Infographic: Countering online vaccine misinformation

- Dec 2023
-
www.ecdc.europa.eu www.ecdc.europa.eu
-
- Aug 2023
-
fortune.com fortune.com
-
What a mish-mash of mixed message here.... ugh.
-
- Apr 2023
-
-
But COVID-19 remains a danger, even though the darker days of overwhelmed hospitals and overflowing morgues appear to be over.
Covid is still a danger and still causes many economic and social problems but there are ways to help us learn to take care of ourselves and others from this as mentioned in the CDC website.
-
- Mar 2023
-
radiolab.org radiolab.org
-
Listened to on 2023-03-11
Much like Richard Feynman kept a list of his 12 favorite problems, Maurice Hilleman kept a running list of diseases for which he was working on developing vaccines to remedy.
-
- Jan 2023
-
euvsdisinfo.eu euvsdisinfo.eu
-
The uptake of mis- and disinformation is intertwined with the way our minds work. The large body of research on the psychological aspects of information manipulation explains why.
In an article for Nature Review Psychology, Ullrich K. H. Ecker et al looked(opens in a new tab) at the cognitive, social, and affective factors that lead people to form or even endorse misinformed views. Ironically enough, false beliefs generally arise through the same mechanisms that establish accurate beliefs. It is a mix of cognitive drivers like intuitive thinking and socio-affective drivers. When deciding what is true, people are often biased to believe in the validity of information and to trust their intuition instead of deliberating. Also, repetition increases belief in both misleading information and facts.
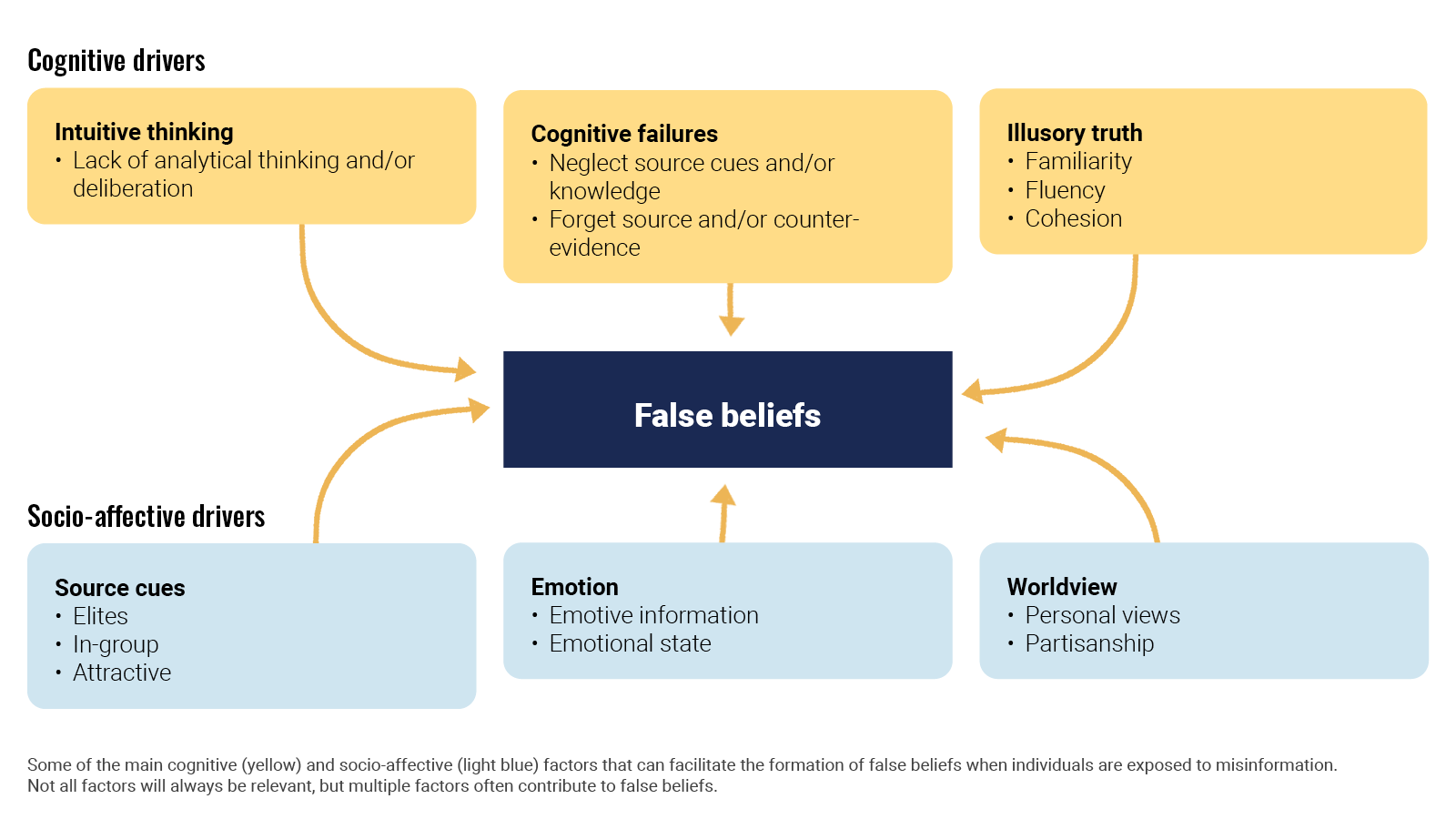
Ecker, U.K.H., Lewandowsky, S., Cook, J. et al. (2022). The psychological drivers of misinformation belief and its resistance to correction.
Going a step further, Álex Escolà-Gascón et al investigated the psychopathological profiles that characterise people prone to consuming misleading information. After running a number of tests on more than 1,400 volunteers, they concluded that people with high scores in schizotypy (a condition not too dissimilar from schizophrenia), paranoia, and histrionism (more commonly known as dramatic personality disorder) are more vulnerable to the negative effects of misleading information. People who do not detect misleading information also tend to be more anxious, suggestible, and vulnerable to strong emotions.
