using RIME and CUT&RUN to explore protein-protein and protein-chromatin interactions. GRHL2 have been implicated in epithelial biology and transcriptional regulation and interaction with steroid hormone receptors has been reported. This study extends the field by showing a functional link between GRHL2 and PR, which has implications for understanding hormone-dependent gene regulation.
The research will primarily interest a specialized audience in transcriptional regulation, chromatin biology, and hormone receptor signaling.
Key words for this reviewer: chromatin biology, transcription factor function, epigenomics, and proteomics.
Note: This preprint has been reviewed by subject experts for Review Commons. Content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
Summary
The manuscript by Aarts et al. explores the role of GRHL2 as a regulator of the progesterone receptor (PR) in breast cancer cells. The authors show that GRHL2 and PR interact in a hormone-independent manner and, based on genomic analyses, propose that they co-regulate target genes via chromatin looping. To support this model, the study integrates both newly generated and previously published datasets, including ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN, RNA-seq, and chromatin interaction assays, in breast cancer cell models (T47DS and T47D).
Major comments:
Minor comments
Page 19: The statement that "PR and GRHL2 trigger extensive chromatin reorganization" is not experimentally supported. ATAC-seq would be an appropriate method to test this directly.
Prior literature on GRHL2 as a steroid receptor co-regulator should be discussed more thoroughly.
The identification of novel PR co-regulators is an important objective, as the mechanistic basis of PR signaling in breast cancer remains incompletely understood. The main strength of this study lies in highlighting GRHL2 as a factor influencing PR genomic binding and transcriptional regulation, thereby expanding the repertoire of regulators implicated in PR biology. That said, the novelty is limited, given the established roles of GRHL2 in ER and AR regulation. Mechanistic insight is underdeveloped, and the reliance on an engineered T47DS model with supra-physiological PR levels reduces the general impact. Without validation in physiologically relevant breast cancer models and clearer separation of direct versus indirect effects, the overall advance remains modest.
The manuscript will be of interest to a specialized audience in the fields of nuclear receptor signaling, breast cancer genomics, and transcriptional regulation. Broader appeal, including translational or clinical relevance, is limited in its current form.
Most of the time categorization process, discrimination process, dehumanization processes
for - genocide - preceded by 10 preliminary stages - 1. classification - 2. symbolization - 3. discrmination - 4. dehumanization - 5. organization - 6. polarization - 7. preparation - 8. persecution - 9. extermination - 10. denial
Analyse de l'Engagement Politique : Concepts, Paradoxes et Contexte
Ce document de synthèse analyse en profondeur les multiples facettes de l'engagement politique en s'appuyant sur les perspectives de la sociologie et de la science politique.
L'analyse révèle quatre axes majeurs.
Premièrement, une distinction conceptuelle fondamentale est établie entre la participation politique, qui inclut des actes peu coûteux comme le vote, et l'engagement, qui désigne des formes d'action plus intenses, publiques et risquées.
L'engagement se décline sur un continuum allant du simple sympathisant au militant permanent, avec des profils variés tels que les "militants par conscience" et les "bénéficiaires directs" de la lutte.
Deuxièmement, le document explore le paradoxe de l'action collective, tel que formulé par Mancur Olson.
Ce paradoxe explique pourquoi des individus rationnels peuvent s'abstenir de participer à une action collective même s'ils en partagent les objectifs, à cause de la tentation du "passager clandestin".
Les solutions à ce paradoxe résident dans les incitations sélectives et, de manière plus sociologique, dans les rétributions symboliques de l'engagement (reconnaissance, plaisir militant, fidélité à ses valeurs) théorisées par Daniel Gaxie.
Troisièmement, l'analyse aborde l'importance du contexte à travers la notion de Structure des Opportunités Politiques (SOP).
Ce concept macro-analytique soutient que le succès et les formes d'un mouvement social (pacifiques ou disruptives) dépendent de l'ouverture ou de la fermeture du système politique.
Bien qu'utile pour comprendre des dynamiques historiques comme le mouvement des droits civiques aux États-Unis, ce concept fait l'objet de critiques importantes pour son statisme et sa vision simplifiée des interactions entre l'État et les mouvements sociaux.
Enfin, le document souligne le rôle crucial des variables socio-démographiques et des socialisations individuelles.
L'engagement est fortement corrélé au capital culturel et à la "disponibilité biographique".
L'analyse met en lumière l'importance des émotions, notamment le "choc moral", en précisant que la capacité à ressentir une indignation face à une situation est elle-même socialement construite.
L'étude de cas du "Freedom Summer" de 1964 démontre de manière saisissante que l'engagement intense a des conséquences biographiques profondes et durables sur la trajectoire de vie des militants.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Une première perplexité soulevée par l'analyse concerne la définition même de l'engagement politique.
Le terme, tel qu'il est parfois utilisé, tend à regrouper toutes les formes d'activité politique, y compris les moins exigeantes.
Cependant, la recherche en sociologie politique opère une distinction cruciale entre la participation et l'engagement.
La participation est la catégorie la plus large, englobant toutes les formes de contribution aux affaires de la cité.
Le vote, l'inscription sur les listes électorales ou la réponse à un sondage sont des formes minimales et peu coûteuses de participation.
Elles sont souvent individuelles, secrètes (comme le vote dans l'isoloir) et n'engagent l'individu que de manière très limitée.
L'engagement, en revanche, désigne des formes de participation plus intenses, exigeantes et coûteuses en temps, en énergie et parfois en ressources.
Il se caractérise par deux dimensions clés :
• L'exposition publique : S'engager, c'est s'exposer publiquement, que ce soit en manifestant, en signant une pétition nominative ou en prenant la parole pour une cause.
• La prise de risque : Cette exposition publique peut entraîner des rétorsions, des controverses, des sanctions professionnelles ou même des risques physiques (violences policières, par exemple).
La figure de l'intellectuel engagé, comme les signataires du Manifeste des 121 contre la guerre d'Algérie, illustre cette prise de risque.
L'engagement s'inscrit donc dans une démarche où l'individu accepte un coût personnel potentiellement élevé en échange de la défense d'une cause collective.
L'engagement peut être vu comme un continuum avec différents degrés d'implication.
• Le sympathisant : Il soutient une cause ou une organisation de l'extérieur, sans adhésion formelle.
Sa participation est souvent ponctuelle, comme le fait de se joindre à une manifestation pour montrer son soutien.
• L'adhérent : Il formalise son soutien en prenant sa carte dans un parti, un syndicat ou une association.
Cet acte implique souvent une contribution financière (cotisation) et marque une identification plus forte. L'adhérent peut dire "nous" en parlant de l'organisation, mais son implication active peut rester limitée.
• Le militant : Il est véritablement partie prenante des activités de l'organisation.
Il consacre du temps et de l'énergie de manière régulière, défend activement les positions du groupe, participe aux actions et s'identifie fortement à ses couleurs.
Au sein même du militantisme, les auteurs McCarthy et Zald distinguent plusieurs statuts au sein des "organisations de mouvement social".
Statut
Description
Volontaires
Militants bénévoles qui participent sur leur temps libre, sans rémunération. Ils constituent la base de nombreuses organisations.
Permanents
Militants salariés par l'organisation pour assurer son fonctionnement quotidien.
Leur statut peut parfois créer des tensions avec les bénévoles.
Cadres (Porte-parole)
Personnes qui incarnent et représentent l'organisation publiquement (président, secrétaire général).
Ils négocient avec les autorités et s'expriment dans les médias.
Leur sélection et leur légitimité sont des enjeux cruciaux au sein des collectifs.
Une autre distinction importante est celle proposée par McCarthy et Zald entre :
• Les bénéficiaires : Ce sont les personnes directement concernées par la lutte et qui en retireront un bénéfice personnel et immédiat en cas de succès (ex: les sans-papiers luttant pour leur régularisation).
• Les militants par conscience : Ce sont des personnes qui soutiennent la cause par conviction, sans attendre de bénéfice direct pour leur situation personnelle (ex: des citoyens français soutenant les sans-papiers).
Cette distinction est essentielle car les logiques d'engagement et les objectifs peuvent différer entre ces deux groupes, créant parfois des tensions au sein d'un même mouvement.
La thèse d'un déclin de l'engagement, souvent associée à la baisse du nombre d'adhérents dans les partis politiques, est nuancée.
Une hypothèse plus fructueuse est que les partis politiques dominants n'ont plus besoin de militants comme par le passé.
Transformés en "machines électorales" peuplées de professionnels de la politique, ils peuvent externaliser des tâches autrefois militantes (collage d'affiches, communication) à des entreprises spécialisées.
De plus, des mécanismes comme les primaires ouvertes ont réduit le rôle des militants dans la sélection des candidats.
Ce phénomène n'entraîne pas la fin de l'envie de s'engager, mais plutôt un report de l'engagement vers d'autres espaces, comme le secteur associatif ou les mouvements sociaux, perçus comme plus concrets et désintéressés par des militants déçus de la vie partisane.
L'un des défis théoriques majeurs pour comprendre l'engagement est d'expliquer pourquoi des actions collectives émergent, alors même que la rationalité individuelle pourrait y faire obstacle.
L'économiste Mancur Olson, dans son ouvrage Logique de l'action collective (1965), a rompu avec les théories antérieures qui postulaient l'irrationalité des foules (Gustave Le Bon) ou expliquaient la révolte par des facteurs psychologiques comme la "frustration relative" (Ted Gurr). Olson part du postulat d'un acteur rationnel et calculateur.
Le paradoxe qu'il met en évidence est le suivant :
1. Une action collective vise à obtenir un bien collectif, c'est-à-dire un avantage qui profitera à tous les membres d'un groupe, qu'ils aient participé à l'action ou non (ex: une augmentation de salaire pour tous les employés d'une entreprise).
2. Participer à l'action a un coût individuel (ex: perte de salaire pendant une grève, temps consacré, risques encourus).
3. L'acteur rationnel sera donc tenté d'adopter la stratégie du "passager clandestin" (free rider) : ne pas payer le coût de l'action tout en espérant bénéficier de ses retombées si les autres se mobilisent.
Si tout le monde suit ce calcul, l'action collective n'a jamais lieu, même si elle serait bénéfique pour tous.
Pour Olson, la solution au paradoxe réside dans les incitations sélectives : des bénéfices (ou des coûts) qui s'appliquent uniquement à ceux qui participent (ou ne participent pas) à l'action.
• Incitations sélectives négatives (coûts) : Rendre la non-participation plus coûteuse que la participation. Exemples : la pression sociale, la stigmatisation des "jaunes" lors d'une grève, voire les menaces physiques d'un piquet de grève.
• Incitations sélectives positives (bénéfices) : Offrir des avantages individuels réservés aux participants.
Olson évoque même des "incitations sélectives érotiques" (le plaisir de rencontrer des gens, de nouer des relations).
Le politiste Daniel Gaxie a sociologisé cette approche en développant le concept de rétributions de l'engagement.
Ces gratifications, qui motivent et soutiennent le militantisme, peuvent être de plusieurs natures :
• Matérielles : Obtention d'un logement social, d'un emploi via le réseau de l'organisation.
• Symboliques : Acquisition de responsabilités, de notoriété, de reconnaissance.
Le fait de passer dans les médias ou d'être le porte-parole d'une lutte est une gratification symbolique puissante.
• Identitaires et morales : Le plaisir d'agir en conformité avec ses valeurs, de "pouvoir se regarder dans la glace".
• Affectives et sociales : Le plaisir de la sociabilité militante, de partager des moments forts avec des camarades, de se sentir membre d'un collectif.
Ces rétributions expliquent pourquoi des "militants par conscience" ne sont pas totalement désintéressés : ils trouvent un intérêt (au sens sociologique) dans leur engagement.
Cette analyse, couplée aux critiques d'Albert Hirschman (qui note que le coût et le bénéfice de l'action peuvent se confondre, comme la fierté tirée d'une lutte difficile), permet de dépasser la vision purement utilitariste d'Olson.
Si le modèle d'Olson se concentre sur l'individu (micro), l'approche par la Structure des Opportunités Politiques (SOP) se place à un niveau macro-structurel pour analyser l'influence du contexte politique sur les mouvements sociaux.
La SOP désigne l'ensemble des éléments du contexte politique qui facilitent ou entravent l'émergence et le succès d'un mouvement social.
Le travail de Doug McAdam sur le mouvement pour les droits civiques aux États-Unis est l'exemple fondateur.
McAdam montre que les organisations noires existaient déjà dans les années 1930 mais piétinaient.
Leur succès dans les années 1950-60 s'explique par une ouverture de la SOP, due à plusieurs facteurs :
• Économiques : La crise du coton dans le Sud et la migration des Noirs vers les industries du Nord.
• Sociaux : Une "libération cognitive" où les Noirs, découvrant un racisme moins institutionnalisé dans le Nord, réalisent que la ségrégation n'est pas une fatalité.
• Électoraux : La population noire devient un enjeu électoral pour le Parti Démocrate dans le Nord.
• Géopolitiques : En pleine Guerre Froide, la ségrégation raciale fragilise l'image des États-Unis face à l'URSS.
Cette ouverture a rendu le système politique plus réceptif aux revendications, permettant au mouvement d'obtenir des succès par des actions largement pacifiques.
Lorsque la SOP s'est refermée dans les années 1970 (arrivée de Nixon, répression du FBI), les formes de protestation se sont radicalisées (Black Power).
L'idée centrale est que la forme de la SOP influence directement les stratégies des mouvements :
• SOP ouverte (système réceptif, procédures de consultation, etc.) : favorise des actions pacifiques, la négociation et le lobbying.
• SOP fermée (système bloqué, centralisé, peu réceptif) : contraint les mouvements à utiliser des répertoires d'action plus perturbateurs et disruptifs pour se faire entendre.
L'exemple comparatif entre la France et la Suisse sur la question des OGM est parlant.
En Suisse, dotée de mécanismes de démocratie directe (votation), les anti-OGM ont pu obtenir des moratoires par des voies institutionnelles.
En France, système plus centralisé et fermé, ils ont dû recourir à des actions illégales (faucheurs volontaires) pour politiser l'enjeu.
Malgré son utilité, le concept de SOP a fait l'objet de nombreuses critiques :
• Ambigüité : La notion est souvent une "auberge espagnole" où l'on peut trouver a posteriori n'importe quel facteur contextuel pour expliquer un résultat.
• Statisme : L'approche tend à figer les systèmes politiques dans des typologies statiques (ouvert/fermé), négligeant la dynamique et les fluctuations.
• Oxymore conceptuel : James Jasper souligne la contradiction entre "structure" (stable, durable) et "opportunité" (fugace, subjectivement perçue).
• Vision simpliste : Le modèle postule une séparation étanche entre les "insiders" (système politique) et les "outsiders" (mouvements), alors que les frontières sont poreuses (des militants peuvent être au sein de l'État).
• Déterminisme univoque : Il suggère que le système politique détermine les mouvements, alors que les mouvements sociaux peuvent eux-mêmes transformer et contraindre le système politique.
En raison de ces limites, le concept de SOP est aujourd'hui moins utilisé dans la recherche, qui privilégie des approches plus dynamiques des interactions.
Au-delà des modèles théoriques, l'engagement dépend fortement de variables socio-démographiques et de processus de socialisation qui prédisposent, ou non, les individus à s'engager.
La recherche confirme de manière constante que l'engagement politique est socialement situé.
• Le capital culturel et scolaire : L'intérêt pour la politique et la compétence politique perçue sont fortement corrélés au niveau de diplôme.
Les individus les plus diplômés sont souvent ceux qui votent le plus, mais aussi ceux qui manifestent et signent le plus de pétitions.
• La disponibilité biographique : L'engagement intense est plus fréquent chez les jeunes (moins de contraintes familiales et professionnelles) et les "jeunes retraités" (plus de temps libre).
Les personnes en milieu de carrière avec des responsabilités familiales sont souvent moins disponibles pour un militantisme chronophage.
Contre l'image d'un acteur purement rationnel, la recherche réintègre la dimension émotionnelle de l'engagement.
Le choc moral, théorisé par James Jasper, désigne l'indignation ou le scandale ressenti face à une situation qui pousse à l'action.
Cependant, il est crucial d'expliquer sociologiquement ce choc moral : tout le monde n'est pas choqué par les mêmes situations.
La capacité à ressentir cette indignation dépend de la socialisation, des valeurs et des expériences passées de l'individu.
• Un individu socialisé dans un environnement pro-corrida ne ressentira pas le même choc moral devant une mise à mort qu'un militant de la cause animale.
• Les militants de Réseau Éducation Sans Frontières (RESF) sont souvent des personnes qui ont elles-mêmes bénéficié de la promotion sociale par l'école ; leur attachement à cette institution les prédispose particulièrement à être indignés par l'expulsion d'enfants scolarisés.
Les émotions ne sont donc pas irrationnelles, mais socialement déterminées.
L'étude de Doug McAdam sur le Freedom Summer (1964) offre un aperçu exceptionnel des effets de l'engagement sur la vie des individus.
Durant cet été, de jeunes militants blancs sont allés dans le Mississippi pour aider les Noirs à s'inscrire sur les listes électorales, un engagement à très haut risque.
Grâce à des archives uniques, McAdam a pu comparer, 20 ans plus tard, le groupe de ceux qui ont participé et un groupe témoin de ceux qui avaient été acceptés mais ne s'y sont finalement pas rendus.
Les résultats sont frappants : les participants au Freedom Summer ont eu, en moyenne :
• Des carrières professionnelles plus chaotiques et des revenus plus faibles.
• Des vies familiales moins stables (plus de divorces, moins d'enfants).
• Un niveau d'engagement militant beaucoup plus élevé et durable.
Cette étude démontre que l'engagement intense n'est pas une simple parenthèse dans une vie, mais un événement fondateur qui a des conséquences biographiques profondes, façonnant durablement les trajectoires professionnelles, familiales et militantes.
C'est également de cette expérience que sont issues de nombreuses futures leaders du mouvement féministe américain, qui y ont pris goût à l'action collective tout en y découvrant la division sexiste du travail militant.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the previous reviews
Reviewer #1 (Public review) :
Comments on revisions:
The revised manuscript has responded to the previous concerns of the reviewers, albeit modestly. The overemphasis on hypoxic adaptation of the clinical isolates persist as a key concern in the paper. The authors have compared the growth-curve of each of the clinical and ATCC strains under normal and hypoxic conditions (Fig. 8), but don't show how mutations in some of the genes identified in Tn-seq would impact the growth phenotype under hypoxia. They largely base their arguments on previously published results.
As I mentioned previously, the paper will be better without over-interpreting the TnSeq data in the context of hypoxia.
Thank you for the comment on the issue of not determining the impact of individual gene mutations identified in TnSeq on the growth phenotypes under hypoxia.
We agree that the lack of validation of TnSeq results is a limitation of this study. Without evidence of growth pattern of each gene-deletion mutant under hypoxia there might be a risk of over-interpretating the data, even though the data are carefully interpreted based on previous reports. We consider that it is necessary to confirm the phenomenon by using knockout mutants.
We have just recently succeeded in constructing the vector plasmids for making knockout mutants of M intracellulare (Tateishi. Microbiol Immunol. 2024). We will proceed to the validation experiment of TnSeq-hit genes by constructing knockout mutants. We already mentioned this point as a limitation of this study in the Discussion (pages 35-36 lines 630-640 in the revised manuscript).
Reference.
Tateishi, Y., Nishiyama, A., Ozeki, Y. & Matsumoto, S. Construction of knockout mutants in Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC13950 strain using a thermosensitive plasmid containing negative selection marker rpsL+. Microbiol Immunol 68, 339-347 (2024).
Other points:
The y-axis legends of plots in Fig.8c are illegible.
Following the comment, we have corrected Figure 8c and checked the uploaded PDF
The statements in lines 376-389 are convoluted and need some explanation. If the clinical strains enter the log phase sooner than ATCC strain under hypoxia, then how come their growth rates (fig. 8c) are lower? Aren't they expected to grow faster?
Thank you for the comment on the interpretation of the difference in bacterial growth under hypoxia between MAC-PD strains and the ATCC type strain. The growth curve consists of the onset of logarithmic growth and its growth speed. In this study, we evaluated the former as timing of midpoint and the latter as growth rate at midpoint. Timing of midpoint and growth rate at midpoint are individual parameters. The early entry to log-phase does not mean the fast growth rate at midpoint.
Our results demonstrated that 5 (M.i.198, M.i.27, M003, M019 and M021) out of 8 clinical MAC-PD strains entered log-phase early and continued to grow logarithmically long time (slow growth). This data suggests the capacity for MAC-PD to continue replication long time under hypoxic conditions. By contrast, the ATCC type strain showed delayed onset of logarithmic growth caused by long-term lag phase. The duration of logarithmic growth was short even once after it started. The log phase soon transited to the stationary phase. This data suggests the lower capacity for the ATCC strain to continue replication under hypoxic conditions.
Following the comment, we have added the interpretation of the growth curve pattern as follows (page 22 lines 379-392 in the revised manuscript): “The growth rate at midpoint under hypoxic conditions was significantly lower in these 5 clinical MAC-PD strains than in ATCC13950. The early entry to log phase followed by long-term logarithmic growth (slow growth rate at midpoint) suggests the capacity for these 5 clinical MAC-PD strains to continue replication long time under hypoxic conditions. On the other hand, the rest 3 clinical MAC-PD strains (M018, M001 and MOTT64) did not show significant change in the growth rate between aerobic and hypoxic conditions, suggesting that there are different levels of capacity in maintaining long-term replication under hypoxia among clinical MAC-PD strains. In ATCC13950, the entry to log phase was significantly delayed under 5% oxygen compared to aerobic conditions, and the growth rate at midpoint was significantly increased under hypoxic conditions compared to aerobic conditions in ATCC13950. Such long-term lag phase followed by short-term log phase suggests lower capacity for ATCC13950 to continue replication under hypoxic conditions compared to clinical MAC-PD strains.”
Reviewer #4 (Public review):
Comments on revisions:
The revised version has satisfactorily addressed my initial comments in the discussion section.
The authors thank the Reviewer for understanding our reply.
Reviewer #5 (Public review):
Comments on revisions:
There is quite a lot of data and this could have been a really impactful study if the authors had channelized the Tn mutagenesis by focusing on one pathway or network. It looks scattered. However, from the previous version, the authors have made significant improvements to the manuscript and have provided comments that fairly address my questions.
The authors thank the Reviewer for understanding our reply. And the authors thank the Reviewer for the comments suggesting the future studies of TnSeq that focus on one pathway or network.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript addresses the important problem of the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation due to hypoxia-ischemia injury in the neonatal brain and provides insight into the neuroprotective mechanisms of hypothermia treatment.
Strengths:
The authors used a combination of in vivo imaging of awake P10 mice and experiments on isolated mitochondria to assess various key parameters of brain metabolism during hypoxia-ischemia with and without hypothermia treatment. This unique approach resulted in a comprehensive data set that provides solid evidence to support the derived conclusions.
Weaknesses:
Several potential weaknesses were identified in the original submission, which the authors subsequently addressed in the revised manuscript. Here is the brief list of the questions:
(1) Is it possible that the observed relatively low baseline OEF and trends of increased OEF and CBF over several hours after the imaging start were partially due to slow recovery from anesthesia?
(2) What was the pain management, and is there a possibility that some of the observations were influenced by the pain-reducing drugs or their absence?
(3) Were P10 mice significantly stressed during imaging in the awake state because they didn't have head-restraint habituation training?
(4) Considering high metabolism and blood flow in the cortex, it could be potentially challenging to predict cortical temperature based on the skull temperature, particularly in the deeper part of the cortex.
(5) The map of estimated CMRO2 looks quite heterogeneous across the brain surface. Could this be partially resulting from the measurement artefact?
(6) It would be beneficial to provide more detailed justification for using P10 mice in the experiments.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Sun et al. present a comprehensive study using a novel photoacoustic microscopy setup and mitochondrial analysis to investigate the impact of hypoxia-ischemia (HI) on brain metabolism and the protective role of therapeutic hypothermia. The authors elegantly demonstrate three connected findings: (1) HI initially suppresses brain metabolism, (2) subsequently triggers a metabolic surge linked to oxidative phosphorylation uncoupling and brain damage, and (3) therapeutic hypothermia mitigates HI-induced damage by blocking this surge and reducing mitochondrial stress.
The study's design and execution are great, with a clear presentation of results and methods. Data is nicely presented, and methodological details are thorough.
However, a minor concern is the extensive use of abbreviations, which can hinder readability. As all the abbreviations are introduced in the text, their overuse may render the text hard to read to non-specialist audiences. Additionally, sharing the custom Matlab and other software scripts online, particularly those used for blood vessel segmentation, would be a valuable resource for the scientific community. In addition, while the study focuses on the short-term effects of HI, exploring the long-term consequences and definitively elucidating HI's impact on mitochondria would further strengthen the manuscript's impact.
Despite these minor points, this manuscript is very interesting.
Comments on revisions:
All addressed.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review)
(1) This manuscript addresses an important problem of the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation due to hypoxia-ischemia injury of the neonatal brain and provides insight into the neuroprotective mechanisms of hypothermia treatment.
The authors used a combination of in vivo imaging of awake P10 mice and experiments on isolated mitochondria to assess various key parameters of the brain metabolism during hypoxia-ischemia with and without hypothermia treatment. This unique approach resulted in a comprehensive data set that provides solid evidence for the derived conclusions
We thank the reviewer for the positive feedback.
(2) The experiments were performed acutely on the same day when the surgery was performed. There is a possibility that the physiology of mice at the time of imaging was still affected by the previously applied anesthesia. This is particularly of concern since the duration of anesthesia was relatively long. Is it possible that the observed relatively low baseline OEF (~20%) and trends of increased OEF and CBF over several hours after the imaging start were partially due to slow recovery from prolonged anesthesia? The potential effects of long exposure to anesthesia before imaging experiments were not discussed.
We thank the reviewer for this important comment and for pointing out the potential influence of anesthesia on the physiological state of the animals. We apologize for any confusion. To clarify, all PAM imaging experiments were conducted in awake animals. Isoflurane anesthesia was used only during two brief surgical procedures: (1) the installation of the head-restraint plastic head plate and (2) the right common carotid artery (CCA) ligation. Each anesthesia session lasted less than 20 minutes.
We have revised the Methods section to provide additional details:
For the subsection Procedures for PAM Imaging on page 17, we clarified the sequence of procedures during the head plate installation, as well as the corresponding anesthesia duration:
“After the applied glue was solidified (~20 min), the animal was first returned to its cage for full recovery from anesthesia, and then carefully moved to the treadmill and secured to the metal arm-piece with two #4–40 screws for awake PAM imaging. The total duration of anesthesia, including preparation and glue solidification, was approximately 20 minutes.”
For the subsection Neonatal Cerebral HI and Hypothermia Treatment on page 19, we also clarified the CCA ligation procedure:
“Briefly, P10 mice of both sexes anesthetized with 2% isoflurane were subjected to the right CCA-ligation. To manage pain, 0.25% Bupivacaine was administered locally prior to the surgical procedures, which took less than 10 minutes. After a recovery period for one hour, awake mice were exposed to 10% O<sub>2</sub> for 40 minutes in a hypoxic chamber at 37 °C.”
