AI is now writing much of the code at Anthropic
for - AI - status - writing most of the code at Anthropic
AI is now writing much of the code at Anthropic
for - AI - status - writing most of the code at Anthropic
morphic genetic codes
for - Michael Levin - morphic genetic code
It's 450 KB (static binary, including templates for this site, gzip compressed) It builds my ~140 page site in 300 ms (wall clock time, on an 11-year-old old laptop) It performs acceptably on a 28-year-old laptop, running NetBSD (Pentium 166 MHz) It's trivial to compile, requiring only a C compiler, GNU Make, sed, and sh
For comparison, ANPD—describing a static site generator as an LP doc that I published in response to Jared's Show HN thread for md2blog, is 126KB. It requires no compiler, because it uses the browser's JS runtime to execute (unlike md2blog, which requires you to download Deno or a binary with Deno embedded to run it).
Note also that the numbers here also differ from the ones Jared had at the time of publication, where he had originally written:
- It's ~270 KB (static binary + templates for this site, gzip compressed)
- It builds my ~140 page site in ~150 ms (wall clock time, on an 11-year-old old laptop)
- It performs acceptably on a 28-year-old laptop, running NetBSD (Pentium 166 MHz)
- It's trivial to compile, requiring only a C compiler, make, and sed
сбора, обработки, хранения и развития
Похоже на этапы CODE у Тьяго Форте и этапов GTD Дэвида Аллена.
unclear instructional materialsand complex information presentation add extraneous cognitive load.
Summary: Defines "extraneous load" as a result of "unclear presentation," supporting the argument that non-standard writing (code-meshing) unnecessarily taxes the reader. This also aligns with findings from Liu.
when essentialinformation is presented too rapidly, it can overload thelearner’s cognitive capacity, leading to cognitive overload.When this happens, the learner cannot process essentialinformation and learning outcomes effectively.
Summary: Provides the consequence of poor structure: "cognitive overload." This supports the argument that unstructured or non-standard writing risks overloading the reader, preventing them from understanding the core message.
Indirectly, this refutes the idea that "code-meshing" is necessary for more accurate communication.
connect together the 1000 pairs of junction boxes which are closest together
The input file contains 1000 boxes. If I connect together 1000 (or as few as 999) pairs following the procedure described above, I end up with one circuit connecting all boxes.
I should actually count the connection within components towards the total of 1000.
In calling the structure of the chromosome fibres a code-script
from where does he draw the idea "code-script"? Is it from the developing information theory of the time? Somewhere else?
There is definitely the idea of a code running in the sense of programming, which was likely not a common conceptualization at the time.
On p. 22 he uses the phrase "law-code" which is likely the closer meaning of code he's using and not the sense of genetic code as understood much later when DNA and the underlying protein coding sequences were unraveled.
Morse code may also be a tangential underlying meaning of his sense of "code" as something unknown but potentially revealable.
# This fails at compile time (missing required field) %User{name: "Alice"} # Error: missing required key :email
It says %User{name: "Alice"} fails at compile time with a missing required field error, but when I tested it, it works fine and just sets the other fields to nil. There doesn't seem to be any required field validation happening here.
↑ fields with defaults
This is pointing to the required fields instead of the fields with defaults
Enum.reduce(numbers, fn x, acc -> x + acc end)
The Python example uses reduce with a default value (0), but the Elixir translation uses Enum.reduce/2 without a default value. For a true equivalent, it should use Enum.reduce(numbers, 0, fn acc, x -> acc + x end) to match the Python behavior.
, do
This syntax is not explained. Why is the comma(,) needed before the do, and why don't we write end, why the colon(:) after the do.
|> System.system_time()
Logic error: Cannot pipe to System.system_time() - this function doesn't accept string input.
System.system_time() :: integer() - takes no arguments and returns an integerSystem.system_time(unit) variant takes only a time unit parameter, not piped string dataRequired for zero-argument functions data |> String.trim()
String.trim() is NOT zero-argument
String.trim/1 requires a string argumentString.trim/2 optionally takes characters to trimComment "zero-argument functions" is wrong
.title()
The Python example uses .title(), but the Elixir version uses String.capitalize() - these don't produce the same output. Should probably use .capitalize() in Python for a true equivalent. since Elixir doesn't have a title() function.
The outputs will also be different because of this.
def clean_name(raw_name) do raw_name |> String.trim() |> String.capitalize() end name = " alice johnson " result = clean_name(name) IO.puts(result) # "Alice Johnson"
The def syntax keeps appearing in examples, but I can't replicate it in the iex terminal. It seems like this only works in .ex files, but there's no explanation on how to create and run those files.
iex(67)> sentences = Enum.map(sentences, fn x -> String.split(x) end) [ ["Hello", "world"], ["Elixir", "is", "fun"], ["I", "love", "programming"], ["Code", "every", "day"] ] iex(73)> words = Enum.filter(words, fn x -> String.length(x) >= 4 end) ["Hello", "world", "Elixir", "love", "programming", "Code", "every"] iex(74)> length(words) 7
This example missed out List.flatten part
# With parentheses (also valid) length([1, 2, 3]) # Also works IO.puts("hello") # Also works String.upcase("hello") # Also works
The parentheses examples could be shown first, since that's what Python devs are already familiar with, then introduce the optional syntax.
