- Feb 2023
-
forum.obsidian.md forum.obsidian.md
-
It’s a big problem with the bullet journal community too, unfortunately.
I'm definitely not the only one to notice this pattern of productivity porn in the bullet journal space.
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
According to Shulman, "Cargo-cult is a belief that mock airplanes made of manure and straw-bale may summon the real airplanes who bring canned beef. Reverse cargo-cult is used by the political elites in countries lagging behind who proclaim that, in the developed world, airplanes are also made of manure and straw-bale, and there is also a shortage of canned beef."[29]
"Екатерина Шульман: Практический Нострадамус, или 12 умственных привычек, которые мешают нам предвидеть будущее". vedomosti/ (in Russian). Retrieved 24 June 2021.
A Note on the Cargo Cult of Zettelkasten
Modern cargo cults can be seen in many technology and productivity spaces where people are pulled in by exaggerated (or sometimes even real claims) of productivity or the general "magic" of a technology or method.
An example is Niklas Luhmann's use of his zettelkasten which has created a cargo cult of zettelkasten aspirants and users who read one or more of the short one page blog posts about his unreasonable productivity and try to mimic it without understanding the system, how it works, or how to make it work for them. They often spend several months collecting notes, and following the motions, but don't realize the promised gains and may eventually give up, sometimes in shame (or as so-called "rubbish men") while watching others still touting its use.
To prevent one's indoctrination into the zettelkasten cult, I'll make a few recommendations:
Distance yourself from the one or two page blog posts or the breathless YouTube delineations. Ask yourself very pointedly: what you hope to get out of such a process? What's your goal? Does that goal align with others' prior uses and their outcomes?
Be careful of the productivity gurus who are selling expensive courses and whose focus may not necessarily be on your particular goals. Some are selling very pointed courses, which is good, while others are selling products which may be so broad that they'll be sure to have some success stories, but their hodge-podge mixture of methods won't suit your particular purpose, or worse, you'll have to experiment with pieces of their courses to discover what may suit your modes of working and hope they'll suffice in the long run. Some are selling other productivity solutions for task management like getting things done (GTD) or bullet journals, which can be a whole other cargo cults in and of themselves. Don't conflate these![^1] The only thing worse than being in a cargo cult is being in multiple at the same time.
If you go the digital route, be extremely wary of shiny object syndrome. Everyone has a favorite tool and will advocate that it's the one you should be using. (Often their method of use will dictate how much they love it potentially over and above the affordances of the tool itself.) All of these tools can be endlessly configured, tweaked, or extended with plugins or third party services. Everyone wants to show you their workflow and set up, lots of which is based on large amounts of work and experimentation. Ignore 99.999% of this. Most tools are converging to a similar feature set, so pick a reasonable one that seems like it'll be around in 5 years (and which has export, just in case). Try out the very basic features for several months before you change anything. Don't add endless plugins and widgets. You're ultimately using a digital tool to recreate the functionality of index cards, a pencil, and a box. How complicated should this really be? Do you need to spend hundreds of hours tweaking your system to save yourself a few minutes a year? Be aware that far too many people touting the system and marketers talking about the tools are missing several thousands of years of uses of some of these basic literacy-based technologies. Don't join their island cult, but instead figure out how the visiting culture has been doing this for ages.[^2] Recall Will Hunting's admonition against cargo cults in education: “You wasted $150,000 on an education you coulda got for $1.50 in late fees at the public library.”[^3]
Most people ultimately realize that the output of their own thinking is only as good as the inputs they're consuming. Leverage this from the moment you begin and ignore the short bite-sized advice for longer form or older advice from those with experience. You're much more likely to get more long term value out of reading Umberto Eco or Mortimer J. Adler & Charles van Doren[^4] than you are an equivalent amount of time reading blog posts, watching YouTube videos, or trolling social media like Reddit and Twitter.
Realize that reaching your goal is going to take honest-to-goodness actual work, though there is potential for fun. No matter how shiny or optimized your system, you've still got to do the daily work of reading, watching, listening and using it to create anything. Focus on this daily work and don't get sidetracked by the minutiae of trying to shave off just a few more seconds.[^5] In short, don't get caught up in the "productivity porn" of it all. Even the high priest at whose altar they worship once wrote on a slip he filed:
"A ghost in the note card index? Spectators visit [my office to see my notes] and they get to see everything and nothing all at once. Ultimately, like having watched a porn movie, their disappointment is correspondingly high." —Niklas Luhmann. <small>“Geist im Kasten?” ZKII 9/8,3. Niklas Luhmann-Archiv. Accessed December 10, 2021. https://niklas-luhmann-archiv.de/bestand/zettelkasten/zettel/ZK_2_NB_9-8-3_V. (Personal translation from German with context added.)</small>
[^1] Aldrich, Chris. “Zettelkasten Overreach.” BoffoSocko (blog), February 5, 2022. https://boffosocko.com/2022/02/05/zettelkasten-overreach/.
[^2]: Blair, Ann M. Too Much to Know: Managing Scholarly Information before the Modern Age. Yale University Press, 2010. https://yalebooks.yale.edu/book/9780300165395/too-much-know.
[^3]: Good Will Hunting. Miramax, Lawrence Bender Productions, 1998.
[^4]: Adler, Mortimer J., and Charles Van Doren. How to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent Reading. Revised and Updated edition. 1940. Reprint, New York: Simon & Schuster, 1972.
[^5]: Munroe, Randall. “Is It Worth the Time?” Web comic. xkcd, April 29, 2013. https://xkcd.com/1205/.
Recommended resources
Choose only one of the following and remember you may not need to read the entire work:
Ahrens, Sönke. How to Take Smart Notes: One Simple Technique to Boost Writing, Learning and Thinking – for Students, Academics and Nonfiction Book Writers. Create Space, 2017.
Allosso, Dan, and S. F. Allosso. How to Make Notes and Write. Minnesota State Pressbooks, 2022. https://minnstate.pressbooks.pub/write/.
Bernstein, Mark. Tinderbox: The Tinderbox Way. 3rd ed. Watertown, MA: Eastgate Systems, Inc., 2017. http://www.eastgate.com/Tinderbox/TinderboxWay/index.html.
Dow, Earle Wilbur. Principles of a Note-System for Historical Studies. New York: Century Company, 1924.
Eco, Umberto. How to Write a Thesis. Translated by Caterina Mongiat Farina and Geoff Farina. 1977. Reprint, Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press, 2015. https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/how-write-thesis.
Gessner, Konrad. Pandectarum Sive Partitionum Universalium. 1st Edition. Zurich: Christoph Froschauer, 1548.
Goutor, Jacques. The Card-File System of Note-Taking. Approaching Ontario’s Past 3. Toronto: Ontario Historical Society, 1980. http://archive.org/details/cardfilesystemof0000gout.
Sertillanges, Antonin Gilbert, and Mary Ryan. The Intellectual Life: Its Spirit, Conditions, Methods. First English Edition, Fifth printing. 1921. Reprint, Westminster, MD: The Newman Press, 1960. http://archive.org/details/a.d.sertillangestheintellectuallife.
Webb, Sidney, and Beatrice Webb. Methods of Social Study. London; New York: Longmans, Green & Co., 1932. http://archive.org/details/b31357891.
Weinberg, Gerald M. Weinberg on Writing: The Fieldstone Method. New York, N.Y: Dorset House, 2005.
-
-
elizabethfilips.podia.com elizabethfilips.podia.com
-
If you don't like Zettlekasten (I have my "own" version of Zettlekasten that I use so it's not 100% the original, but it's very heavily based on it - if you hate Zettlekasten this really isn't going to work).
https://elizabethfilips.podia.com/validation-cohort-muse
Elizabeth Filips is running a validation cohort for a course (presumably called MUSE, the marketing name for her "system" as well) on how to take notes and build a zettelkasten (or a second brain—there's evidence that she's taken Tiago Forte's course). She's got some indications that she's using a zettelkasten-like method for creation, but her burgeoning empire also appears to be firmly centered in the productivity porn space. I'm curious how she views her Muse system being different from a zettelkasten?
She's got an incredibly focused sales funnel web presence here.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Tagging for personal knowledge management is a subject unto itself. Whilenot necessary to get started, I’ve written a free bonus chapter on tags you candownload at Buildingasecondbrain.com/bonuschapter.
Forte's book is a pathway that acts as just another part of his sophisticated sales funnel.
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
This process has as much todo with taking ownership of ideas as it does with apps.
Too many in the productivity porn space focus on the apps and the potential workflows without looking at the question "why" at all. It's rare that any focus on understanding or actual output.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QuzRkac2n-c
Beginning to realize that some of the pattern that I describe as productivity porn is more likely done as a means of creativity, art, or even therapeutic use.
In this one (at the end), she's got a notebook specifically for putting washi tape into because it's calming and therapeutic.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
Eugene P. Wigner, The unreasonable effectiveness of mathematics in thenatural sciences, Comm. Pure Appl. Math. 13 (1960), 1–14.
-
- Jan 2023
-
thedreammachine.substack.com thedreammachine.substack.com
-
If you aren’t visibly producing, you aren’t worthy. In this context, taking time to lie dormant feels greedy, even wasteful.
Wintering
-
Protecting and practicing fallow time is an act of resistance; it can make us feel out of step with what the prevailing culture tells us.
Rest is Resistance
Fallow time, I like that wording
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BpvEY-2dSdU
In this episode, I explain the memory system I created in order to expand my memory to new heights. I call it the Sirianni Method and with it, you can learn how to create an intentional photographic memory.
Who the hell is the Sirianni this is named for, himself? (In the comments he mentions that "it's my italian grandpa's last name, I always liked it and a while back started naming things after it)
tl;dr: He's reinvented the wheel, but certainly not the best version of it.
What he's describing isn't remotely related to the idea of a photographic memory, so he's over-hyping the results, which is dreadful. If it were a photographic memory, he wouldn't need the spaced-repetition portion of his practice. While he mentions how he's regularly reviewing his cards he doesn't mention any of the last century+ of research and work on spaced repetition. https://super-memory.com/articles/20rules.htm is a good place to start for some of this.
A lot of what he's doing is based on associative memory, particularly by drawing connections/links to other things he already knows. He's also taking advantage of visual memory by associating his knowledge with a specific picture.
He highlights emotion and memory, but isn't drawing clear connections between his knowledge and any specific emotions that he's tying or associating them to.
"Intentional" seems to be one of the few honest portions of the piece.
Overview of his Sirianni method: pseudo-zettelkasten notes with written links to things he already knows (but without any Luhmann-esque numbering system or explicit links between cards, unless they're hiding in his connections section, which isn't well supported by the video) as well as a mnemonic image and lots of ad hoc spaced repetition.
One would be better off mixing their note taking practice with associative mnemonic methods (method of loci, songlines, memory palaces, sketchnotes, major system, orality, etc.) all well described by Lynne Kelly (amongst hundreds before her who got smaller portions of these practices) in combination with state of the art spaced repetition.
The description of Luhmann's note taking system here is barely passable at best. He certainly didn't invent the system which was based on several hundred years of commonplace book methodology before him. Luhmann also didn't popularize it in any sense (he actually lamented how people were unimpressed by it when he showed them). Popularization was done post-2013 generally by internet hype based on his prolific academic output.
There is nothing new here other than that he thinks he's discovered something new and is repackaging it for the masses with a new name in a flashy video package. There's a long history of hucksters doing this sort of fabulist tale including Kevin Trudeau with Mega Memory in the 1990s and going back to at least the late 1800s with "Professor" Alphonse Loisette and the system he sold for inordinate amounts to the masses including Mark Twain.
Most of these methods have been around for millennia and are all generally useful and well documented though the cultural West has just chosen to forget most of them. A week's worth of research and reading on these topics would have resulted in a much stronger "system" more quickly.
Beyond this, providing a fuller range of specific options and sub-options in these areas so that individuals could pick and choose the specifics which work best for them might have been a better way to go.
Content research: D- Production value: A+
{syndication link](https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/10ehrbd/comment/j4u495q/?utm_source=share&utm_medium=web2x&context=3)
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
Face To Face with MIKE SHINODA
(16:14)
Mike Shinoda discussing the idea from Stephen King's book "On Writing":
"You should write every day, even if it's torturous, even if you hate it, you sit down and say: "this is not what I wanna be doing, I'm not in the mood, I've got too many things going on". But you should do it anyway, cause it keeps your creative muscles strong, and eventually, even on the bad day, you can come up with something that's remarkable and surprising that you can use later."
-
-
Local file Local file
-
The student should become as little conscious of his notebookas possible , that his mind may act reflexively ; that is, from habit, automatically.
One should strive to become fluent with their note taking materials and tools to the point that both having them at hand and using them them are as second nature as breathing, walking, or speaking.
When it comes to productivity gains, this one thing can be the most helpful. Have a process; know it intimately enough that it is second nature.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Love these PKM-guru wars: lobbing strawman arguments at people in lengthy, rambling articles. Don't take the bait, Tiago!
"PKM-guru wars"!! 🤣
-
- Dec 2022
-
medium.com medium.com
-
Happiness is pushed to some later date in the future while your present self battles with the misery of the current moment.