Regarding the reviewer’s concern about the observed trends in OEF and CBF, we agree that residual effects of anesthesia could, in principle, influence physiological parameters. However, we believe this is unlikely in this study for the following reasons. First, all imaging was conducted in awake animals after a clearly defined recovery period. Second, the trend of increasing OEF and CBF over time was consistent across animals and aligned with expected physiological responses following hypoxic-ischemic injury. In particular, the relatively low baseline OEF (0.21 at 37°C) is consistent with our previous study (0.25; (Cao et al., 2018)). The gradual increase in CBF and OEF reflects metabolic compensation and reperfusion following hypoxia-ischemia, as previously described (Lin and Powers, 2018). Therefore, we believe the observed changes are of physiological origin rather than anesthesia-related artifacts.
(3) The Methods Section does not provide information about drugs administered to reduce the pain. If pain was not managed, mice could be experiencing significant pain during experiments in the awake state after the surgery. Since the imaging sessions were long (my impression based on information from the manuscript is that imaging sessions were ~4 hours long or even longer), the level of pain was also likely to change during the experiments. It was not discussed how significant and potentially evolving pain during imaging sessions could have affected the measurements (e.g., blood flow and CMRO<sub>2</sub>). If mice received pain management during experiments, then it was not discussed if there are known effects of used drugs on CBF, CMRO<sub>2</sub>, and lesion size after 24 hr.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable comment regarding pain management. We confirm that local analgesia was administered to all animals prior to surgical procedures. Specifically, 0.25% Bupivacaine was applied locally before both the head-restraint plate installation and the CCA ligation. These details have now been clarified in the Methods section:
For the subsection Procedures for PAM Imaging on page 16, we added:
“To manage pain, 0.25% Bupivacaine was administered locally prior to the surgical procedures.”
For the subsection Neonatal Cerebral HI and Hypothermia Treatment on page 18, we added:
“To manage pain, 0.25% Bupivacaine was administered locally prior to the surgical procedures, which took less than 10 minutes.”
To our knowledge, Bupivacaine has minimal systemic effects at the dose used and is unlikely to significantly alter CBF, CMRO<sub>2</sub>, or lesion development (Greenberg et al., 1998). No other analgesics (e.g., NSAIDs or opioids) were administered unless distress symptoms were observed—which did not occur in this study.
Additionally, although imaging sessions were extended (up to 2 hours), animals remained calm and showed no signs of pain or distress during or after the procedures. Throughout the experimental period (up to 24 hours post-surgery), animals were monitored for signs of discomfort (e.g., abnormal activity, breathing, or weight gain), but no additional analgesia was required. The neonatal HI procedures are considered minimally invasive, and based on our protocol and prior experience, local Bupivacaine provides effective analgesia during and after the brief surgeries. We have added a corresponding note in the Discussion section (newly added subsection: Limitations in this study, the last paragraph) on page 15:
“We observed no signs of distress or pain and did not use stress- or pain-reducing drugs during imaging. However, potential effects of stress or residual pain on CBF and CMRO<sub>2</sub> cannot be fully ruled out. Future studies could incorporate more detailed pain assessment and stress-mitigation strategies to further enhance physiological reliability.”
(4) Animals were imaged in the awake state, but they were not previously trained for the imaging procedure with head restraint. Did animals receive any drugs to reduce stress? Our experience with well-trained young-adult as well as old mice is that they can typically endure 2 and sometimes up to 3 hours of head-restrained awake imaging with intermittent breaks for receiving the rewards before showing signs of anxiety. We do not have experience with imaging P10 mice in the awake state. Is it possible that P10 mice were significantly stressed during imaging and that their stress level changed during the imaging session? This concern about the potential effects of stress on the various measured parameters was not discussed.
We thank the reviewer for this important comment regarding the potential effects of stress during awake imaging. The neonatal mice used in our study were P10, a stage at which animals are still physiologically immature and relatively inactive. Due to their small size and limited mobility, these animals did not struggle or show signs of distress during the imaging sessions. All animals remained calm and stable throughout the procedure, and no stress-reducing drugs were administered.
We agree that, unlike older animals, P10 mice are not amenable to prior behavioral training. However, their underdeveloped motor activity and natural docility at this stage allowed for stable head-restrained imaging without inducing overt stress responses. Although no behavioral signs of stress were observed, we acknowledge that subtle physiological effects cannot be entirely excluded. We have added a brief discussion in the Discussion section (newly added subsection: Limitations in this study, the last paragraph) on page 15:
“Lastly, for awake imaging, the small size of neonatal mice at P10 aids stability during awake PAM imaging, though it limits the feasibility of prior training, which is typically possible in older animals.”
(5) The temperature of the skull was measured during the hypothermia experiment by lowering the water temperature in the water bath above the animal's head. Considering high metabolism and blood flow in the cortex, it could be challenging to predict cortical temperature based on the skull temperature, particularly in the deeper part of the cortex.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful comment and for highlighting an important technical consideration. We acknowledge that we did not directly measure intracortical tissue temperature during the hypothermia experiments. While we recognize that relying on skull temperature may have limitations—particularly in reflecting temperature changes in deeper cortical regions—this approach is consistent with clinical practice, where intracortical temperature is typically not measured. Moreover, prior studies have shown that skull or brain surface temperature generally reflects cortical thermal dynamics to a reasonable extent under controlled conditions (Kiyatkin, 2007). We have added the following note in the Discussion section (newly added subsection: Limitations in this study, the 2<sup>nd</sup> paragraph) on page 14:
“A technical limitation is the absence of direct intracortical temperature measurements during hypothermia; we relied on skull temperature, which may not fully capture temperature dynamics in deeper cortical layers. However, this approach aligns with clinical practice, where intracortical temperature is not typically measured. Future studies could benefit from more precise intracortical assessments.”
(6) The map of estimated CMRO<sub>2</sub> (Fig. 4B) looks very heterogeneous across the brain surface. Is it a coincidence that the highest CMRO<sub>2</sub> is observed within the central part of the field of view? Is there previous evidence that CMRO<sub>2</sub> in these parts of the mouse cortex could vary a few folds over a 1-2 mm distance?
We appreciate the reviewer’s insightful observation regarding the spatial heterogeneity observed in the estimated CMRO<sub>2</sub> map (Fig. 4B). This heterogeneity is not a result of scanning bias, as uniform contour scanning was performed across the entire field of view. The higher CMRO<sub>2</sub> values observed in the central region are unlikely to be artifacts and more likely reflect underlying physiological variability.
Our CMRO<sub>2</sub> estimation is based on an algorithm we previously developed and validated in other tissues. Specifically, we have successfully applied this algorithm to assess oxygen metabolism in the mouse kidney (Sun et al., 2021) and to monitor vascular adaptation and tissue oxygen metabolism during cutaneous wound healing (Sun et al., 2022). These studies demonstrated the algorithm's capability to capture spatial variations in oxygen metabolism. Although the current application to the brain is novel, the algorithm has been validated in controlled experimental settings and shown to produce consistent results. We acknowledge that the observed range of CMRO<sub>2</sub> appears relatively broad across a 1–2 mm distance; however, such heterogeneity may arise from local differences in vascular density, metabolic demand, or tissue oxygenation — all of which can vary across cortical regions, even within small spatial scales. We have added a brief note in the Discussion (Subsection: Optical CMRO<sub>2</sub> detection in neonatal care) on page 13 to acknowledge this point:
“Additionally, the spatial heterogeneity in estimated CMRO<sub>2</sub> observed in our data may reflect underlying physiological variability, including differences in vascular structure or metabolic demand across cortical regions. Future studies will aim to further validate and interpret these spatial patterns.”
(7) The justification for using P10 mice in the experiments has not been well presented in the manuscript.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out the need to clarify our choice of developmental stage. We chose P10 mice for our hypoxia-ischemia injury model because this stage is widely recognized as developmentally comparable to human term infants in terms of brain maturation. This approach has been validated by several previous studies (Clancy et al., 2007; Mallard and Vexler, 2015; Sheldon et al., 2018). We have added the following clarification to the Methods section (Subsection: Neonatal Cerebral HI and Hypothermia Treatment) on page 18:
“P10 mice were chosen for our experiments as they are widely used to model near-term infants in humans. At this developmental stage, the brain maturation in mice closely parallels that of near-term infants, making them an appropriate model for studying neonatal brain injury and therapeutic interventions (Clancy et al., 2007; Mallard and Vexler, 2015; Sheldon et al., 2018).”
(8) It was not discussed how the observations made in this manuscript could be affected by the potential discrepancy between the developmental stages of P10 mice and human babies regarding cellular metabolism and neurovascular coupling.
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point regarding developmental differences between P10 mice and human infants. We have discussed this issue by adding the following statement to the Discussion section (newly added subsection: Limitations in this study, the 1<sup>st</sup> paragraph) on page 15, where we summarize the overall study design and model selection:
“While P10 mice are widely used to model near-term human infants, developmental differences in cellular metabolism and neurovascular coupling may affect the observed outcomes and limit direct clinical translation (Clancy et al., 2007; Mallard and Vexler, 2015; Sheldon et al., 2018). Nevertheless, the P10 model remains a valuable and widely accepted tool for studying neonatal hypoxia-ischemia mechanisms and evaluating therapeutic interventions.”
(9) Regarding the brain temperature measurements, the authors should use a new cohort of mice, implant the miniature thermocouples 1 mm, 0.5 mm, and immediately below the skull in different mice, and verify the temperature in the brain cortex under conditions applied in the experiments. The same approach could be applied to a few mice undergoing 4-hr-long hypothermia treatment in a chamber, which will provide information about the brain temperature that resulted in observed protection from the injury.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful recommendation. We fully agree that direct intracortical temperature measurement would provide more accurate insight into thermal dynamics during hypothermia treatment. However, the primary aim of this study was not to characterize the precise intracortical temperature response under hypothermic conditions, but rather to examine the effects of hypothermia on CMRO<sub>2</sub> and mitochondrial function. Due to the substantial time and resources required to perform direct intracortical temperature monitoring—and considering the technical focus of the current work—we respectfully suggest reserving such investigations for a future study specifically focused on thermal dynamics in hypoxia-ischemia models.
We have acknowledged this limitation in the subsection Limitations in this study of the Discussion on page 15, noting that skull temperature was used as an approximation of brain temperature and that this approach is consistent with clinical practice, where intracortical temperature is typically not measured. We also note that future studies may benefit from more precise assessments using intracortical probes.
(10) The mean values presented in Fig. 4G are much lower than the peak values in the 2D panels and potentially were calculated as the average values over the entire field of view. Please provide more details on how CMRO<sub>2</sub> was estimated and if the validity of the measurements is expected across the entire field of view. If there are parts of the field of view where the estimation of CMRO<sub>2</sub> is more reliable for technical reasons, maybe one way to compute the mean values is to restrict the usable data to the more centralized part of the field of view.
We thank the reviewer for this thoughtful comment. We confirm that CMRO<sub>2</sub> values shown in Figure 4G were calculated as spatial averages over the entire field of view (FOV; ~5 × 3 mm<sup>2</sup>) encompassing both hemicortices, as shown in Figure 1C. Regarding the observed CMRO<sub>2</sub> values, The apparent difference likely reflects a comparison between two different post-HI time points. Specifically, the ~0.5 value shown for the 37°C ipsilateral group in Figure 4G reflects the average CMRO<sub>2</sub> measured 24 hours after HI, while the ~1.5 value in Figure 2D (red line) corresponds to CMRO<sub>2</sub> during the early 0–2 hour post-HI period. The temporal difference accounts for the apparent discrepancy in magnitude. We understand the importance of consistency across the field of view and have clarified this point in the subsection Procedures for PAM Imaging in the Methods on page 17 “For the imaging field covering both hemicortices between the Bregma and Lambda of the neonatal mouse (5 × 3 mm<sup>2</sup> as shown in Figure 1C, with each hemicortex measuring 2.5 × 3 mm<sup>2</sup>)”, as well as in the Figure 4 legend on page 34 “Correlation of CMRO<sub>2</sub> and post-HI brain infarction in mouse neonates at 24 hours”.
In our model and setup, CMRO<sub>2</sub> estimation is spatially robust across the FOV under standard imaging conditions. We recognize, however, that certain peripheral regions may be more prone to signal attenuation. Future refinement of region selection could further improve spatial averaging strategies. For the current study, full-FOV averaging was used consistently across all groups to maintain comparability.
(11) Minor: Results presented in Supplementary Tables have too many significant digits.
Thank you for the helpful suggestion. We have revised Supplementary Tables S1 and S2 to reduce the number of significant digits and improve clarity.
Reviewer #2 (Public review)
(1) In this study, authors have hypothesized that mitochondrial injury in HIE is caused by OXPHOS-uncoupling, which is the cause of secondary energy failure in HI. In addition, therapeutic hypothermia rescues secondary energy failure. The methodologies used are state-of-the art and include PAM technique in live animal, bioenergetic studies in the isolated mitochondria, and others.
The study is comprehensive and impressive. The article is well written and statistical analyses are appropriate.
We thank the reviewer for the positive feedback.
(2) The manuscript does not discuss the limitation of this animal model study in view of the clinical scenario of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia.
We thank the reviewer for this valuable feedback. In response, we have added a dedicated “Limitations in this study” subsection in the Discussion, where we address the potential limitations of this animal model in the context of the clinical scenario of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in the first paragraph on page 14, including the developmental differences between P10 mice and human infants.
(3) I see many studies on Pubmed on bioenergetics and HI. Hence, it is unclear what is novel and what is known.
We thank the reviewer for this important comment regarding the novelty of our study in the context of existing research on bioenergetics and hypoxia-ischemia (HI). To better clarify the novel aspects of our work, we have highlighted the relevant content in the Abstract (page 4) and Introduction (page 5). Specifically, while many studies have explored HI-related bioenergetic dysfunction, the mechanisms by which therapeutic hypothermia modulates CMRO<sub>2</sub> and mitochondrial function post-HI remain poorly understood.
Abstract on page 4: “However, it is unclear how post-HI hypothermia helps to restore the balance, as cooling reduces CMRO<sub>2</sub>. Also, how transient HI leads to secondary energy failure (SEF) in neonatal brains remains elusive. Using photoacoustic microscopy, we examined the effects of HI on CMRO<sub>2</sub> in awake 10-day-old mice, supplemented by bioenergetic analysis of purified cortical mitochondria.”
Introduction on page 5: “The use of awake mouse neonates avoided the confounding effects of anesthesia on CBF and CMRO<sub>2</sub> (Cao et al., 2017; Gao et al., 2017; Sciortino et al., 2021; Slupe and Kirsch, 2018). In addition, we measured the oxygen consumption rate (OCR), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the membrane potential of mitochondria that were immediately purified from the same cortical area imaged by PAM. This dual-modal analysis enabled a direct comparison of cerebral oxygen metabolism and cortical mitochondrial respiration in the same animal. Moreover, we compared the effects of therapeutic hypothermia on oxygen metabolism and mitochondrial respiration, and correlated the extent of CMRO<sub>2</sub>-reduction with the severity of infarction at 24 hours after HI. Our results suggest that blocking HI-induced OXPHOS-uncoupling is an acute effect of hypothermia and that optical detection of CMRO<sub>2</sub> may have clinical applications in HIE.”
In this study, we propose that uncoupled oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) underlies the secondary energy failure observed after HI, and we demonstrate that hypothermia suppresses this pathological CMRO<sub>2</sub> surge, thereby protecting mitochondrial integrity and preventing injury. Additionally, our use of photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) in awake neonatal mice represents a novel, non-invasive approach to track cerebral oxygen metabolism, with potential clinical relevance for guiding hypothermia therapy.
(4) What are the limitations of ex-vivo mitochondrial studies?
We thank the reviewer for this insightful comment. We acknowledge that ex-vivo mitochondrial assays do not fully replicate in vivo physiological conditions, as they lack systemic factors such as blood flow, cellular interactions, and intact tissue architecture. However, these assays are well-established and widely accepted in the field for evaluating mitochondrial function under controlled conditions (Caspersen et al., 2008; Niatsetskaya et al., 2012). Despite their limitations, they enable direct comparisons of mitochondrial activity across experimental groups and provide valuable mechanistic insights that complement in vivo observations.
(5) PAM technique limits the resolution of the image beyond 500-750 micron depth. Assessing basal ganglia may not be possible with this approach?
We thank the reviewer for this important comment. We agree that the imaging depth of PAM is limited and may not allow assessment of deeper brain structures such as the basal ganglia. However, in our neonatal HI model—as in many clinical cases of HIE—cortical injury is typically more severe and represents a major focus for mechanistic and therapeutic investigations. The cortical regions assessed with PAM are thus highly relevant to the pathophysiology of neonatal HI. We have now acknowledged this depth limitation in the third paragraph of the newly added Limitations in this study subsection of the Discussion on page 15:
“Another limitation of this study is the restricted imaging depth of the PAM technique, which is typically less than 1 mm and therefore does not allow assessment of deeper brain structures such as the basal ganglia. However, in both our neonatal HI model and most clinical cases of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia, cortical injury tends to be more prominent and functionally significant. As such, our cortical measurements remain highly relevant for investigating the mechanisms of injury and evaluating therapeutic interventions.”
(6) Hypothermia in present study reduces the brain temperature from 37 to 29-32 degree centigrade. In clinical set up, head temp is reduced to 33-34.5 in neonatal hypoxia ischemia. Hence a drop in temperature to 29 degrees is much lower relative to the clinical practice. How the present study with greater drop in head temperature can be interpreted for understanding the pathophysiology of therapeutic hypothermia in neonatal HIE. Moreover, in HIE model using higher temperature of 37 and dropping to 29 seems to be much different than the clinical scenario. Please discuss.
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point regarding temperature ranges in our study. In Figure 1, we used a broader temperature range (down to 29°C) to explore the general relationship between temperature and CMRO<sub>2</sub> in uninjured neonatal mice. This experiment was not intended to model therapeutic hypothermia directly, but rather to characterize the baseline physiological responses.
For all experiments involving hypothermia as a therapeutic intervention following HI, we consistently maintained a brain temperature of 32°C, which falls within the clinically accepted mild hypothermia range for neonatal HIE (typically 33–34.5°C). We believe this temperature closely mimics clinical practice and supports the translational relevance of our findings.
(7) NMR was assessed ex-vivo. How does it relate to in vivo assessment. Infants admitted in Neonatal intensive Care Unit, frequently get MRI with spectroscopy. How do the MRS findings in human newborns with HIE correlate with the ex-vivo evaluation of metabolites.
We thank the reviewer for this insightful question. While our study assessed brain metabolites ex vivo, similar metabolic changes have been observed in vivo using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (¹H-MRS) in infants with HIE. Specifically, reductions in N-acetylaspartate (NAA) — a marker of neuronal integrity — have been reported in neonates with severe brain injury, aligning with our ex vivo findings. This correlation between in vivo and ex vivo assessments supports the translational relevance of our model for studying metabolic disruption in neonatal HIE. We have added this point to the subsection Using Optically Measured CMRO<sub>2</sub> to Detect Neonatal HI Brain Injury of the Results on page 8, along with a supporting clinical reference (Lally et al., 2019):
“In addition, in vivo proton MRS in infants with HIE has also shown a reduction in NAA, particularly in cases of severe injury (Lally et al., 2019). This reduction in NAA, observed in neonatal intensive care settings, reflects neuronal and axonal loss or dysfunction and serves as a biomarker for injury severity. The alignment between our ex vivo observations and in vivo MRS findings in clinical studies reinforces the translational relevance of our model for investigating metabolic disturbances in neonatal HIE.”
Reviewer #3 (Public review)
(1) In Sun et al. present a comprehensive study using a novel photoacoustic microscopy setup and mitochondrial analysis to investigate the impact of hypoxia-ischemia (HI) on brain metabolism and the protective role of therapeutic hypothermia. The authors elegantly demonstrate three connected findings: (1) HI initially suppresses brain metabolism, (2) subsequently triggers a metabolic surge linked to oxidative phosphorylation uncoupling and brain damage, and (3) therapeutic hypothermia mitigates HI-induced damage by blocking this surge and reducing mitochondrial stress.
The study's design and execution are great, with a clear presentation of results and methods. Data is nicely presented, and methodological details are thorough.
We thank the reviewer for the positive feedback.
(2) However, a minor concern is the extensive use of abbreviations, which can hinder readability. As all the abbreviations are introduced in the text, their overuse may render the text hard to read to non-specialist audiences. Additionally, sharing the custom Matlab and other software scripts online, particularly those used for blood vessel segmentation, would be a valuable resource for the scientific community. In addition, while the study focuses on the short-term effects of HI, exploring the long-term consequences and definitively elucidating HI's impact on mitochondria would further strengthen the manuscript's impact.
We thank the reviewer for these valuable suggestions. Please find our point-by-point responses below:
Abbreviations: To improve readability, we have added a List of Abbreviations on page 3 to help readers, especially non-specialists, navigate the terminology more easily.
MATLAB Code Availability: The methodology for blood vessel segmentation was described in detail in our previous publication (Sun et al., 2020). We have now updated the subsection Quantification of Cerebral Hemodynamics and Oxygen Metabolism by PAM of the Methods on page 18 to provide additional details and have indicated that the MATLAB scripts are available upon request.
“Briefly, this process involves generating a vascular map using signal amplitude from the Hilbert transformation, selecting a region slightly larger than the vessel of interest, and applying Otsu’s thresholding method to remove background pixels. Isolated or spurious boundary fragments are then removed to improve boundary smoothness. The customized MATLAB code used for vessel segmentation is available upon request.”
Long-Term Effects of Hypothermia: We agree that exploring long-term outcomes would enhance the broader impact of this research. While our study focuses on the acute phase following HI, prior studies have shown long-term neuroprotective benefits of therapeutic hypothermia, such as enhanced white matter development (Koo et al., 2017). We have added this point to the fourth paragraph in the subsection Limitations in this study of the Discussion on page 15:
“While our study focuses on the acute effects of hypothermia, previous research has shown long-term neuroprotective benefits, including improved white matter development post-injury (Koo et al., 2017). These findings highlight hypothermia's potential for both immediate and extended recovery, warranting further study of long-term outcomes.”
(3) Extensive use of abbreviations.
Thank you for the helpful suggestion. To improve readability for a broader audience, we have added a List of Abbreviations on page 3 of the manuscript to assist readers in navigating terminology used throughout the text. This has been included as Response #2 to Reviewer #3.
(4) Share code used to conduct the study.
Thank you for the suggestion. The methodology for vessel segmentation was previously published (Sun et al., 2020), and we have noted in the subsection Quantification of Cerebral Hemodynamics and Oxygen Metabolism by PAM of the Methods on page 18 that the MATLAB code is available upon request. This has also been included as Response #2 to Reviewer #3.
Reference:
Cao R, Li J, Kharel Y, Zhang C, Morris E, Santos WL, Lynch KR, Zuo Z, Hu S. 2018. Photoacoustic microscopy reveals the hemodynamic basis of sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced neuroprotection against ischemic stroke. Theranostics 8:6111–6120. doi:10.7150/thno.29435
Caspersen CS, Sosunov A, Utkina-Sosunova I, Ratner VI, Starkov AA, Ten VS. 2008. An Isolation Method for Assessment of Brain Mitochondria Function in Neonatal Mice with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Developmental Neuroscience 30:319–324. doi:10.1159/000121416
Clancy B, Kersh B, Hyde J, Darlington RB, Anand KJS, Finlay BL. 2007. Web-based method for translating neurodevelopment from laboratory species to humans. Neuroinformatics 5:79–94. doi:10.1385/ni:5:1:79
Greenberg RS, Zahurak M, Belden C, Tunkel DE. 1998. Assessment of oropharyngeal distance in children using magnetic resonance imaging. Anesth Analg 87:1048–1051. doi:10.1097/00000539-199811000-00014
Kiyatkin EA. 2007. Brain temperature fluctuations during physiological and pathological conditions. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:3–17. doi:10.1007/s00421-007-0450-7
Koo E, Sheldon RA, Lee BS, Vexler ZS, Ferriero DM. 2017. Effects of therapeutic hypothermia on white matter injury from murine neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Pediatr Res 82:518–526. doi:10.1038/pr.2017.75
Lally PJ, Montaldo P, Oliveira V, Soe A, Swamy R, Bassett P, Mendoza J, Atreja G, Kariholu U, Pattnayak S, Sashikumar P, Harizaj H, Mitchell M, Ganesh V, Harigopal S, Dixon J, English P, Clarke P, Muthukumar P, Satodia P, Wayte S, Abernethy LJ, Yajamanyam K, Bainbridge A, Price D, Huertas A, Sharp DJ, Kalra V, Chawla S, Shankaran S, Thayyil S, MARBLE consortium. 2019. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy assessment of brain injury after moderate hypothermia in neonatal encephalopathy: a prospective multicentre cohort study. Lancet Neurol 18:35–45. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30325-9
Lin W, Powers WJ. 2018. Oxygen metabolism in acute ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38:1481–1499. doi:10.1177/0271678X17722095
Mallard C, Vexler Z. 2015. Modeling ischemia in the immature brain: how translational are animal models? Stroke 46:3006–3011. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.007776
Niatsetskaya ZV, Sosunov SA, Matsiukevich D, Utkina-Sosunova IV, Ratner VI, Starkov AA, Ten VS. 2012. The Oxygen Free Radicals Originating from Mitochondrial Complex I Contribute to Oxidative Brain Injury Following Hypoxia–Ischemia in Neonatal Mice. J Neurosci 32:3235–3244. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6303-11.2012
Sheldon RA, Windsor C, Ferriero DM. 2018. Strain-Related Differences in Mouse Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia. Dev Neurosci 40:490–496. doi:10.1159/000495880
Sun N, Bruce AC, Ning B, Cao R, Wang Y, Zhong F, Peirce SM, Hu S. 2022. Photoacoustic microscopy of vascular adaptation and tissue oxygen metabolism during cutaneous wound healing. Biomed Opt Express, BOE 13:2695–2706. doi:10.1364/BOE.456198
Sun N, Ning B, Bruce AC, Cao R, Seaman SA, Wang T, Fritsche-Danielson R, Carlsson LG, Peirce SM, Hu S. 2020. In vivo imaging of hemodynamic redistribution and arteriogenesis across microvascular network. Microcirculation 27:e12598. doi:10.1111/micc.12598
Sun N, Zheng S, Rosin DL, Poudel N, Yao J, Perry HM, Cao R, Okusa MD, Hu S. 2021. Development of a photoacoustic microscopy technique to assess peritubular capillary function and oxygen metabolism in the mouse kidney. Kidney International 100:613–620. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2021.06.018
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the previous reviews
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this study, the authors identified an insect salivary protein LssaCA participating viral initial infection in plant host. LssaCA directly bond to RSV nucleocapsid protein and then interacted with a rice OsTLP that possessed endo-β-1,3-glucanase activity to enhance OsTLP enzymatic activity and degrade callose caused by insects feeding. The manuscript suffers from fundamental logical issues, making its central narrative highly unconvincing.
(1) These results suggested that LssaCA promoted RSV infection through a mechanism occurring not in insects or during early stages of viral entry in plants, but in planta after viral inoculation. As we all know that callose deposition affects the feeding of piercing-sucking insects and viral entry, this is contradictory to the results in Fig. S4 and Fig. 2. It is difficult to understand callose functioned in virus reproduction in 3 days post virus inoculation. And authors also avoided to explain this mechanism.
We appreciate your insightful comment and acknowledge that our initial description may not have been sufficiently clear.