# def is also used to create named functions def add(x, y) do x + y end
As per the above explanation, Everything returns a value in Elixir, isn't the def a statement just as in Python in the above example
case
Didn't explain what it was doing, as it seems like a new concept.
IO.puts({x, y} = {1, 2})
I got an undefined error
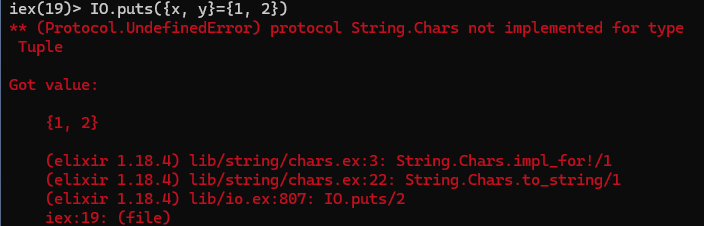
This works in Elixir (but fails in Python):
I got a CompileError when using the ^.
```elixir
iex(7)> x = 6
6
iex(8)> 6 = x
6
iex(9)> 6 = 5 + 1
6
iex(10)> a = 5
5
iex(11)> ^x = ^a + 1
error: misplaced operator ^a
The pin operator ^ is supported only inside matches or inside custom macros. Make sure you are inside a match or all necessary macros have been required └─ iex:11
** (CompileError) cannot compile code (errors have been logged) ```
a + 1 = x
I tried the example, but a + 1 = x throws a compile error. The book says this should work 'both directions like algebra', but Elixir won't let me put an expression on the left side of the match. Am I missing something, or is this example incorrect?
Briefing : Révolutionner la productivité des associations grâce au No-Code et à l'IA
Introduction
Ce briefing récapitule les points clés abordés lors du webinaire organisé par Solidatech, en partenariat avec Contournement et Nocode Forgood.
L'objectif principal de cette session était de démontrer comment les outils "no-code" et l'intelligence artificielle (IA) peuvent permettre aux associations de "gagner des dizaines d’heures par mois" et de renforcer leur impact numérique.
1. Solidatech : Renforcer l'impact numérique des associations
Composée d'une douzaine de personnes, elle opère depuis Paris et les Deux-Sèvres, où se situe sa coopérative d'insertion, les Ateliers du Bocage (mouvement Emmaüs), spécialisée dans le réemploi de matériel bureautique. Solidatech est également le satellite français du réseau international TechSoup.
Public cible :
Plus de 42 000 associations inscrites gratuitement. Divers statuts juridiques : associations (locales ou plus grandes), fondations, fonds de dotation, bibliothèques publiques. Toutes tailles d'organisations, avec ou sans employés (y compris celles composées uniquement de bénévoles).
Piliers d'accompagnement :
2. Le No-Code et l'IA : Définitions et promesses
Erwan Kezzard, cofondateur de Contournement, a introduit les concepts de no-code et d'IA générative comme des leviers majeurs pour optimiser le temps. Il souligne que "le temps... c'est une ressource extrêmement importante, notamment quand on travaille soit aux sources contraintes".
Définition du No-Code :
"Le nocode comme son anxie son son les les l'exprime et l'exige ce sont des outils qui permettent de réaliser visuellement intuitivement des projets numériques sans forcément avoir de compétences informatiques en code."
Permet de créer des sites web, des petites applications, d'automatiser des tâches, de créer des solutions internes, etc., de manière visuelle et intuitive.
Exemple : Excel n'est pas du no-code ; le no-code permet de "créer ses propres outils".
Définition de l'IA Générative :
Il s'agit des IA accessibles comme "les Chat GPT, Mistral et autres qui sont euh bah des technologies auxquelles on peut assez rapidement demander des choses demander de retraiter du contenu demander de faire des recherches et elle nous répond".
Potentiel et Bénéfices :
3. Les Trois Briques Fondamentales du No-Code Erwan Kezzard a illustré les capacités du no-code à travers trois piliers principaux, souvent combinés :
Bases de données visuelles :
Outil clé : Airtable (alternative française : TimeTonic).
Automatisation et interconnexion :
Interfaces (Sites web, applications mobiles/web) :
4. Philosophie et Positionnement de Contournement & Nocode Forgood
Contournement :
Accompagne aussi des publics éloignés de l'emploi.
Nocode France :
Nocode Forgood :
5. Exemples concrets de succès
Ils ont aussi fait appel à une experte Ania pour des projets plus complexes, mais ont aussi décidé de ne pas "nocoder" certains processus peu chronophages.