Journey before destination, don't get caught up in the future, you'll miss the now. Instead, rest in motion
-
Positive fantasies allow you to indulge in the desired future mentally…You can taste the sensations of what it’s like to achieve your goal in the present — this depletes your energy to pursue your desired future.
It's easy to get caught up fantasising about what you could achieve rather than actually taking action to achieve it.
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gartner_hype_cycle

<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Fernando Borretti</span> in Unbundling Tools for Thought (<time class='dt-published'>12/29/2022 15:59:17</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
borretti.me borretti.me
-
https://borretti.me/article/unbundling-tools-for-thought
He covers much of what I observe in the zettelkasten overreach article.
Missing is any discussion of exactly what problem he's trying to solve other than perhaps, I want to solve them all and have a personal log of everything I've ever done.
Perhaps worth reviewing again to pull out specifics, but I just don't have the bandwidth today.
-
-
adjacentpossible.substack.com adjacentpossible.substack.com
-
I quickly found myself in the ironic situation of spending so much time building a tool to help with my schoolwork that I stopped actually doing my schoolwork.
Early example of being overwhelmed by one's tool.
-
-
johnmount.github.io johnmount.github.io
-
Increasing your use of tools without increasing your exposure to distractions is a great way to increase your abilities and get a lot more done.
-
-
jarche.com jarche.com
-
If my interpretation of the Retrieval quadrant is correct, it will become much more difficult to be an average, or even above average, writer. Only the best will flourish. Perhaps we will see a rise in neo-generalists.
This is probably true of average or poor software engineers given that GPT-3 can produce pretty reasonable code snippets
-
- Nov 2022
-
-
Chris Sampson uses the GTD mantra “Delete. Delegate. Delay. Do.” to help him stop reading about productivity hacks, and start getting work done.
Incorporate this into my courseware and productivity notes.
-
-
escapingflatland.substack.com escapingflatland.substack.com
-
A blog post is a very long and complex search query to find fascinating people and make them route interesting stuff to your inbox.
This is a really cool take on blogging. By writing about interesting people and stuff you are increasing your chances of meeting someone cool and indeed increasing your luck
-
-
www.swyx.io www.swyx.io
-
Whatever your thing is, make the thing you wish you had found when you were learning. Don’t judge your results by “claps” or retweets or stars or upvotes - just talk to yourself from 3 months ago
Completely agree, this is a great intrinsic metric to measure the success of your work by.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
www.evernote.com www.evernote.com
-
Powerful, non-judgmental questions
- If you had to guess, what would have to be true for you to...?
- If you did know...
- (on tangent) ...and how does that relate to you?
- What's not allowing you to...?
- What prevents you from asking…?
- Do you want to go into this?
- What's your criteria for saying yes?
- What would have you say yes?
- What are the things we're lacking?
- What's the scary question that you're not asking?
- What are the qualities you want for [being, action, process, etc.]?
- How would you behave if you were the best in the world at what you do?
<script async src="https://platform.twitter.com/widgets.js" charset="utf-8"></script>I'm starting a list of powerful, non-judgmental questions for coaching or just relationships in general. Here's the starting batch https://t.co/ktsYVxkQna pic.twitter.com/Dq1zQnWqAS
— Tiago Forte (@fortelabs) January 15, 2019These questions and similar ones (work this out) could be interesting prompts to be included on a syllabus or as starts for an annotated syllabus. (eg: What do you want to get out of this class? What do you already know about these areas? How can we expand on what you know? What would you like to explore?, etc.)
-
-
mindingourway.com mindingourway.com
-
The actual reward state is not one where you're lazing around doing nothing. It's one where you're keeping busy, where you're doing things that stimulate you, and where you're resting only a fraction of the time. The preferred ground state is not one where you have no activity to partake in, it's one where you're managing the streams of activity precisely, and moving through them at the right pace: not too fast, but also not too slow. For that would be boring
Doing nothing at all is boring. When we "rest" we are actually just doing activities that we find interesting rather than those we find dull or stressful.
-
the work that needs to be done is not a finite list of tasks, it is a neverending stream. Clothes are always getting worn down, food is always getting eaten, code is always in motion. The goal is not to finish all the work before you; for that is impossible. The goal is simply to move through the work. Instead of struggling to reach the end of the stream, simply focus on moving along it.
This is true and worth remembering. It is very easy to fall into the mindset of "I'll rest when I'm finished"
-
-
www.swyx.io www.swyx.io
-
Many people report writers block with blogs, particularly after a big successful post, because it’s almost impossible to consistently pump out bangers.
Certainly true, people go through peaks and troughs of productivity like seasons
-
-
supermemo.guru supermemo.guru
-
Page with many resources on - Learning - Creativity - Intelligence - Sleep - Education - Memory - Health - Productivity - Myths - SuperMemo - Older texts
-
-
www.obsidianroundup.org www.obsidianroundup.org
-
Not every highlight needs to become a "card" — and having things in my notes that are highlighted but don't need to be turned into further notes does not mean that I have failed by "over-highlighting." Useful notes are messy, and time is valuable. A sense of completionism is nice for some things but mostly just gets in the way when it comes to learning. I read about 10% of the articles that show up in my feed. I take highlight about 50% of those, and affirmatively take notes on about 10% of those. This doesn't mean I wasted my time reading, or that I failed at notetaking because I should have done a better job of taking comprehensive notes. It means I used judgment, and used my time wisely, and focused on things that were worthwhile from a return on investment perspective.
While there are rules and processes for taking notes, it's small personal tidbits like this that are harder fought knowledge for the beginner who generally only learns these bits through work and experience.
-
My highlights are littered with notes to self and action items - it's not all pure knowledge.
this is a good example of the personal side of note taking that isn't always outwardly seen
each person's notes will be personal to them
-
-
medium.com medium.com
-
6 min read on tracking tasks with Obsidian. Might be helpful
-
-
curtismchale.ca curtismchale.ca
-
Obsidian Kanban for Someday Maybe
Examples include a separate Kanban board for - camping tasks - home-based tasks - Obsidian management - such as organize old files in database
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
<script async src="https://platform.twitter.com/widgets.js" charset="utf-8"></script>I've been told since the first day I started working at the Division of Hospital Medicine at @UCSF that my work doesn't bring in $ to cover my salary. It's a narrative of manufactured scarcity, a common tactic in capitalism. The CEO is making $1.85 million plus bonuses.
— Rupa Marya, MD (@DrRupaMarya) November 4, 2022
<script async src="https://platform.twitter.com/widgets.js" charset="utf-8"></script>A Hospitalist’s economic value is in what we *save* the system in terms of quality-driven care and patient throughput (DC/unit time), not in how much we bring in through profees. Because of how the system is structured, you’ll only see our value when we aren’t there.
— Rupa Marya, MD (@DrRupaMarya) November 4, 2022This sounds a lot like hospitalists fall under David Graeber's thesis in Bullshit Jobs that the more necessary and useful you are the less you're likely to get paid and be valued.
I suspect the ability to track an employees' direct level of productivity also fits into this thesis. One can track the productivity of an Amazon warehouse worker or driver, but it's much more difficult to track the CEOs direct productivity.
-
-
www.nytimes.com www.nytimes.com
-
Mason Currey’s book “Daily Rituals: Women at Work.” It gives cheerful summaries about how some of the most prolific, successful artists managed their time.
-
- Oct 2022
-
Local file Local file
-
Onesuspected that Paxson's love for his work may have tempted him tolabor too long, and that he established a schedule to protect him-self and the keenness of his mind, to keep himself from his deskinstead of at it, as is some men's purpose.
Pomeroy suspects that Paxson may have kept to a strict work schedule to keep his mind sharp, but he doesn't propose or suspect that it may have been the case that Paxson's note taking practice was the thing which not only helped to keep his mind sharp, but which allowed him the freedom and flexibility to keep very regular work hours.
-
The mass of Paxson's paper work may appear more clearly nowthan the zest with which he labored, but the essence of his methodwas in the spirit rather than in the product.
Ahrens and others following him have argued that there is a sort of lightness imbued both in one's thinking processes and life by making and accumulating notes. The cognitive load is lessened by offloading one's thoughts onto pieces of paper that can be revised, compared, and juxtaposed as a means of building some written or creative endeavor, even if it's slowly over time.
Frederic L. Paxson's mode of life made this seem to be the case for him. There is evidence that he was easier able to manage his daily life by his note taking system. He accumulated no work on his desk and carried none home and was able to more easily give his attention to others.
Is this a result of breaking things down into tiny, bite sized chunks that were difficult to actually interrupt?
Was it the system or his particular temperament? Are there other examples of this easier mode of life for note takers? Is there a pattern? What portions can be attributed to the system and one's ability to stick to it versus their particular temperaments?
Other than small examples in my own life, this may be one of the first examples I've seen of this mode of work. Definitely worth looking at others.
-
And our president must be teacher as well as doer.
Our president must be in equal measures a teacher, a leader, and a doer.
-
-
-
It is possible to take too many notes; the task of sorting, filing and assimilating them can take for ever, so that nothing gets written.
-
-
micro.blog micro.blog
-
https://micro.blog/pimoore/13567345
some interesting perspectives on note taking apps and note taking in general
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Much like the way the Obsidian journal plugin counts words within one's daily journal page, this app counts zettels within a folder to help encourage one to maintain some level of output.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Workflow for capturing and processing online content for use in a Zettlekasten
reply to https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/ye3bvk/workflow_for_capturing_and_processing_online/
While it's possible that some set of tools will work best for you and potentially be more "fun" than other combinations, the upper limit you'll find on efficiency and productivity in this area is limited.
As a result, I'd recommend looking at the quality of the material you're putting into your stream as potentially the best means of improvement at your disposal. The quality of your ideas and thought will increase if you're reading and conversing with the highest quality sources you can get your hands on. Well-researched, long form material (books, journal articles) will have likely done a lot of the filtering and heavy work for you, so use those as input when you can.
Unless you're a sociologist or cultural anthropologist looking for examples of behaviors and material in social media, it may not be the best place to turn. Before I open social media apps I remind myself of note #1267 from Goethe's slipbox (Maxims and Reflections): "Ignorant people raise questions which were answered by the wise thousands of years ago."
Similarly, upon hearing the words "firehose", "drowning", or "information overload", I'm reminded that, presuming you'd even want to make the effort, there's only one way to eat a whale: one bite at a time.
-
-
tuprd-my.sharepoint.com tuprd-my.sharepoint.com
-
For everything there is a season, and atime for every matter under heaven:² a time to be born, and a time to die;a time to plant, and a time to pluck upwhat is planted;³ a time to kill, and a time to heal;a time to break down, and a time to buildup;⁴ a time to weep, and a time to laugh;a time to mourn, and a time to dance;⁵ a time to throw away stones, and a timeto gather stones together;
The writers of the Bible were ostensibly as interested as modern day productivity gurus, bloggers, and influencers in some of the basic principles of productivity.
(Originally scribbled on 2022-10-23)
-
-
www.creativelive.com www.creativelive.com
-
For Tim, the practice is managed by routine.“My quota for writing is two crappy pages a day,” he explains. Those two pages help him get started, matter what other commitments he is meeting that day. And even if they’re bad, they’re at least done.The idea is to set goals that are “easily winnable” so you don’t panic when one day passes and you don’t make that goal, because you always know you can easily pick back up the next day.“If I don’t write my two pages I don’t panic and go into the spiral.”
Tim Ferris has a routine for writing and has indicated "My quota for writing is two crappy pages a day." and "If I don't write my two pages, I don't panic and go into the spiral."
(summary); possibly worth watching video for verifying quotes and pulling out additional practices.
Note that this piece seems to indicate that his writing practice includes an idea of doing "morning pages", but this implication is likely false as Ferriss likely isn't doing this, but writing toward productive goals rather than to "clear his mental space" as is usually implied by morning pages.
-
-
niklas-luhmann-archiv.de niklas-luhmann-archiv.de
-
Das Produktivitätsproblem muss inbezug auf eine Relation gestellt werden,nämlich in bezug auf die Relation vonZettelkasten und Benutzer.
"The productivity problem must be formulated in the context of a relation, in the relation of the ZK and its user." This holds generally I suppose, productivity notions must be placed in the context of the producer and their tools. Where the producer also is the one formulating what counts as productivity. Vgl [[A Practice for Note Card Systems Outputs – Interdependent Thoughts 20221023140227]] Reading this I realise I have little purpose for e.g. economic measures of general population productivity, and e.g. in my company staying away from using billable hours as measure for productivity (but struggling to find another way to have such conversations, about effectiveness perhaps more than productivity)
-
-
Local file Local file
-
For the tools of learning are the same, in any and everysubject; and the person who knows how to use them will, at any age, get themastery of a new subject in half the time and with a quarter of the effortexpended by the person who has not the tools at his command.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
If you're trying out @tana_inc and are not on the slack... why not?? There are so many talented people coming up with awesome workflows
https://twitter.com/syncretizm/status/1581264527336669184
So many in the tools for thought space either have shiny object syndrome or are focusing on "workflows". Eventually you have to quit looking at and building workflows to actually get some work done.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Does anyone else work in project-based systems instead? .t3_y2pzuu._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to u/m_t_rv_s__n https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/y2pzuu/does_anyone_else_work_in_projectbased_systems/
Historically, many had zettelkasten which were commonplace books kept on note cards, usually categorized by subject (read: "folders" or "tags"), so you're not far from that original tradition.