(1) Based on the EPG results, we found that LssaCA deficiency did not significantly affect total feeding time, time to first non-phloem phase, or time to first phloem feeding (Fig. S8A-D in the revised manuscript). However, the continuity of sap ingestion was disturbed—the N4 waveform of dsLssaCA SBPHs was occasionally interrupted for brief periods (newly added Fig. S8E in the revised manuscript), likely due to phloem blockage. In the revised manuscript, we have added this analysis to the Result section (Lines 285-291 and 578-587) and provided the EPG procedure in Material and Methods section (Lines 670-680).
(2) We assessed RSV titers immediately post-feeding to confirm the inoculation viral loads (Fig. 2G) and at 3 dpf (Fig. 2H-I) to assess the in-planta effects following viral inoculation. This did not mean that callose functions in virus reproduction at 3 days post viral inoculation. Rather, callose deposition typically occurs immediately in response to insect feeding and virus inoculation. When measuring callose deposition, we allowed insects to feed for 24 h and quantified the callose levels immediately post feeding. The EPG results showed that sap ingestion continuity was disrupted—the N4 waveform of dsLssaCA-treated SBPHs was occasionally interrupted for brief periods (newly added Fig. S8E in the revised manuscript), likely due to phloem blockage. We have reorganized the description to avoid confusion. Please see Lines 139-144 and Fig. S8E for detail.
(1) Missing significant data. For example, the phenotypes of the transgenic plants, the RSV titers in the transgenic plants (OsTLP OE, ostlp). The staining of callose deposition were also hard to convince. The evidence about RSV NP-LssaCA-OsTLP tripartite interaction to enhance OsTLP enzymatic activity is not enough.
We thank the reviewer for this insightful comment.
(1) We constructed OsTLP overexpression and mutant transgenic plants (OsTLP OE and ostlp) and assessed their phenotypes regarding RSV infection levels. Compared with wild-type plants, OsTLP OE plants exhibited accelerated growth, while ostlp plants showed growth inhibition. Following feeding by viruliferous L. striatellus, OsTLP OE plants had significantly higher RSV titers compared with wild-type plants, whereas ostlp mutant plants exhibited significantly lower RSV titers (Lines 221-228 and new Fig. 3I). These results indicate that OsTLP facilitates RSV infection in planta.
(2) The images showing callose deposition staining are representative of 15 images from 3 independent insect treatments. In addition to the staining images, we quantified fluorescence intensity and measured callose concentration by ELISA.
(2) Figure 4a, there was the LssaCA signal in the fourth lane of pull-down data. Did MBP also bind LsssCA? The characterization of pull-down methods was rough a little bit. The method of GST pull-down and MBP pull-down should be characterized more in more detail.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful comment. MBP did not bind LssaCA. We have repeated the pull-down experiment and provide clearer figure with improved results. We have also revised and provided more detailed descriptions of the GST pull-down and MBP pull-down methods. Please refer to Lines 744-774 and Figure 4A for details.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
The medicinal leech preparation is an amenable system in which to understand how the underlying cellular networks for locomotion function. A previously identified non-spiking neuron (NS) was studied and found to alter the mean firing frequency of a crawl-related motoneuron (DE-3), which fires during the contraction phase of crawling. The data are solid. Identifying upstream neurons responsible for crawl motor patterning is essential for understanding how rhythmic behavior is controlled.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the previous reviews
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
The medicinal leech preparation is an amenable system in which to understand how the underlying cellular networks for locomotion function. A previously identified non-spiking neuron (NS) was studied and found to alter the mean firing frequency of a crawl-related motoneuron (DE-3), which fires during the contraction phase of crawling. The data are mostly solid. Identifying upstream neurons responsible for crawl motor patterning is essential for understanding how rhythmic behavior is controlled.
Review of Revision:
On a positive note, the rationale for the study is clearer to me now after reading the authors' responses to both reviewers, but that information, as described in the authors' responses, is minimally incorporated into the current revised paper. Incorporating a discussion of previous work on the NS cell has, indeed, improved the paper.
I suggested earlier that the paper be edited for clarity but not much text has been changed since the first draft. I will provide an example of the types of sentences that are confusing. The title of the paper is: "Phase-specific premotor inhibition modulates leech rhythmic motor output". Are the authors referring to the inhibition created by premotor neurons (e.g., on to the motoneurons) or the inhibition that the premotor neurons receive?
In this case, this is an interesting ambiguity: NS is inhibited and that inhibition is directly transmitted to the motoneurons because both cells are electrically coupled. We believe that the title does not disguise the findings conveyed by the manuscript.
I also find the paper still confusing with regard to the suggested "functional homology" with the vertebrate Renshaw cells. When the authors set up this expectation of homology (should be analogy) in the introduction and other sections of the paper, one would assume that the NS cell would be directly receiving excitation from a motoneuron (like DE-3) and, in turn, the motoneuron would then receive some sort of inhibitory input to regulate its firing frequency. Essentially, I have always viewed the Renshaw cells as nature's clever way to monitor the ongoing activity of a motoneuron while also providing recurrent feedback or "recurrent inhibition" to modify that cell's excitatory state. The authors present their initial idea below on line 62. Authors write: "These neurons are present as bilateral pairs in each segmental ganglion and are functional homologs of the mammalian Renshaw cells (Szczupak, 2014). These spinal cord cells receive excitatory inputs from motoneurons and, in turn, transmit inhibitory signals to the motoneurons (Alvarez and Fyffe, 2007)."
We agree with Reviewer #2: the correct term is "analogous," not "homologous." Thanks for pointing this out. We changed the term throughout the text.
The Reviewer is also right in the appreciation of the role of Renshaw cells. NS plays exactly the role that the Reviewer expresses. The ONLY difference is that NS is inhibited by the motoneurons, and in turn transmits this inhibition to the motoneurons via the rectifying electrical junctions. Attending the confusion that our description caused in the Reviewer, we have modified the cited sentence accordingly now in lines 65-67.
Minor note:
I suggest re-writing this last sentence as "these" is confusing. Change to: 'In the spinal cord, Renshaw interneurons receive excitatory inputs from motoneurons and, in turn, transmit inhibitory signals to them (Alvarez and Fyffe, 2007).']
Please, see the changes mentioned above.
Furthermore, the authors note that (line 69 on): "In the context of this circuit the activity of excitatory motoneurons evokes chemically mediated inhibitory synaptic potentials in NS. Additionally, the NS neurons are electrically coupled......In physiological conditions this coupling favors the transmission of inhibitory signals from NS to motoneurons." Based on what is being conveyed here, I see a disconnect with the "functional homology" being presented earlier. I may be missing something, but the Renshaw analogy seems to be quite different compared to what looks like reciprocal inhibition in the leech. If the authors want to make the analogy to Renshaw cells clearer, then they should make a simple ball and stick diagram of the leech system and visually compare it to the Renshaw/motoneuron circuit with regard to functionality. This simple addition would help many readers.
We have simplified the description regarding the Renshaw cell (lines 65-67) to avoid the “details” of the connectivity between the two circuits.
This report focuses on NS neurons and their role in crawling; we mention the analogy with Renshaw cells to widen the interest of the results. We do not think that making a special diagram to compare how the two neurons play a similar role via different connections among the players is useful in the context of this manuscript.
The Abstract, Authors write (line 19), "Specifically, we analyzed how electrophysiological manipulation of a premotor nonspiking (NS) neuron, that forms a recurrent inhibitory circuit (homologous to vertebrate Renshaw cells)...."
First, a circuit would not be homologous to a cell, and the term homology implies a strict developmental/evolutionary commonality. At best, I would use the term functionally analogous but even then I am still not sure that they are functionally that similar (see comments above).
Reviewer #2 is right. We changed the sentence in line 20.
Line 22: "The study included a quantitative analysis of motor units active throughout the fictive crawling cycle that shows that the rhythmic motor output in isolated ganglia mirrors the phase relationships observed in vivo." This sentence must be revised to indicate that not all of the extracellular units were demonstrated to be motor units. Revise to: "The study included a quantitative analysis of identified and putative motor units active throughout the fictive crawling cycle that shows.....'
Line 187 regarding identifying units as motoneurons: Authors write, "While multiple extracellular recordings have been performed previously (Eisenhart et al., 2000), these results (Figure 4) present the first quantitative analysis of motor units activated throughout the crawling cycle in this type of recordings." The authors cannot assume that the units in the recorded nerves belong only to motoneurons. Based on their first rebuttal, the authors seem to be reluctant to accept the idea that the extracellularly recorded units might represent a different class of neurons. They admit that some sensory neurons (with somata located centrally) do, indeed, travel out the same nerves recorded, but go on to explain why they would not be active.
The leech has a variety of sensory organs that are located in the periphery, and some of these sensory neurons do show rhythmic activity correlated with locomotor activity (see Blackshaw's early work). The numerous stretch receptors, in fact, have very large axons that pass through all the nerves recorded in the current paper.
In Fig. 4, it is interesting that the waveforms of all the units recorded in the PP nerve exhibit a reversal in waveform as compared to those in the DP nerve, which might indicate (based on bipolar differential recording) that the units in the PP nerve are being propagated in the opposite direction (i.e., are perhaps afferent). Rhythmic presynaptic inhibition and excitation is commonly seen for stretch receptors within the CNS (see the work of Burrows) and many such cells are under modulatory control.
Most likely, the majority of the units are from motoneurons, but we do not really know at this point. The authors should reframe their statements throughout the paper as: 'While multiple extracellular recordings have been performed previously (Eisenhart et al., 2000), these results (Figure 4) present the first quantitative analysis of multiple extracellular units, using spike sorting methods, which are activated throughout the crawling cycle.' In cases where the identity of the unit is known, then it is fine to state that, but when the identity of the unit is not known, then there should be some qualification and stated as 'putative motor units'
We understand the concern of Reviewer #2 regarding the type of neurons active during dopamine-induced crawling in isolated ganglia. However, we believe there is sufficient evidence to support that the recorded spikes originate from motoneurons. As readers may share the same concern, we have added a paragraph explaining why spikes from somatic sensory neurons such as P or T cells, or from stretch receptors, are unlikely to contribute (lines 206-214). We included the term putative in the abstract.
The Methods section:
Needs to include the full parameters that were used to assess whether bursting activity was qualified in ways to be considered crawling activity or not. Typically, crawl-like burst periods of no more than 25 seconds have been the limit for their qualification as crawling activity. In Fig 2F, for example, the inter-burst period is over 35 seconds; that coupled with an average 5 second burst duration would bring the burst period to 40 seconds, which is substantially out of range for there to be bursting relevant to crawl activity. Simply put, long DE-3 burst periods are often observed but may not be indicative of a crawl state as the CV motoneurons are no longer out of phase with DE-3. A number of papers have adopted this criterion.
We now indicate in the methods the range of period values measured in our experiments. For the reviewer informatio we show here histograms depicting the variability of period and duty cycle values recorded in our experiments (control conditions). The Reviewer can see that the bursting activity of DE-3 fall within what has been published.
Author response image 1.
Crawling in isolated ganglia. A. Histogram of periods end-to-end during crawling in isolated ganglia. The dotted line indicates the mean obtained from the averages of all experiments. The solid black line represents the mean of all cycles across all experiments. B. As in A, for the duty cycle calculated using end-to-end periods. (n = 210 cycles from 45 ganglia obtained from 32 leeches in all cases).
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
Minor comments-
Line 100: "In the frame of the recurrent inhibitory circuit, NS is the target of inhibitory signals". Suggestion: 'Within the framework of the recurrent inhibitory circuit, NS is the target of inhibitory signals.'
Changed as suggested (line 107).
Line 163: "This series of experiments proves that, as predicted based on the known circuit (Figure 164 1C), inhibitory signals onto NS premotor neurons were transmitted to DE-3 motoneurons and counteracted their excitatory drive during crawling, limiting their firing frequency". I think this sentence is too strong plus needs some editing. Suggestion: 'As predicted based on the known circuit (Figure 164 1C), this series of experiments indicates that inhibitory signals onto NS premotor neurons are transmitted to DE-3 motoneurons, thus limiting their firing frequency and counteracting their excitatory drive during crawling."
Changed as suggested.
Lines 86, 292 and 304 and Fig 4 legend: "Different from DE-3, In-Phase units showed a marked decrease in the maximum bFF along time." Suggestion: Replace the word "along" with 'across' time. Also replace those words in the Fig 4 legend and Line 80...."along" (replace with 'across') the different stages of crawling.
Changed as suggested.
Line 311: "bursts and a concurrent inhibitory input via NS (Figure 7). Coherent with this interpretation, the activity level of the Anti- Phase units was not influenced by these inhibitory signals". Suggestion: Replace the word "coherent" with 'consistent'.
Changed as suggested.
Line 332: "...offer the particular advantage of allowing electrical manipulation of individual neurons in wildtype adults," I am unsure what the authors are attempting to convey. Not sure what they mean by "wildtype" in this context and why that would matter.
“wildtype” was eliminated
We thank Reviewer #2 for the suggested edits to the text.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This study advances the lab's growing body of evidence exploring higher-order learning and its neural mechanisms. They recently found that NMDA receptor activity in the perirhinal cortex was necessary for integrating stimulus-stimulus associations with stimulus-shock associations (mediated learning) to produce preconditioned fear, but it was not necessary for forming stimulus-shock associations. On the other hand, basolateral amygdala NMDA receptor activity is required for forming stimulus-shock memories. Based on these facts, the authors assessed: 1. why the perirhinal cortex is necessary for mediated learning but not direct fear learning and 2. the determinants of perirhinal cortex versus basolateral amygdala necessity for forming direct versus indirect fear memories. The authors used standard sensory preconditioning and variants designed to manipulate the novelty and temporal relationship between stimuli and shock and, therefore, the attentional state under which associative information might be processed. Under experimental conditions where information would presumably be processed primarily in the periphery of attention (temporal distance between stimulus/shock or stimulus pre-exposure), perirhinal cortex NMDA receptor activation was required for learning indirect associations. On the other hand, when information would likely be processed in focal attention (novel stimulus contiguous with shock), basolateral amygdala NMDA activity was required for learning direct associations. Together, the findings indicate that the perirhinal cortex and basolateral amygdala subserve peripheral and focal attention, respectively. The authors provide support for their conclusions using careful, hypothesis-driven experimental design, rigorous methods, and integrating their findings with the relevant literature on learning theory, information processing, and neurobiology. Therefore, this work will be highly interesting to several fields.
Strengths:
(1) The experiments were carefully constructed and designed to test hypotheses that were rooted in the lab's previous work, in addition to established learning theory and information processing background literature.
(2) There are clear predictions and alternative outcomes. The provided table does an excellent job of condensing and enhancing the readability of a large amount of data.
(3) In a broad sense, attention states are a component of nearly every behavioral experiment. Therefore, identifying their engagement by dissociable brain areas and under different learning conditions is an important area of research.
(4) The authors clearly note where they replicated their own findings, report full statistical measures, effect sizes, and confidence intervals, indicating the level of scientific rigor.
(5) The findings raise questions for future experiments that will further test the authors' hypotheses; this is well discussed.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript presents a series of experiments that further investigate the roles of the BLA and PRH in sensory preconditioning, with a particular focus on understanding their differential involvement in the association of S1 and S2 with shock.
Strengths:
The motivation for the study is clearly articulated, and the experimental designs are thoughtfully constructed. I especially appreciate the inclusion of Table 1, which makes the designs easy to follow. The results are clearly presented, and the statistical analyses are rigorous.
During the revision, the authors have adequately addressed my minor suggestions from the original version.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This study advances the lab's growing body of evidence exploring higher-order learning and its neural mechanisms. They recently found that NMDA receptor activity in the perirhinal cortex was necessary for integrating stimulus-stimulus associations with stimulus-shock associations (mediated learning) to produce preconditioned fear, but it was not necessary for forming stimulus-shock associations. On the other hand, basolateral amygdala NMDA receptor activity is required for forming stimulus-shock memories. Based on these facts, the authors assessed: (1) why the perirhinal cortex is necessary for mediated learning but not direct fear learning, and (2) the determinants of perirhinal cortex versus basolateral amygdala necessity for forming direct versus indirect fear memories. The authors used standard sensory preconditioning and variants designed to manipulate the novelty and temporal relationship between stimuli and shock and, therefore, the attentional state under which associative information might be processed. Under experimental conditions where information would presumably be processed primarily in the periphery of attention (temporal distance between stimulus/shock or stimulus pre-exposure), perirhinal cortex NMDA receptor activation was required for learning indirect associations. On the other hand, when information would likely be processed in focal attention (novel stimulus contiguous with shock), basolateral amygdala NMDA activity was required for learning direct associations. Together, the findings indicate that the perirhinal cortex and basolateral amygdala subserve peripheral and focal attention, respectively. The authors provide support for their conclusions using careful, hypothesis-driven experimental design, rigorous methods, and integrating their findings with the relevant literature on learning theory, information processing, and neurobiology. Therefore, this work will be highly interesting to several fields.
Strengths:
(1) The experiments were carefully constructed and designed to test hypotheses that were rooted in the lab's previous work, in addition to established learning theory and information processing background literature.
(2) There are clear predictions and alternative outcomes. The provided table does an excellent job of condensing and enhancing the readability of a large amount of data.
(3) In a broad sense, attention states are a component of nearly every behavioral experiment. Therefore, identifying their engagement by dissociable brain areas and under different learning conditions is an important area of research.
(4) The authors clearly note where they replicated their own findings, report full statistical measures, effect sizes, and confidence intervals, indicating the level of scientific rigor.
(5) The findings raise questions for future experiments that will further test the authors' hypotheses; this is well discussed.
Weaknesses:
As a reader, it is difficult to interpret how first-order fear could be impaired while preconditioned fear is intact; it requires a bit of "reading between the lines".
We appreciate the Reviewer’s point and have attempted to address on lines 55-63 of the revised paper: “In a recent pair of studies, we extended these findings in two ways. First, we showed that S1 does not just form an association with shock in stage 2; it also mediates an association between S2 and the shock. Thus, S2 enters testing in stage 3 already conditioned, able to elicit fear responses (Wong et al., 2019). Second, we showed that this mediated S2-shock association requires NMDAR-activation in the PRh, as well as communication between the PRh and BLA (Wong et al., 2025). These findings raise two critical questions: 1) why is the PRh engaged for mediated conditioning of S2 but not for direct conditioning of S1; and 2) more generally, what determines whether the BLA and/or PRh is engaged for conditioning of the S1 and/or S2?”
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This paper continues the authors' research on the roles of the basolateral amygdala (BLA) and the perirhinal cortex (PRh) in sensory preconditioning (SPC) and second-order conditioning (SOC). In this manuscript, the authors explore how prior exposure to stimuli may influence which regions are necessary for conditioning to the second-order cue (S2). The authors perform a series of experiments which first confirm prior results shown by the author - that NMDA receptors in the PRh are necessary in SPC during conditioning of the first-order cue (S1) with shock to allow for freezing to S2 at test; and that NMDA receptors in the BLA are necessary for S1 conditioning during the S1-shock pairings. The authors then set out to test the hypothesis that the PRh encodes associations in a peripheral state of attention, whereas the BLA encodes associations in a focal state of attention, similar to the A1 and A2 states in Wagner's theory of SOP. To do this, they show that BLA is necessary for conditioning to S2 when the S2 is first exposed during a serial compound procedure - S2-S1-shock. To determine whether pre-exposure of S2 will shift S2 to a peripheral focal state, the authors run a design in which S2-S1 presentations are given prior to the serial compound phase. The authors show that this restores NMDA receptor activity within the PRh as necessary for the fear response to S2 at test. They then test whether the presence of S1 during the serial compound conditioning allows the PRh to support the fear responses to S2 by introducing a delay conditioning paradigm in which S1 is no longer present. The authors find that PRh is no longer required and suggest that this is due to S2 remaining in the primary focal state.
Strengths:
As with their earlier work, the authors have performed a rigorous series of experiments to better understand the roles of the BLA and PRh in the learning of first- and second-order stimuli. The experiments are well-designed and clearly presented, and the results show definitive differences in functionality between the PRh and BLA. The first experiment confirms earlier findings from the lab (and others), and the authors then build on their previous work to more deeply reveal how these regions differ in how they encode associations between stimuli. The authors have done a commendable job of pursuing these questions.
Table 1 is an excellent way to highlight the results and provide the reader with a quick look-up table of the findings.
Weaknesses:
The authors have attempted to resolve the question of the roles of the PRh and BLA in SPC and SOC, which the authors have explored in previous papers. Laudably, the authors have produced substantial results indicating how these two regions function in the learning of first- and second-order cues, providing an opportunity to narrow in on possible theories for their functionality. Yet the authors have framed this experiment in terms of an attentional framework and have argued that the results support this particular framework and hypothesis - that the PRh encodes peripheral and the BLA encodes focal states of learning. This certainly seems like a viable and exciting hypothesis, yet I don't see why the results have been completely framed and interpreted this way. It seems to me that there are still some alternative interpretations that are plausible and should be included in the paper.
We appreciate the Reviewer’s point and have attempted to address it on lines 566-594 of the Discussion: “An additional point to consider in relation to Experiments 3A, 3B, 4A and 4B is the level of surprise that rats experienced following presentations of the familiar S2 in stage 2. Specifically, in Experiments 3A and 3B, S2 was followed by the expected S1 (low surprise) and its conditioning required activation of NMDA receptors in the PRh and not the BLA. By contrast, in Experiments 4A and 4B, S2 was followed by omission of the expected S1 (high surprise) and its conditioning required activation of NMDA receptors in the BLA and not the PRh. This raises the possibility that surprise, or prediction error, also influences the way that S2 is processed in focal and peripheral states of attention. When prediction error is low, S2 is processed in the peripheral state of attention: hence, learning under these circumstances requires NMDA receptor activation in the PRh and not the BLA. By contrast, when prediction error is high, S2 is preserved in the focal state of attention: hence, learning under these circumstances requires NMDA receptor activation in the BLA and not the PRh. The impact of prediction error on the processing of S2 could be assessed using two types of designs. In the first design, rats are pre-exposed to S2-S1 pairings in stage 1 and this is followed by S2-S3-shock pairings in stage 2. The important feature of this design is that, in stage 2, the S2 is followed by surprise in omission of S1 and presentation of S3. Thus, if a large prediction error maintains processing of the familiar S2 in the BLA, we might expect that its conditioning in this design would require NMDA receptor activation in the BLA (in contrast to the results of Experiment 3B) and no longer require NMDA receptor activation in the PRh (in contrast to the results of Experiment 3A). In the second design, rats are pre-exposed to S2 alone in stage 1 and this is followed by S2-[trace]-shock pairings in stage 2. The important feature of this design is that, in stage 2, the S2 is not followed by the surprising omission of any stimulus. Thus, if a small prediction error shifts processing of the familiar S2 to the PRh, we might expect that its conditioning in this design would no longer require NMDA receptor activation in the BLA (in contrast to the results of Experiment 4B) but, instead, require NMDA receptor activation in the PRh (in contrast to the results of Experiment 4A). Future studies will use both designs to determine whether prediction error influences the processing of S2 in the focus versus periphery of attention and, thereby, whether learning about this stimulus requires NMDA receptor activation in the BLA or PRh.”
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript presents a series of experiments that further investigate the roles of the BLA and PRH in sensory preconditioning, with a particular focus on understanding their differential involvement in the association of S1 and S2 with shock.
Strengths:
The motivation for the study is clearly articulated, and the experimental designs are thoughtfully constructed. I especially appreciate the inclusion of Table 1, which makes the designs easy to follow. The results are clearly presented, and the statistical analyses are rigorous. My comments below mainly concern areas where the writing could be improved to help readers more easily grasp the logic behind the experiments.
Weaknesses:
(1) Lines 56-58: The two previous findings should be more clearly summarized. Specifically, it's unclear whether the "mediated S2-shock" association occurred during Stage 2 or Stage 3. I assume the authors mean Stage 2, but Stage 2 alone would not yet involve "fear of S2," making this expression a bit confusing.
We apologise for the confusion and have revised the summary of our previous findings on lines 55-63. The revised text now states: “In a recent pair of studies, we extended these findings in two ways. First, we showed that S1 does not just form an association with shock in stage 2; it also mediates an association between S2 and the shock. Thus, S2 enters testing in stage 3 already conditioned, able to elicit fear responses (Wong et al., 2019). Second, we showed that this mediated S2-shock association requires NMDAR-activation in the PRh, as well as communication between the PRh and BLA (Wong et al., 2025). These findings raise two critical questions: 1) why is the PRh engaged for mediated conditioning of S2 but not for direct conditioning of S1; and 2) more generally, what determines whether the BLA and/or PRh is engaged for conditioning of the S1 and/or S2?”
(2) Line 61: The phrase "Pavlovian fear conditioning" is ambiguous in this context. I assume it refers to S1-shock or S2-shock conditioning. If so, it would be clearer to state this explicitly.
Apologies for the ambiguity - we have omitted the term “Pavlovian” which may have been the source of confusion: The revised text on lines 60-63 now states: “These findings raise two critical questions: 1) why is the PRh engaged for mediated conditioning of S2 but not for direct conditioning of S1; and 2) more generally, what determines whether the BLA and/or PRh is engaged for conditioning of the S1 and/or S2?”
(3) Regarding the distinction between having or not having Stage 1 S2-S1 pairings, is "novel vs. familiar" the most accurate way to frame this? This terminology could be misleading, especially since one might wonder why S2 couldn't just be presented alone on Stage 1 if novelty is the critical factor. Would "outcome relevance" or "predictability" be more appropriate descriptors? If the authors choose to retain the "novel vs. familiar" framing, I suggest providing a clear explanation of this rationale before introducing the predictions around Line 118.
We have incorporated the suggestion regarding “predictability” while also retaining “novelty” as follows.
L76-85: “For example, different types of arrangements may influence the substrates of conditioning to S2 by influencing its novelty and/or its predictive value at the time of the shock, on the supposition that familiar stimuli are processed in the periphery of attention and, thereby, the PRh (Bogacz & Brown, 2003; Brown & Banks, 2015; Brown & Bashir, 2002; Martin et al., 2013; McClelland et al., 2014; Morillas et al., 2017; Murray & Wise, 2012; Robinson et al., 2010; Suzuki & Naya, 2014; Voss et al., 2009; Yang et al., 2023) whereas novel stimuli are processed in the focus of attention and, thereby, the amygdala (Holmes et al., 2018; Qureshi et al., 2023; Roozendaal et al., 2006; Rutishauser et al., 2006; Schomaker & Meeter, 2015; Wright et al., 2003).”
L116-120: “Subsequent experiments then used variations of this protocol to examine whether the engagement of NMDAR in the PRh or BLA for Pavlovian fear conditioning is influenced by the novelty/predictive value of the stimuli at the time of the shock (second implication of theory) as well as their distance or separation from the shock (third implication of theory; Table 1).”
(4) Line 121: This statement should refer to S1, not S2.
(5) Line 124: This one should refer to S2, not S1.
We have checked the text on these lines for errors and confirmed that the statements are correct. The lines encompassing this text (L121-130) are reproduced here for convenience:
(1) When rats are exposed to novel S2-S1-shock sequences, conditioning of S2 and S1 will be disrupted by a DAP5 infusion into the BLA but not into the PRh (Experiments 2A and 2B);
(2) When rats are exposed to S2-S1 pairings and then to S2-S1-shock sequences, conditioning of S2 will be disrupted by a DAP5 infusion into the PRh but not the BLA whereas conditioning of S1 will be disrupted by a DAP5 infusion into the BLA not the PRh (Experiments 3A and 3B);
(3) When rats are exposed to S2-S1 pairings and then to S2 (trace)-shock pairings, conditioning of S2 will be disrupted by a DAP5 into the BLA not the PRh (Experiments 4A and 4B).