Gagne "énormément de temps". Utilise aussi Notion pour la documentation interne et les ressources textuelles.
6. Bonnes pratiques et avertissements
7. Outils de productivité IA complémentaires
Whisper Flow : Outil de dictée vocale permettant de "dicter et ne plus taper quasiment au clavier". Reconnaissance précise de la syntaxe et de la ponctuation. Dict AI : Application mobile française et souveraine pour "prendre en note les réunions automatiquement" et générer des comptes-rendus.
Conclusion
Le no-code et l'IA représentent une opportunité significative pour les associations de toutes tailles d'améliorer leur efficacité opérationnelle et de se professionnaliser.
Des organisations comme Solidatech, Contournement et Nocode Forgood jouent un rôle essentiel dans la démocratisation de ces technologies, en offrant des ressources, des formations et un accompagnement adapté, tout en soulignant l'importance de l'éthique, de la sécurité des données et d'une approche pragmatique dans leur adoption.
‘The essential point for us is that no such complete ethical code exists.
If it could what would it's mathematical structure look like? Certainly not linear.
We are not concerned here with the question whether it would be desirableto have such a complete ethical code.
The old Republican party that brought Hayek to the fore must be spinning in their graves that the current version not only doesn't have a complete ethical code, but that it seems either wholly inconsistent or altogether absent.
For our push notification system to be fast, we even had to develop a custom C-based service.
#if defined(CONFIG_ENERGY_MODEL) && defined(CONFIG_CPU_FREQ_GOV_SCHEDUTIL) /* Build perf. domains: */ for (i = 0; i < ndoms_new; i++) { for (j = 0; j < n && !sched_energy_update; j++) { if (cpumask_equal(doms_new[i], doms_cur[j]) && cpu_rq(cpumask_first(doms_cur[j]))->rd->pd) { has_eas = true; goto match3; } } /* No match - add perf. domains for a new rd */ has_eas |= build_perf_domains(doms_new[i]);
Policy that creates performance domains if EAS is enabled. This means that the groups of CPUs inside each domain is governed by schedutil + EAS. Schedutil is the only CPU governor that fits EAS.
A lot of it feels like someone who doesn’t like the old code and wants to do it “right.” I can agree that the old code is ugly. But it will take an awful lot of effort to make a new implementation. It’s a lot like what happened to Elvis: A rewrite was going to make it much better, but it took so long, during which Vim added more features, that eventually there are not so many Elvis users. And the rewritten Elvis may have nice code, but users don’t notice that.
Why not a library? We've found it extremely hard to develop a library that: Supports the many database libraries, ORMs, frameworks, runtimes, and deployment options available in the ecosystem. Provides enough flexibility for the majority of use cases. Does not add significant complexity to projects.
Lucia is now a learning resource on implementing auth from scratch.
Lucia, the authentication library that we are using, is deprecated (Q1/2025). However, the author of Lucia decided to make it a learning resource, because Lucia is just a thin wrapper around cryptographic libraries like Oslo. So we are following the migration path on their website and will also use Oslo instead of Lucia.
EditorConfig helps maintain consistent coding styles for multiple developers working on the same project across various editors and IDEs.
Prettier intentionally doesn’t support any kind of global configuration. This is to make sure that when a project is copied to another computer, Prettier’s behavior stays the same. Otherwise, Prettier wouldn’t be able to guarantee that everybody in a team gets the same consistent results.
he Web, sadly, defaults to 8 spaces which is an abomination for every snippet of code that would ike to be instantly readable on Mobile Phones too browsers don't provide a tab size setting anywhere (last time I've checked) to override that horrifying 8 spaces legacy nobody wants or need since tabs were invented
a later comment shows this is incorrect; we have CSS tab-size
I was pretty anti-tabs for the longest time, until I heard the best argument for them, accessibility. Tabs exist for indentation customization, and this is exactly what is needed for people with impaired sight. IMO, this is a pretty good argument for moving towards tabs.
The goal of Lucia v3 was to be the easiest and cleanest way to implement database-backed sessions in your projects. It didn't have to be a library. I just assumed that a library will be the answer. But I ultimately came to conclusion that my assumption was wrong. I don't see this change as me abandoning the project. In fact, I think it's a step forward. If implementing sessions wasn't easy, I wouldn't be deprecating the package. But why wouldn't a library be the answer? It seems like a such an obvious answer. One word - database. I talked about how database adapters were a significant complexity tax to the library. I think a lot of people interpreted that as maintenance burden on myself. That's not wrong, but the bigger issue is how the adapters limit the API. Adapters always felt like a black box to me as both an end user and a maintainer. It's very hard to design something clean around it and makes everything clunky and fragile, especially when you need to deal with TypeScript shenanigans.