Similar to your work pattern, you may find the idea of a "Pile of Index Cards" (PoIC) interesting. See https://lifehacker.com/the-pile-of-index-cards-system-efficiently-organizes-ta-1599093089 and https://www.flickr.com/photos/hawkexpress/albums/72157594200490122 (read the descriptions of the photos for more details; there was also a related, but now defunct wiki, which you can find copies of on Archive.org with more detail). This pattern was often seen implemented in the TiddlyWiki space, but can now be implemented in many note taking apps that have to do functionality along with search and tags. Similarly you may find those under Tiago Forte's banner "Building a Second Brain" to be closer to your project-based/productivity framing if you need additional examples or like-minded community. You may find that some of Nick Milo's Linking Your Thinking (LYT) is in this productivity spectrum as well. (Caveat emptor: these last two are selling products/services, but there's a lot of their material freely available online.)
Luhmann changed the internal structure of his particular zettelkasten that created a new variation on the older traditions. It is this Luhmann-based tradition that many in r/Zettelkasten follow. Since many who used the prior (commonplace-based) tradition were also highly productive, attributing output to a particular practice is wrongly placed. Each user approaches these traditions idiosyncratically to get them to work for themselves, so ignore naysayers and those with purist tendencies, particularly when they're new to these practices or aren't aware of their richer history. As the sub-reddit rules indicate: "There is no [universal or orthodox] 'right' way", but you'll find a way that is right for you.
-
-
mleddy.blogspot.com mleddy.blogspot.com
-
Google "Hawk Sugano" and "PoIC" for the reinvention and updating of a system much in use by the Japanese (Umedao author) and Germans (Buhmann author) in the Sixties and Seventies. Neither of these works has been translated into English...apparently Japan and Germany are jealously holding on to their State Secrets ;)
This post was via Den https://www.blogger.com/profile/15319877273178044093
What are these references to Umedao and Buhmann? Quck searches don't yield much. Need to look deeper.
-
-
www.flickr.com www.flickr.com
-
GTD Card Icon : Square (check box)Tag : 4th block. Squared as open-loop first, and filled later as accomplished. The GTD is advanced To-Do system proposed by David Allen. Next action of your project is described and processed through a certain flow. The GTD cards are classified into this class. 4th block is squared as open-loop first, and filled later as accomplished. The percentage of GTD Cards in my dock is less than 5 %.
-
-
web.archive.org web.archive.org
-
Several months back I'd thought about adapting the 43 folders system to a zettelkasten sort of system. I'm obviously not the first to have done so.
-
-
www.flickr.com www.flickr.com
-
https://www.flickr.com/photos/aki_oda/2684257358/
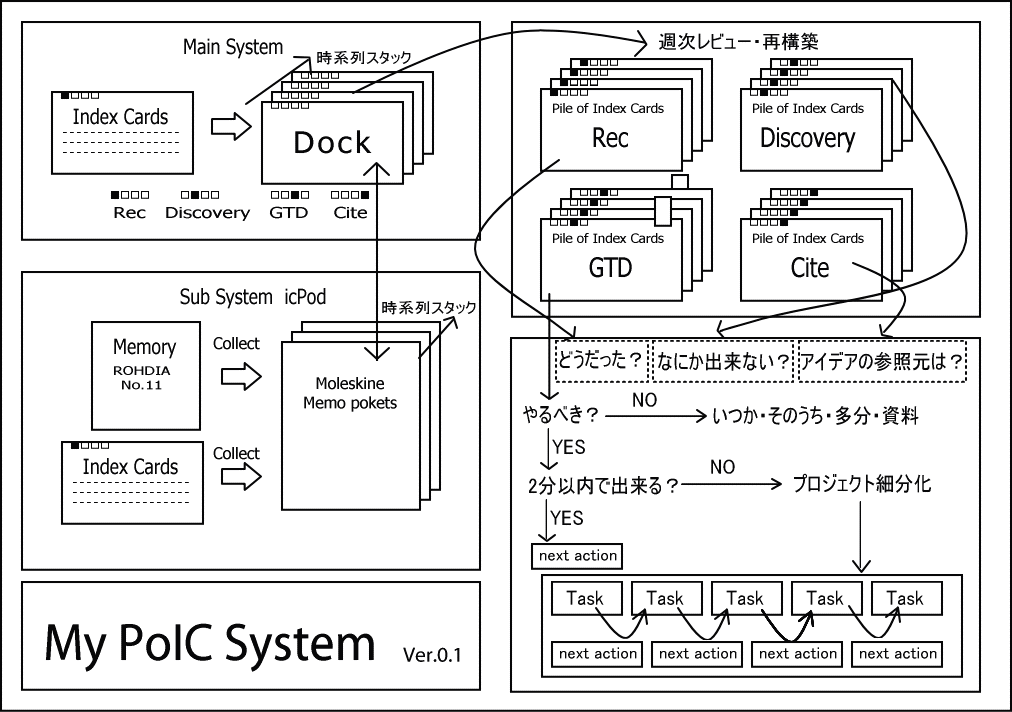
Visual diagram of PoIC system, similar to 43 folders and GTD systems.
-
-
lifehacker.com lifehacker.com
-
https://lifehacker.com/the-pile-of-index-cards-system-efficiently-organizes-ta-1599093089
LifeHacker covers the Hawk Sugano's Pile of Index Cards method, which assuredly helped promote it to the GTD and productivity crowd.
One commenter notices the similarities to Ryan Holiday's system and ostensibly links to https://thoughtcatalog.com/ryan-holiday/2013/08/how-and-why-to-keep-a-commonplace-book/
Two others snarkily reference using such a system to "keep track of books in the library [,,,] Sort them out using decimal numbers on index cards in drawers or something..." and "I need to tell my friend Dewey about this! He would run with it." Obviously they see the intellectual precursors and cousins of the method, though they haven't looked at the specifics very carefully.
One should note that this may have been one of the first systems to mix information management/personal knowledge management with an explicit Getting Things Done set up. Surely there are hints of this in the commonplace book tradition, but are there any examples that go this far?
-
-
Local file Local file
-
there might be a miscellaneous division, which wouldserve as a "tickler" and which might even be equipped with a set ofcalendar guides so that the "follow-up" system may be used.
An example of a ticker file in the vein of getting things done (GTD) documented using index cards and a card file from 1917. Sounds very familiar to the Pile of Index Cards (PoIC) from the early 2000s.
-
Sutherland, Lois Gilbert. “The English Teacher’s Card File.” The English Journal 6, no. 2 (1917): 111–12. https://doi.org/10.2307/801508.
Lois Gilbert Sutherland suggests using a card index system for multiple uses in the classroom including notes, administration, and general productivity.
There are so many parallels from this to how people are using platforms like Obsidian, Roam Research, and Notion in 2022.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.comYouTube1
-
https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=pile+of+index+card
Doesn't look like there's any of the "original" PoIC material on YouTube, but some examples of related practices to check into.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Bouttes contributedfrequently to Barthes’s seminar and gave an unusual paper at thecolloque de Cerisy called ‘Le diamantfoudre’ (‘The diamond-lightning’). He was darkly dazzling, strange, sombre, unexpected.Barthes thought he had something of Des Esseintes about him,witness an anecdote noted in his card index diary: ‘J.L.: in a phasewhere, in the restaurant, he deconstructs the menus, greatlyshocking the waiters. The other evening, at Prunier’s, oysters andoyster gratin, yesterday, at Le Balzar, oeuf en gelée and oysters,coffee ice cream and ice cream.’59
- BNF, NAF 28630, ‘Grand fichier’, 3 January 1975.
Roland Barthes' biographer Tiphaine Samoyault quotes portions of what he calls Barthes' card index diary.
This can also be seen in the published cards which comprise Barthes' Mourning Diary about the period following his mother's death.
Are there other people who've used their card index as a diary the way that some use it for productivity?
-
-
sashachapin.substack.com sashachapin.substack.com
-
https://sashachapin.substack.com/p/notes-against-note-taking-systems
The writer rails against note taking systems, and then suggests a note taking system (commonplace books)?!? What a sad circular argument.
Of course, far too many get stuck in the idea of productivity porn and that is a problem... rail against that...
-
-
Local file Local file
-
Dwyer, Edward J. “File Card Efficiency.” Journal of Reading 26, no. 2 (1982): 171–171.
Ease of use in writing and grading with short assignments by using 4 x 6" index cards in classrooms.
This sounds like some of the articles from 1912 and 1917 about efficiency of card indexes for teaching.
I'm reminded of some programmed learning texts that were card-based (or really strip-based since they were published in book form) in the 1960s and 1970s. Thse books had small strips with lessons or questions on the front with the answers on the reverse. One would read in strips through the book from front to back and then start the book all over again on page one on the second row of strips and so on.
-
-
archive.org archive.org
-
Goutor defines self-help notes as notes which one would use to refresh their memory about what remains to be done or researched, problems that remain to be solved, or information which is needed to be researched or found. (p26) These are akin in some sense to what I call "open questions". He also indicates that these notes might be triggered by one's daily activities or occasional musings which relate to one's project but occur outside of its active pursuit. In this sense, they have a similar feel to the idea of Ahrens' fleeting notes, but in Goutor's practice they aren't defined as occurring while one is doing active reading or research.
He suggests that one keeps these notes in a separate area so that they might be systematically and regularly visited for review, further research, or answering as the opportunities to do so present themselves. Once the questions have been answered and appropriate notes updated or added, these self-help notes can be discarded.
-
Goutor recommended the use of bibliographic cards not only for their standard uses as sourcing, information, and footnotes, but for creating potential scopes of work and research for planning purposes, especially in planning out one's reading and note taking using various archives and resources to make more effective and productive use of one's time. (p13) This can be potentially very useful for visiting archives and sources for which one does not have easy or frequent access.
-
Goutor indicates that "a certain amount of individual in methods is commendable, and indeed necessary." but that "it soon becomes apparent that there are some ways of doing things more efficient and ultimately more productive than others". But he goes on to bemoan that how to manuals offer little help.
(p3, Introduction)
-
- Sep 2022
-
-
The cost of child poverty is not just borne by the poor. When the expenses related tolost productivity, crime, and poor health are added up, it is estimated that child povertycosts the nation between $800 billion and $1.1 trillion per year. This is vastly higherthan the estimated $90 to $111 billion per year it would take to implement a programpackage that would lift half of children out of poverty.
The savings indicated here is almost a factor of 10! How can we not be doing this?
Compare with statistics and descriptions from Why Fewer American Children Are Living in Poverty (New York Times, The Daily, 2022-09-26)
-
-
Local file Local file
-
• Daily writing prevents writer’s block.• Daily writing demystifies the writing process.• Daily writing keeps your research always at the top of your mind.• Daily writing generates new ideas.• Daily writing stimulates creativity• Daily writing adds up incrementally.• Daily writing helps you figure out what you want to say.
What specifically does she define "writing" to be? What exactly is she writing, and how much? What does her process look like?
One might also consider the idea of active reading and writing notes. I may not "write" daily in the way she means, but my note writing, is cumulative and beneficial in the ways she describes in her list. I might further posit that the amount of work/effort it takes me to do my writing is far more fruitful and productive than her writing.
When I say writing, I mean focused note taking (either excerpting, rephrasing, or original small ideas which can be stitched together later). I don't think this is her same definition.
I'm curious how her process of writing generates new ideas and creativity specifically?
One might analogize the idea of active reading with a pen in hand as a sort of Einsteinian space-time. Many view reading and writing as to separate and distinct practices. What if they're melded together the way Einstein reconceptualized the space time continuum? The writing advice provided by those who write about commonplace books, zettelkasten, and general note taking combines an active reading practice with a focused writing practice that moves one toward not only more output, but higher quality output without the deleterious effects seen in other methods.
-
In retrospect, I should have taken my colleagues’ failings as a warning signal. Instead,relying on my own positive experience rather than their negative ones, I became an eagerevangelist for the Boicean cause. With a convert’s zeal, I recited to anyone who would listenthe many compelling reasons why daily writing works
This quote sounds a lot like the sort of dogmatic advice that (Luhmann) zettelkasten converts might give. This process works for them, but it may not necessarily work for those who either aren't willing to invest in it, or for whom it just may not work with how their brains operate. Of course this doesn't mean that there isn't value to it for many.
-
-
www.43folders.com www.43folders.com
-
http://www.43folders.com/2004/09/03/introducing-the-hipster-pda
The original Hipster PDA post? May have been coined before, but this certainly helped to popularize it.
-
-
forum.zettelkasten.de forum.zettelkasten.de
-
Andy 10:31AM Flag Thanks for sharing all this. In a Twitter response, @taurusnoises said: "we are all participating in an evolving dynamic history of zettelkasten methods (plural)". I imagine the plurality of methods is even more diverse than indicated by @chrisaldrich, who seems to be keen to trace everything through a single historical tradition back to commonplace books. But if you consider that every scholar who ever worked must have had some kind of note-taking method, and that many of them probably used paper slips or cards, and that they may have invented methods relatively independently and tailored those methods to diverse needs, then we are looking at a much more interesting plurality of methods indeed.