(6) Additionally, the rationale for Experiment 4 is not introduced before the Results section. While it is understandable that Experiment 4 functions as a follow-up to Experiment 3, it would be helpful to briefly explain the reasoning behind its inclusion.
Experiment 4 follows from the results obtained in Experiment 3; and, as noted, the reasoning for its inclusion is provided locally in its introduction. We attempted to flag this experiment earlier in the general introduction to the paper; but this came at the cost of clarity to the overall story. As such, our revised paper retains the local introduction to this experiment. It is reproduced here for convenience:
“In Experiments 3A and 3B, conditioning of the pre-exposed S1 required NMDAR-activation in the BLA and not the PRh; whereas conditioning of the pre-exposed S2 required NMDAR-activation in the PRh and not the BLA. We attributed these findings to the fact that the pre-exposed S2 was separated from the shock by S1 during conditioning of the S2-S1-shock sequences in stage 2: hence, at the time of the shock, S2 was no longer processed in the focal state of attention supported by the BLA; instead, it was processed in the peripheral state of attention supported by the PRh.
“Experiments 4A and 4B employed a modification of the protocol used in Experiments 3A and 3B to examine whether a pre-exposed S1 influences the processing of a pre-exposed S2 across conditioning with S2-S1-shock sequences. The design of these experiments is shown in Figure 4A. Briefly, in each experiment, two groups of rats were exposed to a session of S2-S1 pairings in stage 1 and, 24 hours later, a session of S2-[trace]-shock pairings in stage 2, where the duration of the trace interval was equivalent to that of S1 in the preceding experiments. Immediately prior to the trace conditioning session in stage 2, one group in each experiment received an infusion of DAP5 or vehicle only into either the PRh (Experiment 4A) or BLA (Experiment 4B). Finally, all rats were tested with presentations of the S2 alone in stage 3. If the substrates of conditioning to S2 are determined only by the amount of time between presentations of this stimulus and foot shock in stage 2, the results obtained in Experiments 4A and 4B should be the same as those obtained in Experiments 3A and 3B: acquisition of freezing to S2 will require activation of NMDARs in the PRh and not the BLA. If, however, the presence of S1 in the preceding experiments (Experiments 3A and 3B) accelerated the rate at which processing of S2 transitioned from the focus of attention to its periphery, the results obtained in Experiments 4A and 4B will differ from those obtained in Experiments 3A and 3B. That is, in contrast to the preceding experiments where acquisition of freezing to S2 required NMDAR-activation in the PRh and not the BLA, here acquisition of freezing to S2 should require NMDAR-activation in the BLA but not the PRh.”
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
I greatly enjoyed reading and reviewing this manuscript, and so I only have boilerplate recommendations.
(1) I might add a couple of sentences discussing how/why preconditioned fear could be intact while first-order fear is impaired. Of course, if I am interpreting the provided interpretation correctly, the reason is that peripheral processing is still intact even when BLA NMDA receptors are blocked, and so mediated conditioning still occurs. Does this mean that mediated conditioning does not require learning the first-order relationship, and that they occur in parallel? Perhaps I just missed this, but I cannot help but wonder whether/how the psychological processes at play might change when first-order learning is impaired, so this would be greatly appreciated.
As noted above, we have revised the general introduction (around lines 55-59) to clarify that the direct S1-shock and mediated S2-shock associations form in parallel. Hence, manipulations that disrupt first-order fear to the S1 (such as a BLA infusion of the NMDA receptor antagonist, DAP5) do not automatically disrupt the expression of sensory preconditioned fear to the S2.
(2) Adding to the above - does the SOP or another theory predict serial vs parallel information flow from focal state to peripheral, or perhaps it is both to some extent?
SOP predicts both serial and parallel processing of information in its focal and peripheral states. That is, some proportion of the elements that comprise a stimulus may decay from the focal state of attention to the periphery (serial processing); hence, at any given moment, the elements that comprise a stimulus can be represented in both focal and peripheral states (parallel processing).
Given the nature of the designs and tools used in the present study (between-subject assessment of a DAP5 effect in the BLA or PRh), we selected parameters that would maximize the processing of the S2 and S1 stimuli in one or the other state of activation; hence the results of the present study. We are currently examining the joint processing of stimulus elements across focal and peripheral states using simultaneous recordings of activity in the BLA and PRh. These recordings are collected from rats trained in the different stages of a within-subject sensory preconditioning protocol. The present study created the basis for this work, which will be published separately in due course.
(3) The organization of PRh vs BLA is nice and consistent across each figure, but I would suggest adding any kind of additional demarcation beyond the colors and text, maybe just more space between AB / CD. The figure text indicating PRh/BLA is a bit small.
Thank you for the suggestion – we have added more space between the top and bottom panels of the figure.
(4) Line 496 typo ..."in the BLA but not the BLA".
Apologies for the type - this has been corrected.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
I found the experiments to be extremely well-designed and the results convincing and exciting. The hypothesis of the focal and peripheral states of attention being encoded by BLA and PRh respectively, is enticing, yet as indicated in the public review, this does not seem to be the only possible interpretation. This is my only serious comment for the authors.
(1) I think it would be worth reframing the article slightly to give credence to alternative hypotheses. Not to say that the authors' intriguing hypothesis shouldn't be an integral part of the introduction, but no alternatives are mentioned. In experiment 2, could the fact that S2 is already being a predictor of S1, not block new learning to S2? In the framework of stimulus-stimulus associations, there would be no surprise in the serial-compound stage of conditioning at the onset of S1. This may prevent direct learning of the S2-shock association within the BLA. This type of association may as well (S2 predicts S1, but it's omitted), which could support learning by S2. fall under the peripheral/focal theory, but I don't think it's necessary to frame this possibility in terms of a peripheral/focal theory. To build on this alternative interpretation, the absence of S1 in experiment 4 may induce a prediction error. The peripheral and focal states appear to correspond to A2 and A1 in SOP extremely well, and I think it would potentially add interest and support. If the authors do intend to make the paper a strong argument for their hypothesis, perhaps a few additional experiments may be introduced. If the novelty of S2 is critical for S2 not to be processed in a focal state during the serial compound stage, could pre-exposure of S2 alone allow for dependence of S2-shock on the PRh? Assuming this is what the authors would predict, this might disentangle the S-S theory mentioned above from the peripheral/focal theory. Or perhaps run an experiment S2-X in stage 1 and S2-S1-shock in stage 2? This said, I think the experiments are more than sufficient for an exciting paper as is, and I don't think running additional experiments is necessary. I would only argue for this if the authors make a hard claim about the peripheral/focal theory, as is the case for the way the paper is currently written.
We appreciate the reviewer’s excellent point and suggestions. We have included an additional paragraph in the Discussion on page 24 (lines 566-594). “An additional point to consider in relation to Experiments 3A, 3B, 4A and 4B is the level of surprise that rats experienced following presentations of the familiar S2 in stage 2. Specifically, in Experiments 3A and 3B, S2 was followed by the expected S1 (low surprise) and its conditioning required activation of NMDA receptors in the PRh and not the BLA. By contrast, in Experiments 4A and 4B, S2 was followed by omission of the expected S1 (high surprise) and its conditioning required activation of NMDA receptors in the BLA and not the PRh. This raises the possibility that surprise, or prediction error, also influences the way that S2 is processed in focal and peripheral states of attention. When prediction error is low, S2 is processed in the peripheral state of attention: hence, learning under these circumstances requires NMDA receptor activation in the PRh and not the BLA. By contrast, when prediction error is high, S2 is preserved in the focal state of attention: hence, learning under these circumstances requires NMDA receptor activation in the BLA and not the PRh. The impact of prediction error on the processing of S2 could be assessed using two types of designs. In the first design, rats are pre-exposed to S2-S1 pairings in stage 1 and this is followed by S2-S3-shock pairings in stage 2. The important feature of this design is that, in stage 2, the S2 is followed by surprise in omission of S1 and presentation of S3. Thus, if a large prediction error maintains processing of the familiar S2 in the BLA, we might expect that its conditioning in this design would require NMDA receptor activation in the BLA (in contrast to the results of Experiment 3B) and no longer require NMDA receptor activation in the PRh (in contrast to the results of Experiment 3A). In the second design, rats are pre-exposed to S2 alone in stage 1 and this is followed by S2-[trace]-shock pairings in stage 2. The important feature of this design is that, in stage 2, the S2 is not followed by the surprising omission of any stimulus. Thus, if a small prediction error shifts processing of the familiar S2 to the PRh, we might expect that its conditioning in this design would no longer require NMDA receptor activation in the BLA (in contrast to the results of Experiment 4B) but, instead, require NMDA receptor activation in the PRh (in contrast to the results of Experiment 4A). Future studies will use both designs to determine whether prediction error influences the processing of S2 in the focus versus periphery of attention and, thereby, whether learning about this stimulus requires NMDA receptor activation in the BLA or PRh.”
(3) I was surprised the authors didn't frame their hypothesis more in terms of Wagner's SOP model. It was minimally mentioned in the introduction or the authors' theory if it were included more in the introduction. I was wondering whether the authors may have avoided this framing to avoid an expectation for modeling SOP in their design. If this were the case, I think the paper stands on its own without modeling, and at least for myself, a comparison to SOP would not require modeling of SOP. If this was the authors' concern for avoiding it, I would suggest to the authors that they need not be concerned about it.
We appreciate the endorsement of Wagner’s SOP theory as a nice way of framing our results. We are currently working on a paper in which we use simulations to show how Wagner’s theory can accommodate the present findings as well as others in the literature on sensory preconditioning. For this reason, we have not changed the current paper in relation to this point.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
I have to preface my evaluation with a disclosure that I lack the mathematical expertise to fully assess what seems to be the authors' main theoretical contribution. I am providing this assessment to the best of my ability, but I cannot substitute for a reviewer with more advanced mathematical/physical training.
Summary:
This paper describes a new theoretical framework for measuring parsimony preferences in human judgments. The authors derive four metrics that they associate with parsimony (dimensionality, boundary, volume, and robustness) and measure whether human adults are sensitive to these metrics. In two tasks, adults had to choose one of two flower beds which a statistical sample was generated from, with or without explicit instruction to choose the flower bed perceptually closest to the sample. The authors conduct extensive statistical analyses showing that humans are sensitive to most of the derived quantities, even when the instructions encouraged participants to choose only based on perceptual distance. The authors complement their study with a computational neural network model that learns to make judgments about the same stimuli with feedback. They show that the computational model is sensitive to the tasks communicated by feedback and only uses the parsimony-associated metrics when feedback trains it to do so.
Strengths:
(1) The paper derives and applies new mathematical quantities associated with parsimony. The mathematical rigor is very impressive and is much more extensive than in most other work in the field, where studies often adopt only one metric (such as the number of causes or parameters). These formal metrics can be very useful for the field.
(2) The studies are preregistered, and the statistical analyses are strong.
(3) The computational model complements the behavioral findings, showing that the derived quantities are not simply equivalent to maximum-likelihood inference in the task.
(4) The speculations in the discussion section (e.g., the idea that human sensitivity is driven by the computational demands each metric requires) are intriguing and could usefully guide future work.
Weaknesses:
(1) The paper is very hard to understand. Many of the key details of the derived metrics are in the appendix, with very little accessible explanation in the main text. The figures helped me understand the metrics somewhat, although I am still not sure how some of them (such as boundary or robustness as measured here) are linked to parsimony. I understand that this is addressed by the derivations in the appendix, but as a computational cognitive scientist, I would have benefited from more accessible explanations. Important aspects of the human studies are also missing from the main text, such as the sample size for Experiment 2.
(2) It is not fully clear whether the sensitivity of human participants to some of the quantities convincingly reported here actually means that participants preferred shapes according to the corresponding aspect of parsimony. The title and framing suggest that parsimony "guides" human decision-making, which may lead readers to conclude that humans prefer more parsimonious shapes. I am not sure the sensitivity findings alone support this framing, but it might just be my misunderstanding of the analyses.
(3) The stimulus set included only four combinations of shapes, each designed to diagnostically target one of the theoretical quantities. It is unclear whether the results are robust or specific to these particular 4 stimuli.
(4) The study is framed as measuring "decision-making," but the task resembles statistical inference (e.g., which shape generated the data) or perceptual judgment. This is a minor point since "decision-making" is not well defined in the literature, yet the current framing in the title gave me the initial impression that humans would be making preference choices and learning about them over time with feedback.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This is a very interesting paper that documents how humans use a variety of factors that penalize model complexity and integrate over a possible set of parameters within each model. By comparison, trained neural networks also use these biases, but only on tasks where model selection was part of the reward structure. In the situation where training emphasizes maximum-likelihood decisions, only neural networks, but not humans, were able to adapt their decision-making. Humans continue to use model integration simplicity biases.
Strengths:
This study used a pre-registered plan for analyzing human data, which exceeds the standards compared to other current studies.
The results are technically correct.
Weaknesses:
The presentation of the results could be improved.
Author response:
Reviewer #1 (Public review)
I have to preface my evaluation with a disclosure that I lack the mathematical expertise to fully assess what seems to be the authors' main theoretical contribution. I am providing this assessment to the best of my ability, but I cannot substitute for a reviewer with more advanced mathematical/physical training.
Summary:
This paper describes a new theoretical framework for measuring parsimony preferences in human judgments. The authors derive four metrics that they associate with parsimony (dimensionality, boundary, volume, and robustness) and measure whether human adults are sensitive to these metrics. In two tasks, adults had to choose one of two flower beds which a statistical sample was generated from, with or without explicit instruction to choose the flower bed perceptually closest to the sample. The authors conduct extensive statistical analyses showing that humans are sensitive to most of the derived quantities, even when the instructions encouraged participants to choose only based on perceptual distance. The authors complement their study with a computational neural network model that learns to make judgments about the same stimuli with feedback. They show that the computational model is sensitive to the tasks communicated by feedback and only uses the parsimony-associated metrics when feedback trains it to do so.
Strengths:
(1) The paper derives and applies new mathematical quantities associated with parsimony. The mathematical rigor is very impressive and is much more extensive than in most other work in the field, where studies often adopt only one metric (such as the number of causes or parameters). These formal metrics can be very useful for the field.
(2) The studies are preregistered, and the statistical analyses are strong.
(3) The computational model complements the behavioral findings, showing that the derived quantities are not simply equivalent to maximum-likelihood inference in the task.
(4) The speculations in the discussion section (e.g., the idea that human sensitivity is driven by the computational demands each metric requires) are intriguing and could usefully guide future work.
Weaknesses:
(1) The paper is very hard to understand. Many of the key details of the derived metrics are in the appendix, with very little accessible explanation in the main text. The figures helped me understand the metrics somewhat, although I am still not sure how some of them (such as boundary or robustness as measured here) are linked to parsimony. I understand that this is addressed by the derivations in the appendix, but as a computational cognitive scientist, I would have benefited from more accessible explanations. Important aspects of the human studies are also missing from the main text, such as the sample size for Experiment 2.
(2) It is not fully clear whether the sensitivity of human participants to some of the quantities convincingly reported here actually means that participants preferred shapes according to the corresponding aspect of parsimony. The title and framing suggest that parsimony "guides" human decision-making, which may lead readers to conclude that humans prefer more parsimonious shapes. I am not sure the sensitivity findings alone support this framing, but it might just be my misunderstanding of the analyses.
(3) The stimulus set included only four combinations of shapes, each designed to diagnostically target one of the theoretical quantities. It is unclear whether the results are robust or specific to these particular 4 stimuli.
(4) The study is framed as measuring "decision-making," but the task resembles statistical inference (e.g., which shape generated the data) or perceptual judgment. This is a minor point since "decision-making" is not well defined in the literature, yet the current framing in the title gave me the initial impression that humans would be making preference choices and learning about them over time with feedback.
We are grateful for the supportive comments highlighting the rigor of our experimental design and data analysis. The Reviewer lists four points under “weaknesses”, to which we reply below.
(1) The paper is very hard to understand
In the revised version of the paper, we will expand the main text to include a more detailed and intuitive description of the terms of the Fisher Information Approximation, in particular clarifying the interpretation of robustness and boundary as parsimony. We also will include more details that are now given only in Methods, such as the sample size for the second experiment.
(2) Sensitivity of human participants
We do argue, and believe, that our data show that people tend to prefer simpler shapes. However, giving a well-posed definition of "preference" in this context turns out to be nontrivial.
At the very least, any statement such as "people prefer shape A over B" should be qualified with something like “when the distance of the data from both shapes is the same.” In other words, one should control for goodness-of-fit. Even before making any reference to our behavioral model, this phenomenon (a preference for the simpler model when goodness of fit is matched between models) is visible in Figure 3a, where the effective decision boundary used by human participants is closer to the more complex model than the cyan line representing the locus of points with equal goodness of fit under the two models (or equivalently, with the same Euclidean distance from the two shapes). The goal of our theory and our behavioral model is precisely to systematize this sort of control, extending it beyond just goodness-of-fit and allowing us to control simultaneously for multiple features of model complexity that may affect human behavior in different ways. In other words, it allows us not only to ask whether people prefer shape A over B after controlling for the distance of the data to the shapes, but also to understand to what extent this preference is driven by important geometrical features such as dimensionality, volume, curvature, and boundaries of the shapes. More specifically, and importantly, our theory makes it possible to measure the strength of the preference, rather than merely asserting its existence. In our modeling framework, the existence of a preference for simpler shapes is captured by the fact that the estimated sensitivities to the complexity penalties are positive (and although they differ in magnitude, all are statistically reliable).
(3) Generalization to different shapes
Thank you for bringing up this important topic. First, note that while dimensionality and volume are global properties of models and only take two possible values in our human tasks, the boundary and robustness penalties depend on the model and on the data and therefore assume a continuum of values through the tasks (note also that the boundary penalty is relevant for all task types, not just the one designed specifically to study it, because all models except the zero-dimensional dot have boundaries). Therefore, our experimental setting is less restrictive of what it may seem, because it explores a range of possible values for two of the four model features. However, we agree that it would be interesting to repeat our experiment with a broader range of models, perhaps allowing their dimensionality and volume to vary more. In the same spirit, it would be interesting to study the dependence of human behavior on the amount of available data. We believe that these are all excellent ideas for further study that exceed the scope of the present paper. We will include these important points in a revised Discussion.
(4) Usage of “decision making” vs “perceptual judgment”
Thank you. We will clarify better in the text that our usage of “decision making” overlaps with the idea of a perceptual judgment and that our experiments do not tackle sequential aspects of repeated decisions.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
This manuscript presents a sophisticated investigation into the computational mechanisms underlying human decision-making, and it presents evidence for a preference for simpler explanations (Occam's razor). The authors dissect the simplicity bias into four different components, and they design experiments to target each of them by presenting choices whose underlying models differ only in one of these components. In the learning tasks, participants must infer a "law" (a logical rule) from observed data in a way that operationalizes the process of scientific reasoning in a controlled laboratory setting. The tasks are complex enough to be engaging but simple enough to allow for precise computational modeling.
As a further novel feature, authors derive a further term in the expansion of the logevidence, which arises from boundary terms. This is combined with a choice model, which is the one that is tested in experiments. Experiments are run, but with humans and with artificial intelligence agents, showing that humans have an enhanced preference for simplicity as compared to artificial neural networks.
Overall, the work is well written, interesting, and timely, bridging concepts in statistical inference and human decision making. Although technical details are rather elaborate, my understanding is that they represent the state of the art.
I have only one main comment that I think deserves more comments. Computing the complexity penalty of models may be hard. It is unlikely that humans can perform such a calculation on the fly. As authors discuss in the final section, while the dimensionality term may be easier to compute, others (e.g., the volume term, which requires an integral) may be considerably harder to compute (it is true that they should be computed once and for all for each task, but still...). I wonder whether the sensitivity of human decision making with reference to the different terms is so different, and in particular whether it aligns with computational simplicity, or with the possibility of approximating each term by simple heuristics. Indeed, the sensitivity to the volume term is significantly and systematically lower than that of other terms. I wonder whether this relation could be made more quantitative using neural networks, using as a proxy of computational hardness the number of samples needed to reach a given error level in learning each of these terms.
Thank you. The computational complexity associated with calculating the different terms and its potential connection to human sensitivity to the terms is an intriguing topic. As we hinted at in the discussion, we agree with the reviewer that this is a natural candidate for further research, which likely deserves its own study and exceeds the scope of the present paper.
As a minor aside, at least for the present task the volume term may not be that hard to compute, because it can be expressed with the number of distinguishable probability distributions in the model (Balasubramanian 1996). Given the nature of our task, where noise is Gaussian, isotropic and with known variance, the geometry of the model is actually the Euclidean geometry of the plane, and the volume is simply the (log of the) length of the line that represents the one-dimensional models, measured in units of the standard deviation of the noise.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This is a very interesting paper that documents how humans use a variety of factors that penalize model complexity and integrate over a possible set of parameters within each model. By comparison, trained neural networks also use these biases, but only on tasks where model selection was part of the reward structure. In the situation where training emphasizes maximum-likelihood decisions, only neural networks, but not humans, were able to adapt their decision-making. Humans continue to use model integration simplicity biases.
Strengths:
This study used a pre-registered plan for analyzing human data, which exceeds the standards compared to other current studies.
The results are technically correct.
Weaknesses:
The presentation of the results could be improved.
We thank the reviewer for their appreciation of our experimental design and methodology, and for pointing out (in the separate "recommendations to authors") a few passages of the paper where the presentation could be improved. We will clarify these passages in the revision.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
The study by Klotzsche et al. examines whether emotional facial expressions can be decoded from EEG while participants view 3D faces in immersive VR and whether stereoscopic depth cues affect these neural representations. Participants viewed computer-generated faces (three identities, four emotions) rendered either stereoscopically or monoscopically, while performing an emotion recognition task. Time-resolved multivariate decoding revealed above-chance decodability of facial expressions from EEG. Importantly, decoding accuracy did not differ between monoscopic and stereoscopic viewing. This indicates that the neural representation of expressions is robust against stereoscopic disparity for the relevant features. However, a separate classifier could distinguish the depth condition (mono vs. stereo) from EEG, i.e., the pattern of neuronal activity differs between conditions, but not in ways relevant for the decoding of emotions. It had an early peak and a temporal profile similar to identity decoding, suggesting that early, task-irrelevant visual differences are captured neurally. Cross-decoding further demonstrated that expression decoders trained in one depth condition could generalize to the other, supporting the idea of representational invariance. Eye-tracking analyses showed that expressions and identities could be decoded from gaze patterns, but not the depth condition, and EEG- and gaze-based decoding performances were not correlated across participants. Overall, this work shows that EEG decoding in VR is feasible and sensitive, and suggests that stereoscopic cues are represented in the brain but do not influence the neural processing of facial expressions. This study addresses a relevant question with state-of-the-art experimental and data analysis techniques.
Strengths:
(1) It combines EEG, virtual reality stereoscoptic and monoscopic presentation of visual stimuli, and advanced data analysis methods to address a timely question.
(2) The figures are of very high quality.
(3) The reference list is appropriate and up to date.
Weaknesses:
(1) The introduction-results-discussion-methods order makes it hard to follow the Results without repeatedly consulting the Methods. Please introduce minimal, critical methodological context at the start of each Results subsection; reserve technical details for Methods/Supplement.
(2) Many Results subsections begin with a crisp question and present rich analyses, but end without a short synthesis. Please add 1-2 sentences that explicitly answer the opening question and state what the analyses demonstrate.
(3) The Results compellingly show that (a) expressions are decodable from EEG and (b) mono vs stereo trials are decodable from EEG; yet expression decoding is comparable across mono and stereo. It would help if you articulate why depth is neurally distinguishable while leaving expression representations unchanged. Maybe improve the discussion of the results of source localization and give a more detailed connection to what we already know about the processing of disparity.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This study investigates two main questions:
(1) whether brain activity recorded during immersive virtual reality can differentiate facial expressions and stereoscopic depth, and
(2) whether depth cues modulate facial information processing.
The results show that both expression and depth information can be decoded from multivariate EEG recorded in a head-mounted VR setup. However, the results show that the decoding performance of facial expressions does not benefit from depth information.
Strengths:
The study is technically strong and well executed. EEG data are of high quality despite the challenges of recording inside a head-mounted VR system. The work effectively combines stereoscopic stimulus presentation, eye-tracking to monitor gaze behavior, and time-resolved multivariate decoding techniques. Together, these elements provide an exemplary demonstration of how to collect and analyze high-quality EEG data in immersive VR environments.
Weaknesses:
The major limitation concerns the theoretical question about how stereoscopic depth modulates facial expression processing. While previous work has suggested that stereoscopic depth cues can shape natural face perception and emphasize the importance of binocular information in recognizing facial expressions (lines 95-97), the present study reports a null effect of depth. However, the stimulus configuration they used likely constrained the ability to detect any depth-related effects. All facial stimuli were static, frontal, and presented at a fixed distance. This design leads to near-ceiling behavioral performance and no behavioral effect of depth on expression recognition. It makes the null modulation of depth on expression processing unsurprising and limits the theoretical reach of the study. Adding more subtle or naturalistic features (such as various viewing angles and dynamic expressions) to the stimulus set if the authors aim to advance a strong theoretical claim about the role of binocular disparity. Or reframing the work as a technical validation of EEG decoding in this context.
Another issue relates to the claim that eye movements cannot explain the EEG decoding results. It is a real challenge to remove eye-movement-related artifacts and confounds, as the VR setup tends to encourage viewers to explore the environment freely. However, nearly half of the eye-tracking datasets were lost (usable in only 17 of 33 participants), which substantially weakens the evidence for EEG-gaze dissociation. Moreover, it would be almost impossible to decode facial information from only two-dimensional gaze direction, given that with 60 EEG channels, the decoding accuracy was modest (AUC ≈ 0.60). These two factors together limited the strength of the reported null correlation between neural and eye-data decoding.
The decoding analysis appears to use all 60 EEG channels as input features. I wonder why the authors did not examine using more spatially specific channel subsets. Facial expression and depth cues are known to preferentially engage occipito-temporal regions (e.g., N170-related sites), yet the current approach treats all sensors equally. Including all the channels may add noise and irrelevant signals to facial information decoding. Besides, using a subset of spatial-specific channels would align more directly with the subsequent source reconstruction.
Author response:
We thank the reviewers for their thoughtful and constructive comments. We are pleased that they found the study technically strong and the integration of EEG decoding, immersive VR, and eye tracking valuable.
Across all three reviews, several points of clarification emerged. In our revision, we will focus on:
(1) Improving clarity and structure of the manuscript (Reviewer #1).
We will strengthen the flow between the Methods and Results subsections and include explicit concluding statements for the single results.
(2) Emphasize methodological scope and limitations in terms of stimulus set and generalizability (Reviewers #2 and #3).
We will further emphasize that a key objective was to establish, for the first time, the methodological feasibility of decoding facial features (especially emotional expressions) under VR conditions, and that our stimulus set (consisting of facial expressions that were easy to distinguish) limits (a) the task-relevance (and thus possibly the neural integration) of depth information and (b) the generalizability to less easily distinguishable settings. We appreciate the suggestion of an inverted-face control to further investigate the extent to which the decoding results were based on low-level features; however, we do not plan a follow-up experiment at this stage; instead, we will discuss this limitation more explicitly.