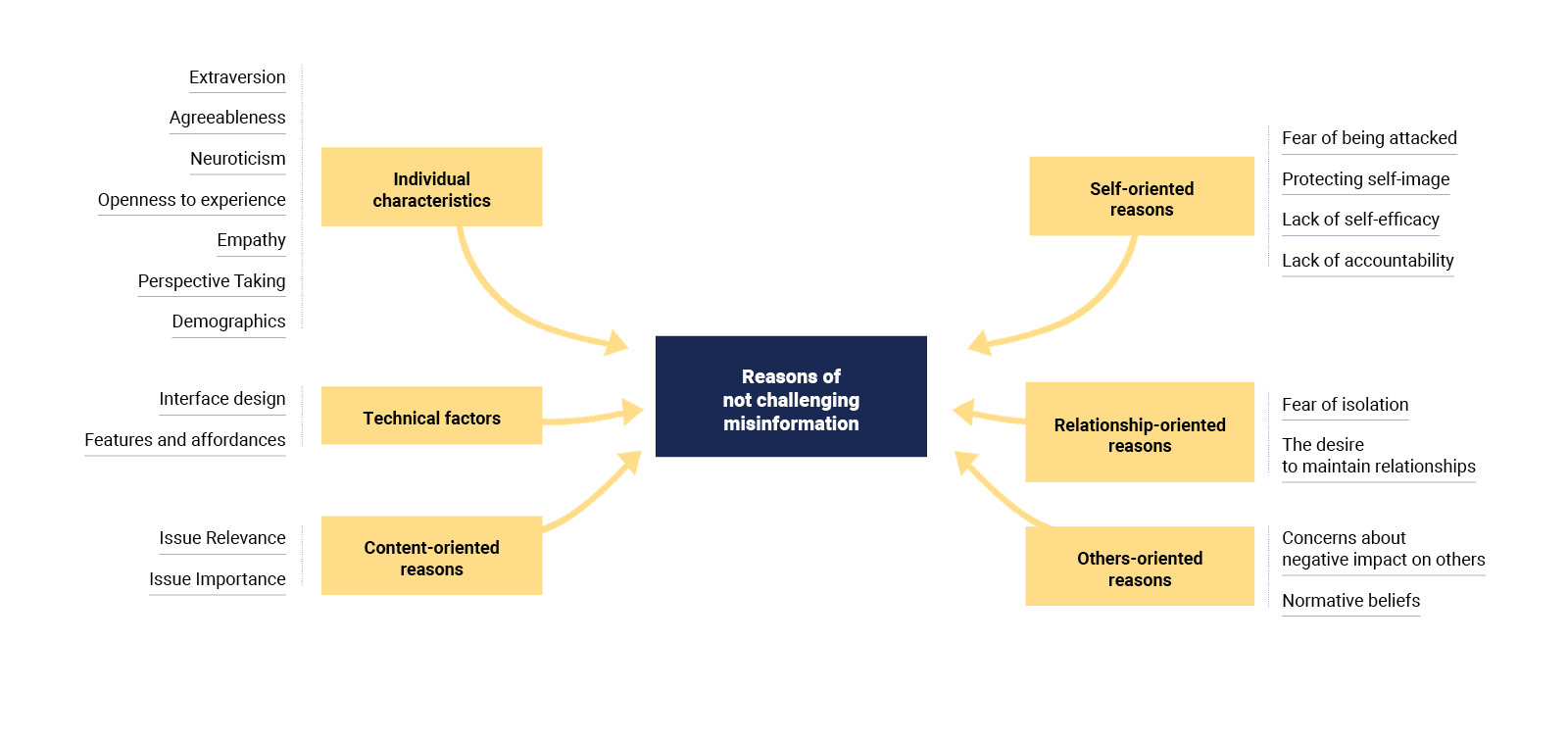
-
-
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
In 2003 five northern Nigerian states boycotted the oral polio vaccine due to fears that it was unsafe. Though the international responses have been scrutinised in the literature, this paper argues that lessons still need to be learnt from the boycott: that the origins and continuation of the boycott were due to specific local factors.
Origin and continuation boycott made this unique.
-
-
www.ids.ac.uk www.ids.ac.uk
-
Indeed ‘anti-vaccination rumours’ have been defined as a major threat to achieving vaccine coverage goals. This is demonstrated in this paper through a case study of responses to the Global Polio Eradication Campaign (GPEI) in northern Nigeria where Muslim leaders ordered the boycott of the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV). A 16-month controversy resulted from their allegations that the vaccines were contaminated with anti-fertility substances and the HIV virus was a plot by Western governments to reduce Muslim populations worldwide.
-
- Dec 2022
-
www.danielpipes.org www.danielpipes.org
-
The polio-vaccine conspiracy theory has had direct consequences: Sixteen countries where polio had been eradicated have in recent months reported outbreaks of the disease – twelve in Africa (Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Mali, Sudan, and Togo) and four in Asia (India, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen). Yemen has had the largest polio outbreak, with more than 83 cases since April. The WHO calls this "a major epidemic."
-
-
historyofvaccines.org historyofvaccines.org
-
History of Anti-Vaccination Movements
- What do Vaccines do?
- How are Vaccines Made?
- Ethical Issues and Vaccines
- Misconceptions about Vaccines
- Debunked: The Polio Vaccine and HIV Link
- History of Anti-Vaccination Movements
- The Future of Immunization
- Careers in Vaccine Research
- General Vaccine Timeline
-
-
eva.ecdc.europa.eu eva.ecdc.europa.eu
-
Aim: This study aimed to investigate how exposure to online misinformation around COVID-19 vaccines affects intention to vaccinate in the UK and US.
Method: Participants were shown images of misinformation related to COVID-19.
Findings: The researchers found that exposure to misinformation led to a decline in intention to vaccinate of approximately 6 percentage points among those who previously said they would definitely accept a vaccine. They also found that some groups were affected more than others by exposure to misinformation, and scientific-sounding misinformation was also more strongly associated with declines in vaccination intent. These findings have important implications for informing the design of vaccination campaigns and combatting online misinformation.
Reference: Loomba, S., de Figueiredo, A., Piatek, S.J. et al. Measuring the impact of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation on vaccination intent in the UK and USA. Nat Hum Behav 5, 337–348 (2021)
-
The five Cs model
The five Cs model of vaccine acceptance is based on five factors that can affect an individual's vaccination behaviour: confidence, constraints, complacency, calculation, and collective responsibility.
-
-
misinforeview.hks.harvard.edu misinforeview.hks.harvard.edu
-
Surveys of nearly 2,500 Americans, conducted during a measles outbreak, suggest that users oftraditional media are less likely to be misinformed about vaccines than are users of social media. Resultsalso suggest that an individual’s level of trust in medical experts affects the likelihood that a person’sbeliefs about vaccination will change
-
-
journals.plos.org journals.plos.org
-
Beliefs in the autism/vaccines link and in vaccines side effects, along with intention to vaccinate a future child, were evaluated both immediately after the correction intervention and after a 7-day delay to reveal possible backfire effects. Results show that existing strategies to correct vaccine misinformation are ineffective and often backfire, resulting in the unintended opposite effect, reinforcing ill-founded beliefs about vaccination and reducing intentions to vaccinate. The implications for research on vaccines misinformation and recommendations for progress are discussed.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.remnantmd.com www.remnantmd.com
-
forced on the population
at least in the US, no one is being forced to get a vaccine. Not only that, but there's no evidence anyone's even considered it: https://www.snopes.com/fact-check/forced-vaccines-covid-19/
Maybe they're talking about another population?
-
-
link.springer.com link.springer.com
-
We analyzed URLs cited in Twitter messages before and after the temporary interruption of the vaccine development on September 9, 2020 to investigate the presence of low credibility and malicious information. We show that the halt of the AstraZeneca clinical trials prompted tweets that cast doubt, fear and vaccine opposition. We discovered a strong presence of URLs from low credibility or malicious websites, as classified by independent fact-checking organizations or identified by web hosting infrastructure features. Moreover, we identified what appears to be coordinated operations to artificially promote some of these URLs hosted on malicious websites.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
We found that misinformation-exposure scores are significantly positively related to language toxicity (Fig. 3a; b = 0.129, 95% CI = [0.098, 0.159], SE = 0.015, t (4121) = 8.323, p < 0.001; b = 0.319, 95% CI = [0.274, 0.365], SE = 0.023, t (4106) = 13.747, p < 0.001 when controlling for estimated ideology) and expressions of moral outrage (Fig. 3b; b = 0.107, 95% CI = [0.076, 0.137], SE = 0.015, t (4143) = 14.243, p < 0.001; b = 0.329, 95% CI = [0.283,0.374], SE = 0.023, t (4128) = 14.243, p < 0.001 when controlling for estimated ideology). See Supplementary Tables 1, 2 for full regression tables and Supplementary Tables 3–6 for the robustness of our results.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Exposure to elite misinformation is associated with sharing news from lower-quality outlets and with conservative estimated ideology.