Andy, I take that much broader view you're describing. I definitely wouldn't say I'm keen to trace things through one (or even more) historical traditions, and to be sure there have been very many. I'm curious about a broad variety of traditions and variations on them; giving broad categorization to them can be helpful. I study both the written instructions through time, but also look at specific examples people have left behind of how they actually practiced those instructions. The vast majority of people are not likely to invent and evolve a practice alone, but are more likely likely to imitate the broad instructions read from a manual or taught by teachers and then pick and choose what they feel works for them and their particular needs. It's ultimately here that general laziness is likely to fall down to a least common denominator.
Between the 8th and 13th Centuries florilegium flouished, likely passed from user to user through a religious network, primarily facilitated by the Catholic Church and mendicant orders of the time period. In the late 1400s to 1500s, there were incredibly popular handbooks outlining the commonplace book by Erasmus, Agricola, and Melancthon that influenced generations of both teachers and students to come. These traditions ebbed and flowed over time and bent to the technologies of their times (index cards, card catalogs, carbon copy paper, computers, internet, desktop/mobile/browser applications, and others.) Naturally now we see a new crop of writers and "influencers" like Kuehn, Ahrens, Allosso, Holiday, Forte, Milo, and even zettelkasten.de prescribing methods which are variously followed (or not), understood, misunderstood, modified, and changed by readers looking for something they can easily follow, maintain, and which hopefully has both short term and long term value to them.
Everyone is taking what they want from what they read on these techniques, but often they're not presented with the broadest array of methods or told what the benefits and affordances of each of the methods may be. Most manuals on these topics are pretty prescriptive and few offer or suggest flexibility. If you read Tiago Forte but don't need a system for work or project-based productivity but rather need a more Luhmann-like system for academic writing, you'll have missed something or will only have a tool that gets you part of what you may have needed. Similarly if you don't need the affordances of a Luhmannesque system, but you've only read Ahrens, you might not find the value of simplified but similar systems and may get lost in terminology you don't understand or may not use. The worst sin, in my opinion, is when these writers offer their advice, based only on their own experiences which are contingent on their own work processes, and say this is "the way" or I've developed "this method" over the past decade of grueling, hard-fought experience and it's the "secret" to the "magic of note taking". These ideas have a long and deep history with lots of exploration and (usually very little) innovation, but an average person isn't able to take advantage of this because they're only seeing a tiny slice of these broader practices. They're being given a hammer instead of a whole toolbox of useful tools from which they might choose. Almost none are asking the user "What is the problem you're trying to solve?" and then making suggestions about what may or may not have worked for similar problems in the past as a means of arriving at a solution. More often they're being thrown in the deep end and covered in four letter acronyms, jargon, and theory which ultimately have no value to them. In other cases they're being sold on the magic of productivity and creativity while the work involved is downplayed and they don't get far enough into the work to see any of the promised productivity and creativity.
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3FipKTzkTD4
A lot of this sounds similar to some of Benjamin Franklin's old planning system and values...
-
-
www.linkingyourthinking.com www.linkingyourthinking.com
- Aug 2022
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Should I always create a Bib-note? .t3_x2f4hn._2FCtq-QzlfuN-SwVMUZMM3 { --postTitle-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postTitleLink-VisitedLinkColor: #9b9b9b; --postBodyLink-VisitedLinkColor: #989898; }
reply to: https://www.reddit.com/r/antinet/comments/x2f4hn/should_i_always_create_a_bibnote/
If you want to be lazy you could just create the one card with the quote and full source and save a full bibliographical note. Your future self will likely be pleasantly surprised if you do create a full bib note (filed separately) which allows for a greater level of future findability and potential serendipity, It may happen when you've run across that possibly obscure author multiple times and it may spur you to read other material by them or cross reference other related authors. It's these small, but seemingly "useless", practices in the present that generate creativity and serendipity over longer periods of time that really bring out the compounding value of ZK.
More and more I find that the randomly referenced and obscure writer or historical figure I noted weeks/months/years ago pops up and becomes a key player in research I'm doing now, but that I otherwise would have long forgotten and thus not able to connect or inform my current pursuits. These golden moments are too frequently not written about or highlighted properly in much of the literature about these practices.
Naturally, however, everyone's practices may differ. You want to save the source at the very least, even if it's just on that slip with the quote. If you're pressed for time now, save the step and do it later when you install the card.
Often is the time that I don't think of anything useful contemporaneously but then a week or two later I'll think of something relevant and go back and write another note or two, or I'll want to recommend it to someone and then at least it's findable to recommend.
Frequently I find that the rule "If it's worth reading, then it's worth writing down the author, title, publisher and date at a minimum" saves me from reading a lot of useless material. Of course if you're researching and writing about the broader idea of "listicles" then perhaps you have other priorities?
-
-
medium.com medium.com
-
The most important contribution management needs to make in the 21st century is similarly to increase the productivity of knowledge work and knowledge workers.”
!- For : Indyweb - Can Indyweb play a role in increasing productivity by 50x?
-
-
martinfowler.com martinfowler.com
-
there is research that indicates it can take up to 23 minutes to get back into the state of flow and return to high productivity.
-
-
-
In his book The Principles of Psychology, the pioneering philosopher and psychologist William James described living creatures as “bundles of habits”, explaining that developing habits “simplifies the movements required to achieve a given result.”
The source of the "bundles of habits" quote.
-
-
-
I'm working on my zettelkasten—creating literature notes and permanent notes—for 90 min a day from Monday to Friday but I struggle with my permanent note output. Namely, I manage to complete no more than 3-4 permanent notes per week. By complete I mean notes that are atomic (limited to 1 idea), autonomous (make sense on their own), connected (link to at least 3 other notes), and brief (no more than 300 words).That said, I have two questions:How many permanent notes do you complete per week on average?What are your tips to increase your output?
reply to: https://www.reddit.com/r/Zettelkasten/comments/wjigq6/how_do_you_increase_your_permanent_note_output
In addition to all the other good advice from others, it might be worth taking a look at others' production and output from a historical perspective. Luhmann working at his project full time managed to average about 6 cards a day.1 Roland Barthes who had a similar practice for 37 years averaged about 1.3 cards a day.2 Tiago Forte has self-reported that he makes two notes a day, though obviously his isn't the same sort of practice nor has he done it consistently for as long.3 As you request, it would be useful to have some better data about the output of people with long term, consistent use.
Given even these few, but reasonably solid, data points at just 90 minutes a day, one might think you're maybe too "productive"! I suspect that unless one is an academic working at something consistently nearly full time, most are more likely to be in the 1-3 notes a day average output at best. On a per hour basis Luhmann was close to 0.75 cards while you're at 0.53 cards. Knowing this, perhaps the best advice is to slow down a bit and focus on quality over quantity. This combined with continued consistency will probably serve your enterprise much better in the long run than in focusing on card per hour or card per day productivity.
Internal idea generation/creation productivity will naturally compound over time as your collection grows and you continue to work with it. This may be a better sort of productivity to focus on in the long term compared with short term raw inputs.
Another useful tidbit that some neglect is the level of quality and diversity of the reading (or other) inputs you're using. The better the journal articles and books you're reading, the more value and insight you're likely to find and generate more quickly over time.
-
-
news.ycombinator.com news.ycombinator.com
-
This is what I observed in hyper productive people: some of them have a unique, novel system of organizing their knowledge, but many of them don't. So, having such a system is probably not that important.
I see these sorts of statements often, and never taken into account is the diversity of ways of thought, general intelligence, quality of memory, or many other factors that make individuals different as well as their outcomes different.
Different people are going to use different tools differently and have different outcomes.
-
-
ljvmiranda921.github.io ljvmiranda921.github.io
-
Tools are instruments to achieve something, and systems are the organization of such.
Feels like there's more here if we delve a bit deeper...
-
-
In the world of productivity porn, it sounds edgy to say “I use pen and paper.”
I'm not the only one talking about "productivity porn"....
-
Sometimes, I find digital apps urging me to integrate with another application or extension: connect to calendar, install this, install that (and sure, it may also be my own damn fault). They force me to get into a “system” rather than focus on what the tool provides. It’s overwhelming. Over-optimization leads to empty work, giving me a feeling of productivity in the absence of output, like quicksand. It hampers me from doing actual work.
-
-
www.tana.inc www.tana.incTana1
-
https://www.tana.inc/
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
idstuff.blogspot.com idstuff.blogspot.com
-
Also, your issue isn't feeling exhausted due to "not being with smart people in a room". Those same smart people are on Zoom. Your issue is the overabundance of meetings and zoom fatigue.
There's also some cherry picking here (in Kim's original piece). I love a good F2F meeting, but let's remember "conference room fatigue". Some gatherings of smart people consume more energy than they produce. (Like "zoom fatigue" sometimes it's the affordances of the room - bad lighting, uncomfortable chairs, etc - and sometimes it's because of behavior in the meeting.)
-
-
thoughtcatalog.com thoughtcatalog.com
-
As Raymond Chandler put it, “when you have to use your energy to put those words down, you are more apt to make them count.”
-
-
lifehacker.com lifehacker.com
-
https://lifehacker.com/im-ryan-holiday-and-this-is-how-i-work-1485776137
An influential productivity article from 2013-12-18 that is seen quoted over the blogosphere for the following years that broadened the idea of the commonplace book and the later popularity of the zettelkasten.
Note that zettelkasten.de was just starting up at about this time period, though it follows the work of Manfred Kuehn's note taking blog.
-
I use the same 4x6 index cards I use for my commonplace book to write down my daily tasks
Ryan Holiday's note taking practice extends to using the same 4x6 inch index cards for his to do lists.
-
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
But 70- and 80-somethings loving their work so much that they never retire is awfully close to something I’ve called workism—the idea that work has, for many elites, become a kind of personal religion in an era of otherwise declining religiosity.
This is right. And, I think it's ironically more acute in ministry.
-
This has created what the writer Paul Millerd calls a “Boomer blockade” at the top of many organizations, keeping Gen-X and Millennial workers from promotions. As older workers remain in advanced positions in politics and business, younger workers who would have ascended the ranks in previous decades are getting stuck in the purgatory of upper-middle management.
This is the problem, haha.
-
-
uxdesign.cc uxdesign.cc
-
As Tiago Forte writes in his excellent book, ‘Building a Second Brain’, “every bit of energy we spend straining to recall things is energy not spent doing the thinking that only humans can do: inventing new things, crafting stories, recognising patterns, following our intuition, collaborating with others, investigating new subjects, making plans, testing theories”.
This is exactly the kind of language that is driving people psychotic: that there's only 2 modes - recalling and creating. Yes, there are these 2 modes. But there are others too, the most important of which are "resting", "reflecting", and "gestating". Without these others, which we must visit in balance with recalling and creating, we will end up in a rubber room.
-
- Jul 2022
-
developassion.gumroad.com developassion.gumroad.com
-
https://developassion.gumroad.com/l/obsidian-starter-kit
Sébastien Dubois selling an Obsidian Starter Kit for €19.99 on Gumroad.
Looks like it's got lots of support and description of many of the big buzz words in the personal knowledge management space. Not sure how it would work with everything and the kitchen sink thrown in.
found via https://www.reddit.com/r/PersonalKnowledgeMgmt/comments/w8dw94/obsidian_starter_kit/
-
-
deleteme-z4xq4hvfe.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com deleteme-z4xq4hvfe.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
-
you can't do a proj-ect, you can only do the action steps it requires.
link to: - https://hypothes.is/a/mVBBYgvIEe22ej8FOn5Cqg
-
-
docdrop.org docdrop.org
-
The excitement over PKM has spilled over into blogs,YouTube channels, online courses, and books. Like otherproductivity hacks of the past (The One Minute Manager,Getting Things Done, etc.), techniques such as “LinkingYour Thinking”, “Writing Smart Notes”, or “Building aSecond Brain” contain a lot of useful ideas and havesometimes launched careers for their authors.
a.k.a. productivity porn
-
-
medium.com medium.com
-
In his interviews, he likes to emphasize that, in each book, he’s back to square one.
Where does Robert Greene specifically say this?
With a commonplace book repository, one is never really starting from square one. Anyone who says otherwise is missing the point.
-
-
winnielim.org winnielim.org
-
If we can rightly identify the seeds (or spores) we will know what type of conditions they will thrive in. In similar ways, some people need different care, handling and environment to thrive. Perhaps with the right conditions, they too can make contributions to the world in small but meaningful ways – and who can truly judge the true magnitude of something?
Conditions of care are individual
There will be a range of environmental and supportive measures…perhaps even smoothing like a bell curve distribution with people that thrive in conditions on the long tails on the long tails (or need long tails of support to thrive).
-
-
scattered-thoughts.net scattered-thoughts.net
-
none of that saves me any time in the long run
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
-
never open the browser without knowing where it's going and i never get caught up in that stupid trick where you know you start going to so you don't need to and you forget why you're on the internet
Deep inter-app linking to combat unfocused app activation
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Jun 2022
-
Local file Local file
-
You might have arrived at this book because you heard about thisnew field called personal knowledge management, or maybe whenyou were trying to find guidance in how to use a cool new notetakingapp. Maybe you were drawn in by the promise of new techniques forenhancing your productivity, or perhaps it was the allure of asystematic approach to creativity.