We believe these revisions will substantially strengthen the manuscript and further highlight its methodological focus.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
In the present manuscript, de Bos and Kutay investigate the functional implications of persistent microtubule-ER contacts as cells go through mitosis. To do so, they resorted to investigating phosphorylation mutants of the ER-Microtubule crosslinker Climp63. They found that phosphodeficient Climp63 mutants induce a severe SAC-dependent mitotic delay after normal chromosome alignment, with an impressive mitotic index of approximately 75%. Strikingly, this was often associated with massive nuclear fragmentation into up to 30 micronuclei that are able to recruit both core and non-core nuclear envelope components. One particular residue (S17) that is phosphorylated by Cdk1 seems to account for most, if not all, these phenotypes. Furthermore, the authors use the impact on mitosis as an indirect way to map the microtubule binding domain of Climp63, which has remained controversial, and found that it is mostly restricted to the N-terminal 28 residues of Climp63. Of note, despite the strong impact on mitosis, persistent microtubule-ER contacts did not affect the distribution of other organelles during mitosis, such as mitochondria or lysosomes.
Strengths:
Overall, this work provides important mechanistic insight into the functional implications of ER-microtubule network remodelling during mitosis and should be of great interest to a vast readership of cell biologists.
Weaknesses:
Some of the key findings appear somewhat preliminary and would be worth exploring further to substantiate some of the claims and clarify the respective impact on mitosis and nuclear envelope reassembly on the resulting micronuclei.
The following suggestions would significantly clarify some key points:
(1) The striking increase in mitotic index in cells expressing the Climp63 phosphodefective mutant, together with their live cell imaging data indicating extensive mitotic delays that can be relieved by SAC inhibition, suggests that SAC silencing is significantly delayed or even impossible to achieve. The fact that most chromosomes align in 12 min, irrespective of the expression of the Climp63 phosphodefective mutant, suggests that initial microtubule-kinetochore interactions are not compromised, but maybe cannot be stably maintained. Alternatively, the stripping of SAC proteins from kinetochores by dynein along attached microtubules might be compromised, despite normal microtubule-kinetochore attachments. The authors allude to both these possibilities, but unfortunately, they never really test them. This could easily be done by immunofluorescence with a Mad1 or c-Mad2 antibody to inspect which fraction of kinetochores (co-stained with a constitutive kinetochore marker, such as CENP-A or CENP-C) are positive for these SAC proteins. If just a small fraction, then the stability of some attachments is likely the cause. If most/all kinetochores retain Mad1/c-Mad2, then it is probably an issue of silencing the SAC.
(2) The authors use the increase in mitotic index (H3 S10 phosphorylation levels) as a readout for the MT binding efficiency of Climp63 and respective mutants. Although suggestive, this is fairly indirect and requires additional confirmation. For example, the authors could perform basic immunofluorescence in fixed cells to inspect co-localization of Climp63 (and its mutants) with microtubules.
(3) The authors refer in the discussion that the striking nuclear fragmentation seen upon mitotic exit of cells expressing Climp63 phosphodefective mutant has not been reported before, and yet it is strikingly similar to what has been previously observed in cells treated with taxol (they cite Samwer et al. 2017, but they might elect to cite also Mitchison et al., Open Biol, 2017 and most relevantly Jordan et al., Cancer Res, 1996). This striking similarity and given the extensive mitotic delay observed in the Climp63 phosphodefective mutant, it is tempting to speculate that these cells are undergoing mitotic slippage (i.e., cells exit mitosis without ever satisfying the SAC) because they are unable to silence/satisfy the SAC. Indeed, the scattered micronuclei morphology has also been observed in cells undergoing mitotic slippage (e.g., Brito and Rieder, Curr Biol., 2006). The experiment suggested in point #1 should also shed light on this problem. The authors might want to consider discussing this possible explanation to interpret the observed phenotypes.
(4) One of the most significant implications of the findings reported in this paper is that microtubule proximity does not seem to impact the assembly of either core or non-core nuclear envelope proteins on micronuclei (that possibly form due to mitotic slippage, rather than normal anaphase). These results challenge some models explaining nuclear envelope defects in micronuclei derived from lagging chromosomes due to the proximity of microtubules, and, as the authors point out at the very end, other reasons might underlie these defects. Along this line, the authors might elect to cite Afonso et al. Science, 2014, and Orr et al., Cell Reports, 2022, who provide evidence that a spindle midzone-based Aurora B gradient, rather than microtubules per se, underlie the nuclear envelope defects commonly seen in micronuclei derived from lagging chromosomes during anaphase.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study addresses the hypothesis that the strikingly higher prevalence of autoimmune diseases in women could be the result of biased thymic generation or selection of TCR repertoires. The biological question is important, and the hypothesis is valuable. Although the topic is conceptually interesting and the dataset is rich, the study has a number of major issues that require substantial improvement. In several instances, the authors conclude that there are no sex-associated differences for specific parameters, yet inspection of the data suggests visible trends that are not properly quantified. The authors should either apply more appropriate statistical approaches to test these trends or provide stronger evidence that the observed differences are not significant. In other analyses, the authors report the differences between sexes based on a pulled analysis of TCR sequences from all the donors, which could result in differences driven by one or two single donors (e.g., having particular HLA variants) rather than reflect sex-related differences.
Strengths:
The key strength of this work is the newly generated dataset of TCR repertoires from sorted thymocyte subsets (DP and SP populations). This approach enables the authors to distinguish between biases in TCR generation (DP) and thymic selection (SP). Bulk TCR sequencing allows deeper repertoire coverage than single-cell approaches, which is valuable here, although the absence of TRA-TRB pairing and HLA context limits the interpretability of antigen specificity analyses. Importantly, this dataset represents a valuable community resource and should be openly deposited rather than being "available upon request."
Weaknesses:
Major:
(1) The authors state that there is "no clear separation in PCA for both TRA and TRB across all subsets." However, Figure 2 shows a visible separation for DP thymocytes (especially TRA, and to a lesser degree TRB) and also for TRA of Tregs. This apparent structure should be acknowledged and discussed rather than dismissed.
(2) Supplementary Figures 2-5 involve many comparisons, yet no correction for multiple testing appears to be applied. After appropriate correction, all the reported differences would likely lose significance. These analyses must be re-evaluated with proper multiple-testing correction, and apparent differences should be tested for reproducibility in an external dataset (for example, the pediatric thymus and peripheral blood repertoires later used for motif validation).
(3) Supplementary Figure 6 suggests that women consistently show higher Rényi entropies across all subsets. Although individual p-values are borderline, the consistent direction of change is notable. The authors should apply an integrated statistical test across subsets (for example, a mixed-effects model) to determine whether there is an overall significant trend toward higher diversity in females.
(4) Figures 4B and S8 clearly indicate enrichment of hydrophobic residues in female CDR3s for both TRA and TRB (excluding alanine, which is not strongly hydrophobic). Because CDR3 hydrophobicity has been linked to increased cross-reactivity and self-reactivity (see, e.g., Stadinski et al., Nat Immunol 2016), this observation is biologically meaningful and consistent with higher autoimmune susceptibility in females.
(5) The majority of "hundreds of sex-specific motifs" are probably donor-specific motifs confounded by HLA restriction. This interpretation is supported by the failure to validate motifs in external datasets (pediatric thymus, peripheral blood). The authors should restrict analysis to public motifs (shared across multiple donors) and report the number of donors contributing to each motif.
(6) When comparing TCRs to VDJdb or other databases, it is critical to consider HLA restriction. Only database matches corresponding to epitopes that can be presented by the donor's HLA should be counted. The authors must either perform HLA typing or explicitly discuss this limitation and how it affects their conclusions.
(7) Although the age distributions of male and female donors are similar, the key question is whether HLA alleles are similarly distributed. If women in the cohort happen to carry autoimmune-associated alleles more often, this alone could explain observed repertoire differences. HLA typing and HLA comparison between sexes are therefore essential.
(8) In some analyses (e.g., Figures 8C-D) data are shown per donor, while others (e.g., Fig. 8A-B) pool all sequences. This inconsistency is concerning. The apparent enrichment of autoimmune or bacterial specificities in females could be driven by one or two donors with particular HLAs. All analyses should display donor-level values, not pooled data.
(9) The reported enrichment of matches to certain specificities relative to the database composition is conceptually problematic. Because the reference database has an arbitrary distribution of epitopes, enrichment relative to it lacks biological meaning. HLA distribution in the studied patients and HLA restrictions of antigens in the database could be completely different, which could alone explain enrichment and depletions for particular specificities. Moreover, differences in Pgen distributions across epitopes can produce apparent enrichment artifacts. Exact matches typically correspond to high-Pgen "public" sequences; thus, the enrichment analysis may simply reflect variation in Pgen of specific TCRs (i.e., fraction of high-Pgen TCRs) across epitopes rather than true selection. Consequently, statements such as "We observed a significant enrichment of unique TRB CDR3aa sequences specific to self-antigens" should be removed.
(10) The overrepresentation of self-specific TCRs in females is the manuscript's most interesting finding, yet it is not described in detail. The authors should list the corresponding self-antigens, indicate which autoimmune diseases they relate to, and show per-donor distributions of these matches.
(11) The concept of polyspecificity is controversial. The authors should clearly explain how polyspecific TCRs were defined in this study and highlight that the experimental evidence supporting true polyspecificity is very limited (e.g., just a single TCR from Figure 5 from Quiniou et al.).
Minor:
(1) Clarify why the Pgen model was used only for DP and CD8 subsets and not for others.
(2) The Methods section should define what a "high sequence reliability score" is and describe precisely how the "harmonized" database was constructed.
(3) The statement "we generated 20,000 permuted mixed-sex groups" is unclear. It is not evident how this permutation corrects for individual variation or sex bias. A more appropriate approach would be to train the Pgen model separately for each individual's nonproductive sequences (if the number of sequences is large enough).
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This paper explores how spatial attention affects foveal information processing across different spatial frequencies. The results indicate that exogenously directed attention enhances contrast sensitivity for low- to mid-range spatial frequencies (4-8 CPD), with no significant benefits for higher spatial frequencies (12-20 CPD). However, asymptotic performance increased as a result of spatial attention independently of spatial frequency.
Strengths:
The strengths of this article lie in its methodological approach, which combines a psychophysical experiment with precise control over the information presented in the foveola.
Weaknesses:
The authors acknowledge that they used the standard approach of analyzing observer-averaged data, but recognize that this method has limitations: it ignores the uncertainty associated with parameter estimates and the relationships between different parameters of the psychometric model. This may affect the interpretation of attentional effects. In the future, mixed-effects models at the trial level could overcome these limitations.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
The study from Wu and Turrigiano investigates how disruption of taste coding in a mouse model of autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) affects aversive learning in the context of a conditioned taste aversion (CTA) paradigm. The experiments combine 2-photon calcium imaging of neurons in the gustatory portion of the anterior insular cortex (i.e., gustatory cortex) with behavioral training and testing. The authors rely on Shank3 knockout mice as a model for ASDs. The authors found that Shank3 mice learn CTA more slowly and extinguish the memory more rapidly than control subjects. Calcium imaging identified impairments in taste-evoked activity associated with memory encoding and extinction. During memory encoding, the authors found less suppressed neuronal activity and increased correlated variability in Shank3 mice compared to controls. During extinction, they observed a faster loss of taste selectivity and degradation of taste discriminability in mutants compared to controls.
Strengths:
This is a well-written manuscript that presents interesting findings. The results on the learning and extinction deficits in Shank3 mice are of particular interest. Analyses of neural activity are well conducted and provide important information on the type of impaired cortical activity that may correlate with behavioral deficits.
Weaknesses:
(1) The experiments rely on three groups: CS-only WT, CTA WT, and CTA KO. Can the authors provide a rationale for not having a CS-only KO group?
(2) The authors design an effective behavioral paradigm comparing consumption of water and saccharin and tracking extinction (Figure 3). This paradigm shows differences in licking across distinct behavioral conditions. For instance, during T1, licking to water strongly differs from licking to saccharin for both WT and KO. During T2, licking to water strongly differs from licking to saccharin only for WT (much less for KO), and licking to saccharin in WT differs from that in KO. These differences in taste sampling across conditions could contribute to some of the effects on neural activity and discriminability reported in Figures 5 and 6. That is sucrose and water trials may be highly discriminable because in one case the mouse licks and in the other it does not (or licks much less). The author may want to address this issue.
(3) Are there any omission trials following CTA? If so, they should be quantified and reported. How are the omission trials treated with regard to the analyses?
(4) The authors describe the extinction paradigm as "alternative choice". In decision-making, alternative choice paradigms typically require 2 lateral spouts to report decisions following the sampling from a central spout. To avoid confusion, the authors may want to define their paradigm as alternative sampling.
(5) Figure 4 reports that CTA increases the proportion of neurons that consistently respond to saccharin and water across days. While the saccharin result could be an effect of aversive learning, it is less clear why the phenomenon would generalize to water as well. Can the authors provide an explanation?
(6) The recordings are performed in the part of the anterior insular cortex that is typically defined as "gustatory cortex" (GC). Given the functional heterogeneity of the anterior insular cortex (AIC) and given that the authors do not sample all of the anteroposterior extent of AIC, I would suggest being more explicit about their positioning in GC. Also, some citations (e.g., Gogolla et al, 2014) refer to the posterior insular cortex, which is considered more inherently multimodal than GC. GC multimodality is typically associative in nature, as only a few neurons respond to sound and light in naïve animals.
(7) It would be useful to add summary figures showing the extent of viral spread as well as GRIN lens placement.
(8) I encourage the authors to add Ns every time percentages are reported. How many neurons have been recorded in each condition? Can the authors provide the average number of neurons recorded per session and per animal?
(9) It looks like some animals learned more than others (Figure 1E or Figure 3C). Is it possible to compare neural activity across animals that showed different degrees of learning?
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Wu and Turrigiano investigated how cortical taste coding during conditioned taste aversion (CTA) learning is affected in Shank3 knockout (KO) mice, a model of monogenic ASD. Using longitudinal two-photon calcium imaging of AIC neurons, the authors show that Shank3 KO mice exhibit reduced suppression of activity in a subset of neurons and a higher correlated variability in neural activity. This is accompanied by slower learning and faster extinction of aversive taste memories. These results suggest that Shank3 loss compromises the flexibility and stability of cortical representations underlying adaptive behaviour.
Major strengths:
(1) Conceptual significance: The study connects a molecular ASD risk gene (Shank3) to flexible sensory encoding, bridging genetics, systems neuroscience, and behaviour.
(2) Technical rigour: Longitudinal calcium imaging with cell-registration across learning and extinction sessions is technically demanding and well-executed.
(3) Behavioural paradigm: The use of both acquisition and extinction paradigms provides a more nuanced picture of learning dynamics.
(4) Analyses: Correlated variability, discriminability indices, and population decoding analyses are robust and appropriate for addressing behavioural and network-level coding changes.
Major weaknesses:
(1) Causality: The paper infers that increased correlated variability causes learning deficits, but no causal tests (e.g., optogenetic modulation of inhibition or interneuron rescue) are presented to confirm this.
(2) Behavioural scope: The study focuses exclusively on taste aversion; generalisation to other flexible learning paradigms (e.g., reversal or probabilistic tasks) is not addressed.
(3) Mechanistic insights: While providing interesting findings of altered sensory perception and extinction of learning-related signals in AIC, it offered nearly no mechanistic insights. This makes the interpretation, especially on how generalisable these findings are, difficult. Also, different reported findings are "potentially" connected, but the exact relation between increased correlated variability and faster loss of taste selectivity cannot be assessed.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
In this study, Wu & Turrigiano investigate an ethologically relevant form of associative learning (conditioned taste aversion - CTA) and its extinction in the Shank3 KO mouse model of ASD. They also examine the underlying circuits in the anterior insular cortex (AIC) simultaneously, using two-photon calcium imaging through a GRIN lens. They report that Shank3 KO mice learn CTA slower and suggest that this is mediated by a reduction in tastant-stimulus activity suppression of AIC neurons and a reduced signal-to-noise ratio due to increased noise correlations in AIC neurons. Interestingly, once Shank3 KO mice acquire CTA, they extinguish the aversive memory more rapidly than wild-type mice. This accelerated extinction is accompanied by a faster loss of neuronal and population-level taste selectivity and coding in the AIC compared to WT mice.
This is an important study that uses in vivo methods to assess circuit dysfunction in a mouse model of ASD, related to sensory perception valence (in this case, taste). The study is well executed, the data are of high quality, and the analytical procedures are detailed. Furthermore, the behavioural paradigm is well thought out, particularly the approach for assessing extinction through repeated retrieval sessions (T1-T5), which effectively tests discrimination between saccharin and water rather than relying solely on lick counts or total consumption as a measure of extinction. Finally, the statistical tests used are appropriate and justified.
There is, however, a missing link between the behavioural findings and the underlying mechanisms. More specifically:
(1) The authors don't make a causal link between the behaviour and AIC neurophysiology, both the percentage of suppressed cells and the coactivity measurements. For the % of suppressed cells, it seems that both WT and KO cells are suppressed in the transition between CST1 and CST2 (Figure 1L), yet only the WT mice exhibit CTA (at least by CST2). For the taste-elicited coactivity measure, it seems that there is an increase in coactivity from CST1 to CST2 in WT (Figure 2C - blue, although not statistically tested?), but persistently higher coactivity in KO. Is this change of coactivity in WT important for the expression of CTA? Plotting behavioral performance (from Figure 1G) against coactivity (from Figure 2C) for each animal would be informative.
(2) Shank3 KO cells already show an increase in baseline coactivity (Figure 2- figure supplement 1), and the authors never examine CS-only responses in the KO group, therefore making it difficult to determine whether elevated coactivity and noise correlations reflect a generalized AIC abnormality in Shank3 KOs (perhaps through impaired PV-mediated inhibition in insular cortex - Gogolla et al, 2014) that is not directly responsible/related to CTA?
(3) How do the authors interpret the large range of lick ratios (Figure 1G) for WT (almost bi-modal distribution)? Is there a within-subject correlation with any of the neurophysiological measurements to suggest a relationship between AIC neurophysiology and behavioural expression of CTA?
(4) Indeed, CTA appears to be successfully achieved for Shank3 KO mice delayed by 1 day, as the level of saccharin aversion during the first retrieval session (T1) is comparable between Shank3 KO and WTs. In this context, not extending the first part of the paradigm to include CST3 seems to be a missed opportunity. Doing so would have allowed for within-cell and within-subject comparison of taste-elicited pairwise correlation across the learning and to investigate the neural mechanism of delayed extinction in KOs more effectively.
(5) How to interpret Figure 5F: Absolute discriminability is lower for T5 for CTA WT and CTA KO compared to CS-only? Why would AIC neurons have less information on taste identity by the end of extinction than during the unconditioned (CS-only) condition? And if that is the case, how is decoding accuracy in Figure 6C higher in T5 for CTA WT vs CS-only?
Neuralink Overview, Fall 2025
"The day after he got Telepathy, he was playing [Civilization VI] for 9 hours straight" 3:36
Hun systeem wordt nu voor 100% in Europa geproduceerd en weegt 30 gram, tegenover 176 gram voor concurrenten die op Jetson zijn gebaseerd. Het heeft een stroomverbruik van 3 watt, een efficiëntieverbetering van 88%.
a sixth in weight, power reduction from 15 to 3 Watt range.
https://www.amazon.com/MicroSpark-Heavyweight-Checklist-Strategy-Tinplate/dp/B0DHYKG6VT?th=1 MicroSpark 3x5" index card product with holder and tin can
Article 29: The dowry is fixed at 3 cows: one for the girl, two for the father and mother.
One thing I noticed about medieval west Africa and even pre medieval times is that the cattle or cow is a big currency. The cow is a bid currency because of their milk and the offspring they bear. Even today some places and tribes in west Africa herd their cattle and trade them. Also being a sign of a abundance of wealth.- Abdoulaye Gueye
Article 4: The society is divided into age groups. Those born during a period of three years in succession belong to the same age-group. The members of the intermediary class between young and old people, should be invited to take part in the making of important decisions concerning the society
I find this Interesting because, today in many west African societies you are bundled are within a friend group as your age group. The age group are usually anything between 3 years. And middle-aged people are usually in charge of holding ceremonies or functions. - Abdoulaye Gueye
/hyperpost/🌐/🧊/index.html
Think carefully before you post. Anything you share online can stay there a long time, even after you delete it.
This section provides practical ways to reduce targeted advertising and protect personal data online. I personally use a combination of clearing cookies regularly and a privacy focused browser extension like Privacy Badger, which seems to block most trackers without slowing down browsing. I’m curious if anyone has experience using Tor for everyday browsing, does it significantly impact speed or usability? Also, opting out of personalized ads on Google seems simple, but I wonder how effective it really is in reducing tracking across multiple websites.
Losing Your Job Because of Social Media
This section highlights how even private social media posts can impact your professional life. It makes me think about how careful we need to be with our online presence, even in seemingly personal spaces. I wonder how teachers and students can balance freedom of expression with the potential career risks of posting online. Are there strategies, like adjusting privacy settings or separating professional and personal accounts, that effectively protect people from these consequences?
You’ll learn more about privacy and settings in the privacy section of this chapter.
The chapter mentions adjusting privacy settings on social media to limit who can see your information. What strategies have other students used to balance staying connected online while protecting personal data? Are there specific settings or tools that are particularly effective in preventing tracking?
There are three different radiation sensors measuring at the OpenLiving Lab: two pyranometers and a quantum sensor, which are shown in the image below. The pyranometers measure short-wave radiation, or solar radiation, in W m super negative two . One measures incoming short-wave radiation: that is, the solar radiation received at the surface. The other pyranometer is downward-facing and measures outgoing short-wave radiation, or the reflected solar radiation from the surface. The quantum sensor measures radiation in the visible range, from 400–700 nm. This is the photosynthetically active radiation described earlier in this session, so these sensors are commonly referred to as PAR sensors. In addition, in the urban woodland site, there is a second PAR sensor below the canopy.
3 sensors at OL lab 2 pryanometers and a quaantum Pryanometers measure short wave or solar in Wm-2 One measures incoming SW (SR received at the surace) The other faces down and measures outgoing SW Quantum measures visible radiation - known as a PAR sensor
The values of irradiance discussed above are for solar radiation reaching the top of the atmosphere. Solar radiation then has to travel through the atmosphere and, even though this is a very small distance relative to the overall journey from the Sun, the atmosphere has an important effect on the nature of the radiation reaching the Earth’s surface and the overall energy balance of the Earth because of interactions solar radiation has with the constituents of the atmosphere. We’ll discuss these interactions and their implications in the next study session, but first we need to understand a bit more about the nature of solar radiation.
The atmosphere has a big affect on the radiation coming thrugh and chances the energy balance
Another term when considering the solar radiation that reaches Earth is insolation, which is the energy arriving per unit area over a given time period (e.g. a day, month or year). That is, solar insolation is the cumulative solar irradiance over a given time period. You may also come across this term in the context of solar power installations and the potential energy capture of a given location.
Solar insolation is the energy arrivign by unit area of a time period - its a cumulative soalr irradiance
The total energy output per second from the Sun, or radiative power, is an enormous 3.85 multiplication 10 super 26 W. This solar energy is emitted in all directions from the Sun, and the power of solar radiation that hits the top of the Earth’s atmosphere is a tiny fraction of it, about 1.735 multiplication 10 super 17 W (or 4.5 multiplication 10 super negative eight %). This value represents an average over the year, as it varies by a few per cent with the distance of the Earth from the Sun, due to the elliptical orbit of the Earth around the Sun. The power per unit area of solar radiation (for a surface perpendicular to the Sun’s rays) is termed solar irradiance and has units of W m super negative two . The solar irradiance when the Earth is at the average distance from the Sun (1 astronomical unit, AU) is termed the solar constant and is 1361 W m super negative two . This is illustrated in Figure 2.1.10. By the time solar radiation reaches Earth, the rays are essentially parallel due to the large distance between the Sun and Earth, and the intensity of the radiation crossing an imaginary plane perpendicular to the Sun’s rays defines the solar constant.
The suns radiation is 3.85x10^26W, but Earth only gets 1.735x10^17 over the year The solar radiation pwoer er unit area is called the solar irradiance, units of Wm-2, The solar constant, for the avergage Earth distance from the SUn is 1361 Wm-2 By the time the suns ray hit earth they're parallel
Virtually all the energy available on Earth originates from the Sun in the form of solar radiation or from electromagnetic radiation. All objects, including stars, planets, living beings and inanimate objects at a temperature above 0 K also emit electromagnetic radiation and, on balance, most energy lost from the Earth-atmosphere system to space is terrestrial radiation (radiation emitted from the Earth). The intensity and wavelength distribution of emitted radiation depends on the temperature of the object.
All energy originates from soalr or electromagnetic radiation
Everything above 0 K emit electromagnetic radiation
Most energy lost from earth is terrestrial radiation
Intensity and wavelength distribution of radiation depends on the temp of an object
goups of atoms that exhibit a chaacteistic eactivity. A paticulafunctional goup will almost always display its distinctive chemical behaviowhen it is pesent in a compound. Because of theiimpotance in undestanding oganic chemisty, functional goups have specific names that often cay ovein the naming of individual compounds incopoating the goups.
If you download the pdf, it's a lot better.
Afer painting this grim picture, they declared thatthe China that I was visiting, the China outside of those heavy doors that theyhad just eagerly denounced, was not in fact “the real China.”2 Te real China, aland of rites and etiquette (liyi zhi bang), and a global exemplar of morality andharmony, was based in the “Great Way” (da dao) that extended from the begin-ning of time to modernity.3 But this Great Way had been lost decades ago, andhad been replaced by an inferior way (xiao dao), in which people were solely con-cerned with convenience, ease, speed, money, and their own selfsh interests. Now,
This statement feels kind of wild, it’s like the teachers honestly believe they’re the ones preserving the “real” China. It shows how nostalgia can turn into a comforting fantasy people use to avoid facing how much the world has changed. It also makes me feel like the academy isn’t just teaching manners at all, it’s creating its own little imagined universe.
978-3-7518-7001-6
Concerning elapid venoms, the low immunogenicity of 3FTXs makes generating homogeneous antivenoms difficult [2]. The elapid 3FTXs are peptides with associated non-enzymatic activity, ranging from 60 to 85 amino acids. They contain eight highly conserved cysteine residues that form 4 disulfide bridges that stabilize their hydrophobic core, from which emerge three loops that bear 3–5 antiparallel beta-strands. Besides, some 3FTXs also contain an extra pair of cysteine residues that forms one more disulfide bridge located at one of the loops. 3FTXs encompass many proteins with diverse functions like cytotoxicity (e.g. cardiotoxins) [3], [4] and neurotoxicity (e.g. α-neurotoxins, fasciculins, muscarinic toxins, L-type calcium channel blockers) [5], [6], [7]. Snake venom composition from elapids and from their related colubrids show that PLA2 and 3FTXs are not only the most abundant protein families [8], [9], but also, the most toxic ones [10].
what is 3ftx? - they are the most abundent in elapid snakes
El conocer no es una experiencia sensorial.
El conocimiento no es una sensación.