The mainline is an active branch, with regular drops of new and modified code. Keeping it healthy is important so that when people start new work, they are starting off a stable base. If it's healthy enough, you can also release code directly from mainline into production.
Culturally engaged digital humanities— de la Michigan State University en Estados Unidos, es decir, un tipo de humanidades digitales conectadas con el trabajo comunitario, y la puesta en práctica de valores humanistas por medio de tecnologías y métodos digitales.
Another problem is that now your business logic is obfuscated inside the ORM layer. If you look at the structure of the source code of a typical Rails application, all you see are these nice MVC buckets. They may reveal the domain models of the application, but you can’t see the Use Cases of the system, what it’s actually meant to do.
Uncovering secrets of the proteome: Alternate RNA decoding & Protein asymmetry shaping cell fate
This presentation "Uncovering the secrets of the human proteome" was given in May 2024 at the 50th anniversary celebration of the Barnett Institute. It focused on progress in proteomics and two new discoveries: 1. Alternate RNA decoding results in stable and abundant proteins in mammals 2. Proteome asymmetry in mouse and human embryos before fate specification
The vastness and complexity of the human proteome have hampered its exploration. New mass spectrometry technologies are transcending those limitations and allowing for large gains in sensitivity, sequence coverage, spatial and temporal resolution. I will discuss the conceptual drivers of this progress and provide examples of how it will advance our understanding of the human proteome and enable better therapeutics.
Il veille également à la mixité sociale des publics scolarisés au sein des établissements d'enseignement
This is an example comment that can be left on the page. You can leave notes, updates, comments or requests for clarification here using Hypothesis.
think about how many of those applications were built by people that you know didn't have the capabilities to just build this massive infrastructure they just wrote some code and deployed it to you and now you have it and now you have a superpower uh this is a a remarkable uh kind of Technology
for - Internet Protocol - superpower - code it and make capability available
A "mill" is distinguished from normal typewriters by having all caps (9 point, sans serif) and having numbers "1" and "slashed 0" on the top row. Note: Portable models were typically used elsewhere than in the radio room, but still have the same key/type layout.
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_PTE_DEVMAP) && defined(CONFIG_TRANSPARENT_HUGEPAGE) static int __gup_device_huge(unsigned long pfn, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { int nr_start = *nr; struct dev_pagemap *pgmap = NULL; do { struct page *page = pfn_to_page(pfn); pgmap = get_dev_pagemap(pfn, pgmap); if (unlikely(!pgmap)) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); break; } if (!(flags & FOLL_PCI_P2PDMA) && is_pci_p2pdma_page(page)) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); break; } SetPageReferenced(page); pages[*nr] = page; if (unlikely(try_grab_page(page, flags))) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); break; } (*nr)++; pfn++; } while (addr += PAGE_SIZE, addr != end); put_dev_pagemap(pgmap); return addr == end; } static int __gup_device_huge_pmd(pmd_t orig, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long fault_pfn; int nr_start = *nr; fault_pfn = pmd_pfn(orig) + ((addr & ~PMD_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); if (!__gup_device_huge(fault_pfn, addr, end, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; if (unlikely(pmd_val(orig) != pmd_val(*pmdp))) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); return 0; } return 1; } static int __gup_device_huge_pud(pud_t orig, pud_t *pudp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long fault_pfn; int nr_start = *nr; fault_pfn = pud_pfn(orig) + ((addr & ~PUD_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); if (!__gup_device_huge(fault_pfn, addr, end, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; if (unlikely(pud_val(orig) != pud_val(*pudp))) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); return 0; } return 1; } #else static int __gup_device_huge_pmd(pmd_t orig, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { BUILD_BUG(); return 0; } static int __gup_device_huge_pud(pud_t pud, pud_t *pudp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { BUILD_BUG(); return 0; } #endif
seems like a check to see if pages can be grabbed. A quick skim maybe hints possible checks if huge pages can be grabbed?