The broad audiences for this book.
This may have been better place in the introduction to draw these people in.
-
The Essential Habits ofDigital Organizers
This chapter is too entailed with productivity advice, which can be useful to some, but isn't as note taking focused for those who probably need more of that.
What is the differentiator between knowledge workers, knowledge creators, students, researchers, academics. How do we even clearly delineate knowledge worker as a concept. It feels far too nebulous which makes it more difficult to differentiate systems for them to use for improving productivity and efficiency.
-
Here are more specific examples of what those opportunitiesmight look like
He's got a very specific type of notes for productivity compared with the sort of notes a student, academic, or researcher might take. This has consequences to the sort of system one has and how productive or not it is.
At some point in the book he sounds as if he's talking about notes for content creation/production, but he's also mixing in work productivity sorts of notes which can be treated dramatically differently.
Modern systems need to better distinguish between these two sorts of modes. (Are there others?) What should we even call these things to distinguish them and how they might be differently handled?
What do the two things have in common that allow them to be conflated? What is different that suggests distinguishing them and separating them?
Which digital tools are better for each of these? Do some handle both well? Should there be a mental or physical separation of them?
Am I just wholly wrong here?
-
This fundamental tension—between quality and quantity—is atension we share as knowledge workers. We also must producework to an extremely high standard, and we must do it fast,continuously, all year long. We are like sprinters who are also tryingto run a marathon.
Do we? Really? This definitely needs reframing and books like this that play on these sorts of fears are both partially responsible, but are also preying on an atmosphere which they're propagating.
This is the sort of sad thing that a productivity guru would say...
-
TIAGO FORTE is one of the world’s foremost experts on productivity
-
By dropping or reducing or postponing the least importantparts, we can unblock ourselves and move forward even when timeis scarce.
When working on a project, to stave off potential procrastination on finishing, one should focus on the minimum viable version and finish that. They can then progressively enhance portions and add on addition pieces which may be beneficial or even nice to have.
Spending too much time on the things that sound nice or that one "might want to have" in the future will be the death of the thing.
link to: - you ain't gonna need it - bikeshedding for procrastination
questions: - Does the misinterpreted-effort hypothesis play a role in creating our procrastination and/or lead to decision fatigue?
-
If we overlay the four steps of CODE onto the model ofdivergence and convergence, we arrive at a powerful template forthe creative process in our time.
The way that Tiago Forte overlaps the idea of C.O.D.E. (capture/collect, organize, distill, express) with the divergence/convergence model points out some primary differences of his system and that of some of the more refined methods of maintaining a zettelkasten.
 <small>Overlapping ideas of C.O.D.E. and divergence/convergence from Tiago Forte's book Building a Second Brain (Atria Books, 2022) </small>
<small>Overlapping ideas of C.O.D.E. and divergence/convergence from Tiago Forte's book Building a Second Brain (Atria Books, 2022) </small>Forte's focus on organizing is dedicated solely on to putting things into folders, which is a light touch way of indexing them. However it only indexes them on one axis—that of the folder into which they're being placed. This precludes them from being indexed on a variety of other axes from the start to other places where they might also be used in the future. His method requires more additional work and effort to revisit and re-arrange (move them into other folders) or index them later.
Most historical commonplacing and zettelkasten techniques place a heavier emphasis on indexing pieces as they're collected.
Commonplacing creates more work on the user between organizing and distilling because they're more dependent on their memory of the user or depending on the regular re-reading and revisiting of pieces one may have a memory of existence. Most commonplacing methods (particularly the older historic forms of collecting and excerpting sententiae) also doesn't focus or rely on one writing out their own ideas in larger form as one goes along, so generally here there is a larger amount of work at the expression stage.
Zettelkasten techniques as imagined by Luhmann and Ahrens smooth the process between organization and distillation by creating tacit links between ideas. This additional piece of the process makes distillation far easier because the linking work has been done along the way, so one only need edit out ideas that don't add to the overall argument or piece. All that remains is light editing.
Ahrens' instantiation of the method also focuses on writing out and summarizing other's ideas in one's own words for later convenient reuse. This idea is also seen in Bruce Ballenger's The Curious Researcher as a means of both sensemaking and reuse, though none of the organizational indexing or idea linking seem to be found there.
This also fits into the diamond shape that Forte provides as the height along the vertical can stand in as a proxy for the equivalent amount of work that is required during the overall process.
This shape could be reframed for a refined zettelkasten method as an indication of work
Forte's diamond shape provided gives a visual representation of the overall process of the divergence and convergence.
But what if we change that shape to indicate the amount of work that is required along the steps of the process?!
Here, we might expect the diamond to relatively accurately reflect the amounts of work along the path.
If this is the case, then what might the relative workload look like for a refined zettelkasten? First we'll need to move the express portion between capture and organize where it more naturally sits, at least in Ahren's instantiation of the method. While this does take a discrete small amount of work and time for the note taker, it pays off in the long run as one intends from the start to reuse this work. It also pays further dividends as it dramatically increases one's understanding of the material that is being collected, particularly when conjoined to the organization portion which actively links this knowledge into one's broader world view based on their notes. For the moment, we'll neglect the benefits of comparison of conjoined ideas which may reveal flaws in our thinking and reasoning or the benefits of new questions and ideas which may arise from this juxtaposition.

This sketch could be refined a bit, but overall it shows that frontloading the work has the effect of dramatically increasing the efficiency and productivity for a particular piece of work.
Note that when compounded over a lifetime's work, this diagram also neglects the productivity increase over being able to revisit old work and re-using it for multiple different types of work or projects where there is potential overlap, not to mention the combinatorial possibilities.
--
It could be useful to better and more carefully plot out the amounts of time, work/effort for these methods (based on practical experience) and then regraph the resulting power inputs against each other to come up with a better picture of the efficiency gains.
Is some of the reason that people are against zettelkasten methods that they don't see the immediate gains in return for the upfront work, and thus abandon the process? Is this a form of misinterpreted-effort hypothesis at work? It can also be compounded at not being able to see the compounding effects of the upfront work.
What does research indicate about how people are able to predict compounding effects over time in areas like money/finance? What might this indicate here? Humans definitely have issues seeing and reacting to probabilities in this same manner, so one might expect the same intellectual blindness based on system 1 vs. system 2.
Given that indexing things, especially digitally, requires so little work and effort upfront, it should be done at the time of collection.
I'll admit that it only took a moment to read this highlighted sentence and look at the related diagram, but the amount of material I was able to draw out of it by reframing it, thinking about it, having my own thoughts and ideas against it, and then innovating based upon it was incredibly fruitful in terms of better differentiating amongst a variety of note taking and sense making frameworks.
For me, this is a great example of what reading with a pen in hand, rephrasing, extending, and linking to other ideas can accomplish.
-
One of my favorite rules of thumb is to “Only start projects that are already 80percent done.” That might seem like a paradox, but committing to finishprojects only when I’ve already done most of the work to capture, organize,and distill the relevant material means I never run the risk of startingsomething I can’t finish.
This same sort of principle is seen in philanthropy circles where the group already has commitments for a large proportion of the end goal before they even announce the campaign.
Is there a rule of thumb for this in philanthropy? 50%? What is it called, ie does it have a specific name?
What relation does it have to the Pareto principle, if any?
-
eventually you’ll have so many IPs at yourdisposal that you can execute entire projects just by assemblingpreviously created IPs. This is a magical experience that willcompletely change how you view productivity.
another example of the idea of "magical" experience that comes when taking notes. This one isn't about idea creation or even serendipity though, but relates specifically to being "bulk productive".
-
UsingPARA is not just about creating a bunch of folders to put things in. Itis about identifying the structure of your work and life—what you arecommitted to, what you want to change, and where you want to go.
Using the P.A.R.A. method puts incredible focus on immediate projects and productivity toward them. This is a dramatically different focus from the zettelkasten method.
The why's of the systems are dramatically different as well.
-
Your efforts to capture content for future use will be tremendouslyeasier and more effective if you know what that content is for.
Within the P.A.R.A. framework it's helpful if you know what your note capture is meant for, but it's wholly against a lot of note taking for things which may simply spark joy. This may be helpful for the work-a-day productivity person, but is painfully out of sync with keeping notes as a means of generating new ideas. Many of these sorts of notes will be hidden away in an archive and thus broadly unusable in the long run.
Sorting ideas into folders is still an older classical way of thinking instead of linking an idea to related things that make it imminently more usable. Cross linked ideas seem wholly more interesting, vibrant and more useable to me.
-
Instead of organizing ideas according to where they come from, Irecommend organizing them according to where they are going
This is a useful distinction.
-
The goal of organizing our knowledge is to move our goalsforward, not get a PhD in notetaking.
HA! Though many do fall into this trap.
-
Archives: Things I’ve Completed or Put on Hold
The P.A.R.A. method seems like an admixture of one's projects/to do lists and productivity details and a more traditional commonplace book. Keeping these two somewhat separate mentally may help users with respect to how these folders should be used.
Tags
- behavioral economics
- rules of thumb
- knowledge creators
- divergence/convergence
- examples
- synthetic associations
- procrastination
- scope creep
- decision fatigue
- reviews
- GTD
- productivity guru
- Tiago Forte
- project management
- P.A.R.A.
- commonplace books
- note taking
- Pareto principle
- year in reviews
- organization
- knowledge work
- fear
- progressive enhancement
- bikeshedding
- magic of note taking
- audience
- putting in the work
- note taking methods
- work
- visualizations
- commonplace books vs. zettelkasten
- fund raising goals
- focus
- compounding value
- knowledge workers
- writing
- YAGNI
- cognitive bias
- innovation
- misinterpreted-effort hypothesis
- fund raising campaigns
- tools for creativity
- productivity fallacy
- personal knowledge management
- self-appellations
- combinatorial creativity
- efficiency
- fear uncertainty and doubt
- decision making
- C.O.D.E.
- zettelkasten
- productivity
- zettelkasten overreach
- writing for understanding
- time
- imitation for innovation
- idea links
- minimum viable product
- note taking applications
- scope
- philanthropy
Annotators
-
-
effectiviology.com effectiviology.com
-
Interleaving is a learning technique that involves mixing together different topics or forms of practice, in order to facilitate learning. For example, if a student uses interleaving while preparing for an exam, they can mix up different types of questions, rather than study only one type of question at a time.Interleaving, which is sometimes referred to as mixed practice or varied practice, is contrasted with blocked practice (sometimes referred to as specific practice), which involves focusing on only a single topic or form of practice at a time.
Interleaving (aka mixed practice or varied practice) is a learning strategy that involves mixing different topics, ideas, or forms of practice to improve outcomes as well as overall productivity. Its opposite and less effective strategy is blocking (or block study or specific practice) which focuses instead on working on limited topics or single forms of practice at the same time.
This may be one of the values of of the Say Something In Welsh method which interleaves various new nouns and verbs as well as verb tenses in focused practice.
Compare this with the block form which would instead focus on lists of nouns in a single session and then at a later time lists of verbs in a more rote fashion. Integrating things together in a broader variety requires more work, but is also much more productive in the long run.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
-
higher order learning can lead to greater levels of productivity than lower order or rote methods
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Tiago's book follows the general method of the commonplace book, but relies more heavily on a folder-based method and places far less emphasis and value on having a solid index. There isn't any real focus on linking ideas other than putting some things together in the same folder. His experience with the history of the space in feels like it only goes back to some early Ryan Holiday blog posts. He erroneously credits Luhmann with inventing the zettelkasten and Anne-Laure Le Cunff created digital gardens. He's already retracted these in sketch errata here: https://www.buildingasecondbrain.com/endnotes.
I'll give him at least some credit that there is some reasonable evidence that he actually used his system to write his own book, but the number and depth of his references and experience is exceptionally shallow given the number of years he's been in the space, particularly professionally. He also has some interesting anecdotes and examples of various people including and array of artists and writers which aren't frequently mentioned in the note taking space, so I'll give him points for some diversity of players as well. I'm mostly left with the feeling that he wrote the book because of the general adage that "thought leaders in their space should have a published book in their area to have credibility". Whether or not one can call him a thought leader for "re-inventing" something that Rudolphus Agricola and Desiderius Erasmus firmly ensconced into Western culture about 500 years ago is debatable.
Stylistically, I'd call his prose a bit florid and too often self-help-y. The four letter acronyms become a bit much after a while. It wavers dangerously close to those who are prone to the sirens' call of the #ProductivityPorn space.
If you've read a handful of the big articles in the note taking, tools for thought, digital gardens, zettelkasten space, Ahren's book, or regularly keep up with r/antinet or r/Zettelkasten, chances are that you'll be sorely disappointed and not find much insight. If you have friends that don't need the horsepower of Ahrens or zettelkasten, then it might be a reasonable substitute, but then it could have been half the length for the reader.
-
-
-
All I know for sure is that they are trapped in the box.My solution for them: This isn’t working. Free yourself. Get out of this box. Putit away for another day and start a new box.
Don't get trapped in a particular project. Sometimes variety of projects can be just the medicine the doctor ordered. The zettelkasten method works, in part, because it makes it easier to work on things which inspire you while still knowing that you can slip away for a while, but still come back and find all your prior work there waiting for you. This is particularly useful even if you've forgotten that work.