With reference to Undersecretary Lovett’s top secret message of March 3 (telegram no. 566),1
Test annotazione FRUS
RRID:CVCL_0030
DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00581-3
Resource: (BCRC Cat# 60005, RRID:CVCL_0030)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:CVCL_0030
RRID:CVCL_0063
DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00581-3
Resource: (RRID:CVCL_0063)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:CVCL_0063
RRID:CVCL_0042
DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00581-3
Resource: (RRID:CVCL_0042)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:CVCL_0042
RRID:CVCL_0023
DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00581-3
Resource: (CCLV Cat# CCLV-RIE 1035, RRID:CVCL_0023)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:CVCL_0023
RRID:SCR_002798
DOI: 10.1038/s41698-025-01190-3
Resource: GraphPad Prism (RRID:SCR_002798)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:SCR_002798
RRID:CVCL_0045
DOI: 10.1038/s41698-025-01190-3
Resource: (DSMZ Cat# ACC-305, RRID:CVCL_0045)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:CVCL_0045
RRID:SCR_000154
DOI: 10.1038/s41698-025-01190-3
Resource: DESeq (RRID:SCR_000154)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:SCR_000154
RRID:SCR_014782
DOI: 10.1038/s41698-025-01190-3
Resource: OncoKB (RRID:SCR_014782)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:SCR_014782
In this current context of scientific explosionat all levels (although the exponential growth is not thesame in all scientific disciplines), we find the advent ofnew disciplines and subdisciplines that help us toclassify the areas of knowledge.Thus, to order this informative explosion, itwas convenient to establish a classification system forthe different areas of study. The UNESCO InternationalNomenclature for the fields of Science and Technologywas proposed in 1973 and 1974 by the Science andTechnology Policy Divisions of Science andTechnology of UNESCO and adopted by the Scientificand Technical Research Advisory Commission. It is aknowledge classification system widely used in themanagement of research projects and doctoral theses.And, as a sign that science always brings newhorizons to knowledge, new actors are alwaysappearing in this classification system.In the field that occupies us, however, we findourselves with a great absence. The "Astrobiology",does not appear in the listings of UNESCO. But yes, wefind in them the term "Exobiology" [2, 3]. This "partial"absence denotes the novelty that is still today toscientifically consider the study of life outside Earth.Indeed, until very recently and by manyscientists, it was considered "Exobiology" or"Astrobiology" (which we will consider synonyms), ascience without an area of study. This was especiallytrue until 1995, when Michel Mayor and Didier Quelozdiscovered the first extrasolar planet, 51 Pegasi b.Fortunately, today things are beginning to change andmore and more scientists believe that life will be aubiquitous phenomenon, which will occur anywhere inthe universe where the conditions are right for it.Life will then be an epiphenomenon, an eventthat has no choice but to occur, as soon as thecomplexity of the chemical organization of matterreaches the critical point of interaction between thetrace elements, the essential elements for life. At thebase of it we will find carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur.As life will be a ubiquitous phenomenon,finally today we already intuit that not even a planet isnecessary for life to prosper, and that life could bemaintained in interstellar space, without planetarysubstratum. But before continuing, it is convenient tofix some definitions.The debate on what is life? has occupied allgenerations of thinkers. It is a very difficult concept todefine. Currently there is consensus in affirming thatlife is a self-contained, autopoietic chemical system(self-sufficient exchanging energy with theenvironment in which it is located), capable ofreproducing itself and experiencing evolution [4]. It isa broad definition. In it the minerals could fit, and eventhe stars themselves, as we will see later.So, in view of the complexity of theknowledge that we are slowly acquiring about theuniverse, and given the challenges posed by thepossibility of assuming that life will be found virtuallyanywhere, it is convenient to establish a series of ethicalvalues that allow a positive integration in the culturalbaggage of society of the new limits of knowledge thatscience gives us.For this reason, a "Philosophy of Science" -code UNESCO 7205.01- was established, under whichsince the 80s we can find the "Philosophy of Biology".Before delving into the Philosophy ofAstrobiology, we will give its definition, based on theconcepts of "Philosophy" and "Astrobiology".
Authors argue that the growth of the sciences in human culture has driven the need to expand the ontology of scientific categories. As astrobiology matures, more complex studies across disciplines are needed to address evolving areas - e.g., exobiology, philosophy of astrobiology, or my own term exoastronomy which I coined in 2018. These are missing from the UNESCO International nomenclature as of 2025/2026.
In recent times, decade of the 40s of thetwentieth century, another of the pioneers ofAstrobiology was the Soviet astronomer GavriilAdrianovich Tikhov, who laid the foundations of anincipient "Astrobotany".Tikhov studied the albedo formations of Mars,speculating that the origin of chromatic and brightnesschanges on the Martian surface were caused byseasonal cycles of falling leaves in forests populated bydeciduous trees [7], (see Fig. 1).Figure 1. Albedo formations of Mars during the greatopposition of Mars in 2003. (Source: Rafael BalaguerRosa, Astrogirona, Astronomical Society of Girona).3. Astrobiology in ancestral societies.But these conceptions are very modern.Perhaps the idea that life thrives in the entire universe,and that maybe the inhabitants of Earth are sons of anextraterrestrial life, are rooted in our deepest psychefrom the very beginning of our species, Homo sapiens,(and maybe other human species, too), more than200,000 years ago.This idea is based on the fact that manyancestral cultures, different and located throughout theplanet, have interpreted that our human origins, and thevery origin of life on Earth, is actually of extraterrestrialorigin. This certainty is born of the shamanicexperience of the altered states of consciousness, wherethe subjective experiences (and then shared andcollective) suggest the real existence of spiritual orhigher beings, who descend from the sky, from space.
Soviet astronomer Gavriil Tikhov speculated about life on Mars due to albedo changes. He was a Soviet astronomer becoming one of the very first pioneers in astrobiology and astrobotany (being appointed the head of astrobotany in Alma-Ata to investigate life on planets in the Solar System). He was also an astronomer at the Pulkovo Observatory from 1906 until 1941.
Synthèse du Webinaire : Utiliser Canva pour les Actions Associatives
Ce document de synthèse résume les points clés et les enseignements du webinaire "Apprendre à utiliser Canva pour vos actions associatives", organisé par Solidatech.
La session, animée par des expertes de Canva, visait à doter les associations des connaissances nécessaires pour utiliser efficacement la plateforme Canva dans leurs communications, avec un focus particulier sur la création d'affiches pour le recrutement de bénévoles.
Les principaux points à retenir sont les suivants :
1. Canva Solidaire : L'information la plus cruciale pour les associations est l'existence de "Canva Solidaire", une offre qui donne un accès gratuit et complet à Canva Pro pour les associations loi 1901 éligibles, permettant d'intégrer jusqu'à 10 membres d'équipe.
2. Principes de Conception Graphique : Une bonne conception d'affiche repose sur cinq piliers fondamentaux : la hiérarchisation de l'information, le branding (identité visuelle), la visibilité (impact visuel), la lisibilité (confort de lecture) et la composition (équilibre des éléments).
3. Fonctionnalités Clés : La plateforme Canva est un outil tout-en-un puissant et intuitif. Les fonctionnalités essentielles présentées incluent l'utilisation de modèles (templates), la personnalisation via le "Kit d'Identité Visuelle" (marque), la manipulation des calques, et la déclinaison rapide des créations pour différents formats (réseaux sociaux, impression).
4. Intelligence Artificielle (IA) : Canva intègre des outils d'IA accessibles ("Studio Magique") qui permettent de réaliser des tâches complexes simplement, comme la suppression ou la génération d'arrière-plans, la capture de texte sur une image aplatie, et même la génération de code HTML pour des formulaires.
5. Ressources et Formation : Les participants ont été encouragés à explorer la Canva Design School, une section de la plateforme offrant des cours et tutoriels gratuits.
De plus, pour trouver des modèles spécifiquement créés par des graphistes français, il est conseillé d'utiliser le mot-clé de recherche "FR association".
En conclusion, le webinaire a positionné Canva comme un allié stratégique pour les associations, leur permettant de professionnaliser leur communication visuelle avec des ressources limitées, tout en favorisant la collaboration et l'efficacité.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Le webinaire a été organisé par Solidatech pour accompagner les associations dans leur transformation numérique. L'événement a accueilli deux intervenantes expertes de la communauté Canva pour présenter la plateforme et ses applications concrètes pour le secteur associatif.
• Organisateur : Solidatech, représenté par Camille.
• Intervenantes Canva :
◦ Anne-Gaël : Community Manager de la communauté des "Créators" (graphistes créant les modèles pour la bibliothèque Canva) et des "Édus Créateurs" (enseignants créant du contenu pédagogique). ◦ Alisée : Directrice artistique, Brand Consultante et ambassadrice Canva, spécialisée dans l'accompagnement des porteurs de projet et des associations.
• Thème Principal : Utiliser Canva pour créer des supports de communication, spécifiquement des affiches de recrutement de bénévoles, en lien avec la Journée Internationale des Bénévoles.
Solidatech
Solidatech est une coopérative d'utilité sociale et environnementale dont la mission est d'aider les associations à renforcer leur impact grâce au numérique. L'organisation accompagne plus de 45 000 associations. Son action repose sur deux piliers :
1. Réaliser des économies :
◦ Logiciels : Identification de solutions gratuites ou obtention de remises sur des logiciels payants. ◦ Matériel : Fourniture de matériel reconditionné (par leur coopérative d'insertion Les Ateliers du Bocage) et de matériel neuf (en partenariat avec Dell).
2. Monter en compétence sur le numérique :
◦ Formation : Organisme de formation certifié proposant des formations sur les enjeux du numérique et sur des outils spécifiques. ◦ Diagnostic : Outil de diagnostic numérique gratuit pour évaluer la maturité numérique d'une association. ◦ Ressources : Mise à disposition de contenus gratuits (articles, newsletters, webinaires).
Canva
Canva est une entreprise australienne fondée en 2013 par Mélanie Perkins avec la mission de "donner au monde le pouvoir de créer" (Empower the world to design). L'objectif est de démocratiser le design en rendant la création visuelle simple et accessible à tous, notamment grâce à un système de glisser-déposer.
Indicateur Clé
Chiffre
Présence mondiale
190 pays
Employés
Plus de 5 000
Utilisateurs actifs mensuels
260 millions
Revenu annualisé
3,5 milliards de dollars
Créations depuis 2013
40 milliards
Créations par seconde
Plus de 400
Utilisateurs (étudiants/enseignants)
Plus de 100 millions
Organisations à but non lucratif
Plus d'un million
Les valeurs de Canva incluent le fait d'être une "bonne personne", de simplifier la complexité, de viser l'excellence et d'œuvrer pour le bien commun.
Une partie importante de la présentation a été consacrée à Canva Solidaire, l'offre dédiée au secteur associatif.
• Principe : Canva Solidaire est l'équivalent de Canva Pro, mais offert gratuitement aux organisations éligibles.
• Avantages : Accès à toutes les fonctionnalités de Canva Pro, y compris plus de modèles, de photos, d'éléments, le Kit d'Identité Visuelle, la planification de contenu, et la possibilité d'intégrer jusqu'à 10 personnes gratuitement dans l'équipe.
• Éligibilité : L'offre s'adresse principalement aux associations loi 1901. Sont exclues les administrations publiques, les organisations éducatives (qui ont leur propre programme gratuit), et les clubs sportifs professionnels, entre autres.
• Procédure d'inscription :
1. Se rendre sur la page dédiée de Canva Solidaire.
2. Cliquer sur "Demander un compte Canva Solidaire".
3. S'inscrire ou se connecter avec un compte Canva existant.
4. Rechercher le nom de son association. Dans la plupart des cas, Canva la reconnaît via son numéro de déclaration en préfecture et valide le compte automatiquement.
5. Si l'association n'est pas trouvée, il est nécessaire de joindre des documents justificatifs (déclaration en préfecture, statuts de l'association).
6. Le support Canva confirme ensuite l'accès par e-mail.
Alisée a présenté une cartographie des fonctionnalités principales de l'interface Canva pour familiariser les utilisateurs, même débutants.
• Page d'accueil : Présente des raccourcis vers différents formats (présentations, réseaux sociaux, vidéos) et des menus pour accéder aux modèles, aux projets existants et à la planification.
• Modèles (Templates) : Le point de départ recommandé pour les débutants. Il s'agit d'une vaste bibliothèque de créations réalisées par les "Créators".
Astuce : Pour trouver des formats spécifiquement français (ex: marque-page), il est conseillé d'ajouter une astérisque (*) à la recherche.
• Menu de gauche (dans l'éditeur) :
◦ Design/Modèles : Pour rechercher et appliquer un nouveau modèle.
◦ Éléments : Contient les formes, illustrations, photos, vidéos, et audios.
◦ Marque : Section cruciale où l'association peut configurer son identité visuelle (logos, couleurs, polices). Une fois configuré, ce kit peut être appliqué en un clic à n'importe quel design pour garantir la cohérence.
◦ Importer : Pour ajouter ses propres fichiers (images, logos, vidéos).
◦ Texte, Projets, Applications : Autres outils de création et d'organisation.
• Sauvegarde automatique : Canva enregistre les créations en temps réel, évitant ainsi toute perte de travail en cas de problème technique.
Pour créer une affiche percutante, Alisée a détaillé cinq principes de design essentiels :
1. La Hiérarchisation : Organiser les informations de la plus importante à la moins importante.
Le titre doit attirer l'œil en premier, suivi des informations clés (date, lieu), puis des détails secondaires. L'œil humain "hiérarchise avant de comprendre".
2. Le Branding : Utiliser de manière cohérente les éléments de l'identité visuelle de l'association (couleurs, logo, polices, style d'illustration).
Cela permet une reconnaissance immédiate et renforce le professionnalisme. Par exemple, utiliser du vert pour une association écologique.
3. La Visibilité : S'assurer que l'affiche est visible et attire l'attention.
Cela passe par le choix des polices, la présence claire du logo, et l'intégration d'un appel à l'action ("Call to Action") clair et engageant (ex : "Rejoignez-nous !", "Devenez bénévole").
4. La Lisibilité : Garantir que le message est facile et agréable à lire. Il faut prêter attention au contraste des couleurs, à la taille des polices (éviter les polices fantaisistes pour les paragraphes longs), à l'espacement entre les lignes (interlignage) et aux marges. Le regard a tendance à balayer une page en "Z".
5. La Composition : L'agencement global des éléments sur la page.
Il faut travailler avec les alignements, les marges, les espaces négatifs (le "vide") pour créer un équilibre visuel et guider le regard du spectateur, assurant une bonne compréhension du message.
Le webinaire a présenté quelques outils d'IA intégrés dans le Studio Magique de Canva, conçus pour simplifier des tâches complexes.
• Génération d'arrière-plan : Possibilité de sélectionner une photo, de supprimer l'arrière-plan existant et d'en générer un nouveau à partir d'une simple description textuelle (prompt).
Par exemple, transformer une photo de bénévoles sur une plage en une scène dans la nature.
• Capture de texte : Cet outil permet de "détecter" le texte sur une image aplatie (comme un PDF ou un JPEG) et de le rendre entièrement modifiable.
C'est très utile pour mettre à jour une ancienne affiche dont on n'a plus le fichier source.
• Génération de code : Une fonctionnalité plus avancée a été montrée, où l'IA de Canva a généré le code HTML pour un formulaire de contact destiné au recrutement de bénévoles.
Ce code peut ensuite être intégré sur un site web ou dans un document.
Un enjeu majeur pour les associations est d'adapter leurs visuels pour différents canaux (flyer, publication Instagram, bannière web, etc.).
Deux méthodes ont été présentées :
1. Méthode 1 (Multi-formats dans un seul document) :
◦ Dans un design existant (ex: une affiche A4), on peut ajouter une nouvelle "page" et lui assigner un type de format différent (ex: publication Instagram, vidéo, présentation).
◦ Cela permet de conserver tous les éléments de base et de les réorganiser manuellement pour chaque format au sein d'un seul et même projet.
2. Méthode 2 (Fonction "Redimensionner" - Canva Pro) :
◦ Cette fonction permet de dupliquer automatiquement un design dans un ou plusieurs autres formats.
◦ L'utilisateur sélectionne les nouveaux formats désirés (ex: Story Instagram, Bannière Facebook).
◦ Canva crée de nouvelles versions du design aux bonnes dimensions, en tentant d'adapter les éléments.
Des ajustements manuels sont souvent nécessaires.
◦ Conseil d'experte : Il est crucial d'utiliser l'option "Copier et redimensionner" plutôt que "Redimensionner ce design" pour conserver le fichier original intact.
Pour permettre aux associations d'aller plus loin, les intervenantes ont partagé deux ressources clés :
• Trouver des modèles français : En utilisant le code de recherche FR association dans la barre de recherche de modèles, les utilisateurs peuvent accéder à une sélection de templates créés spécifiquement par la communauté des "Créators" français pour les besoins du secteur associatif.
• Canva Design School : Accessible directement depuis le menu de la plateforme, c'est une "école de design" gratuite intégrée.
Elle propose des cours, des leçons vidéos en français, et des activités pratiques pour maîtriser des outils spécifiques (vidéo, IA, etc.) et se perfectionner en design graphique.
La fin du webinaire a permis de clarifier plusieurs points importants :
• Droit d'utilisation des images : Toutes les images de la bibliothèque Canva sont libres de droit pour une utilisation dans des créations.
Il est possible de vendre des produits (t-shirts, tasses) avec un design créé sur Canva, à condition qu'il s'agisse d'une composition originale (texte, autres éléments ajoutés) et non d'une simple image de la bibliothèque apposée sur le produit.
• Nombre de polices : Pour une affiche, il est recommandé d'utiliser deux à trois polices (typos) maximum pour garantir la clarté et l'harmonie visuelle.
• Newsletters : Canva permet de créer le design d'une newsletter, mais n'est pas un outil d'envoi d'e-mails.
Le design doit être exporté (par exemple en lien HTML) pour être intégré dans un outil de mailing dédié (ex: Mailchimp).
• Confidentialité : Les créations réalisées sur un compte Canva sont privées et ne sont pas ajoutées à la bibliothèque publique de modèles.
• Langue de l'IA : Les outils d'IA de Canva comprennent et fonctionnent parfaitement avec des instructions en français.
Note: This preprint has been reviewed by subject experts for Review Commons. Content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
In this manuscript the authors evaluate the role of Microtubule Associated Protein 7 (MAP7) in postnatal Sertoli cell development. The authors build two novel transgenic mouse lines (Map7-eGFP, Map7 knockout) which will be useful tools to the community. The transgenic mouse lines are used in paired advanced sequencing experiments and advanced imaging experiments to determine how Sertoli cell MAP7 is involved in the first wave of spermatogenesis. The authors identify MAP7 as an important regulator of Sertoli cell polarity and junction formation with loss of MAP7 disrupting intracellular microtubule and F-actin arrangement and Sertoli cell morphology. These structural issues impact the first wave of spermatogenesis causing a meiotic delay that limits round spermatid numbers. The authors also identify possible binding partners for MAP7, key among those MYH9.
The authors did a great job building a complex multi-modal project that addressed the question of MAP7 function from many angles. The is an excellent balance of using many advanced methods while still keeping the project narrowed, to use only tools to address the real questions. The lack of quality testing on the germ cells outside of TUNEL is disappointing, but the Conclusion section implies that this sort of work is being done currently so the omission in this manuscript is acceptable. However, there is an issue with the imaging portion of the work on MYH9. The conclusions from the MYH9 data is currently overstated, super-resolution imaging of Map7 knockouts with microtubule and F-actin stains, and imaging that uses MYH9 with either Map7-eGFP or anti-MAP7 are also needed to both support the MAP7-MYH9 interaction normally and lack of interaction with failure of MYH9 to localize to microtubules and F-actin in knockouts. Since a Leica SP8 was used for the imaging, using either Leica LIGHTNING or just higher magnification will likely be the easiest solution.
This manuscript is nicely organized with almost all of the results spelled out very clearly and almost always paired with figures that make compelling and convincing support for the conclusions. There are minor revision suggestions for improving the manuscript listed below. These include synching up Figure and Supplemental Figure reference mismatches. There are also many minor, but important, details that need to be added to the Methods section including many catalog numbers and some references.
Referee cross-commenting
I generally agree with Reviewer 1 and specifically concur related to adding details about fertility assessment of the Map7 Knockout line, and enhancing the SEM imaging.
There are mouse lines, and datasets that will be useful resources to the field. This work also advances our understanding of a period in Sertoli cell development that is critical to fertility but very understudied.
Note: This preprint has been reviewed by subject experts for Review Commons. Content has not been altered except for formatting.
Learn more at Review Commons
Summary:
A previous study by Komada et al. demonstrated that MAP7 is expressed in both Sertoli and germ cells, and that Map7 gene-trap mutant mice display disrupted microtubule bundle formation in Sertoli cells, accompanied by defects in spermatid manchettes and germ cell loss. In the current study, Kikuchi et al. investigated the role of MAP7 in the formation of the Sertoli cell apical domain during the first wave of spermatogenesis. They generated a GFP-tagged MAP7 mouse line and demonstrated that the endogenous MAP7 protein localizes to the apical microtubules in Sertoli cells and to the manchette microtubules in step 9-11 spermatids. They also generated a new Map7 knockout (KO) mouse line in a genetic background distinct from the one used in the previous study. Focusing on stages before the emergence of step 9-11 spermatids, the authors aimed to isolate defects caused by the function of MAP7 in Sertoli cells. They report that loss of MAP7 impairs Sertoli cell polarity and apical domain formation, accompanied by the microtubule remodeling defect. Using the GFP-tagged MAP7 line, they performed immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry and identified several MAP7-interacting proteins in the testis, including MYH9. They further observed that MAP7 deletion alters the distribution of MYH9. Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed that the loss of MAP7 in Sertoli cells resulted in slight transcriptomic shifts but had no significant impact on their functional differentiation. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis also showed delayed meiotic progression in the MAP7-deficient testis. Overall, while the study provides some interesting discoveries of early Sertoli cell defects in MAP7-deficient testes, some conclusions are premature and not fully supported by the presented data. The mechanistic investigations remain limited in depth.
Major comments:
Minor comments:
Referee cross-commenting
I concur with Reviewer 2 that the Map7-eGFP mouse model is a valuable tool for the research community. I also agree that performing MAP7-MYH9 double immunofluorescence staining to demonstrate their colocalization would further strengthen the authors' conclusions regarding their interaction. My overall assessment of the manuscript remains unchanged: the study represents an incremental advance that extends previous findings on MAP7 function but provides limited new mechanistic insight.
This study investigates the role of the microtubule-associated protein MAP7 in Sertoli cell polarity and apical domain formation during early stages of spermatogenesis. Using GFP-tagged and MAP7 knockout mouse models, the authors show that MAP7 localizes to apical microtubules and is required for Sertoli cell cytoskeletal organization and germ cell development. While the study identifies early Sertoli cell defects and candidate MAP7-interacting proteins, the mechanistic insights remain limited, and several conclusions require stronger experimental support. Overall, the discovery represents an incremental advance that extends prior findings on MAP7 function, providing additional but modest insights into the role of MAP7 in cytoskeletal regulation in male reproduction.
When you send a message on your Meshtastic companion app, it is relayed to the radio using Bluetooth, Wi-Fi/Ethernet or serial connection. That message is then broadcasted by the radio. If it hasn't received a confirmation from any other device after a certain timeout, it will retransmit the message up to three times. When a receiving radio captures a packet, it checks to see if it has heard that message before. If it has it ignores the message. If it hasn't heard the message, it will rebroadcast it. For each message a radio rebroadcasts, it marks the "hop limit" down by one. When a radio receives a packet with a hop limit of zero, it will not rebroadcast the message. The radio will store a small amount of packets (around 30) in its memory for when it's not connected to a client app. If it's full, it will replace the oldest packets with newly incoming text messages only.
You use your phone or 'companion app'(?) to send a msg to a radio (over BT, wifi or wire). The radio broadcasts incoming messages, including the one you provide through the app.
Msgs that are not acknowledged by another radion will be send at most 3 times. (will you be able to see it has not propagated?)
A radio that receives msgs already received will not rebroadcast it. Any broadcasted msg has a 'hop limit' and if it hits 0 it will not be rebroadcast. This limits the spread of a message, no? What is the default hop limit? Otoh the hoplimit does not limit the initial number of paths for broadcasting. So it's an attenuation over paths.
Theoretically in a dense network, my msg may reach Y number of other radios that all start out with the same hop limit.
I do not see here yet how you could intentionally set and reach a specific recipient. This description provides attenuated propagation of messages but no direction/addressee?
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public Review):
Faiz et al. investigate small molecule-driven direct lineage reprogramming of mouse postnatal mouse astrocytes to oligodendrocyte lineage cells (OLCs). They use a combination of in vitro, in vivo, and computational approaches to confirm lineage conversion and to examine the key underlying transcription factors and signaling pathways. Lentiviral delivery of transcription factors previously reported to be essential in OLC fate determination-Sox10, Olig2, and Nkx2.2-to astrocytes allows for lineage tracing. They found that these transcription factors are sufficient in reprogramming astrocytes to iOLCs, but that the OLCs range in maturity level depending on which factor they are transfected with. They followed up with scRNA-seq analysis of transfected and control cultures 14DPT, confirming that TF-induced astrocytes take on canonical OLC gene signatures. By performing astrocyte lineage fate mapping, they further confirmed that TF-induced astrocytes give rise to iOLCs. Finally, they examined the distinct genetic drivers of this fate conversion using scRNA-seq and deep learning models of Sox10- astrocytes at multiple time points throughout the reprogramming. These findings are certainly relevant to diseases characterized by the perturbation of OLC maturation and/or myelination, such as Multiple Sclerosis and Alzheimer's Disease. Their application of such a wide array of experimental approaches gives more weight to their findings and allows for the identification of additional genetic drivers of astrocyte to iOLC conversion that could be explored in future studies. Overall, I find this manuscript thoughtfully constructed and only have a few questions to be addressed.
(1) The authors suggest that Sox10- and Olig2- transduced astrocytes result in distinct subpopulations iOLCs. Considering it was discussed in the introduction that these TFs cyclically regulate one another throughout differentiation, could they speculate as to why such varying iOLCs resulted from the induction of these two TFs?
We thank the Reviewer for the opportunity to speculate. We hypothesize that Sox10 and Olig2 may induce different OLCs as a result of differential activation of downstream genes within the gene regulatory network, which are important for OPC, committed OLC and mature OL identity [1]. In support of this, we found different expression levels of genes involved in downstream OLC specification networks [1], including Sox6, Tcfl2 and Myrf, at D14 (Author response image 1), following further analysis of our RNA-seq data.
Author response image 1.
Expression of OLC regulatory network genes in Sox10- and Olig2- cultures. Violin plots show gene expression levels (log-normalized) of downstream OLC regulatory genes (Sox6, Zeb2, Tcf7l2, Myrf, Zfp488, Nfatc2, Hes5, Id2) between Sox10 and Olig2 treated OLCs at 14 days post transduction. Analysis was performed on oligodendrocyte progenitor and mature oligodendrocyte clusters (from Manuscript Figure 1D, clusters 3 and 8).
(2) In Figure 1B it appears that the Sox10- MBP+ tdTomato+ cells decreases from D12 to D14. Does this make sense considering MBP is a marker of more mature OLCs?
Thank you for this comment. To address this, we compared the number of MBP+tdTomato+ Sox10 cells across reprogramming timepoints. We saw no difference between the number of MBP+tdTomato+ OLs at D12 and D14 (Author response image 2, p = 0.2314). However, we do see a [nonsignificant] decrease in MBP+tdTomato+ Sox10 cells from D12 to D22 (Manuscript Supplementary Figure 3B, Author response image 2, p= 0.0543), which suggests that culture conditions are not optimal for longer-term cell survival [2], [3], [4].
Author response image 2.