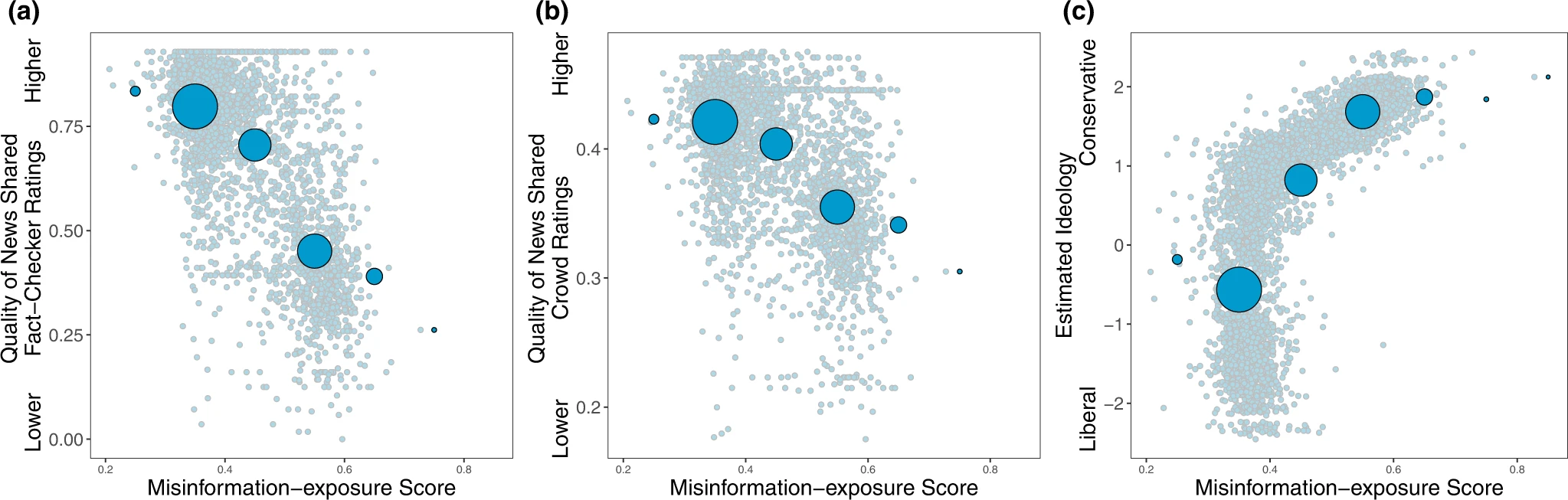
Shown is the relationship between users’ misinformation-exposure scores and (a) the quality of the news outlets they shared content from, as rated by professional fact-checkers21, (b) the quality of the news outlets they shared content from, as rated by layperson crowds21, and (c) estimated political ideology, based on the ideology of the accounts they follow10. Small dots in the background show individual observations; large dots show the average value across bins of size 0.1, with size of dots proportional to the number of observations in each bin.
-
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
Notice that Twitter’s account purge significantly impacted misinformation spread worldwide: the proportion of low-credible domains in URLs retweeted from U.S. dropped from 14% to 7%. Finally, despite not having a list of low-credible domains in Russian, Russia is central in exporting potential misinformation in the vax rollout period, especially to Latin American countries. In these countries, the proportion of low-credible URLs coming from Russia increased from 1% in vax development to 18% in vax rollout periods (see Figure 8 (b), Appendix).
-
Interestingly, the fraction of low-credible URLs coming from U.S. dropped from 74% in the vax devel-opment period to 55% in the vax rollout. This large decrease can be directly ascribed to Twitter’s moderationpolicy: 46% of cross-border retweets of U.S. users linking to low-credible websites in the vax developmentperiod came from accounts that have been suspended following the U.S. Capitol attack (see Figure 8 (a), Ap-pendix).
-
Considering the behavior of users in no-vax communities,we find that they are more likely to retweet (Figure 3(a)), share URLs (Figure 3(b)), and especially URLs toYouTube (Figure 3(c)) than other users. Furthermore, the URLs they post are much more likely to be fromlow-credible domains (Figure 3(d)), compared to those posted in the rest of the networks. The differenceis remarkable: 26.0% of domains shared in no-vax communities come from lists of known low-credibledomains, versus only 2.4% of those cited by other users (p < 0.001). The most common low-crediblewebsites among the no-vax communities are zerohedge.com, lifesitenews.com, dailymail.co.uk (consideredright-biased and questionably sourced) and childrenshealthdefense.com (conspiracy/pseudoscience)
-
We find that, during the pandemic, no-vax communities became more central in the country-specificdebates and their cross-border connections strengthened, revealing a global Twitter anti-vaccinationnetwork. U.S. users are central in this network, while Russian users also become net exporters ofmisinformation during vaccination roll-out. Interestingly, we find that Twitter’s content moderationefforts, and in particular the suspension of users following the January 6th U.S. Capitol attack, had aworldwide impact in reducing misinformation spread about vaccines. These findings may help publichealth institutions and social media platforms to mitigate the spread of health-related, low-credibleinformation by revealing vulnerable online communities
-
-
www.mdpi.com www.mdpi.com
-
Therefore, although the social bot individual is “small”, it has become a “super spreader” with strategic significance. As an intelligent communication subject in the social platform, it conspired with the discourse framework in the mainstream media to form a hybrid strategy of public opinion manipulation.
-
In Figure 6, the node represented by human A is a high-degree centrality account with poor discrimination ability for disinformation and rumors; it is easily affected by misinformation retweeted by social bots. At the same time, it will also refer to the opinions of other persuasive folk opinion leaders in the retweeting process. Human B represents the official institutional account, which has a high in-degree and often pushes the latest news, preventive measures, and suggestions related to COVID-19. Human C represents a human account with high media literacy, which mainly retweets information from information sources with high credibility. It has a solid ability to identify information quality and is not susceptible to the proliferation of social bots. Human D actively creates and spreads rumors and conspiracy theories and only retweets unverified messages that support his views in an attempt to expand the influence. Social bots K, M, and N also spread unverified information (rumors, conspiracy theories, and disinformation) in the communication network without fact-checking. Social bot L may be a social bot of an official agency.