Link this to examples of Luhmann and Ahren's descriptions of not becoming bored with their zettelkasten.
-
I also like the simplicity of a box. There’s a purpose here, and it has a lot to dowith efficiency. A writer with a good storage and retrieval system can write faster.He isn’t spending a lot of time looking things up, scouring his papers, and patrollingother rooms at home wondering where he left that perfect quote. It’s in the box.
A card index can be a massive boon to a writer as a well-indexed one, in particular, will save massive amounts of time which might otherwise be spent searching for quotes or ideas that they know they know, but can't easily recreate.
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
How to stop forgetting stuff you read.
- Taking notes (highlighting and taking notes)
- Re-engage with ideas and your notes to get around the "forgetting curve Review
- Integrating (putting it all into a database)
- Summarize. Take quick notes on things you've read.
When summarizing you can put general thoughts and other stuff, like how you discovered it, favorite quotes, etc.
The whole point is to engage with the material.
Zettelkasten method is recommended.
Literature notes are quick notes that should get converted to evergreen or permanent notes.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
thebrain.com thebrain.com
-
Are there examples of people using The Brain in public as more extensive commonplace books or zettelkasten?
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qf4caUoi5bo
Scott Scheper shows how he uses his paper zettelkasten for planning six week sprints. Only a very rough outline of what this looks like, though he does show using his index to cross reference the card with the actual details.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
davidepstein.com davidepstein.com
-
WHY GENERALISTS TRIUMPH IN A SPECIALIZED WORLD “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes “The most important business — and parenting — book of the year.” — Forbes ‹›
Many university presidents site the value of basic research to fuel the more specialized research spaces.
Example: we didn't have any application for x-rays when their basic science was researched, but now they're integral to a number of areas of engineering, physics, and health care.
What causes this effect? Is it the increased number of potential building blocks that provide increased flexibility and complexity to accelerate the later specializations?
Link this to: https://hyp.is/-oEI3OF5EeybM_POWlI9WQ/www.maggiedelano.com/garden/helpful-books
-
-
www.maggiedelano.com www.maggiedelano.com
-
A recent book that advocates for this idea is Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized world by David Epstein. Consider reading Cal Newport’s So Good They Can’t Ignore You along side it: So Good They Can’t Ignore You focuses on building up “career capital,” which is important for everyone but especially people with a lot of different interests.1 People interested in interdisciplinary work (including students graduating from liberal arts or other general programs) might seem “behind” at first, but with time to develop career capital these graduates can outpace their more specialist peers.
Similar to the way that bi-lingual/dual immersion language students may temporarily fall behind their peers in 3rd and 4th grade, but rocket ahead later in high school, those interested in interdisciplinary work may seem to lag, but later outpace their lesser specializing peers.
What is the underlying mechanism for providing the acceleration boosts in these models? Are they really the same or is this effect just a coincidence?
Is there something about the dual stock and double experience or even diversity of thought that provides the acceleration? Is there anything in the pedagogy or productivity research space to explain it?
-
- May 2022
-
Local file Local file
-
.Adopting the habit of knowledge capture has immediate benefitsfor our mental health and peace of mind. We can let go of the fearthat our memory will fail us at a crucial moment. Instead of jumpingat every new headline and notification, we can choose to consumeinformation that adds value to our lives and consciously let go of therest.
Immediate knowledge capture by highlighting, annotating, or other means when taking notes can help to decrease cognitive load. This is similar to other productivity methods like quick logging within a bullet journal system, writing morning pages, or Getting Things Done (GTD). By putting everything down in one place, you can free your mind of the constant need to remember dozens of things. This frees up your working memory to decrease stress as you know you've captured the basic idea for future filtering, sorting, and work at a later date.
-
So many of us share the feeling that we are surrounded byknowledge, yet starving for wisdom. That despite all the mind-expanding ideas we have access to, the quality of our attention isonly getting worse. That we are paralyzed by the conflict betweenour responsibilities and our most heartfelt passions, so that we’renever quite able to focus and also never quite able to rest
We're 13% into the book already and still being sold on the why we need this... Can we move it along please? Perhaps some will need the "why" story, but in a book about productivity...
-
A revolutionary approach to enhancing productivity,creating flow, and vastly increasing your ability tocapture, remember, and benefit from the unprecedentedamount of information all around us.
Some great marketing copy, but I'm anticipating a book that is going to lay out some general techniques that go under the topic of commonplace book, a concept that goes back over 2,000 years. This is the opposite of revolutionary.
-
-
www.otherlife.co www.otherlife.co
-
Apps and courses that help you make these pretty pictures are not helping you to advance your knowledge or to write increasingly insightful works.
Based on my preliminary reading of Tiago Forte's forthcoming book, this seems broadly true.
-
The concept of the Knowledge Graph deserves the classification of bullshit because its allure derives primarily from the false impression that it can mechanistically deliver—or substitute for—the brute, linear willfulness that defines all non-trivial writing.
In watching the space and seeing the sorts of conversations and questions I see online in Twitter, Reddit, and other fora, I too often see people talking about the system(s) and not actually using the systems. Very few get to a critical mass of well written notes, which I estimate to be about 500 to 1000 before they give up. Most aren't taking good notes and are imposing far more structure on them as if they're writing wiki articles instead of taking notes. Too many things go wrong in their processes before they're giving up and moving on. This has the effect of making the enterprise appear to be a failure.
I suspect that the author of this piece is in this last group and instead of thinking about why they're failing, they're lashing out about the hype in the space. Certainly there is way too much hype, and that isn't necessarily a good thing. But there's also not nearly enough practice and that is far worse.
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
Someone considering re-creating Tiago Forte's Building a Second Brain business, but with pen and paper.
-
-
xeiaso.net xeiaso.net
-
the process for putting something on the internet to just be a git push and trust that the machine will just take care of it
-
-
themanagershandbook.com themanagershandbook.com
-
The first rule in time management is to ruthlessly protect your time.
-
-
howisfelix.today howisfelix.today
-
45% less time spent in video & audio calls that day
I can relate with the author. Spending time in a high number of video/audio calls can drastically decrease my mood
-
-
cbea.ms cbea.ms
-
What may be a hassle at first soon becomes habit, and eventually a source of pride and productivity for all involved.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Apr 2022
-
winnielim.org winnielim.org
-
I think we are obsessed with speed to our own detriment, and there is a lot of joy and meaning in learning to appreciate slowness, or phenomenon that may not be clearly measurable.
—Winnie Lim
-
Speed comes at a cost. The visibility of the cost is often delayed, and sometimes the awareness of it arrives too late.
If speed comes at a cost, then one should be cautious when working on ideas around productivity. When does one become too productive? Be sure to create some balance in your processes.
Amazon warehouses optimize for worker productivity, but this comes at the expense burning out the workforce. If the CEO and senior executives couldn't or work at a similar pace for weeks on end, then they should be loathe to force their low paid workforce to do the same.
-
-
www.goodreads.com www.goodreads.comRest1
-
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Winnie Lim</span> in peeking into people’s routines (<time class='dt-published'>04/24/2022 02:40:01</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
www.themarginalian.org www.themarginalian.org
-
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Winnie Lim</span> in peeking into people’s routines (<time class='dt-published'>04/24/2022 02:40:01</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
www.reddit.com www.reddit.com
-
ellem52Op · 17 days ago There have been some amazing apps with small teams in the past. Three that jump out to me are Xobni, Mailbox, and Accompli. All three were bought by huge companies. Xobni got bought by Yahoo! who shut it down right after buying it. Mailbox by Dropbox who almost immediately dropped it - what a waste. Accompli is actually the mobile version of Outlook. (Like ToDo is actually Wunderlist.)TickTick has that same feel to me, like they're waiting for someone like Apple, or MS to buy them.
Ohhh yeah that definitely makes things far more concerning. Not only do I like having apps that are independent and focused on improving their products, and I definitely wouldn't want Todoist to be bought out by a bigger company, the history of these acquisitions would not inspire any confidence in their long-term stability. I never even heard of these apps before.
-
I've used a lot of these apps. RTM is actually my favorite but like MinimaList it's essentially closed to itself. Microsoft ToDo (nee Wunderlist) was actually pretty good too but the mixing of work/home was not something I wanted.
I believe RTM is "Remember the Milk." I have heard this brought up a few times and the name is kind of odd, which makes me even more curious about what's special about it.
Before moving to Todoist, I used Microsoft To Do, but I wanted something more. I used TickTick for a bit but I barely remember anything from it. Todoist was the one that clicked with me.
On a side note, MinimaList is such a cute pun.
-
- Mar 2022
-
roam.elaptics.co.uk roam.elaptics.co.uk
-
As James Clear said in Atomic Habits:
You do not rise to the level of your goals. You fall to the level of your systems —James Clear, Atomic Habits
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x22OB55bysc
Hilarious clickbait title for someone who makes productivity videos on YouTube, but she talks about finding some balance.
She's definitely selling something though...
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5jUbukComgU
The problems with productivity.... You have to appreciate that she sees the issues in this space.
Before looking at productivity, ask "What is your goal?"
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lnFHwl2Dbr0
- System should be as frictionless as possible.
- Capture in one location. (She says as few as possible, but this is too wishy-washy: she's got a "Readwise page" and a "Links page".)
- There needs to be levels of processing.
- Split out based on future value.
- Everything has resources. How to capture metadata and be able to cite it?
Everything needs to have a "Why"? What is the context for capturing? What is the reason? How will it be used in the future? Why was it interesting?
She also describes how she collects notes in various formats (books, online articles, Kindle, Twitter, etc.) It primarily involves using Notion along with a variety of other sub-applications including Instapaper for sharing to Notion.
Dramatically missing from this presentation is the answer to the question "why" collect all this stuff? How is she using it in the future? What is the overall value? She touches on writing the why for herself as she's taking notes, but I get the impression that she's not actively practicing what she preaches, and I suspect that many don't. This leaves me with the impression that she's collecting with no end goal, which for many may be fine.
She's got a gaping hole in the processing section which likely needs a video unto itself and which would probably go a long way toward answer the "why" question above.
In looking at her other videos, I see she's using the phrase "second brain" and words like productivity. There seems to be a high level of disconnect between those using "second brain" and the "why do this?" question other than the simple idea of "productivity" which seems to be a false trap that gets people into the mindset of being a collector for collections' sake.
Almost hilariously she's got videos with titles like: - "I'm a productivity guru and I hate it." - "Productivity YouTube is brainwashing you"
She's titled the final portion of the video "Outro" which is actually displayed on the video UI. This might be useful for production purposes but should be changed or omitted for actual consumption.
The title "How I Remember Everything I Read" is pure clickbait here. It's more aptly titled, "How I Take and Save Notes". Where's the how I use this after? or how I review over it all to actually remember it/memorize it? There's nothing here to support this end of things which is the promise given in the title.
-
-
alexturek.com alexturek.com
-
This isn’t MAIN_PRIORITY, so we aren’t going to do it until at least ESTIMATED_DONE_DATE. Right now our priority is MAIN_PRIORITY because of ONE_SENTENCE_JUSTIFICATION, and this is 100% our shipping focus. I agree this sounds like a really useful feature - once we finish MAIN_PRIORITY, should we consider dropping SECOND_PRIORITY and do it?
Templates for saying NO
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Feb 2022
-
every.to every.to
-
https://every.to/superorganizers/the-fall-of-roam
A user talks about why they've stopped using Roam Research.
I suspect that a lot of people have many of the same issues and to a great extent, it's a result of them not understanding the underlying use cases of the problems they're trying to solve.
This user is focusing on it solving the problem of where one is placing their data in hopes that it will fix all their problems, but without defining the reason why they're using the tool and what problems they hope for it to solve.
Note taking is a much broader idea space than many suppose.
-
-
Local file Local file
-
A coach is not there to do the work,but to show us how to use our time and effort in the most effectiveway.
Much as coaches help their athletes become better, teachers are there to help students use their time and work efforts in the most effective ways.
-
Give Each Task the Right Kind of Attention
Ahrens talks about the variety of different tasks that underpin writing and the varieties of attention that each can take. He suggests that for increased productivity that one focus on one sort or type of tasks at a time in each part of the process.
This sort of structural planning in one's work is possibly the most important planning one can do.
-
Unfortunately, the most common way people organise their writingis by making plans. Although planning is almost universallyrecommended by study guides, it’s the equivalent of putting oneselfon rails.Don’t make plans. Become an expert.
Planning and especially overplanning your writing work can be counter-intuitively non-productive. A smarter reading and note taking approach can allow one to be playful and creative in a way that more focused, goal-oriented writing would never allow. It's also an incredibly valuable tool for when one becomes "stuck" and working on something else seems easier or more profitable.
An example of this is the Ahren's extended use of the shipping container metaphor with respect to the zettelkasten. By having a variety of ideas stewing in his zettelkasten, a simple search or link using the word box allowed him to create a fantastic metaphor for reshaping one's note taking practice. It's a bit sad that he didn't take a moment to point this out explicitly (though perhaps this isn't the way things came about?)
-
Only after aligning every single part of the delivery chain, frompackaging to delivery, from the design of the ships to the design ofthe harbours, was the full potential of the container unleashed.