Comparison of Sox10- induced MBP+tdTomato+ iOLCs over time. Quantification of MBP<sup>+</sup>tdTomato<sup>+</sup> iOLs in Sox10 cultures at D8 (n=5), D10 (n=5), D12 (n=5), D14 (n=7) and D22 (n=3) post transduction. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, each data point represents one individual cell culture experiment, Brown-Forsythe and Welch ANOVA on transformed percentages with Dunnett’s T3 multiple comparisons test (*= p<0.05).
(3) Previous studies have shown that MBP expression and myelination in vitro occurs at the earliest around 4-6 weeks of culturing. When assessing whether further maturation would increase MBP positivity, authors only cultured cells up to 22 DPT and saw no significant increase. Has a lengthier culture timeline been attempted?
We agree with the Reviewer that previous studies of pluripotent stem cell derived (hESCs or iPSCs) have shown MBP+ OLCs in vitro around 4-6 weeks [5], [6], [7]. However, studies of neural stem cells [8] or fibroblasts [9] conversion show OLC appearance after 7 and 24 days, respectively, demonstrating that OLCs can be generated in vitro within 1-3 weeks of plating. Moreover, as noted above in response to #2, we see fewer MBP+ cells at 22DPT, suggesting that extended time in culture may require additional factors for support. Therefore, we did not attempt longer timepoints.
(4) Figure S4D is described as "examples of tdTomatonegzsGreen+OLCmarker+ cells that arose from a tdTomatoneg cell with an astrocyte morphology." The zsGreen+ tdTomato- cell is not convincingly of "astrocyte morphology"; it could be a bipolar OLC. To strengthen the conclusions and remove this subjectivity, more extensive characterizations of astrocyte versus OLC morphology in the introduction or results are warranted. This would make this observation more convincing since there is clearly an overlap in the characteristics of these cell types.
We thank the reviewer for this excellent suggestion. To assess astrocyte morphology, we measured the cell size, nucleus size, number of branches and branch thickness of 70 Aldh1l1+tdTomato+ astrocytes in tamoxifen-labelled Aldh1l1-CreERT2;Ai14 cultures (new Supplemental Table 1). To assess OPC morphology, we performed IHC for PDGFRa in iOLC cultures and measured the same parameters in 70 PDGFRa+ OPCs (new Supplemental Table 1). We found that astrocytes were characterized by larger branch thickness, cell length and nucleus size, while OPCs showed a larger number of branches (new Supplemental Figure 1, and Author response image 3 below). Based on this framework, the AAV9-GFAP::zsGreen<sup>pos</sup>Aldh1l1-tdTomato<sup>neg</sup> and AAV9-GFAP::zsGreen<sup>pos</sup>Aldh1l1-tdTomato<sup>pos</sup>starting cells tracked fall within the bounds of ‘astrocytes’. We have revised the manuscript to include this more rigorous characterization (Line 119-124, Page 4; Line 307-312, Page 9; Line 323-326, Page 9). We also demonstrate (below) that the GFAP::zsGreen<sup>pos</sup> Aldh1l1-tdTomato<sup>pos</sup> and GFAP::zsGreen<sup>pos</sup>Aldh1l1-tdTomato<sup>neg</sup> starting cell depicted in Figure 2G and Supplemental Figure 5D is consistent with astrocyte morphology (Author response image 3).
Author response image 3.
Morphological characterization of astrocytes, oligodendrocyte lineage cells, and starting cells. Quantification of the (A) cell length, (B) nucleus size, (C) number of branches, and (D) branch thickness iAldh1l1+tdTomato+ and PDGFRα+ OPCs (n= 70 per cell type, data are presented as mean ± SEM). Orange line indicates parameter value for GFAP::zsGreen<sup>pos</sup>Aldh1l1-tdTomato<sup>pos</sup> starting cell in Figure 2G. Green line indicates parameter value for GFAP::zsGreen<sup>pos</sup> Aldh1l1-tdTomato<sup>neg</sup> starting cell in Supplemental Figure 5D.
Reviewer #2 (Public Review):
The study by Bajohr investigates the important question of whether astrocytes can generate oligodendrocytes by direct lineage conversion (DLR). The authors ectopically express three transcription factors - Sox10, Olig2 and Nkx6.2 - in cultured postnatal mouse astrocytes and use a combination of Aldh1|1-astrocyte fate mapping and live cell imaging to demonstrate that Sox10 converts astrocytes to MBP+ oligodendrocytes, whereas Olig2 expression converts astrocytes to PDFRalpha+ oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Nkx6.2 does not induce lineage conversion. The authors use single-cell RNAseq over 14 days post-transduction to uncover molecular signatures of newly generated iOLs.
The potential to convert astrocytes to oligodendrocytes has been previously analyzed and demonstrated. Despite the extensive molecular characterization of the direct astrocyteoligodendrocyte lineage conversion, the paper by Bajohr et al. does not represent significant progress. The entire study is performed in cultured cells, and it is not demonstrated whether this lineage conversion can be induced in astrocytes in vivo, particularly at which developmental stage (postnatal, adult?) and in which brain region. The authors also state that generating oligodendrocytes from astrocytes could be relevant for oligodendrocyte regeneration and myelin repair, but they don't demonstrate that lineage conversion can be induced under pathological conditions, particularly after white matter demyelination. Specific issues are outlined below.
We thank the reviewer for this summary. We agree that there are a handful of reports of astrocytelike cells to OLC conversion [10], [11]. However, our study is the first study to confirm bonafide astrocyte to OLC conversion, which is important given the recent controversy in the field of in vivo astrocyte to neuron reprogramming [12]. In addition, the extensive characterization of the molecular timeline of reprogramming, highlights that although conversion of astrocytes is possible by ectopic expression of any of the three factors, the subtypes of astrocytes converted and maturity of OLCs produced may vary depending on the choice of TF delivered. Our findings will inform future in vivo studies of iOLC generation that aim to understand the impact of brain region, age, pathology, and sex, which are especially important given the diversity of astrocyte responses to disease [13], [14], [15].
(1) The authors perform an extensive characterization of Sox10-mediated DLR by scRNAseq and demonstrate a clear trajectory of lineage conversion from astrocytes to terminally differentiated MBP+ iOLCs. A similar type of analysis should be performed after Olig2 transduction, to determine whether transcriptomics of olig2 conversion overlaps with any phase of sox10 conversion.
We thank the Reviewer for this excellent comment. We chose to include an in-depth analysis of Sox10 in the manuscript, as Sox10-transduced cultures showed a higher percentage of mature iOLCs compared to Olig2 in our studies. We have added this specific rationale to the manuscript (Line 329-330-Page 9).
Nonetheless, we also agree that understanding the underpinnings of Olig2-mediated conversion is important. Therefore, we used Cell Oracle [16] to understand the regulation of cell identity by Olig2. in silico overexpression of Olig2 in our control time course dataset (D0, D3, D8 and D14) showed cell movement from cluster 1, characterized by astrocyte genes [Mmd2[17], Entpd2[18], H2-D1[19]], towards cluster 5, characterized by OPC genes [Pdgfra[20], Myt1[21]] validating astrocyte to OLC conversion by Olig2 (Author response image 4).
We hypothesize that reprogramming via Sox10 and Olig2 take different conversion paths to oligodendrocytes for the following reasons.
(1) Differential astrocyte gene expression at D14 when cells are exposed to Sox10 and Olig2 (Manuscript Figure 1D-E [Sox10 characterized by Lcn2[19], C3[19]; Olig2 characterized by Slc6a11[22], Slc1a2[23]].
(2) Differential expression of key OLC gene regulatory network genes at D14 between cells treated with Sox10 and Olig2 (Author response image 1).
Author response image 4.
in silico modeling of Olig2 reprogramming (A) UMAP clustering of Cre control treated cells from 0, 3, 8, and 14 days post transduction (DPT). (B) UMAP clustering from (A) overlayed with timepoint and treatment group. (C) Cell Oracle modeling of predicted cell trajectories following Olig2 knock in (KI), overlaid onto UMAP plot. Arrows indicate cell movement prediction with Olig2 KI perturbation.
(2) A complete immunohistochemical characterization of the cultures should be performed at different time points after Sox10 and Olig2 transduction to confirm OL lineage cell phenotypes.
We performed a complete immunohistochemical characterization of Ai14 cultures transduced with GFAP::Sox10-Cre and GFAP::Olig2-Cre. This system allows permanent labelling and therefore, enabled the tracking of transduced cells through the process or DLR, which we believe is the most appropriate way to characterize iOLC conversion efficiencies. We then confirmed the conversion of Aldh1l1+ astrocytes in Aldh1l1-CreERT2;Ai14 cultures transduced with GFAP::Sox10-zsGreen and GFAP::Olig2-zsGreen. In this system, GFAP drives the expression of zsGreen, and therefore, may not faithfully track all cells and lead to an underestimate of the numbers of converted cells. For example, iOLCs from Aldh1l1<sup>neg</sup> astrocytes or iOLCs that have lost zsGreen expression following conversion. Therefore we use this system only to confirm astrocyte origin.
Nonetheless, we appreciate this comment and recognize that there may be differences in conversion efficiencies when analyzing Aldh1l1+ astrocytes versus all transduced cells. Therefore, we have softened the language in the manuscript (see below) regarding Olig2 and Sox10 generating different OLC phenotypes and now claim iOLC generation from both Sox10 and Olig2. We thank the Reviewer for this comment, and believe it has strengthened the discussion.
Line 240, Page 7
Line 261-263, Page 8
Line 304-307, Page 8/9
Line 413-414, Page 11
References
(1) E. Sock and M. Wegner, “Using the lineage determinants Olig2 and Sox10 to explore transcriptional regulation of oligodendrocyte development,” Dev Neurobiol, vol. 81, no. 7, pp. 892–901, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.1002/dneu.22849.
(2) B. A. Barres, M. D. Jacobson, R. Schmid, M. Sendtner, and M. C. Raff, “Does oligodendrocyte survival depend on axons?,” Current Biology, vol. 3, no. 8, pp. 489–497, Aug. 1993, doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90039-Q.
(3) A.-N. Cho et al., “Aligned Brain Extracellular Matrix Promotes Differentiation and Myelination of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Oligodendrocytes,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 11, no. 17, pp. 15344–15353, May 2019, doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b03242.
(4) E. G. Hughes and M. E. Stockton, “Premyelinating Oligodendrocytes: Mechanisms Underlying Cell Survival and Integration,” Front. Cell Dev. Biol., vol. 9, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.714169.
(5) M. Ehrlich et al., “Rapid and efficient generation of oligodendrocytes from human induced pluripotent stem cells using transcription factors,” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, vol. 114, no. 11, pp. E2243–E2252, Mar. 2017, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1614412114.
(6) Y. Liu, P. Jiang, and W. Deng, “OLIG gene targeting in human pluripotent stem cells for motor neuron and oligodendrocyte differentiation,” Nat Protoc, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 640–655, May 2011, doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.310.
(7) S. A. Goldman and N. J. Kuypers, “How to make an oligodendrocyte,” Development, vol. 142, no. 23, pp. 3983–3995, Dec. 2015, doi: 10.1242/dev.126409.
(8) M. Faiz, N. Sachewsky, S. Gascón, K. W. A. Bang, C. M. Morshead, and A. Nagy, “Adult Neural Stem Cells from the Subventricular Zone Give Rise to Reactive Astrocytes in the Cortex after Stroke,” Cell Stem Cell, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 624–634, Nov. 2015, doi:10.1016/j.stem.2015.08.002.
(9) F. J. Najm et al., “Transcription factor–mediated reprogramming of fibroblasts to expandable, myelinogenic oligodendrocyte progenitor cells,” Nat Biotechnol, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 426–433, May 2013, doi: 10.1038/nbt.2561.
(10) A. Mokhtarzadeh Khanghahi, L. Satarian, W. Deng, H. Baharvand, and M. Javan, “In vivo conversion of astrocytes into oligodendrocyte lineage cells with transcription factor Sox10; Promise for myelin repair in multiple sclerosis,” PLoS One, vol. 13, no. 9, p. e0203785, Sep. 2018, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203785.
(11) S. Farhangi, S. Dehghan, M. Totonchi, and M. Javan, “In vivo conversion of astrocytes to oligodendrocyte lineage cells in adult mice demyelinated brains by Sox2,” Mult Scler Relat Disord, vol. 28, pp. 263–272, Feb. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2018.12.041.
(12) L.-L. Wang, C. Serrano, X. Zhong, S. Ma, Y. Zou, and C.-L. Zhang, “Revisiting astrocyte to neuron conversion with lineage tracing in vivo,” Cell, vol. 184, no. 21, pp. 5465-5481.e16, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.09.005.
(13) I Matias, J. Morgado, and F. C. A. Gomes, “Astrocyte Heterogeneity: Impact to Brain Aging and Disease,” Front. Aging Neurosci., vol. 11, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00059.
(14) N. Habib et al., “Disease-associated astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease and aging,” Nat Neurosci, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 701–706, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0624-8.
(15) M. A. Wheeler et al., “MAFG-driven astrocytes promote CNS inflammation,” Nature, vol. 578, no. 7796, pp. 593–599, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1999-0.
(16) K. Kamimoto, B. Stringa, C. M. Hoffmann, K. Jindal, L. Solnica-Krezel, and S. A. Morris, “Dissecting cell identity via network inference and in silico gene perturbation,” Nature, vol. 614, no. 7949, pp. 742–751, Feb. 2023, doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05688-9.
(17) P. Kang et al., “Sox9 and NFIA coordinate a transcriptional regulatory cascade during the initiation of gliogenesis,” Neuron, vol. 74, no. 1, pp. 79–94, Apr. 2012, doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.01.024.
(18) K. Saito et al., “Microglia sense astrocyte dysfunction and prevent disease progression in an Alexander disease model,” Brain, vol. 147, no. 2, pp. 698–716, Nov. 2023, doi:10.1093/brain/awad358.
(19) S. A. Liddelow et al., “Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia,” Nature, vol. 541, no. 7638, pp. 481–487, Jan. 2017, doi: 10.1038/nature21029.
(20) Q. Zhu et al., “Genetic evidence that Nkx2.2 and Pdgfra are major determinants of the timing of oligodendrocyte differentiation in the developing CNS,” Development, vol. 141, no. 3, pp. 548–555, Feb. 2014, doi: 10.1242/dev.095323.
(21) J. A. Nielsen, J. A. Berndt, L. D. Hudson, and R. C. Armstrong, “Myelin transcription factor 1 (Myt1) modulates the proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte lineage cells,” Mol Cell Neurosci, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 111–123, Jan. 2004, doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2003.10.001.
(22) J. Liu, X. Feng, Y. Wang, X. Xia, and J. C. Zheng, “Astrocytes: GABAceptive and GABAergic Cells in the Brain,” Front. Cell. Neurosci., vol. 16, Jun. 2022, doi:10.3389/fncel.2022.892497.
(23) A. Sharma et al., “Divergent roles of astrocytic versus neuronal EAAT2 deficiency on cognition and overlap with aging and Alzheimer’s molecular signatures,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 116, no. 43, pp. 21800–21811, Oct. 2019, doi:10.1073/pnas.1903566116
Rainbowism or “rainbow nationalism“ (Gqola: 2001,qf Slade 2015) is described as an ‘unintentional‘ act of“invoking the rainbow nation as means of silencingdissenting voices with regards to the status quo in thecountry...[...] and with regards to race and apartheid past“(Slade; 2015: 3). The concept of the rainbow nation;censorship
He's talking about self-censorship, burying the past, avoiding historical memory. The fears are in place, I'd argue, but simultaneously, for a society to really move on it must reconcile with its past and repair those who had been wronged, else the "survivors" remain silenced, displaced, existing but unseen... and this too can be the seed of radicalisation and accumulating hatred.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This study explores the connectivity patterns that could lead to fast and slow undulating swim patterns in larval zebrafish using a simplified theoretical framework. The authors show that a pattern of connectivity based only on inhibition is sufficient to produce realistic patterns with a single frequency. Two such networks couple with inhibition but with distinct time constants can produce a range of frequencies. Adding excitatory connections further increases the range of obtainable frequencies, albeit at the expense of sudden transitions in mid-frequency range.
Strengths:
(1) This is an eloquent approach to answering the question of how spinal locomotor circuits generate coordinated activity using a theoretical approach based on moving bump models of brain activity.
(2) The models make specific predictions on patterns of connectivity while discounting the role of connectivity strength or neuronal intrinsic properties in shaping the pattern.
(3) The models also propose that there is an important association between cell-type-specific intersegmental patterns and the recruitment of speed-selective subpopulations of interneurons.
(4) Having a hierarchy of models creates a compelling argument for explaining rhythmicity at the network level. Each model builds on the last and reveals a new perspective on how network dynamics can control rhythmicity. I liked that each model can be used to probe questions in the next/previous model.
Comments on revisions:
I am very happy to see the simplified biophysical model supporting the original findings. The authors have done an excellent job addressing my comments.
Just a small note, please change C. Elegans to C. elegans.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
Central pattern generator (CPG) circuits underly rhythmic motor behaviors. Till date, it is thought that these CPG networks are rather local and multiple CPG circuits are serially connected to allow locomotion across the entire body. Distributed CPG networks that incorporate long-range connections have not been proposed although such connectivity has been experimentally shown for several different spinal populations. In this manuscript, the authors use this existing literature on long-range spinal interneuron connectivity to build a new computational model that reproduces basic features of locomotion like left-right alternation, rostrocaudal propagation and independent control of frequency and amplitude. Interestingly, the authors show that a model solely based on inhibitory neurons can recapitulate these basic locomotor features. Excitatory sources were then added that increased the dynamic range of frequencies generated. Finally, the authors were also able to reproduce experimentally observed consequences of cell-type-specific ablations showing that local and long range, cell-type-specific connectivity could be sufficient for generating locomotion.
Strengths:
This work is novel, providing an interesting alternative of distributed CPGs to the local networks traditionally predicted. It shows cell type-specific network connectivity is as important if not more than intrinsic cell properties for rhythmogenesis and that inhibition plays a crucial role in shaping locomotor features. Given the importance of local CPGs in understanding motor control, this alternative concept will be of broad interest to the larger motor control field including invertebrate and vertebrate species.
Weaknesses:
The main weaknesses were addressed in the revision.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
(1)How is this simplified model representative of what is observed biologically? A bump model does not naturally produce oscillations. How would the dynamics of a rhythm generator interact with this simplistic model?
Bump models naturally produce sequential activity, and can be engineered to repeat this sequential activity periodically (Zhang, 1996; Samsonovich and McNaughton, 1997; Murray and Escola, 2017). This is the basis for the oscillatory behavior in the model presented here. As we describe in our paper, such a model is consistent with numerous neurobiological observations about cell-type-specific connectivity patterns. The reviewer is, however, correct to point out that our model does not incorporate other key neurobiological features--in particular, intracellular dynamical properties--that have been shown to play important roles in rhythm generation. Our aim in this work is to establish a circuit-level mechanism for rhythm generation, complementary to classical models that rely on intracellular dynamics for rhythm generation. Whether and how these mechanisms work together is something that we plan to explore in future work, and we have added a sentence to the Discussion to this effect.
(2) Would this theoretical construct survive being expressed in a biophysical model? It seems that it should, but even a simple biological model with the basic patterns of connectivity shown here would greatly increase confidence in the biological plausibility of the theory.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out this way to strengthen our paper. We implemented the connectivity developed in the rate models in a spiking neuron model which used EI-balanced Poisson noise as input drive. We found that we could reproduce all the main results of our analysis. In particular, with a realistic number of neurons, we observed swimming activity characterized by (i) left-right alternation, (ii) rostal-caudal propagation, and (iii) variable speed control with constant phase lag. The spiking model demonstrates that the connectivity-motif based mechanisms for rhythmogenesis that we propose are robust in a biophysical setting.
We included these results in the updated manuscript in a new Results subsection titled “Robustness in a biophysical model.”
(3) How stable is this model in its output patterns? Is it robust to noise? Does noise, in fact, smooth out the abrupt transitions in frequency in the middle range?
The newly added spiking model implementation of the network demonstrates that the core mechanisms of our models are robust to noise, since the connectivity is randomly chosen and the input drive is Poisson noise.
To test the effect of noise as it is parametrically varied, we also added noise directly to the rate models in the form of white noise input to each unit. Namely, the rate model was adapted to obey the stochastic differential equation
\[
\tau_i \frac{dr_i(t)}{dt} = -r_i(t) + \left[ \sum_j W_{ij} r_j(t - \Delta_{ij}) + D_i + \sigma\xi_t \right]_+
\]
Here $\xi_t$ is a standard Gaussian white noise and $\sigma$ sets the strength of the noise. We found that the swimming patterns were robust at all frequencies up to $\sigma = 0.05$. Above this level, coherent oscillations started to break down for some swim frequencies. To investigate whether the noise smoothed out abrupt transitions, we swept through different values of noise and modularity of excitatory connections. The results showed very minor improvement in controllability (see figure below), but this was not significant enough to include in the manuscript.
Author response image 1.
(4) All figure captions are inadequate. They should have enough information for the reader to understand the figure and the point that was meant to be conveyed. For example, Figure 1 does not explain what the red dot is, what is black, what is white, or what the gradations of gray are. Or even if this is a representative connectivity of one node, or if this shows all the connections? The authors should not leave the reader guessing.
All figure captions have been updated to enhance clarity and address these concerns.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
(1) Figure 1A, if I interpret Figure 1B correctly, should there not be long descending projections as well that don't seem to be illustrated?
Thank you for highlighting this potential point of confusion. The diagram in question was only intended to be a rough schematic of the types of connections present in the model. We have added additional descending connections as requested
(2)Page 5, It would be good to define what is meant by slow and fast here, as this definition changes with age in zebrafish (what developmental age)?
We have updated the manuscript to include the sentence: “These values were chosen to coincide with observed ranges from larval zebrafish.” with appropriate citation.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
(1) The authors describe a single unit as a neuron, be it excitatory or inhibitory, and the output of the simulation is the firing rate of these neurons. Experimentally and in other modeling studies, motor neurons are incorporated in the model, and the output of the network is based on motor neuron firing rate, not the interneurons themselves. Why did the authors choose to build the model this way?
We chose to leave out the motor neurons from our models for a few reasons. While motor neurons read out the rhythmic activity generated by the interneurons and may provide some feedback, they are not required for rhythmogenesis. In fact, interneuron activity (especially in the excitatory V2a neurons (Agha et al., 2024)) is highly correlated with the ventral root bursts within the same segment. This suggests that motor neurons are primarily a local readout of the rhythmic activity of interneurons; therefore, the rhythmic swimming activity can be deduced directly from the interneurons themselves.
Moreover, there is a lack of experimental observation of the connectivity between all the cell types considered in our model and motor neurons. Hence, it was unclear how we should include them in the model. To address this, we are currently developing a data-driven approach that will determine the proper connectivity between the motor neurons and the interneurons, including intrasegmental connections.
(2) In the single population model (Figure 1), the authors use ipsilateral inhibitory connections that are long-range in an ascending direction. Experimentally, these connections have been shown to be local, while long-range ipsilateral connections have been shown to be descending. What were the reasons the authors chose this connectivity? Do the authors think local ascending inhibitions contribute to rostrocaudal propagation, and how?
The long-range ascending ipsilateral inhibitory connections arises from a limitation of our modeling framework. The V1 neurons that provide these connections have been shown experimentally to fire later than other neurons (especially descending V2a neurons) within the same hemisegment (Jay et al., J Neurosci, 2023); however, our model can only produce synchronized local activity. Hence, we replace local phase offsets with spatial offsets to produce correctly structured recurrent phasic inputs. We are currently investigating a data-driven method for determining intrasegmental connectivity which should be able to produce the local phase offset and address this concern; however, this is beyond the scope of the current paper.
(3) In the two-population model, the authors show independent control of frequency and rhythm, as has been reported experimentally. However, in these previous experimental studies, frequency and amplitude are regulated by different neurons, suggesting different networks dedicated to frequency and amplitude control. However, in the current model, the same population with the same connections can contribute to frequency or amplitude depending on relative tonic drive. Can the authors please address these differences either by changes in the model or by adding to the Discussion?
Our prior experimental results that suggested a separation of frequency and amplitude control circuits focus on motor neuron recruitment, instead of interneuron activity (Jay et al., J Neurosci 2023; Menelaou and McLean, Nat Commun 2019). To avoid potential confusion about amplitudes of interneurons vs. of motor neurons, we have removed the results from Figure 3 about control of amplitude in the 2-population model, instead focusing this figure on the control of frequency via speed-module recruitment. For the same reason, we have removed the panel showing the effects of targeted ablations on interneuron amplitudes in Figure 7. We have kept the result about amplitude control in our Supplemental Figure S2 for the 8-population model, but we try to make it clear in the text that any relationship between interneuron amplitude and motor neuron amplitude would depend on how motor neurons are modeled, which we do not pursue in this work.
(4) It would be helpful to add a paragraph in the Discussion on how these results could be applicable to other model systems beyond zebrafish. Cell intrinsic rhythmogenesis is a popular concept in the field, and these results show an interesting and novel alternative. It would help to know if there is any experimental evidence suggesting such network-based propagation in other systems, invertebrates, or vertebrates.
We have expanded a paragraph in the Discussion to address these questions. In particular, we highlight how a recent study of mouse locomotor circuits produced a model with similar key features (Komi et al., 2024). These authors made direct use of experimentally determined connectivity structure and cell-type distributions, which informed a model that produced purely network-based rhythmogenesis. We also point out that inhibition-dominated connectivity has been used for understanding oscillatory behavior in neural circuits outside the context of motor control (Zhang, 1996; Samsonovich and McNaughton, 1997; Murray and Escola, 2017). Finally, we address a study that used the cell-type specific connectivity within the C. Elegans locomotor circuit as the architecture for an artificial motor control system and found that the resulting system could more efficiently learn motor control tasks than general machine learning architectures (Bhattasali et al. 2022). Like our model, the Komi et al. and Bhattasali et al. models generate rhythm via structured connectivity motifs rather than via intracellular dynamical properties, suggesting that these may be a key mechanism underlying locomotion across species.
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Express this modeling construct in a simple biophysical model.
See the new Results subsection titled “Robustness in a biophysical model.”
(2) Please cite the classic models of Kopell, Ermentrout, Williams, Sigvardt etc., especially where you say "classic models".
We have added relevant citations including the mentioned authors.
(3) "Rhythmogenesis remain incompletely understood" changed to "Rhythmogenesis remains incompletely understood".
We chose not to make this change since the ‘remain’ refers to the plural ‘core mechanisms’ not the singular ‘rhythmogenesis’.
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) The figures are well made; however, it would help to add more details to the figure legends. For example, what neuron's firing rate is shown in Figure 1C? What is the red dot in 1B? Figures 3E,F,G: what is being plotted? Mean and SD? Blue dot in Figure 5C?
All figure captions have been updated to enhance clarity and address these concerns.
(2) A, B text missing in Figure 7.
We have revised this figure and its caption; please see our response to Comment 3 above.
(3) It would be nice to see the tonic drive pattern that is fed to the model for each case, along with the different firing rates in the figures. It would help understand how the tonic drive is changed to rhythmic activity.
The tonic drive in the rate models is implemented as a constant excitatory input that is uniform across all units within the same speed-population. There is no patterning in time or location to this drive.