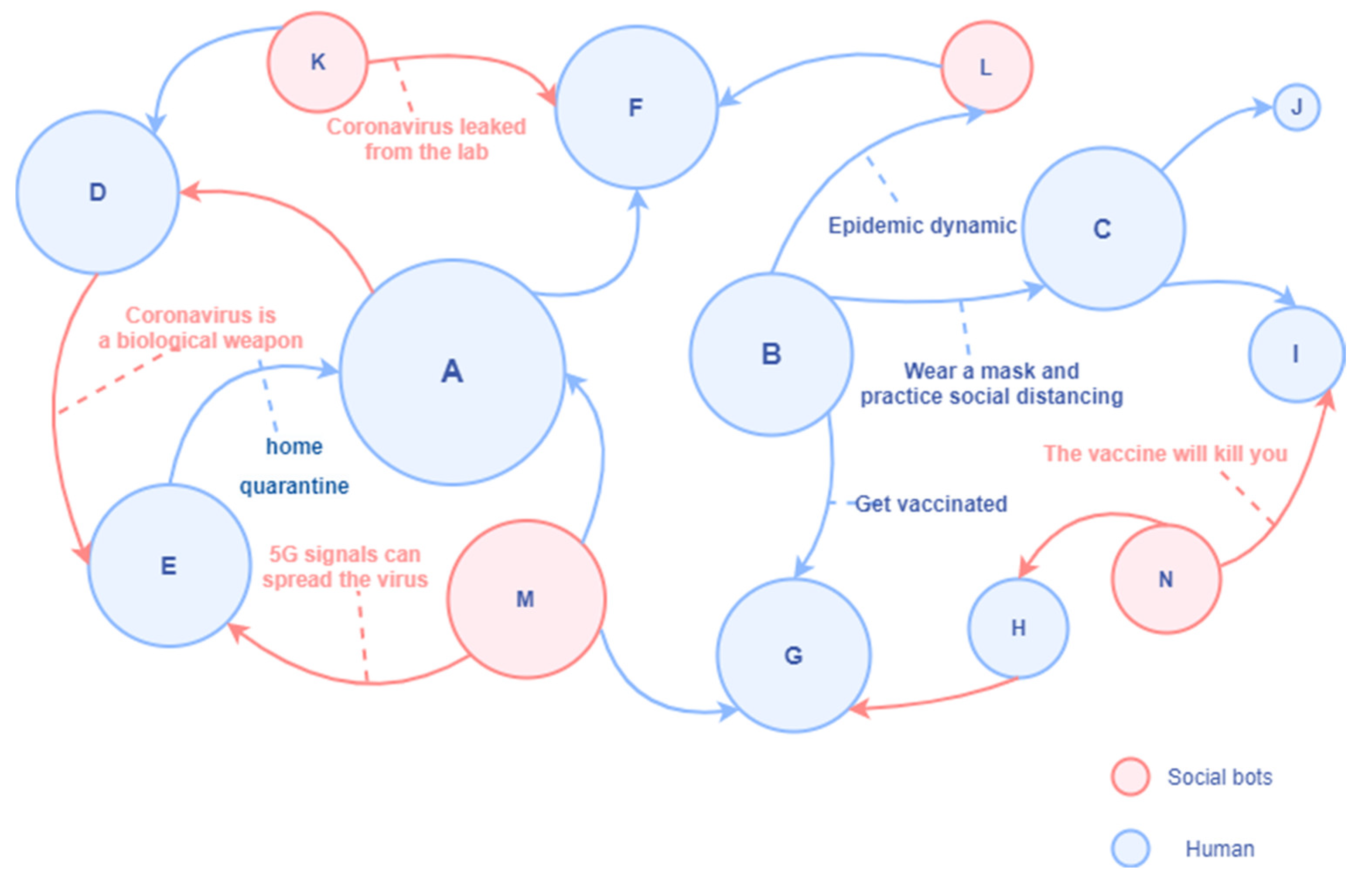
-
We analyzed and visualized Twitter data during the prevalence of the Wuhan lab leak theory and discovered that 29% of the accounts participating in the discussion were social bots. We found evidence that social bots play an essential mediating role in communication networks. Although human accounts have a more direct influence on the information diffusion network, social bots have a more indirect influence. Unverified social bot accounts retweet more, and through multiple levels of diffusion, humans are vulnerable to messages manipulated by bots, driving the spread of unverified messages across social media. These findings show that limiting the use of social bots might be an effective method to minimize the spread of conspiracy theories and hate speech online.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Conspiracy theories that provide names of the beneficiaries of political, social and economic disasters help people to navigate the complexities of the globalized world, and give simple answers as to who is right and who is wrong. If you add to this global communication technologies that help to rapidly develop and spread all sorts of conspiracy theories, these theories turn into a powerful tool to target subnational, national and international communities and to spread chaos and doubt. The smog of subjectivity created by user-generated content and the crisis of expertise have become a true gift to the Kremlin’s propaganda.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Effect of network viewership on weekly vaccination rates by age group, 2021 (2SLS). Coefficient plots with 95% CIs from 2SLS regressions showing the effect of one standard deviation changes in viewership on weekly vaccinations per 100 people, by age group. Viewerships are instrumented using the lineup channel positions. Regressions include demographic and cable-system controls. Standard errors are clustered by state.
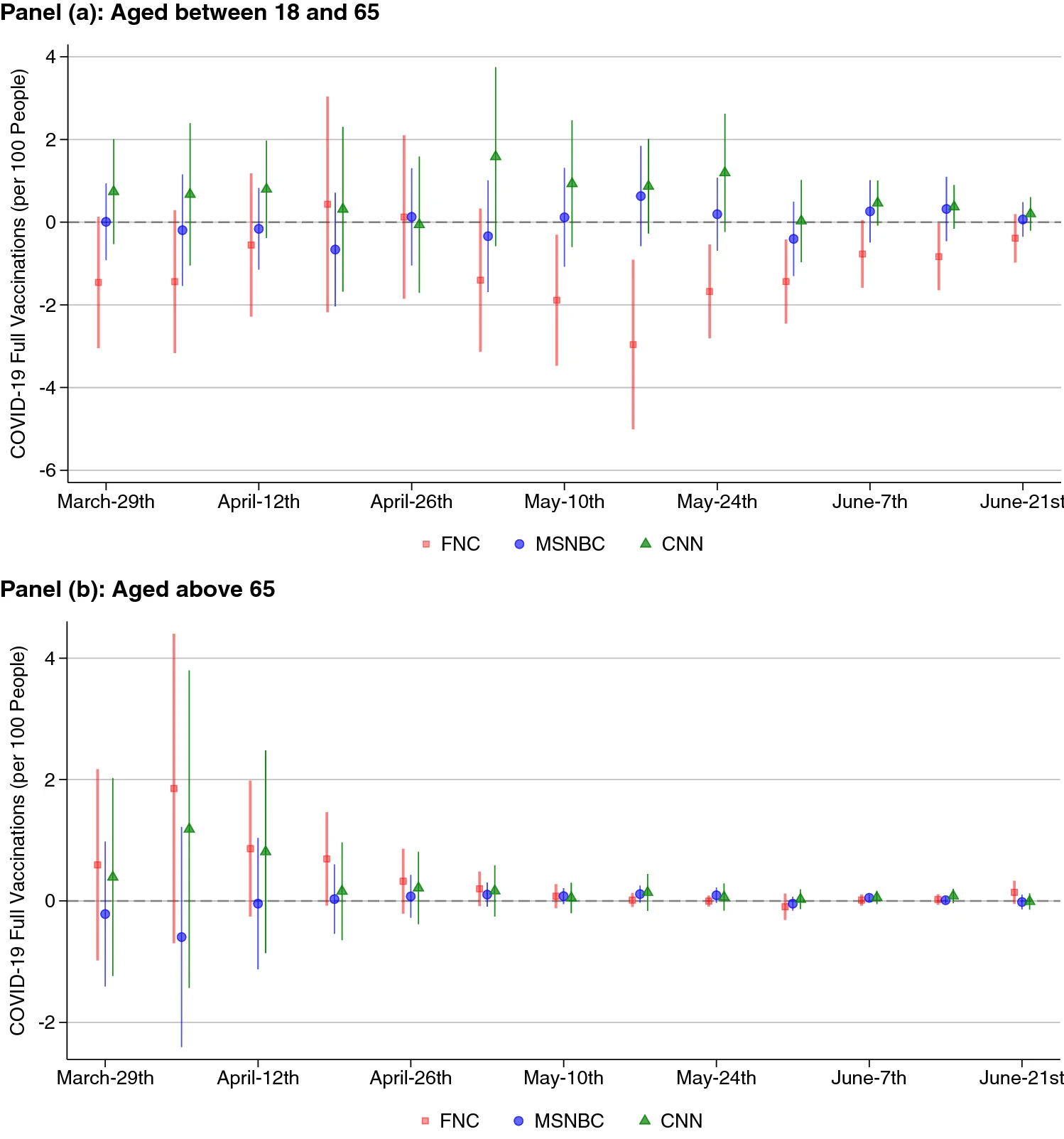
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Our results show that Fox News is reducing COVID-19 vaccination uptake in the United States, with no evidence of the other major networks having any effect. We first show that there is an association between areas with higher Fox News viewership and lower vaccinations, then provide an instrumental variable analysis to account for endogeneity, and help pin down the magnitude of the local average treatment effect.