Streamlining one's entire workflow from start to finish can unleash tremendous amounts of additional system-wide productivity. Starting out by tinkering with small things here and there is more likely to doom these smaller individual changes to failure with out associated global changes.
Once the overall system has been redesigned and reconfigured, then one can make and perfect smaller scale local changes.
Link this to the idea of kelp and sailing/rowing from The West Wing.
-
We need a reliable and simple external structure tothink in that compensates for the limitations of our brains
Let's be honest that there are certainly methods for doing all of this within our brains and not needing to rely on external structures. This being said, using writing, literacy, and external structures does allow us to process things faster than before.
Can we calculate what the level of greater efficiency allows for doing this? What is the overall throughput difference in being able to forget and write? Not rely on communication with others? What does a back of the envelope calculation for this look like?
-
A good structure is something you can trust. It relieves you fromthe burden of remembering and keeping track of everything. If youcan trust the system, you can let go of the attempt to hold everythingtogether in your head and you can start focusing on what isimportant:
Whether it's for writing, to do lists, or other productivity spaces, a well designed system is something that one can put their absolute trust into. This allows one to free themselves from the burden of tracking and dealing with minutiae so they can get serious work done.
Tags
- orality and memory
- teachers
- shipping containers
- analogies
- exercise
- attention
- global changes
- topology
- planning
- writing process
- design
- tools for thought
- open questions
- to do lists
- boxes
- efficiency
- orality
- zettelkasten
- external structures for thought
- local changes
- productivity
- Llullan combinatorial arts
- internal structures for thought
- putting in the work
Annotators
-
-
reallifemag.com reallifemag.com
-
qbatten annotates on Jan 11, 2022:
Why note-taking is bad. Why you shouldn't take notes. Taking notes shouldn't be the end in itself!
I'll agree that "taking notes shouldn't be the end in itself", but they've drawn the completely wrong conclusion about note taking being bad or that this flimsy argument indicates that one shouldn't take notes.
Not everyone who wields a hammer is going to be a master craftsman and it's even less likely that someone who tinkers with one for a few months or even a few years will get there without some significant help. There's no evidence here of anything but desire for methods to work. Where was the deep practice, research into these systems described?
From the start, the featured image in the original article of a crazy person's conception of a massive collection of piles of paper to represent the process is highly illustrative of so many misconceptions.
-
https://reallifemag.com/rank-and-file/
An interesting example of someone who fell into the trap of thinking that a particular tool or tools would magically make them smarter or help them do a particular line of work without showing any deep evidence of knowing what they were doing. The discussion here flows over a number of mixed note taking domains with no clear thrust for what they were using it pointedly for. The multiple directions and lack of experience likely doomed them to failure here.
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
I ought to spend some more time learning some of these keyboard shortcuts.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windows_key
https://www.wired.com/story/quick-select-keyboard-shortcuts-no-mouse/
-
-
every.to every.to
-
Based on that lived, visceral experience, I’ve tried to pay more attention to the feeling of momentum when I get it, and really lean into it.
Not everyone has a job where they can drop what they're doing and go work on something more interesting. But being able to switch gears to lean into creative momentum can help to increase and encourage productivity with respect to creative work and endeavors. This switching can be dramatically facilitated by having a wealth of alternate interesting options to delve into.
-
I've observed for myself that not all weeks of writing are made equal. When I do try to impose a schedule on myself – like resolving that ‘I'll write for three hours every day and hit 1200 words’ – it can work out OK, but it’s usually not that great.But I have learned that when I’m really on a roll – when I’ve found a voice that’s really working and that I’m excited about – I need to just clear the decks and go with it. I will empty my schedule, dive in, and stay up late in order to be as productive as I can. I would say this is how I got both of my novels written.
Robin Sloan's writing process sounds similar to that of Niklas Luhmann where he chose to work on things that seemed exciting and fun. This is, in part, helped by having a large quantity of interesting notes to work off of. They both used them as stores to fire their internal motivation to get work done.
-
- Jan 2022
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
just speaking instead of having to type with my with my fingers is that i can 00:02:11 kind of think out loud a little bit more and get more information and i sometimes find i generate more insights being able to speak versus uh type things so i find that really useful
Voiceliner advantage for Obsidian and Logseq
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
scattered-thoughts.net scattered-thoughts.net
-
Exposing myself to addictive interactions trained me to self-interrupt - whenever I encountered a difficult decision or a tricky bug I would find myself switching to something easier and more immediately rewarding. Making progress on hard problems is only possible if I don't allow those habits to be reinforced.
Highlighting this, but really the whole section is almost perfectly written. Hardest is achieving your desired inner discipline and then having to fight with people who don't understand this shit (because their performance never matters, or they don't give a damn).
-
-
www.theatlantic.com www.theatlantic.com
-
Organizations as varied as Y Combinator, MIT’s Radiation Lab, and ARPA have astonishing track records in catalyzing progress far beyond their confines.
Are they really the ones pushing the progress and innovating, or are they benefiting from filtering out only the highest level potential producers and simply supporting them?
Would we get more overall benefit from raising the level of the ocean so that all boats rise instead of a select few?
Another example, how was Hungary able to produce so many Nobel Prize winners?
-
In a recent paper, Pierre Azoulay and co-authors concluded that Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s long-term grants to high-potential scientists made those scientists 96 percent more likely to produce breakthrough work. If this finding is borne out, it suggests that present funding mechanisms are likely to be far from optimal, in part because they do not focus enough on research autonomy and risk taking.
Risk taking and the potential return are key pieces of progress.
Most of our research funding apparatus isn't set up with a capitalistic structure. Would that be good or bad for accelerating progress?
-
Along these lines, the world would benefit from an organized effort to understand how we should identify and train brilliant young people, how the most effective small groups exchange and share ideas, which incentives should exist for all sorts of participants in innovative ecosystems (including scientists, entrepreneurs, managers, and engineers), how much different organizations differ in productivity (and the drivers of those differences), how scientists should be selected and funded, and many other related issues besides.
These are usually incredibly political questions that aren't always done logically.
See for example Malcolm Gladwell's podcast episode My Little Hundred Million.
-
-
twitter.com twitter.com
-
Productivity is a virtue only to the person you're producing for.
-Abel Undercity
-
-
github.com github.com
-
https://github.com/lynchjames/obsidian-day-planner
Looks interesting, but I'll resist trying it out.
-
-
-
https://github.com/shabegom/obsidian-reminders
This plugin also does reminders for Obsisian, but doesn't look very well supported and hasn't been updated in a while. Not sure I like the general format as much as the other version in any case.
-
-
julian.digital julian.digital
-
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'> Alexander Wang </span> in Alexander Wang on Twitter: "After discovering the idea of "A Meta-Layer for Notes" (https://t.co/EioyyptzCb), I started to try reading in this way ↓. https://t.co/lOhRyeytXZ" / Twitter (<time class='dt-published'>01/11/2022 09:15:59</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
eleanorkonik.com eleanorkonik.com
-
-
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Manfred Kuehn</span> in Taking note: "How to take notes like an 'alpha-geek'" (<time class='dt-published'>12/31/2021 21:44:32</time>)</cite></small>
-
- Dec 2021
-
austinkleon.com austinkleon.com
-
“What is your definition of success?” I hemmed and hawed a bit, until I finally said, “I suppose success is your days looking the way you want them to look.”
-
-
luhmann.surge.sh luhmann.surge.sh
-
It is impossible to think without writing; at least it is impossible in any sophisticated or networked (anschlußfähig) fashion.
The sentiment that it is impossible to think without writing is patently wrong. While it's an excellent tool, it takes an overly textual perspective and completely ignores the value of orality an memory in prehistory.
Modern culture has lost so many of our valuable cultural resources that we have completely forgotten that they even existed.
Oral cultures certainly had networked thought, Luhmann and others simply can't imagine how it may have worked. We're also blinded by the imagined size of societies in pre-agricultural contexts. The size and scope of cities and city networks makes the history of writing have an outsized appearance.
Further, we don't have solid records of these older netowrks, a major drawback of oral cultures which aren't properly maintained, but this doesn't mean that they didn not exist.
-
- Nov 2021
-
tim.blog tim.blog
-
Have an external to-do system.
Email is a chaotic task list organised by other people. When you think of it like that, it makes sense to get those tasks out of your email inbox and into another system that you control.
-
-
nesslabs.com nesslabs.com
-
Set your focus: define the problem or area you will be looking at. It can be as narrow as a specific annoyance you face in your life, and as broad as a whole industry, but you can’t just have a vague brainstorm with no predefined focus.Gather new material: give yourself—and the team if it’s a group brainstorm—time to familiarise yourself with the area of focus. This means reading articles, watching videos, etc. If it’s a group brainstorm, this step should ideally happen before the session to give time to your brain to incubate these ideas, but if not you can block a bit of time at the beginning of the session.Generate ideas: remember, quantity over quality. Use the three creative modes presented earlier. Combinational to mix old ideas together, exploratory to investigate new potential ideas within the rules of a given space, transformational to break the rules and come up with radical ideas.Test your ideas: this is where most brainstorming sessions fail to take the one extra but necessary step. Instead of selecting your ideas on the spot, you need to test them in the real world. Select the few most promising candidates, and see how your audience reacts. For a book, write a blog post. For an app, build a landing page or a quick MVP.Select and refine your ideas: use the feedback your receive to adapt or drop your ideas. If a particular problem or area keeps on coming back in the feedback… Go back to step 1.
In che modo si può strutturare una sessione di #brainstorm davvero efficace?
- Stabilire il focus: bisogna decidere il problema o l'area su sui ci si concentrerà nel generare nuove idee, la sola regola è che non sia qualcosa di vago;
- Dai il tempo per raccogliere e processare del materiale di referenza: senza questo tempo e questo materiale uno dei tipi di creatività (quello combinativo) non si potrà attivare;
- Generare idee: seguendo i tre principi ed i tre tipi di creatività si passa a generare le idee;
- Testa le tue idee: questa è una delle fasi che più vengono tralasciate, ma è anche tra le più importanti perché mette in pratica il [[first principle thinking]] e lo si fa tramite il test diretto con la realtà delle nostre idee, è quindi necessario prevedere un processo di scelta delle idee atto a metterle in pratica direttamente;
- Utilizza il feedback sull'idea per avviare nuove sessioni di #brainstorm
-
Remember the principles laid out earlier: quantity versus quality, building a creative routine, and using all three creative modes to ensure you don’t leave any ideas off the table.
Quali sono i principi fondamentali per fare un #brainstorm efficace?
- La quantità è meglio della qualità;
- Rendi l'esercizio creativo parte della tua routine;
- Utilizza le tre tipologie di creatività per aumentare il numero di idee generate;
-
Transformational creativity: this method takes things even further. Instead of exploring a space and questioning its rules, transformational creativity is about ignoring fundamental rules to come up with potentially impossible but highly creative ideas.
Quale tipo di creatività è il più innovativo?
È la creatività di trasformazione, si tratta di quella creatività che, invece di esplorare all'interno dei confini e delle regole di un'area, ignora i confini di un'area e porta ad idee probabilmente impossibili ma molto creative.
-
Exploratory creativity: in academia, exploratory creativity is defined as “the process of searching an area of conceptual space governed by certain rules.” This means that you try to generate new ideas within a given space, taking into account its specific rules
Quale è un altro tipo di creatività che possiamo sfruttare ed in che modo si collega al [[first principle thinking]] ?
Si tratta di una creatività esplorativa, è quella creatività che emerge quando esploriamo i concetti all'interno di un'area definita da specifiche regole.
Quando andiamo a contestare queste regole, a validarle allora mettiamo i confini dell'area in movimento e questo porta i concetti a mischiarsi, spostarsi.
-
Combinational creativity: we are often seeking original ideas, when in reality most creative concepts are a combination of old ideas. First, collect as many old ideas as possible. This can be done by reading science fiction or just taking notes every time you hear a commonplace idea in a conversation. Then, let these old ideas incubate for a while. Yes, there’s no second step. Let your brain do the work.
Quale è il primo tipo di creatività che possiamo sfruttare per generare nuove idee?
Questa è quella creatività che deriva dal collatio, dall'unione di idee già presenti nel mondo. Si basa sul concetto che non si può pensare a qualcosa che non sia stato già pensato. Un'idea davvero nuova allora si potrà generare solo combinando idee vecchie già presenti.
Per mettere in pratica questo tipo di creatività è essenziale collezionare ed annotare tutte le idee che incontriamo nel mondo reale (generalmente leggendo), bisogna lasciare poi queste idee, lasciarle nel nostro cervello a crescere.
Quando sarà il momento giusto, il nostro cervello le riporterà a galla dopo averle messe in collegamento con altre idee che abbiamo collezionato in passato: di solito questa cosa accade quando siamo rilassati (tipo sotto la doccia).
-
Whether your goal is to write a book, become a better illustrator, or build an app, don’t leave creativity to random bursts of inspiration. Block some time every day or every week to generate new ideas and new work. I personally use mindframing to ensure my daily creative output aligns with my bigger goals, but as long as you flex your creative muscle consistently, you will be on your way to do your best creative work.
Perché è essenziale rendere l'esercizio creativo una parte integrante della nostra routine quotidiana?