References
(1) Moneeza A Agha, Sandeep Kishore, and David L McLean. Cell-type-specific origins of locomotor rhythmicity at different speeds in larval zebrafish. eLife, July 2024
(2) Nikhil Bhattasali, Anthony M Zador, and Tatiana Engel. Neural circuit architectural priors for embodied control. In S. Koyejo, S. Mohamed, A. Agarwal, D. Belgrave, K. Cho, and A. Oh, editors, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 35, pages 12744–12759. Curran Associates, Inc., 2022.
(3) Salif Komi, August Winther, Grace A. Houser, Roar Jakob Sørensen, Silas Dalum Larsen, Madelaine C. Adamssom Bonfils, Guanghui Li, and Rune W. Berg. Spatial and network principles behind neural generation of locomotion. bioRxiv, 2024
(4) James M Murray and G Sean Escola. Learning multiple variable-speed sequences in striatum via cortical tutoring. eLife, 6:e26084, May 2017.
(5) Alexei Samsonovich and Bruce L McNaughton. Path integration and cognitive mapping in a continuous attractor neural network model. Journal of Neuroscience, 17(15):5900–5920, 1997.
(6) K Zhang. Representation of spatial orientation by the intrinsic dynamics of the head-direction cell ensemble: a theory. Journal of Neuroscience, 16(6):2112–2126, 1996.
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the previous reviews
Public Reviews:
We thank the Reviewers for their thorough attention to our paper and the interesting discussion about the findings. Before responding to more specific comments, here some general points we would like to clarify:
(1) Ecological niche models are indeed correlative models, and we used them to highlight environmental factors associated with HPAI outbreaks within two host groups. We will further revise the terminology that could still unintentionally suggest causal inference. The few remaining ambiguities were mainly in the Discussion section, where our intent was to interpret the results in light of the broader scientific literature. Particularly, we will change the following expressions:
- “Which factors can explain…” to “Which factors are associated with…” (line 75);
- “the environmental and anthropogenic factors influencing” to “the environmental and anthropogenic factors that are correlated with” (line 273);
- “underscoring the influence” to “underscoring the strong association” (line 282).
(2) We respectfully disagree with the suggestion that an ecological niche modelling (ENM) approach is not appropriate for this work and the research question addressed therein. Ecological niche models are specifically designed to estimate the spatial distribution of the environmental suitability of species and pathogens, making them well suited to our research questions. In our study, we have also explicitly detailed the known limitations of ecological niche models in the Discussion section, in line with prior literature, to ensure their appropriate interpretation in the context of HPAI.
(3) The environmental layers used in our models were restricted to those available at a global scale, as listed in Supplementary Information Resources S1 (https://github.com/sdellicour/h5nx\_risk\_mapping/blob/master/Scripts\_%26\_data/SI\_Resource\_S1.xlsx). Naturally, not all potentially relevant environmental factors could be included, but the selected layers are explicitly documented and only these were assessed for their importance. Despite this limitation, the performance metrics indicate that the models performed well, suggesting that the chosen covariates capture meaningful associations with HPAI occurrence at a global scale.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
The authors aim to predict ecological suitability for transmission of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) using ecological niche models. This class of models identify correlations between the locations of species or disease detections and the environment. These correlations are then used to predict habitat suitability (in this work, ecological suitability for disease transmission) in locations where surveillance of the species or disease has not been conducted. The authors fit separate models for HPAI detections in wild birds and farmed birds, for two strains of HPAI (H5N1 and H5Nx) and for two time periods, pre- and post-2020. The authors also validate models fitted to disease occurrence data from pre-2020 using post-2020 occurrence data. I thank the authors for taking the time to respond to my initial review and I provide some follow-up below.
Detailed comments:
In my review, I asked the authors to clarify the meaning of "spillover" within the HPAI transmission cycle. This term is still not entirely clear: at lines 409-410, the authors use the term with reference to transmission between wild birds and farmed birds, as distinct to transmission between farmed birds. It is implied but not explicitly stated that "spillover" is relevant to the transmission cycle in farmed birds only. The sentence, "we developed separate ecological niche models for wild and domestic bird HPAI occurrences ..." could have been supported by a clear sentence describing the transmission cycle, to prime the reader for why two separate models were necessary.
We respectfully disagree that the term “spillover” is unclear in the manuscript. In both the Methods and Discussion sections (lines 387-391 and 409-414), we explicitly define “spillover” as the introduction of HPAI viruses from wild birds into domestic poultry, and we distinguish this from secondary farm-to-farm transmission. Our use of separate ecological niche models for wild and domestic outbreaks reflects not only the distinction between primary spillover and secondary transmission, but also the fundamentally different ecological processes, surveillance systems, and management implications that shape outbreaks in these two groups. We will clarify this choice in the revised manuscript when introducing the separate models. Furthermore, on line 83, we will add “as these two groups are influenced by different ecological processes, surveillance biases, and management contexts”.
I also queried the importance of (dead-end) mammalian infections to a model of the HPAI transmission risk, to which the authors responded: "While spillover events of HPAI into mammals have been documented, these detections are generally considered dead-end infections and do not currently represent sustained transmission chains. As such, they fall outside the scope of our study, which focuses on avian hosts and models ecological suitability for outbreaks in wild and domestic birds." I would argue that any infections, whether they are in dead-end or competent hosts, represent the presence of environmental conditions to support transmission so are certainly relevant to a niche model and therefore within scope. It is certainly understandable if the authors have not been able to access data of mammalian infections, but it is an oversight to dismiss these infections as irrelevant.
We understand the Reviewer’s point, but our study was designed to model HPAI occurrence in avian hosts only. We therefore restricted our analysis to wild birds and domestic poultry, which represent the primary hosts for HPAI circulation and the focus of surveillance and control measures. While mammalian detections have been reported, they are outside the scope of this work.
Correlative ecological niche models, including BRTs, learn relationships between occurrence data and covariate data to make predictions, irrespective of correlations between covariates. I am not convinced that the authors can make any "interpretation" (line 298) that the covariates that are most informative to their models have any "influence" (line 282) on their response variable. Indeed, the observation that "land-use and climatic predictors do not play an important role in the niche ecological models" (line 286), while "intensive chicken population density emerges as a significant predictor" (line 282) begs the question: from an operational perspective, is the best (e.g., most interpretable and quickest to generate) model of HPAI risk a map of poultry farming intensity?
We agree that poultry density may partly reflect reporting bias, but we also assumed it a meaningful predictor of HPAI risk. Its importance in our models is therefore expected. Importantly, our BRT framework does more than reproduce poultry distribution: it captures non-linear relationships and interactions with other covariates, allowing a more nuanced characterisation of risk than a simple poultry density map. Note also that we distinguished in our models intensive and extensive chicken poultry density and duck density. Therefore, it is not a “map of poultry farming intensity”.
At line 282, we used the word “influence” while fully recognising that correlative models cannot establish causality. Indeed, in our analyses, “relative influence” refers to the importance metric produced by the BRT algorithm (Ridgeway, 2020), which measures correlative associations between environmental factors and outbreak occurrences. These scores are interpreted in light of the broader scientific literature, therefore our interpretations build on both our results and existing evidence, rather than on our models alone. However, in the next version of the paper, we will revise the sentence as: “underscoring the strong association of poultry farming practices with HPAI spread (Dhingra et al., 2016)”.
I have more significant concerns about the authors' treatment of sampling bias: "We agree with the Reviewer's comment that poultry density could have potentially been considered to guide the sampling effort of the pseudo-absences to consider when training domestic bird models. We however prefer to keep using a human population density layer as a proxy for surveillance bias to define the relative probability to sample pseudo-absence points in the different pixels of the background area considered when training our ecological niche models. Indeed, given that poultry density is precisely one of the predictors that we aim to test, considering this environmental layer for defining the relative probability to sample pseudo-absences would introduce a certain level of circularity in our analytical procedure, e.g. by artificially increasing to influence of that particular variable in our models." The authors have elected to ignore a fundamental feature of distribution modelling with occurrence-only data: if we include a source of sampling bias as a covariate and do not include it when we sample background data, then that covariate would appear to be correlated with presence. They acknowledge this later in their response to my review: "...assuming a sampling bias correlated with poultry density would result in reducing its effect as a risk factor." In other words, the apparent predictive capacity of poultry density is a function of how the authors have constructed the sampling bias for their models. A reader of the manuscript can reasonably ask the question: to what degree are is the model a model of HPAI transmission risk, and to what degree is the model a model of the observation process? The sentence at lines 474-477 is a helpful addition, however the preceding sentence, "Another approach to sampling pseudo-absences would have been to distribute them according to the density of domestic poultry," (line 474) is included without acknowledgement of the flow-on consequence to one of the key findings of the manuscript, that "...intensive chicken population density emerges as a significant predictor..." (line 282). The additional context on the EMPRES-i dataset at line 475-476 ("the locations of outbreaks ... are often georeferenced using place name nomenclatures") is in conflict with the description of the dataset at line 407 ("precise location coordinates"). Ultimately, the choices that the authors have made are entirely defensible through a clear, concise description of model features and assumptions, and precise language to guide the reader through interpretation of results. I am not satisfied that this is provided in the revised manuscript.
We thank the Reviewer for this important point. To address it, we compared model predictive performance and covariate relative influences obtained when pseudo-absences were weighted by poultry density versus human population density (Author response table 1). The results show that differences between the two approaches are marginal, both in predictive performance (ΔAUC ranging from -0.013 to +0.002) and in the ranking of key predictors (see below Author response images 1 and 2). For instance, intensive chicken density consistently emerged as an important predictor regardless of the bias layer used.
Note: the comparison was conducted using a simplified BRT configuration for computational efficiency (fewer trees, fixed 5-fold random cross-validation, and standardised parameters). Therefore, absolute values of AUC and variable importance may differ slightly from those in the manuscript, but the relative ranking of predictors and the overall conclusions remain consistent.
Given these small differences, we retained the approach using human population density. We agree that poultry density partly reflects surveillance bias as well as true epidemiological risk, and we will clarify this in the revised manuscript by noting that the predictive role of poultry density reflects both biological processes and surveillance systems. Furthermore, on line 289, we will add “We note, however, that intensive poultry density may reflect both surveillance intensity and epidemiological risk, and its predictive role in our models should be interpreted in light of both processes”.
Author response table 1.
Comparison of model predictive performances (AUC) between pseudo-absence sampling were weighted by poultry density and by human population density across host groups, virus types, and time periods. Differences in AUC values are shown as the value for poultry-weighted minus human-weighted pseudo-absences.
Author response image 1.
Comparison of variable relative influence (%) between models trained with pseudo-absences weighted by poultry density (red) and human population density (blue) for domestic bird outbreaks. Results are shown for four datasets: H5N1 (<2020), H5N1 (>2020), H5Nx (<2020), and H5Nx (>2020).
Author response image 2.
Comparison of variable relative influence (%) between models trained with pseudo-absences weighted by poultry density (red) and human population density (blue) for wild bird outbreaks. Results are shown for three datasets: H5N1 (>2020), H5Nx (<2020), and H5Nx (>2020).
The authors have slightly misunderstood my comment on "extrapolation": I referred to "environmental extrapolation" in my review without being particularly explicit about my meaning. By "environmental extrapolation", I meant to ask whether the models were predicting to environments that are outside the extent of environments included in the occurrence data used in the manuscript. The authors appear to have understood this to be a comment on geographic extrapolation, or predicting to areas outside the geographic extent included in occurrence data, e.g.: "For H5Nx post-2020, areas of high predicted ecological suitability, such as Brazil, Bolivia, the Caribbean islands, and Jilin province in China, likely result from extrapolations, as these regions reported few or no outbreaks in the training data" (lines 195-197). Is the model extrapolating in environmental space in these regions? This is unclear. I do not suggest that the authors should carry out further analysis, but the multivariate environmental similarly surface (MESS; see Elith et al., 2010) is a useful tool to visualise environmental extrapolation and aid model interpretation.
On the subject of "extrapolation", I am also concerned by the additions at lines 362-370: "...our models extrapolate environmental suitability for H5Nx in wild birds in areas where few or no outbreaks have been reported. This discrepancy may be explained by limited surveillance or underreporting in those regions." The "discrepancy" cited here is a feature of the input dataset, a function of the observation distribution that should be captured in pseudo-absence data. The authors state that Kazakhstan and Central Asia are areas of interest, and that the environments in this region are outside the extent of environments captured in the occurrence dataset, although it is unclear whether "extrapolation" is informed by a quantitative tool like a MESS or judged by some other qualitative test. The authors then cite Australia as an example of a region with some predicted suitability but no HPAI outbreaks to date, however this discussion point is not linked to the idea that the presence of environmental conditions to support transmission need not imply the occurrence of transmission (as in the addition, "...spatial isolation may imply a lower risk of actual occurrences..." at line 214). Ultimately, the authors have not added any clear comment on model uncertainty (e.g., variation between replicated BRTs) as I suggested might be helpful to support their description of model predictions.
Many thanks for the clarification. Indeed, we interpreted your previous comments in terms of geographic extrapolations. We thank the Reviewer for these observations. We will adjust the wording to further clarify that predictions of ecological suitability in areas with few or no reported outbreaks (e.g., Central Asia, Australia) are not model errors but expected extrapolations, since ecological suitability does not imply confirmed transmission (for instance, on Line 362: “our models extrapolate environmental suitability” will be changed to “Interestingly, our models extrapolate geographical”). These predictions indicate potential environments favorable to circulation if the virus were introduced.
In our study, model uncertainty is formally assessed when comparing the predictive performances of our models (Fig. S3, Table S1), the relative influence (Table S3) and response curves (Fig. 2) associated with each environmental factor (Table S2). All the results confirming a good converge between these replicates. Finally, we indeed did not use a quantitative tool such as a MESS to assess extrapolation but did rely on qualitative interpretation of model outputs.
All of my criticisms are, of course, applied with the understanding that niche modelling is imperfect for a disease like HPAI, and that data may be biased/incomplete, etc.: these caveats are common across the niche modelling literature. However, if language around the transmission cycle, the niche, and the interpretation of any of the models is imprecise, which I find it to be in the revised manuscript, it undermines all of the science that is presented in this work.
We respectfully disagree with this comment. The scope of our study and the methods employed are clearly defined in the manuscript, and the limitations of ecological niche modelling in this context are explicitly acknowledged in the Discussion section. While we appreciate the Reviewer’s concern, the comment does not provide specific examples of unclear or imprecise language regarding the transmission cycle, niche, or interpretation of the models. Without such examples, it is difficult to identify further revisions that would improve clarity.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
The geographic range of highly pathogenic avian influenza cases changed substantially around the period 2020, and there is much interest in understanding why. Since 2020 the pathogen irrupted in the Americas and the distribution in Asia changed dramatically. This study aimed to determine which spatial factors (environmental, agronomic and socio-economic) explain the change in numbers and locations of cases reported since 2020 (2020--2023). That's a causal question which they address by applying correlative environmental niche modelling (ENM) approach to the avian influenza case data before (2015--2020) and after 2020 (2020--2023) and separately for confirmed cases in wild and domestic birds. To address their questions they compare the outputs of the respective models, and those of the first global model of the HPAI niche published by Dhingra et al 2016.
We do not agree with this comment. In the manuscript, it is well established that we are quantitatively assessing factors that are associated with occurrences data before and after 2020. We do not claim to determine the causality. One sentence of the Introduction section (lines 75-76) could be confusing, so we intend to modify it in the final revision of our manuscript.
ENM is a correlative approach useful for extrapolating understandings based on sparse geographically referenced observational data over un- or under-sampled areas with similar environmental characteristics in the form of a continuous map. In this case, because the selected covariates about land cover, use, population and environment are broadly available over the entire world, modelled associations between the response and those covariates can be projected (predicted) back to space in the form of a continuous map of the HPAI niche for the entire world.
We fully agree with this assessment of ENM approaches.
Strengths:
The authors are clear about expected bias in the detection of cases, such geographic variation in surveillance effort (testing of symptomatic or dead wildlife, testing domestic flocks) and in general more detections near areas of higher human population density (because if a tree falls in a forest and there is no-one there, etc), and take steps to ameliorate those. The authors use boosted regression trees to implement the ENM, which typically feature among the best performing models for this application (also known as habitat suitability models). They ran replicate sets of the analysis for each of their model targets (wild/domestic x pathogen variant), which can help produce stable predictions. Their code and data is provided, though I did not verify that the work was reproducible.
The paper can be read as a partial update to the first global model of H5Nx transmission by Dhingra and others published in 2016 and explicitly follows many methodological elements. Because they use the same covariate sets as used by Dhingra et al 2016 (including the comparisons of the performance of the sets in spatial cross-validation) and for both time periods of interest in the current work, comparison of model outputs is possible. The authors further facilitate those comparisons with clear graphics and supplementary analyses and presentation. The models can also be explored interactively at a weblink provided in text, though it would be good to see the model training data there too.
The authors' comparison of ENM model outputs generated from the distinct HPAI case datasets is interesting and worthwhile, though for me, only as a response to differently framed research questions.
Weaknesses:
This well-presented and technically well-executed paper has one major weakness to my mind. I don't believe that ENM models were an appropriate tool to address their stated goal, which was to identify the factors that "explain" changing HPAI epidemiology.
Here is how I understand and unpack that weakness:
(1) Because of their fundamentally correlative nature, ENMs are not a strong candidate for exploring or inferring causal relationships.
(2) Generating ENMs for a species whose distribution is undergoing broad scale range change is complicated and requires particular caution and nuance in interpretation (e.g., Elith et al, 2010, an important general assumption of environmental niche models is that the target species is at some kind of distributional equilibrium (at time scales relevant to the model application). In practice that means the species has had an opportunity to reach all suitable habitats and therefore its absence from some can be interpreted as either unfavourable environment or interactions with other species). Here data sets for the response (N5H1 or N5Hx case data in domestic or wild birds ) were divided into two periods; 2015--2020, and 2020--2023 based on the rationale that the geographic locations and host-species profile of cases detected in the latter period was suggestive of changed epidemiology. In comparing outputs from multiple ENMs for the same target from distinct time periods the authors are expertly working in, or even dancing around, what is a known grey area, and they need to make the necessary assumptions and caveats obvious to readers.
We thank the Reviewer for this observation. First, we constrained pseudo-absence sampling to countries and regions where outbreaks had been reported, reducing the risk of interpreting non-affected areas as environmentally unsuitable. Second, we deliberately split the outbreak data into two periods (2015-2020 and 2020-2023) because we do not assume a single stable equilibrium across the full study timeframe. This division reflects known epidemiological changes around 2020 and allows each period to be modeled independently. Within each period, ENM outputs are interpreted as associations between outbreaks and covariates, not as equilibrium distributions. Finally, by testing prediction across periods, we assessed both niche stability and potential niche shifts. These clarifications will be added to the manuscript to make our assumptions and limitations explicit.
Line 66, we will add: “Ecological niche model outputs for range-shifting pathogens must therefore be interpreted with caution (Elith et al., 2010). Despite this limitation, correlative ecological niche models remain useful for identifying broad-scale associations and potential shifts in distribution. To account for this, we analysed two distinct time periods (2015-2020 and 2020-2023).”
Line 123, we will revise “These findings underscore the ability of pre-2020 models in forecasting the recent geographic distribution of ecological suitability for H5Nx and H5N1 occurrences” to “These results suggest that pre-2020 models captured broad patterns of suitability for H5Nx and H5N1 outbreaks, while post-2020 models provided a closer fit to the more recent epidemiological situation”.
(3) To generate global prediction maps via ENM, only variables that exist at appropriate resolution over the desired area can be supplied as covariates. What processes could influence changing epidemiology of a pathogen and are their covariates that represent them? Introduction to a new geographic area (continent) with naive population, immunity in previously exposed populations, control measures to limit spread such as vaccination or destruction of vulnerable populations or flocks? Might those control measures be more or less likely depending on the country as a function of its resources and governance? There aren't globally available datasets that speak to those factors, so the question is not why were they omitted but rather was the authors decision to choose ENMs given their question justified? How valuable are insights based on patterns of correlation change when considering different temporal sets of HPAI cases in relation to a common and somewhat anachronistic set of covariates?
We agree that the ecological niche models trained in our study are limited to environmental and host factors, as described in the Methods section with the selection of predictors. While such models cannot capture causality or represent processes such as immunity, control measures, or governance, they remain a useful tool for identifying broad associations between outbreak occurrence and environmental context. Our study cannot infer the full mechanisms driving changes in HPAI epidemiology, but it does provide a globally consistent framework to examine how associations with available covariates vary across time periods.
(4) In general the study is somewhat incoherent with respect to time. Though the case data come from different time periods, each response dataset was modelled separately using exactly the same covariate dataset that predated both sets. That decision should be understood as a strong assumption on the part of the authors that conditions the interpretation: the world (as represented by the covariate set) is immutable, so the model has to return different correlative associations between the case data and the covariates to explain the new data. While the world represented by the selected covariates \*may\* be relatively stable (could be statistically confirmed), what about the world not represented by the covariates (see point 3)?
We used the same covariate layers for both periods, which indeed assumes that these environmental and host factors are relatively stable at the global scale over the short timeframe considered. We believe this assumption is reasonable, as poultry density, land cover, and climate baselines do not change drastically between 2015 and 2023 at the resolution of our analysis. We agree, however, that unmeasured processes such as control measures, immunity, or governance may have changed during this time and are not captured by our covariates.
Recommendations for the Authors:
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
- Line 400-401: "over the 2003-2016 periods" has an extra "s"; "two host species" (with reference to wild and domestic birds) would be more precise as "two host groups".
- Remove comma line 404
Many thanks for these comments, we have modified the text accordingly.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
Most of my work this round is encapsulated in the public part of the review.
The authors responded positively to the review efforts from the previous round, but I was underwhelmed with the changes to the text that resulted. Particularly in regard to limiting assumptions - the way that they augmented the text to refer to limitations raised in review downplayed the importance of the assumptions they've made. So they acknowledge the significance of the limitation in their rejoinder, but in the amended text merely note the limitation without giving any sense of what it means for their interpretation of the findings of this study.
The abstract and findings are essentially unchanged from the previous draft.
I still feel the near causal statements of interpretation about the covariates are concerning. These models really are not a good candidate for supporting the inference that they are making and there seem to be very strong arguments in favour of adding covariates that are not globally available.
We never claimed causal interpretation, and we have consistently framed our analyses in terms of associations rather than mechanisms. We acknowledge that one phrasing in the research questions (“Which factors can explain…”) could be misinterpreted, and we are correcting this in the revised version to read “Which factors are associated with…”. Our approach follows standard ecological niche modelling practice, which identifies statistical associations between occurrence data and covariates. As noted in the Discussion section, these associations should not be interpreted as direct causal mechanisms. Finally, all interpretive points in the manuscript are supported by published literature, and we consider this framing both appropriate and consistent with best practice in ecological niche modelling (ENM) studies.
We assessed predictor contributions using the “relative influence” metric, the terminology reported by the R package “gbm” (Ridgeway, 2020). This metric quantifies the contribution of each variable to model fit across all trees, rescaled to sum to 100%, and should be interpreted as an association rather than a causal effect.
L65-66 The general difficulty of interpreting ENM output with range-shifting species should be cited here to alert readers that they should not blithely attempt what follows at home.
I believe that their analysis is interesting and technically very well executed, so it has been a disappointment and hard work to write this assessment. My rough-cut last paragraph of a reframed intro would go something like - there are many reasons in the literature not to do what we are about to do, but here's why we think it can be instructive and informative, within certain guardrails.
To acknowledge this comment and the previous one, we revised lines 65-66 to: “However, recent outbreaks raise questions about whether earlier ecological niche models still accurately predict the current distribution of areas ecologically suitable for the local circulation of HPAI H5 viruses. Ecological niche model outputs for range-shifting pathogens must therefore be interpreted with caution (Elith et al., 2010). Despite this limitation, correlative ecological niche models remain useful for identifying broad-scale associations and potential shifts in distribution.”
We respectfully disagree with the Reviewer’s statement that “there are many reasons in the literature not to do what we are about to do”. All modeling approaches, including mechanistic ones, have limitations, and the literature is clear on both the strengths and constraints of ecological niche models. Our manuscript openly acknowledges these limits and frames our findings accordingly. We therefore believe that our use of an ENM approach is justified and contributes valuable insights within these well-defined boundaries.
Reference: Ridgeway, G. (2007). Generalized Boosted Models: A guide to the gbm package. Update, 1(1), 2007.
KNET. This is a default and recommended transport introduced in Corosync 3.
^
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
In this manuscript, Davis and colleagues aimed to identify the molecular sensors and signaling cascade that enable collecting lymphatic vessels to increase their spontaneous contraction frequency in response to intraluminal pressure (pressure-induced chronotropy). They tested whether the process is similar to blood vessel myogenic constriction by relying on cation channels (TRPC6, TRPM4, PKD2, PIEZO1, etc.) or instead require the activation of G-protein-coupled receptors (presumably mechanosensitive GNAQ/GNA11-coupled receptors), using ex vivo pressure myography of mouse popliteal lymphatics, smooth muscle-specific conditional knockouts, quantitative PCR validation, and single-cell RNA sequencing for target prioritization. The authors convincingly demonstrate that pressure-induced chronotropy does not require the cation channels implicated in arterial myogenic tone but is blunted by deletion of GNAQ/GNA11 or IP3 receptor 1, supporting a model of GPCR > IP3 > Ca2+ release > Cl⁻ channel activation > depolarization. The core conclusion is robust. The work redefines lymphatic pacemaking as G-protein-coupled receptor-dependent mechanotransduction, distinct from arterial mechanisms, and provides a genetically validated toolkit that is useful for studying lymphatic function and dysfunction.
Strengths:
(1) The data are of high quality and highly sensitive functional readouts
(2) The systematic genetic targeting is a major strength that overcomes pharmacological artifacts
(3) Careful quantitative analyses of frequency-pressure slopes
Weaknesses:
(1) The use of inguinal-axillary vessels for single-cell RNA sequencing rather than the popliteal segment studied functionally.
(2) No direct testing of the specific G-protein-coupled receptor involved.
Dostáváte 3letou záruku na konstrukci stanů Octa Go a 10letý pozáruční servis.
Poskytujeme záruku 3 roky na konstrukci + náhradní díly skladem.
RRID: AB_94975
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Millipore Cat# MAB386, RRID:AB_94975)
Curator: @evieth
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_94975
RRID:AB_10694505
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 5568, RRID:AB_10694505)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_10694505
RRID:AB_2307391
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Jackson ImmunoResearch Labs Cat# 111-035-144, RRID:AB_2307391)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_2307391
RRID:AB_561053
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 2118, RRID:AB_561053)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_561053
RRID:AB_2307392
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Jackson ImmunoResearch Labs Cat# 115-035-146, RRID:AB_2307392)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_2307392
RRID:AB_303248
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Abcam Cat# ab2723, RRID:AB_303248)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_303248
Addgene_12260
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: RRID:Addgene_12260
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:Addgene_12260
RRID:AB_331757
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 9139, RRID:AB_331757)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_331757
RRID:AB_330744
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 9102, RRID:AB_330744)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_330744
RRID:AB_2315112
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 4370, RRID:AB_2315112)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_2315112
RRID:AB_915783
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Cell Signaling Technology Cat# 4691, RRID:AB_915783)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_915783
RRID:AB_1080976
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (GeneTex Cat# GTX100118, RRID:AB_1080976)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_1080976
RRID:AB_2534121
DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00903-3
Resource: (Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat# A-11077, RRID:AB_2534121)
Curator: @scibot
SciCrunch record: RRID:AB_2534121