-
Overall, an additional weekly hour of Fox News viewership for the average household accounts for a reduction of 0.35–0.76 weekly full vaccinations per 100 people during May and June 2021. This result is not only driven by Fox News’ anti-science messaging, but also by the network’s skeptic coverage of COVID-19 vaccinations.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
highlights the need for public health officials to disseminate information via multiple media channels to increase the chances of accessing vaccine resistant or hesitant individuals.
-
Engagement of religious leaders, for example, has been documented as an important approach to improve vaccine acceptance16,57. Key to the preparation of a COVID-19 vaccine is, therefore, the early and frequent engagement of religious and community-leaders58, and for health authorities to work collaboratively with multiple societal stakeholders to avoid the feeling that they are only acting on behalf of government authorities59.
-
Interestingly, while vaccine hesitant and resistant individuals in Ireland and the UK varied in relation to their social, economic, cultural, political, and geographical characteristics, both populations shared similar psychological profiles. Specifically, COVID-19 vaccine hesitant or resistant persons were distinguished from their vaccine accepting counterparts by being more self-interested, more distrusting of experts and authority figures (i.e. scientists, health care professionals, the state), more likely to hold strong religious beliefs (possibly because these kinds of beliefs are associated with distrust of the scientific worldview) and also conspiratorial and paranoid beliefs (which reflect lack of trust in the intentions of others).
-
They were also more likely to believe that their lives are primarily under their own control, to have a preference for societies that are hierarchically structured and authoritarian, and to be more intolerant of migrants in society (attitudes that have been previously hypothesised to be consistent with, and understandable in the context of, evolved responses to the threat of pathogens)56. They were also more impulsive in their thinking style, and had a personality characterised by being more disagreeable, more emotionally unstable, and less conscientious.
-
Consistent with previous research39, vaccine resistance was associated with lower income in the UK and Ireland with all earning categories below the highest income bracket associated with COVID-19 vaccine resistance.
-
Across the Irish and UK samples, similarities and differences emerged regarding those in the population who were more likely to be hesitant about, or resistant to, a vaccine for COVID-19. Three demographic factors were significantly associated with vaccine hesitance or resistance in both countries: sex, age, and income level. Compared to respondents accepting of a COVID-19 vaccine, women were more likely to be vaccine hesitant, a finding consistent with a number of studies identifying sex and gender-related differences in vaccine uptake and acceptance37,38. Younger age was also related to vaccine hesitance and resistance.
-
Similar rates of vaccine hesitance (26% and 25%) and resistance (9% and 6%) were evident in the Irish and UK samples, with only 65% of the Irish population and 69% of the UK population fully willing to accept a COVID-19 vaccine. These findings align with other estimates across seven European nations where 26% of adults indicated hesitance or resistance to a COVID-19 vaccine7 and in the United States where 33% of the population indicated hesitance or resistance34. Rates of resistance to a COVID-19 vaccine also parallel those found for other types of vaccines. For example, in the United States 9% regarded the MMR vaccine as unsafe in a survey of over 1000 adults35, while 7% of respondents across the world said they “strongly disagree” or “somewhat disagree” with the statement ‘Vaccines are safe’36. Thus, upwards of approximately 10% of study populations appear to be opposed to vaccinations in whatever form they take. Importantly, however, the findings from the current study and those from around Europe and the United States may not be consistent with or reflective of vaccine acceptance, hesitancy, or resistance in non-Western countries or regions.
-
There were no significant differences in levels of consumption and trust between the vaccine accepting and vaccine hesitant groups in the Irish sample. Compared to vaccine hesitant responders, vaccine resistant individuals consumed significantly less information about the pandemic from television and radio, and had significantly less trust in information disseminated from newspapers, television broadcasts, radio broadcasts, their doctor, other health care professionals, and government agencies.
-
In the Irish sample, the combined vaccine hesitant and resistant group differed most pronouncedly from the vaccine acceptance group on the following psychological variables: lower levels of trust in scientists (d = 0.51), health care professionals (d = 0.45), and the state (d = 0.31); more negative attitudes toward migrants (d’s ranged from 0.27 to 0.29); lower cognitive reflection (d = 0.25); lower levels of altruism (d’s ranged from 0.17 to 0.24); higher levels of social dominance (d = 0.22) and authoritarianism (d = 0.14); higher levels of conspiratorial (d = 0.21) and religious (d = 0.20) beliefs; lower levels of the personality trait agreeableness (d = 0.15); and higher levels of internal locus of control (d = 0.14).
-
- Nov 2022
-
threadreaderapp.com threadreaderapp.com
-
-
a more nuanced view of context.
Almost every new technology goes through a moral panic phase where the unknown is used to spawn potential backlashes against it. Generally these disappear with time and familiarity with the technology.
Bicycles cause insanity, for example...
Why does medicine and vaccines not follow more of this pattern? Is it lack of science literacy in general which prevents it from becoming familiar for some?
-
- Jun 2022
-
www.gavi.org www.gavi.org
-
COVID has demonstrated how easy it is to bring life and the economy to a complete standstill, instant reliable result testing is the only way forward, without it, we are at risk of going backwards and bring yet more pressure on the health system, businesses and the public.
-
- May 2022
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
Edwards died from a smallpox inoculation shortly after beginning the presidency at the College of New Jersey in Princeton.[7]
-
- Apr 2022
-
-
Humans’ tendency to“overimitate”—to reproduce even the gratuitous elements of another’s behavior—may operate on a copy now, understand later basis. After all, there might begood reasons for such steps that the novice does not yet grasp, especially sinceso many human tools and practices are “cognitively opaque”: not self-explanatory on their face. Even if there doesn’t turn out to be a functionalrationale for the actions taken, imitating the customs of one’s culture is a smartmove for a highly social species like our own.
Is this responsible for some of the "group think" seen in the Republican party and the political right? Imitation of bad or counter-intuitive actions outweights scientifically proven better actions? Examples: anti-vaxxers and coronavirus no-masker behaviors? (Some of this may also be about or even entangled with George Lakoff's (?) tribal identity theories relating to "people like me".
Explore this area more deeply.
Another contributing factor for this effect may be the small-town effect as most Republican party members are in the countryside (as opposed to the larger cities which tend to be more Democratic). City dwellers are more likely to be more insular in their interpersonal relations whereas country dwellers may have more social ties to other people and groups and therefor make them more tribal in their social interrelationships. Can I find data to back up this claim?
How does link to the thesis put forward by Joseph Henrich in The WEIRDest People in the World: How the West Became Psychologically Peculiar and Particularly Prosperous? Does Henrich have data about city dwellers to back up my claim above?
What does this tension have to do with the increasing (and potentially evolutionary) propensity of humans to live in ever-increasingly larger and more dense cities versus maintaining their smaller historic numbers prior to the pre-agricultural timeperiod?
What are the biological effects on human evolution as a result of these cultural pressures? Certainly our cultural evolution is effecting our biological evolution?
What about the effects of communication media on our cultural and biological evolution? Memes, orality versus literacy, film, radio, television, etc.? Can we tease out these effects within the socio-politico-cultural sphere on the greater span of humanity? Can we find breaks, signs, or symptoms at the border of mass agriculture?
total aside, though related to evolution: link hypercycles to evolution spirals?