Perché rende lo sforzo creativo un abitudine, mette in esercizio il nostro muscolo creativo e ci induce ad aumentare in maniera esorbitante il fattore di quantità, rendendoci capaci di arrivare all'elemento di qualità.
-
It may sound counterintuitive, but science shows that quantity yields quality when it comes to creativity. In simpler terms, this means that the more ideas and work you produce, the more creative they will be.
Cosa dice la scienza riguardo l'assunto che la quantità sia nemica della qualità?
La scienza dice che in realtà non è così, quando si parla di lavoro creativo, la quantità è presupposto fondamentale per ottenere risultati di qualità prima o poi.
Le probabilità di ottenere un risultati di qualità aumentano mano a mano che la quantità aumenta.
Fonte: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4479710/
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
- Oct 2021
-
www.digitaloase.com www.digitaloase.com
-
Too bad there wasn't more information in the citations, even just the author & title, let alone a short summary. I wouldn't follow the link.
-
-
yishunlai.medium.com yishunlai.medium.com
-
Holiday’s is project-based, or bucket-based.
Ryan Holiday's system is a more traditional commonplace book approach with broad headings which can feel project-based or bucket-based and thus not as flexible or useful to some users.
-
-
greyzonepages.com greyzonepages.com
-
https://greyzonepages.com/2019/03/29/how-to-use-the-hobonichi-cousin-daily-layout/
I haven't been logging them all since they've been so repetitive and fluffy, but this is one of the more interesting and thorough takes I've seen for the Hobonichi Cousin Daily Layout
-
-
-
Here's a framing I like from Gary Bernhardt (not set off in a quote block since this entire section, another than this sentence, is his). People tend to fixate on a single granularity of analysis when talking about efficiency. E.g., "thinking is the most important part so don't worry about typing speed". If we step back, the response to that is "efficiency exists at every point on the continuum from year-by-year strategy all the way down to millisecond-by-millisecond keystrokes". I think it's safe to assume that gains at the larger scale will have the biggest impact. But as we go to finer granularity, it's not obvious where the ROI drops off. Some examples, moving from coarse to fine: The macro point that you started with is: programming isn't just thinking; it's thinking plus tactical activities like editing code. Editing faster means more time for thinking. But editing code costs more than just the time spent typing! Programming is highly dependent on short-term memory. Every pause to edit is a distraction where you can forget the details that you're juggling. Slower editing effectively weakens your short-term memory, which reduces effectiveness. But editing code isn't just hitting keys! It's hitting keys plus the editor commands that those keys invoke. A more efficient editor can dramatically increase effective code editing speed, even if you type at the same WPM as before. But each editor command doesn't exist in a vacuum! There are often many ways to make the same edit. A Vim beginner might type "hhhhxxxxxxxx" when "bdw" is more efficient. An advanced Vim user might use "bdw", not realizing that it's slower than "diw" despite having the same number of keystrokes. (In QWERTY keyboard layout, the former is all on the left hand, whereas the latter alternates left-right-left hands. At 140 WPM, you're typing around 14 keystrokes per second, so each finger only has 70 ms to get into position and press the key. Alternating hands leaves more time for the next finger to get into position while the previous finger is mid-keypress.) We have to choose how deep to go when thinking about this. I think that there's clear ROI in thinking about 1-3, and in letting those inform both tool choice and practice. I don't think that (4) is worth a lot of thought. It seems like we naturally find "good enough" points there. But that also makes it a nice fence post to frame the others.
-
Another common reason for working on productivity is that mastery and/or generally being good at something seems satisfying for a lot of people. That's not one that resonates with me personally, but when I've asked other people about why they work on improving their skills, that seems to be a common motivation.
-
As with this post on reasons to measure, while this post is about practical reasons to improve productivity, the main reason I'm personally motivated to work on my own productivity isn't practical. The main reason is that I enjoy the process of getting better at things, whether that's some nerdy board game, a sport I have zero talent at that will never have any practical value to me, or work. For me, a secondary reason is that, given that my lifespan is finite, I want to allocate my time to things that I value, and increasing productivity allows me to do more of that, but that's not a thought i had until I was about 20, at which point I'd already been trying to improve at most things I spent significant time on for many years.
-
A specific example of something moving from one class of item to another in my work was this project on metrics analytics. There were a number of proposals on how to solve this problem. There was broad agreement that the problem was important with no dissenters, but the proposals were all the kinds of things you'd allocate a team to work on through multiple roadmap cycles. Getting a project that expensive off the ground requires a large amount of organizational buy-in, enough that many important problems don't get solved, including this one. But it turned out, if scoped properly and executed reasonably, the project was actually something a programmer could create an MVP of in a day, which takes no organizational buy-in to get off the ground. Instead of needing to get multiple directors and a VP to agree that the problem is among the org's most important problems, you just need a person who thinks the problem is worth solving.
-
Unlike most people who discuss this topic online, I've actually looked at where my time goes and a lot of it goes to things that are canonical examples of things that you shouldn't waste time improving because people don't spend much time doing them. An example of one of these, the most commonly cited bad-thing-to-optmize example that I've seen, is typing speed (when discussing this, people usually say that typing speed doesn't matter because more time is spent thinking than typing). But, when I look at where my time goes, a lot of it is spent typing.
-
It is commonly accepted, verging on a cliche, that you have no idea where your program spends time until you actually profile it, but the corollary that you also don't know where you spend your time until you've measured it is not nearly as accepted.
-
I'm not a naturally quick programmer. Learning to program was a real struggle for me and I was pretty slow at it for a long time (and I still am in aspects that I haven't practiced). My "one weird trick" is that I've explicitly worked on speeding up things that I do frequently and most people have not.
-
-
getpolarized.io getpolarized.io
-
aliabdaal.com aliabdaal.com
-
I spend a huge amount of time in front of a computer/laptop. I’d like to think that most of that time is reasonably productive, i.e.: I’m getting stuff done (as opposed to simply browsing Facebook/Reddit/Youtube etc). I feel it’s really important, therefore, for me to attempt to maximise the efficiency of the process. I don’t mean in the sense of “ensure that I don’t waste time on Facebook”, but more the sense of “I know what small action I want to accomplish at this moment, and I’d like for my computer to obey me as fast as possible
Obeying is the key.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
-
en.wikipedia.org en.wikipedia.org
-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Historiated_initial
I wonder if these still exist in the new spaces of productivity porn in within journaling? Perhaps the application of stickers in peoples' planners sort of serves some of this functionality, though I'd consider them to be more in the drollery family.
-
- Sep 2021
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.comYouTube1
-
This video talks about blah blah blah
-
-
forum.artofmemory.com forum.artofmemory.com
-
Some interesting finds Josh.
Related to some of the bullet journal (aka BuJo) and journaling space you will eventually come across the idea of "morning pages" which is a technique where you spend a block of time (usually in the morning, but ideally just before you want to do your creative thinking work) where you write for a set amount of time or number of pages. The goal of this method (and to some extent bullet journaling) is to clear the cruft and extraneous details out of your head to be able to better prioritize and focus on your creative work. There's a relatively large group of people doing this as a technique, so even knowing the phrase can help one to find the literature.
Tangentially related to this and memory (via our old friend rhetoric), I've been doing some significant research into the commonplace book tradition and general note taking with an eye towards knowledge acquisition, creation, and spaced repetition systems. This has led into research into the areas of the zettelkasten, digital note taking, digital gardens and the like. All fascinating areas which overlap memory via rhetoric. I suspect that many mnemonists in the Renaissance used commonplace books as physical written memory palaces, though I've yet to find anything in my research that directly links them other than the relationship they have in the long tradition of rhetoric in Western culture. Since you mention music and writing lyrics, I recently noted that Eminem has a commonplace technique which he calls "stacking ammo" by which he compiles ideas for his lyrics. His method is certainly less structured than a traditional commonplace book, but the overall form traces back to our friends Aristotle, Cicero, and Quintilian.
If you delve into some of the Bullet Journal and journaling literature you'll find a subculture of people (YouTube has hundreds of people with entire channels dedicated to the topic) who write into their daily/weekly planners and decorate them with stickers, washi tape, photos, calligraphy, drawings, etc. I've called some of this "productivity porn" before, but if you search commonplace book on Instagram or Pinterest you'll find examples of people whose journals and notes are becoming physical memory palaces where the visuals are likely helping them remember portions of their lives or what they're writing. The stickers and images to some extent are serving the purpose of drolleries seen in Medieval manuscripts as mnemonic devices.
And finally, tangentially related to all of this is another interesting sub-genre of memory and note taking called sketchnotes which combines active listening, writing, and drawing into a mnemonic related note taking activity. I'm actually a bit surprised to find so little on the technique here on the forum. Searching for sketchnotes on social media will provide lots of examples and there are many "What are sketchnotes" short videos on YouTube that will give you an idea of what's going on. Many of these talk about a memory component, but not being mired into the sub-topic of rhetoric, they're usually not using the same framings we would (here on the forum), though the effects one might expect are the same.
Some related richer resources for these areas, to help people from going down the rabbit hole within the performative social media spaces:
- How to Take Smart Notes: One Simple Technique to Boost Writing, Learning and Thinking–for Students, Academics and Nonfiction Book Writers by Sönke Ahrens
- This touches on note taking within a zettelkasten framing, but is also applicable to the commonplace book tradition
- Sketchnote Handbook, The: the illustrated guide to visual note taking by Mike Rohde
- This is one of the bibles in the space and gives a solid overview of what, why, how, etc.
- A Brief History & Ethos of the Digital Garden by Maggie Appleton
- How to Take Smart Notes: One Simple Technique to Boost Writing, Learning and Thinking–for Students, Academics and Nonfiction Book Writers by Sönke Ahrens
-
-
www.youtube.com www.youtube.com
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oX-rpV5PPQ4
Reasons people quit:
- Time 29.9%
- Overwhelm 28.7%
- Performance 14.9%
- Perfectionism 13.8%
- Comparison 12.6%
Most of the reasons relate to social media and pressure of perfectionism related to it. Definitely fits into my productivity porn thesis.
These are all things for people in the digital garden space to watch out for in the future. Presenting one's learning in public can eventually evolve into something negative if not done for the correct reasons. Bullet Journal's rise to popularity in coordination with the rise of social media can be a means for forcing people to quit it all.
-
-
sakai.duke.edu sakai.duke.edu
-
mill dam, attending a Baptist association and a public hanging.56 This general irregularity must be placed within the irregular cycle of the working week (and indeed of the working year) which provoked so much lament from moralists and mercantilists in the seventeenth and eighteenth centu
The irregularity of the work day of the common people in the 17th and 18th centuries ran counter to the desires of both moralists and mercantilists.
What might this tension tell us about both power structures both then and today?
While specialization since that time has increased the value of goods we produce, does it help in the value of our lives and happiness?
-
-
punctumbooks.com punctumbooks.com
-
<small><cite class='h-cite via'>ᔥ <span class='p-author h-card'>Suzanne Conklin Akbari</span> in Growing a Research Network: Approaches to Global Book History | Penn Libraries (<time class='dt-published'>09/12/2021 21:11:23</time>)</cite></small>
-
-
finiteeyes.net finiteeyes.net
-
Build pathways between communal and private work. Too often, we celebrate one or the other, but thinking actually works best when it has the opporunity to be done both in private and alongside other people. Proximity and ease of movement between the two modes matters. If a person can work on ideas alone and privately for a little while, then easily bring those ideas to a group, then move back to the private space, and continue this cycle as necessary, the thinking will be better.
This is a model that is tacitly being used by the IndieWeb in slowly developing better social media and communication on the web.
-
-
theconversation.com theconversation.com
-
But despite this understanding, and the gains made more generally in promoting workplace diversity, prejudices keep the employment prospects for neurodiverse individuals shockingly low. The cost is personal — denying individuals the chance to do meaningful work — as well as social, sending individuals to the dole queue. It also means workplaces are failing to benefit from highly valuable employees, and missing the opportunity to become better organisations in the process.
I posted this article in the class Slack for a couple of reasons. First, this particular argument reminds me of Benjamin, which we're currently reading, and how she shows that the problem of underexposure wasn't taken seriously until it interfered with capital. But, second, I also used it to point out that despite that, it's important to remember that we sometimes have to make arguments for specific audiences--i.e., that it isn't necessarily that Daley only cares about workplace productivity, or even that she prioritizes it, but that she's writing for an audience that does prioritize workplace productivity over basic humanity. So, the rhetorical situation may call for making such an argument rather than appealing to humanity, morality, or equity.
-
-
nesslabs.com nesslabs.com
-
https://nesslabs.com/eisenhower-matrix
The Eisnehower matrix is a means of helping one to implement the Pareto principle.
Seen this basic idea so many times before and have it generally implemented in the bullet journal portion of my digital commonplace book. I should spend more time gardening in there regularly though.
-
-
nesslabs.com nesslabs.com
-
https://nesslabs.com/plus-minus-next
The big benefit of this is that it tacitly gets you focused on planning the next thing instead of dwelling on the past.
-
draw three columns. At the top of each column, write “+” for what worked, “–” for what didn’t go so well, and “→” for what you plan to do next.
The basic prescription of plus, minus, next journaling.
Tags
Annotators
URL
-