Tags
- comparative anthropology
- imitation > innovation
- evolution
- relationships
- spatial relationships
- identity
- imitation
- city vs. town
- WEIRD
- human evolution
- culture
- anthropology
- anti-science
- Joseph Henrich
- Big History
- anti-intellectualism
- follow the herd
- anti-vaccines
- urban vs. rural
- group think
- evolution spirals
- hypercycle
Annotators
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
nature. (2021, April 16). Coronavirus variants: Where do they come from? How do we spot them? What do they mean for COVID vaccines, and future of the pandemic? Https://t.co/NRbORu2hoF [Tweet]. @Nature. https://twitter.com/Nature/status/1383093697374474240
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci on Twitter: ‘RT @TheLancetInfDis: Newsdesk in March issue: #COVID19 among American Indians and Alaska Natives https://t.co/cJj2815IYw’ / Twitter. (n.d.). Retrieved 3 March 2021, from https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1367060643896053760
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci. (2022, January 31). RT @fascinatorfun: Interesting as 🇩🇰 Omicron BA2 wave started sooner than 🇬🇧 “We conclude that Omicron BA.2 is inherently substantially m… [Tweet]. @SciBeh. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1488152457012297736
-
- Mar 2022
-
www.bmj.com www.bmj.com
-
Pottegård, A., & Klungel, O. H. (2022). The neurological safety of covid-19 vaccines. BMJ, 376, o522. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.o522
-
-
psyarxiv.com psyarxiv.com
-
Böhm, Robert, Cornelia Betsch, Yana Litovsky, Philipp Sprengholz, Noel Brewer, Gretchen Chapman, Julie Leask, et al. ‘Crowdsourcing Interventions to Promote Uptake of COVID-19 Booster Vaccines’. PsyArXiv, 10 February 2022. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/n5b6x.
-
-
www.pharmaceutical-technology.com www.pharmaceutical-technology.com
-
Pharmaceutical Technology. ‘Infectious Diseases Trends: Covid-19 Most Mentioned on Twitter Feb. 2022’, 4 March 2022. https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/comment/infectious-diseases-trends-covid-most-mentioned-twitter-february/.
-
- Feb 2022
-
globalnews.ca globalnews.ca
-
COVID-19 disinformation sharing by Canadian doctors ‘extremely concerning’: Ontario health minister | Globalnews.ca. (n.d.). Global News. Retrieved February 11, 2022, from https://globalnews.ca/news/8523550/covid-19-disinformation-ontario-doctors-christine-elliott/
-
- Jan 2022
-
retractionwatch.com retractionwatch.com
-
Marcus, A. A. (2022, January 13). COVID-19 spike protein paper earns an expression of concern. Retraction Watch. https://retractionwatch.com/2022/01/13/covid-19-spike-protein-paper-earns-an-expression-of-concern/
-
-
www.nbcnewyork.com www.nbcnewyork.com
-
Millman • •, Jennifer. ‘NY Pre-Christmas COVID Testing Delivers Record Total Just Shy of 50,000 Cases in Single Day’. NBC New York (blog). Accessed 3 January 2022. https://www.nbcnewyork.com/news/coronavirus/ny-pre-christmas-covid-testing-delivers-record-total-just-shy-of-50000-cases-in-single-day/3468284/.
-
- Dec 2021
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
Zhang, S. (2021, December 8). Omicron’s Explosive Growth Is a Warning Sign. The Atlantic. https://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2021/12/omicron-spread-infection-severity/620948/
-
- Nov 2021
-
jamanetwork.com jamanetwork.com
-
It remains unclear whether the reduction in the neutralization sensitivity of the N501Y.V2 strain to vaccine-induced antibodies is enough to seriously reduce vaccine efficacy. First, mRNA vaccines also induce virus-specific helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells, both of which might be involved in protection against challenge. Also, the mRNA vaccines, in particular, induce such a strong NAb response that there could be enough “spare capacity” to deal with reductions in the sensitivity of the variant to NAbs. In other words, N501Y.V2 (and the related virus from Brazil) may be less sensitive to NAbs, but not to an extent that will cause widespread vaccine failure.
Variants that show reduced sensitivity to NAbs don't necessarily mean mRNA vaccine failure
New variants may emerge that show reduced sensitivity to NAbs.
This may not result in vaccine failure because:
- The mRNA vaccines induce such a strong NAb response, there will be enough spare capacity to deal with the virus.
- The mRNA vaccines also induce other virus specific protection such as helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells, which may not be affected by the reduction in NAb sensitivity.
-
-
www.abc.net.au www.abc.net.au
-
‘A Small Number of Fully Vaccinated People with COVID-19 in NSW Have Died — Here’s Why’. ABC News, 28 September 2021. https://www.abc.net.au/news/2021-09-29/why-a-small-number-of-fully-vaccinated-people-have-died-of-covid/100497770.
-
-
-
Readministration of influenza vaccine has become an annual event for much of the population, in response to both waning immunity and the appearance of variants, termed antigenic drift, necessitating updated vaccines. Even when there is no substantial drift, revaccination is recommended because of waning immunity. But antigenic drift is a constant issue and is monitored globally, with vaccine composition updated globally twice a year on the basis of recommendations from a World Health Organization consultation.
Influenza vaccines need to be updated yearly to counter (1) waning immunity and (2) antigenic drift.
Antigenic drift is monitored globally and the WHO makes recommendations for the updates.
-
Thus, the value of influenza vaccines, now given to as many as 70% of people in some age groups, lies not in eliminating outbreaks but in reducing them and preventing severe complications.
The goal of influenza vaccines is to prevent severe complications and to reduce outbreaks — not to prevent them.
As many as 70% of some age groups get influenza vaccines.
-
Vaccine effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed symptomatic infection is never higher than 50 to 60%, and in some years it is much lower.
Vaccine effectiveness for influenza vaccines for symptomatic infection is never higher than 50-60% and some years it is much slower.
-
The effect on asymptomatic infections was a welcome surprise, because it has been thought that most vaccines for respiratory illnesses, including influenza, are “leaky” — that is, they allow some degree of asymptomatic infection and are better at preventing symptomatic infection.
Most vaccines for respiratory illnesses are leaky.
The efficacy the mRNA vaccines showed in preventing asymptomatic transmission was therefore a welcome surprise.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Oct 2021
-
fullfact.org fullfact.org
-
Full Fact. ‘What Do We Know about the Covid-19 Vaccines Crossing the Placenta?’, 16:58:51+00:00. https://fullfact.org/pregnant-then-screwed/vaccines-crossing-placenta/.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Dolgin, Elie. ‘The Tangled History of MRNA Vaccines’. Nature 597, no. 7876 (14 September 2021): 318–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-02483-w.
-
- Sep 2021
-
link.springer.com link.springer.com
-
Published clinical data on the safety of mRNA-LNP vaccines are scarce, in comparison with siRNA, and are limited to local administration (ID and IM).
Safety of mRNA vaccines.
-
Although LNPs are promising delivery systems, safety issues need to be addressed to enable proper clinical development of LNP-formulated mRNA vaccines. LNPs’ potential toxicity could be complex and might manifest in systemic effects due to innate immune activation (induction of pro-inflammatory cytokine production), and/or in local, cellular toxicity due to accumulation of lipids in tissues (Hassett et al. 2019; Semple et al. 2010; Sabnis et al. 2018). Toxicity could potentially be abrogated, or reduced, by the administration of prophylactic anti-inflammatory steroids or other molecules and/or using biodegradable lipids (Hassett et al. 2019; Abrams et al. 2010; Tabernero et al. 2013; Tao et al. 2011). LNPs can also activate the complement system and might potentially elicit a hypersensitivity reaction known as complement activation-related pseudoallergy (CARPA) (Dezsi et al. 2014; Mohamed et al. 2019; Szebeni 2005, 2014), which can be alleviated using different strategies such as steroid and anti-allergic premedication (i.e., dexamethasone, acetaminophen, and antihistaminic drugs) or the use of low infusion rates during intravenous administration (Mohamed et al. 2019; Szebeni et al. 2018). Alternatively, co-delivery of regulatory cytokines (i.e., IL-10) using LNPs might be a viable strategy to reduce potential LNP-associated adverse events.
Safety of mRNA Liquid Nanoparticles
-
- Jul 2021
-
euvsdisinfo.eu euvsdisinfo.eu
-
The Culture of Resentment Revisited. (2021, March 11). EU vs DISINFORMATION. https://euvsdisinfo.eu/the-culture-of-resentment-revisited/
-
-
-
‘Covid: UK Sends Nine Million Vaccines to Vulnerable Countries’. BBC News, 28 July 2021, sec. UK Politics. https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-politics-58004934.
-
-
bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com
-
Drury, John, Guanlan Mao, Ann John, Atiya Kamal, G. James Rubin, Clifford Stott, Tushna Vandrevala, and Theresa M. Marteau. ‘Behavioural Responses to Covid-19 Health Certification: A Rapid Review’. BMC Public Health 21, no. 1 (24 June 2021): 1205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11166-0.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci. ‘RT @sailorrooscout: I Figured It Was Best to Make a Comprehensive Thread Concerning the Study out of The Lancet Concerning Variant B.1.617.…’. Tweet. @SciBeh (blog), 4 June 2021. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1401215508968398848.
-
-
www.bloomberg.com www.bloomberg.com
-
‘Social Networks Are Exporting Disinformation About Covid Vaccines’. Bloomberg.Com, 20 May 2021. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-05-20/facebook-instagram-twitter-export-covid-vaccine-misinformation-from-u-s.
-
- Jun 2021
-
-
"Fertility Regulating Vaccines," World Health Organization, 1993.
Title: Fertility Regulating Vaccines
Subtitle: "Report of a meeting between women's health advocates and scientists to review the current status of the development of fertility regulating vaccines."
Event: Geneva, Switzerland 17-18 August, 1992
Publisher: World Health Organization
-
-
-
Callaway, E. (2021). Mix-and-match COVID vaccines trigger potent immune response. Nature, 593(7860), 491–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-01359-3
-
- May 2021
-
www.theguardian.com www.theguardian.com
-
Japan denies planning to prioritise Olympic athletes for Covid vaccine. (2021, April 8). The Guardian. http://www.theguardian.com/sport/2021/apr/08/japan-considering-vaccinating-tokyo-olympic-athletes-before-rest-of-population
-
-
www.dw.com www.dw.com
-
Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. ‘Access to COVID Vaccine Patents Is Not the Same as Access to Vaccines | DW | 06.05.2021’. DW.COM. Accessed 11 May 2021. https://www.dw.com/en/access-to-covid-vaccine-patents-is-not-the-same-as-access-to-vaccines/a-57448750.
Tags
- Joe Biden
- government
- health activists
- pharma companies
- India
- patent protection
- European Commission
- Vaccine Rollout
- EU
- deadly second wave
- South Africa
- vaccine access
- vaccines
- Britain
- hope
- COVID-19
- lang:en
- public health activist
- IP waiver
- access
- US
- is:website
- pharmaceutical companies
Annotators
URL
-
- Apr 2021
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
Maryland offers a microcosm of the issues states face as they rush to open enough vaccination sites to meet President Biden’s goal of making every adult eligible for Covid-19 shots by May 1. It has encountered nearly all the geographic, demographic and human behavioral challenges that come with a public health task of this scale.
Hi Ben
-
- Mar 2021
-
www.thelancet.com www.thelancet.com
-
Burki, T. (2021). COVID-19 among American Indians and Alaska Natives. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 21(3), 325–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00083-9
-
-
www.newscientist.com www.newscientist.com
-
Page, Michael Le. ‘What You Need to Know about the New Variant of Coronavirus in the UK’. New Scientist. Accessed 25 February 2021. https://www.newscientist.com/article/2263077-what-you-need-to-know-about-the-new-variant-of-coronavirus-in-the-uk/.
-
-
-
Weber, Hannah Recht, Lauren. ‘As Vaccine Rollout Expands, Black Americans Still Left Behind’. Kaiser Health News (blog), 29 January 2021. https://khn.org/news/article/as-vaccine-rollout-expands-black-americans-still-left-behind/.
-
-
journals.plos.org journals.plos.org
-
Pariente, Nonia, and on behalf of the PLOS Biology Staff Editors. ‘We Need Leaders That Believe in Scientific Evidence’. PLOS Biology 18, no. 10 (22 October 2020): e3000992. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000992.
-
-
www.bmj.com www.bmj.com
-
Clift, Ash K., Carol A. C. Coupland, Ruth H. Keogh, Karla Diaz-Ordaz, Elizabeth Williamson, Ewen M. Harrison, Andrew Hayward, et al. ‘Living Risk Prediction Algorithm (QCOVID) for Risk of Hospital Admission and Mortality from Coronavirus 19 in Adults: National Derivation and Validation Cohort Study’. BMJ 371 (20 October 2020): m3731. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3731.
-
-
zeynep.substack.com zeynep.substack.com
- Feb 2021
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci. (2021, February 12). RT @NatureNews: The science behind how and when to give vaccines doses. Https://t.co/S75TXESOG9 [Tweet]. @SciBeh. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1360489348223893505
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Thompson, B., Baker, N., & Ledford, H. (2021). Coronapod: Is mixing COVID vaccines a good idea? Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-00390-8
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Patel, M. (2021). Test behavioural nudges to boost COVID immunization. Nature, 590(7845), 185–185. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-00329-z
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
ReconfigBehSci. (2021, February 13). RT @NatureNews: We need to start learning now how best to ‘nudge’ people to receive their vaccinations. Https://t.co/vTmKpqizuU [Tweet]. @SciBeh. https://twitter.com/SciBeh/status/1360900272269197312
-
-
www.bbc.co.uk www.bbc.co.uk
-
Covid vaccines extremely safe, finds UK regulator. (2021, February 5). BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/health-55946912
-
- Dec 2020
-
insights.som.yale.edu insights.som.yale.edu
-
Forman. H. P. Three Questions about COVID-19 Infection and Immunity. Yale Insights. Retrieved from: https://insights.som.yale.edu/insights/three-questions-about-covid-19-infection-and-immunity?utm_source=YaleToday&utm_medium=Email&utm_campaign=YT_YaleToday-Staff_9-3-2020
-
- Sep 2020
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Krammer, Florian. ‘SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Development’. Nature, 23 September 2020, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2798-3.
-
-
www.nature.com www.nature.com
-
Leask, Julie. ‘Vaccines — Lessons from Three Centuries of Protest’. Nature 585, no. 7826 (21 September 2020): 499–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-02671-0.
-
- Aug 2020
-
www.nber.org www.nber.org
-
Vu, Jonathan T, Benjamin K Kaplan, Shomesh Chaudhuri, Monique K Mansoura, and Andrew W Lo. ‘Financing Vaccines for Global Health Security’. Working Paper. Working Paper Series. National Bureau of Economic Research, May 2020. https://doi.org/10.3386/w27212.
-
-
arxiv.org arxiv.org
-
Bracci, Alberto, Matthieu Nadini, Maxwell Aliapoulios, Damon McCoy, Ian Gray, Alexander Teytelboym, Angela Gallo, and Andrea Baronchelli. ‘The COVID-19 Online Shadow Economy’. ArXiv:2008.01585 [Physics], 6 August 2020. http://arxiv.org/abs/2008.01585.
-
- Jul 2020
-
www.cnn.com www.cnn.com
-
The vaccine uses messenger RNA (mRNA), which are cells used to build proteins -- in this case, the proteins that are needed to build the coronavirus' spike protein, which the virus uses to attach itself to and infect human cells. Once the immune system learns to recognize this target -- thanks to the vaccine -- it can mount a response faster than if it encountered the virus for the first time due to an infection.
This explanation is garbled and misstated. Genetic material is stored in DNA in the nucleus of the cell. Messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules carry the information stored within the DNA to the rest of the cell. Both DNA and RNA are a type of molecule called a "nucleic acid." Once outside the nucleus, the information in the messenger RNA can then be read, or "translated," to create proteins, such as the spike protein used by SARS-CoV-2. These proteins in turn carry out a wide variety of tasks that allow cells to function. This process is known as the "Central Dogma of Molecular Biology".
-
- May 2019
-
-
To Gorski's statement, Stickland tweeted, "Look, another guy in a white coat who thinks he’s a better parent than everyone else! #shocking #notreally Why do you want to run my life and own my kids?"
-
- Apr 2018
-
jbhandleyblog.com jbhandleyblog.com
-
With a title like that, many will not take the time to read, and that's unfortunate.
-
- Mar 2018
-
-
says the flu vaccine is laced with cancer-causing ingredients.
This statement has been analyzed by a member of the International Fact Checking Network. This annotation is provided by Hypothesis as a public service.
-
- Jun 2017
-
www.tokyotimes.com www.tokyotimes.com
-
Side effects in young girls take Gardasil out from Japanese market
Partly false. Gardasil hasn't been taken out of the market
-
- Mar 2017
-
newamericannews.com newamericannews.com
-
SHOWS
In the original article, it was said that vaccines directly cause brain disorders, which is not what the study found. The study said that there was a time-oriented association (not even a coorelation) between the amount of certain diagnosed brain disorders and antecendant vaccines. The study never makes the claim of causation, though the phrasing of the title (out of onctext, that is) is common for clickbait articles such as this. While not completely made up, the original research as a completely different tone than what is being presented by this article. In addition, the original artice discuses limitation that are completely thrown out by this article: they mention that doctors diagnose disorders differently than other doctors, which is something readers/sharers of the article ought to be aware of.
Though I found the original research, the message of this article has completely distorted Yale's findings. The study was writen from a HINDSIGHT perspective. Meaning, they mentioned vaccines are received more often by those who have any of the aforementioned disorders. For exaple, they say, "The principal findings of this study are as follows: (i) children with OCD, AN, anxiety disorder, and tic disorder were more likely to have received influenza vaccine during the preceding 1-year period". The entire study was merely showing (seemingly unintentionaly so) that those who have mental disorders are more likely to hae received vaccinations in the past several years. Not even close to stating that they are directly caused by vaccines. The article doesn't mention this, but one reason may be socioeconomic status, IE the wealthy have better doctors who diagnose, and they can afford more vaccines for their cildren. The article has completely distorted the findings and ignored the mentioned limitations of the article.
Citations: Webber, P. (2017, February 10). BREAKING: Yale Study SHOWS Vaccines Cause Brain Disorders - RFK Jr. Retrieved March 30, 2017, from http://newamericannews.com/yale-study-shows-vaccines-cause-brain-disorders-rfk-jr/#
Leslie, D. L., Kobre, R. A., Richmand, B. J., Guloksuz, S. A., & Leckman, J. F. (2017, January 04). Temporal Association of Certain Neuropsychiatric Disorders Following Vaccination of Children and Adolescents: A Pilot Case–Control Study. Retrieved March 30, 2017, from http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00003/full
-
-
pediatrics.aappublications.org pediatrics.aappublications.org
-
Caregivers completed the Achenbach Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL),11 a well-validated questionnaire designed to measure behavioral and emotional functioning in preschoolers (1.5 to 5 years old) in research and clinical settings
Interesting, this is related to something else I know about.
-
- Aug 2016
-
www.sciencebasedmedicine.org www.sciencebasedmedicine.org
-
Credibull score = 5.17 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.sciencebasedmedicine.org www.sciencebasedmedicine.org
-
Credibull score = 6.44 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.sciencebasedmedicine.org www.sciencebasedmedicine.org
-
Credibull score = 6.15 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.sciencebasedmedicine.org www.sciencebasedmedicine.org
-
Credibull score = 6.52 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
-
Credibull score = 2.01 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
vactruth.com vactruth.com
-
Credibull score = 0.33 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
avn.org.au avn.org.au
-
Credibull score = 2.75 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.educate4theinjured.org www.educate4theinjured.org
-
Credibull score = 3.34 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
avscientificsupportarsenal.wordpress.com avscientificsupportarsenal.wordpress.com
-
Credibull score = 1.75 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
vaccinationdecisions.net vaccinationdecisions.net
-
Credibull score = 3.59 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.activistpost.com www.activistpost.com
-
Credibull score = 1.69 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.collective-evolution.com www.collective-evolution.com
-
Credibull score = 2.17 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.davidwolfe.com www.davidwolfe.com
-
Credibull score = 1.01 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.fourteenstudies.org www.fourteenstudies.org
-
Credibull score = 0.99 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.greenmedinfo.com www.greenmedinfo.com
-
Credibull score = 3.09 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.greenmedinfo.com www.greenmedinfo.com
-
Credibull score = 3.19 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
articles.mercola.com articles.mercola.com
-
Credibull score = 2.79 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
articles.mercola.com articles.mercola.com
-
Credibull score = 3.19 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.nvic.org www.nvic.org
-
Credibull score = 2.87 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
justthevax.blogspot.com justthevax.blogspot.com
-
Credibull score = 6.15 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.skepticalraptor.com www.skepticalraptor.com
-
Credibull score = 5.13 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.voicesforvaccines.org www.voicesforvaccines.org
-
Credibull score = 5.04 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
thelogicofscience.com thelogicofscience.com
-
Credibull score = 5.96 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.babycenter.com www.babycenter.com
-
Credibull score = 4.25 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.webmd.com www.webmd.com
-
Credibull score = 1.31 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
-
Credibull score = 8.31 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.health.harvard.edu www.health.harvard.edu
-
Credibull score = 7.31 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.dailymail.co.uk www.dailymail.co.uk
-
Credibull score = 2.52 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.pbs.org www.pbs.org
-
Credibull score = 3.86 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.naturalnews.com www.naturalnews.com
-
Credibull score = 0.80 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.naturalnews.com www.naturalnews.com
-
Credibull score = 0.10 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.huffingtonpost.com www.huffingtonpost.com
-
Credibull score = 0.61 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
-
Credibull score = 2.83 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.healthline.com www.healthline.com
-
Credibull score = 4.60 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
thinkprogress.org thinkprogress.org
-
Credibull score = 4.74 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.iflscience.com www.iflscience.com
-
Credibull score = 4.66 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.medicaldaily.com www.medicaldaily.com
-
Credibull score = 3.54 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
news.nationalgeographic.com news.nationalgeographic.com
-
Credibull score = 4.35 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.abc.net.au www.abc.net.au
-
Credibull score = 5.62 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.newsweek.com www.newsweek.com
-
Credibull score = 4.90 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.pbs.org www.pbs.org
-
Credibull score = 6.71 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
-
Credibull score = 1.73 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
immunise.health.gov.au immunise.health.gov.au
-
Credibull score = 5.63 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.nova.org.au www.nova.org.au
-
Credibull score = 6.55 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
-
www.publichealth.org www.publichealth.org
-
Credibull score = 6.13 / 10
To provide feedback on the score fill in the form available here
What is Credibull? getcredibull.com
-
- Jan 2015
-
vactruth.com vactruth.com
-
These include death, sudden infant death syndrome, auto-immune disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, allergies, asthma, ADHD, autism, Guillian-Barré Syndrome and other neurological damage.
A lot of generic accusations, what about sources?
-
 </a>
</a>