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_HUGEPD static unsigned long hugepte_addr_end(unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned long sz) { unsigned long __boundary = (addr + sz) & ~(sz-1); return (__boundary - 1 < end - 1) ? __boundary : end; } static int gup_hugepte(pte_t *ptep, unsigned long sz, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long pte_end; struct page *page; struct folio *folio; pte_t pte; int refs; pte_end = (addr + sz) & ~(sz-1); if (pte_end < end) end = pte_end; pte = huge_ptep_get(ptep); if (!pte_access_permitted(pte, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) return 0; /* hugepages are never "special" */ VM_BUG_ON(!pfn_valid(pte_pfn(pte))); page = nth_page(pte_page(pte), (addr & (sz - 1)) >> PAGE_SHIFT); refs = record_subpages(page, addr, end, pages + *nr); folio = try_grab_folio(page, refs, flags); if (!folio) return 0; if (unlikely(pte_val(pte) != pte_val(ptep_get(ptep)))) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!pte_write(pte) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, &folio->page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } *nr += refs; folio_set_referenced(folio); return 1; } static int gup_huge_pd(hugepd_t hugepd, unsigned long addr, unsigned int pdshift, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { pte_t *ptep; unsigned long sz = 1UL << hugepd_shift(hugepd); unsigned long next; ptep = hugepte_offset(hugepd, addr, pdshift); do { next = hugepte_addr_end(addr, end, sz); if (!gup_hugepte(ptep, sz, addr, end, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } while (ptep++, addr = next, addr != end); return 1; } #else static inline int gup_huge_pd(hugepd_t hugepd, unsigned long addr, unsigned int pdshift, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { return 0; } #endif /* CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_HUGEPD */ static int gup_huge_pmd(pmd_t orig, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { struct page *page; struct folio *folio; int refs; if (!pmd_access_permitted(orig, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) return 0; if (pmd_devmap(orig)) { if (unlikely(flags & FOLL_LONGTERM)) return 0; return __gup_device_huge_pmd(orig, pmdp, addr, end, flags, pages, nr); } page = nth_page(pmd_page(orig), (addr & ~PMD_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); refs = record_subpages(page, addr, end, pages + *nr); folio = try_grab_folio(page, refs, flags); if (!folio) return 0; if (unlikely(pmd_val(orig) != pmd_val(*pmdp))) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!pmd_write(orig) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, &folio->page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } *nr += refs; folio_set_referenced(folio); return 1; } static int gup_huge_pud(pud_t orig, pud_t *pudp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { struct page *page; struct folio *folio; int refs; if (!pud_access_permitted(orig, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) return 0; if (pud_devmap(orig)) { if (unlikely(flags & FOLL_LONGTERM)) return 0; return __gup_device_huge_pud(orig, pudp, addr, end, flags, pages, nr); } page = nth_page(pud_page(orig), (addr & ~PUD_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); refs = record_subpages(page, addr, end, pages + *nr); folio = try_grab_folio(page, refs, flags); if (!folio) return 0; if (unlikely(pud_val(orig) != pud_val(*pudp))) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!pud_write(orig) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, &folio->page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } *nr += refs; folio_set_referenced(folio); return 1; } static int gup_huge_pgd(pgd_t orig, pgd_t *pgdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { int refs; struct page *page; struct folio *folio; if (!pgd_access_permitted(orig, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) return 0; BUILD_BUG_ON(pgd_devmap(orig)); page = nth_page(pgd_page(orig), (addr & ~PGDIR_MASK) >> PAGE_SHIFT); refs = record_subpages(page, addr, end, pages + *nr); folio = try_grab_folio(page, refs, flags); if (!folio) return 0; if (unlikely(pgd_val(orig) != pgd_val(*pgdp))) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!pgd_write(orig) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, &folio->page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, refs, flags); return 0; } *nr += refs; folio_set_referenced(folio); return 1; } static int gup_pmd_range(pud_t *pudp, pud_t pud, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long next; pmd_t *pmdp; pmdp = pmd_offset_lockless(pudp, pud, addr); do { pmd_t pmd = pmdp_get_lockless(pmdp); next = pmd_addr_end(addr, end); if (!pmd_present(pmd)) return 0; if (unlikely(pmd_trans_huge(pmd) || pmd_huge(pmd) || pmd_devmap(pmd))) { /* See gup_pte_range() */ if (pmd_protnone(pmd)) return 0; if (!gup_huge_pmd(pmd, pmdp, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (unlikely(is_hugepd(__hugepd(pmd_val(pmd))))) { /* * architecture have different format for hugetlbfs * pmd format and THP pmd format */ if (!gup_huge_pd(__hugepd(pmd_val(pmd)), addr, PMD_SHIFT, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (!gup_pte_range(pmd, pmdp, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } while (pmdp++, addr = next, addr != end); return 1; } static int gup_pud_range(p4d_t *p4dp, p4d_t p4d, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long next; pud_t *pudp; pudp = pud_offset_lockless(p4dp, p4d, addr); do { pud_t pud = READ_ONCE(*pudp); next = pud_addr_end(addr, end); if (unlikely(!pud_present(pud))) return 0; if (unlikely(pud_huge(pud) || pud_devmap(pud))) { if (!gup_huge_pud(pud, pudp, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (unlikely(is_hugepd(__hugepd(pud_val(pud))))) { if (!gup_huge_pd(__hugepd(pud_val(pud)), addr, PUD_SHIFT, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (!gup_pmd_range(pudp, pud, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } while (pudp++, addr = next, addr != end); return 1; } static int gup_p4d_range(pgd_t *pgdp, pgd_t pgd, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long next; p4d_t *p4dp; p4dp = p4d_offset_lockless(pgdp, pgd, addr); do { p4d_t p4d = READ_ONCE(*p4dp); next = p4d_addr_end(addr, end); if (p4d_none(p4d)) return 0; BUILD_BUG_ON(p4d_huge(p4d)); if (unlikely(is_hugepd(__hugepd(p4d_val(p4d))))) { if (!gup_huge_pd(__hugepd(p4d_val(p4d)), addr, P4D_SHIFT, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } else if (!gup_pud_range(p4dp, p4d, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return 0; } while (p4dp++, addr = next, addr != end); return 1; } static void gup_pgd_range(unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { unsigned long next; pgd_t *pgdp; pgdp = pgd_offset(current->mm, addr); do { pgd_t pgd = READ_ONCE(*pgdp); next = pgd_addr_end(addr, end); if (pgd_none(pgd)) return; if (unlikely(pgd_huge(pgd))) { if (!gup_huge_pgd(pgd, pgdp, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return; } else if (unlikely(is_hugepd(__hugepd(pgd_val(pgd))))) { if (!gup_huge_pd(__hugepd(pgd_val(pgd)), addr, PGDIR_SHIFT, next, flags, pages, nr)) return; } else if (!gup_p4d_range(pgdp, pgd, addr, next, flags, pages, nr)) return; } while (pgdp++, addr = next, addr != end); } #else static inline void gup_pgd_range(unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { }
policy use functions for gup_huge pte policy code function above (not right above, gotta scroll probably to find it)
static int internal_get_user_pages_fast(unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { unsigned long len, end; unsigned long nr_pinned; int locked = 0; int ret; if (WARN_ON_ONCE(gup_flags & ~(FOLL_WRITE | FOLL_LONGTERM | FOLL_FORCE | FOLL_PIN | FOLL_GET | FOLL_FAST_ONLY | FOLL_NOFAULT | FOLL_PCI_P2PDMA | FOLL_HONOR_NUMA_FAULT))) return -EINVAL; if (gup_flags & FOLL_PIN) mm_set_has_pinned_flag(¤t->mm->flags); if (!(gup_flags & FOLL_FAST_ONLY)) might_lock_read(¤t->mm->mmap_lock); start = untagged_addr(start) & PAGE_MASK; len = nr_pages << PAGE_SHIFT; if (check_add_overflow(start, len, &end)) return -EOVERFLOW; if (end > TASK_SIZE_MAX) return -EFAULT; if (unlikely(!access_ok((void __user *)start, len))) return -EFAULT; nr_pinned = lockless_pages_from_mm(start, end, gup_flags, pages); if (nr_pinned == nr_pages || gup_flags & FOLL_FAST_ONLY) return nr_pinned; /* Slow path: try to get the remaining pages with get_user_pages */ start += nr_pinned << PAGE_SHIFT; pages += nr_pinned; ret = __gup_longterm_locked(current->mm, start, nr_pages - nr_pinned, pages, &locked, gup_flags | FOLL_TOUCH | FOLL_UNLOCKABLE); if (ret < 0) { /* * The caller has to unpin the pages we already pinned so * returning -errno is not an option */ if (nr_pinned) return nr_pinned; return ret; } return ret + nr_pinned; } /** * get_user_pages_fast_only() - pin user pages in memory * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying pin behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * * Like get_user_pages_fast() except it's IRQ-safe in that it won't fall back to * the regular GUP. * * If the architecture does not support this function, simply return with no * pages pinned. * * Careful, careful! COW breaking can go either way, so a non-write * access can get ambiguous page results. If you call this function without * 'write' set, you'd better be sure that you're ok with that ambiguity. */ int get_user_pages_fast_only(unsigned long start, int nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { /* * Internally (within mm/gup.c), gup fast variants must set FOLL_GET, * because gup fast is always a "pin with a +1 page refcount" request. * * FOLL_FAST_ONLY is required in order to match the API description of * this routine: no fall back to regular ("slow") GUP. */ if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_GET | FOLL_FAST_ONLY)) return -EINVAL; return internal_get_user_pages_fast(start, nr_pages, gup_flags, pages); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(get_user_pages_fast_only); /** * get_user_pages_fast() - pin user pages in memory * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying pin behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * * Attempt to pin user pages in memory without taking mm->mmap_lock. * If not successful, it will fall back to taking the lock and * calling get_user_pages(). * * Returns number of pages pinned. This may be fewer than the number requested. * If nr_pages is 0 or negative, returns 0. If no pages were pinned, returns * -errno. */ int get_user_pages_fast(unsigned long start, int nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { /* * The caller may or may not have explicitly set FOLL_GET; either way is * OK. However, internally (within mm/gup.c), gup fast variants must set * FOLL_GET, because gup fast is always a "pin with a +1 page refcount" * request. */ if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_GET)) return -EINVAL; return internal_get_user_pages_fast(start, nr_pages, gup_flags, pages); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(get_user_pages_fast); /** * pin_user_pages_fast() - pin user pages in memory without taking locks * * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying pin behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * * Nearly the same as get_user_pages_fast(), except that FOLL_PIN is set. See * get_user_pages_fast() for documentation on the function arguments, because * the arguments here are identical. * * FOLL_PIN means that the pages must be released via unpin_user_page(). Please * see Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for further details. * * Note that if a zero_page is amongst the returned pages, it will not have * pins in it and unpin_user_page() will not remove pins from it. */ int pin_user_pages_fast(unsigned long start, int nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_PIN)) return -EINVAL; return internal_get_user_pages_fast(start, nr_pages, gup_flags, pages); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(pin_user_pages_fast); /** * pin_user_pages_remote() - pin pages of a remote process * * @mm: mm_struct of target mm * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying lookup behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * @locked: pointer to lock flag indicating whether lock is held and * subsequently whether VM_FAULT_RETRY functionality can be * utilised. Lock must initially be held. * * Nearly the same as get_user_pages_remote(), except that FOLL_PIN is set. See * get_user_pages_remote() for documentation on the function arguments, because * the arguments here are identical. * * FOLL_PIN means that the pages must be released via unpin_user_page(). Please * see Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for details. * * Note that if a zero_page is amongst the returned pages, it will not have * pins in it and unpin_user_page*() will not remove pins from it. */ long pin_user_pages_remote(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages, int *locked) { int local_locked = 1; if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, locked, &gup_flags, FOLL_PIN | FOLL_TOUCH | FOLL_REMOTE)) return 0; return __gup_longterm_locked(mm, start, nr_pages, pages, locked ? locked : &local_locked, gup_flags); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(pin_user_pages_remote); /** * pin_user_pages() - pin user pages in memory for use by other devices * * @start: starting user address * @nr_pages: number of pages from start to pin * @gup_flags: flags modifying lookup behaviour * @pages: array that receives pointers to the pages pinned. * Should be at least nr_pages long. * * Nearly the same as get_user_pages(), except that FOLL_TOUCH is not set, and * FOLL_PIN is set. * * FOLL_PIN means that the pages must be released via unpin_user_page(). Please * see Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for details. * * Note that if a zero_page is amongst the returned pages, it will not have * pins in it and unpin_user_page*() will not remove pins from it. */ long pin_user_pages(unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, unsigned int gup_flags, struct page **pages) { int locked = 1; if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_PIN)) return 0; return __gup_longterm_locked(current->mm, start, nr_pages, pages, &locked, gup_flags); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(pin_user_pages); /* * pin_user_pages_unlocked() is the FOLL_PIN variant of * get_user_pages_unlocked(). Behavior is the same, except that this one sets * FOLL_PIN and rejects FOLL_GET. * * Note that if a zero_page is amongst the returned pages, it will not have * pins in it and unpin_user_page*() will not remove pins from it. */ long pin_user_pages_unlocked(unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, struct page **pages, unsigned int gup_flags) { int locked = 0; if (!is_valid_gup_args(pages, NULL, &gup_flags, FOLL_PIN | FOLL_TOUCH | FOLL_UNLOCKABLE)) return 0; return __gup_longterm_locked(current->mm, start, nr_pages, pages, &locked, gup_flags); }
fast gup functions
if ((flags & FOLL_DUMP) && (vma_is_anonymous(vma) || !vma->vm_ops->fault)) return ERR_PTR(-EFAULT); return NULL;
explained in comments
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_PTE_SPECIAL /* * Fast-gup relies on pte change detection to avoid concurrent pgtable * operations. * * To pin the page, fast-gup needs to do below in order: * (1) pin the page (by prefetching pte), then (2) check pte not changed. * * For the rest of pgtable operations where pgtable updates can be racy * with fast-gup, we need to do (1) clear pte, then (2) check whether page * is pinned. * * Above will work for all pte-level operations, including THP split. * * For THP collapse, it's a bit more complicated because fast-gup may be * walking a pgtable page that is being freed (pte is still valid but pmd * can be cleared already). To avoid race in such condition, we need to * also check pmd here to make sure pmd doesn't change (corresponds to * pmdp_collapse_flush() in the THP collapse code path). */ static int gup_pte_range(pmd_t pmd, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { struct dev_pagemap *pgmap = NULL; int nr_start = *nr, ret = 0; pte_t *ptep, *ptem; ptem = ptep = pte_offset_map(&pmd, addr); if (!ptep) return 0; do { pte_t pte = ptep_get_lockless(ptep); struct page *page; struct folio *folio; /* * Always fallback to ordinary GUP on PROT_NONE-mapped pages: * pte_access_permitted() better should reject these pages * either way: otherwise, GUP-fast might succeed in * cases where ordinary GUP would fail due to VMA access * permissions. */ if (pte_protnone(pte)) goto pte_unmap; if (!pte_access_permitted(pte, flags & FOLL_WRITE)) goto pte_unmap; if (pte_devmap(pte)) { if (unlikely(flags & FOLL_LONGTERM)) goto pte_unmap; pgmap = get_dev_pagemap(pte_pfn(pte), pgmap); if (unlikely(!pgmap)) { undo_dev_pagemap(nr, nr_start, flags, pages); goto pte_unmap; } } else if (pte_special(pte)) goto pte_unmap; VM_BUG_ON(!pfn_valid(pte_pfn(pte))); page = pte_page(pte); folio = try_grab_folio(page, 1, flags); if (!folio) goto pte_unmap; if (unlikely(folio_is_secretmem(folio))) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } if (unlikely(pmd_val(pmd) != pmd_val(*pmdp)) || unlikely(pte_val(pte) != pte_val(ptep_get(ptep)))) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } if (!folio_fast_pin_allowed(folio, flags)) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } if (!pte_write(pte) && gup_must_unshare(NULL, flags, page)) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } /* * We need to make the page accessible if and only if we are * going to access its content (the FOLL_PIN case). Please * see Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for * details. */ if (flags & FOLL_PIN) { ret = arch_make_page_accessible(page); if (ret) { gup_put_folio(folio, 1, flags); goto pte_unmap; } } folio_set_referenced(folio); pages[*nr] = page; (*nr)++; } while (ptep++, addr += PAGE_SIZE, addr != end); ret = 1; pte_unmap: if (pgmap) put_dev_pagemap(pgmap); pte_unmap(ptem); return ret; } #else /* * If we can't determine whether or not a pte is special, then fail immediately * for ptes. Note, we can still pin HugeTLB and THP as these are guaranteed not * to be special. * * For a futex to be placed on a THP tail page, get_futex_key requires a * get_user_pages_fast_only implementation that can pin pages. Thus it's still * useful to have gup_huge_pmd even if we can't operate on ptes. */ static int gup_pte_range(pmd_t pmd, pmd_t *pmdp, unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, unsigned int flags, struct page **pages, int *nr) { return 0; } #endif /* CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_PTE_SPECIAL */
non concurrent fast gup approach that checks for pinned page and unmaps pte or clears it
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_FAST_GUP /* * Used in the GUP-fast path to determine whether a pin is permitted for a * specific folio. * * This call assumes the caller has pinned the folio, that the lowest page table * level still points to this folio, and that interrupts have been disabled. * * Writing to pinned file-backed dirty tracked folios is inherently problematic * (see comment describing the writable_file_mapping_allowed() function). We * therefore try to avoid the most egregious case of a long-term mapping doing * so. * * This function cannot be as thorough as that one as the VMA is not available * in the fast path, so instead we whitelist known good cases and if in doubt, * fall back to the slow path. */ static bool folio_fast_pin_allowed(struct folio *folio, unsigned int flags) { struct address_space *mapping; unsigned long mapping_flags; /* * If we aren't pinning then no problematic write can occur. A long term * pin is the most egregious case so this is the one we disallow. */ if ((flags & (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_LONGTERM | FOLL_WRITE)) != (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_LONGTERM | FOLL_WRITE)) return true; /* The folio is pinned, so we can safely access folio fields. */ if (WARN_ON_ONCE(folio_test_slab(folio))) return false; /* hugetlb mappings do not require dirty-tracking. */ if (folio_test_hugetlb(folio)) return true; /* * GUP-fast disables IRQs. When IRQS are disabled, RCU grace periods * cannot proceed, which means no actions performed under RCU can * proceed either. * * inodes and thus their mappings are freed under RCU, which means the * mapping cannot be freed beneath us and thus we can safely dereference * it. */ lockdep_assert_irqs_disabled(); /* * However, there may be operations which _alter_ the mapping, so ensure * we read it once and only once. */ mapping = READ_ONCE(folio->mapping); /* * The mapping may have been truncated, in any case we cannot determine * if this mapping is safe - fall back to slow path to determine how to * proceed. */ if (!mapping) return false; /* Anonymous folios pose no problem. */ mapping_flags = (unsigned long)mapping & PAGE_MAPPING_FLAGS; if (mapping_flags) return mapping_flags & PAGE_MAPPING_ANON; /* * At this point, we know the mapping is non-null and points to an * address_space object. The only remaining whitelisted file system is * shmem. */ return shmem_mapping(mapping); }
policy logic. avoids locks unlike get user pages unlocked/locked which seems risky so its not supposed to be used on concurrent gup logic
#ifdef CONFIG_MIGRATION /* * Returns the number of collected pages. Return value is always >= 0. */ static unsigned long collect_longterm_unpinnable_pages( struct list_head *movable_page_list, unsigned long nr_pages, struct page **pages) { unsigned long i, collected = 0; struct folio *prev_folio = NULL; bool drain_allow = true; for (i = 0; i < nr_pages; i++) { struct folio *folio = page_folio(pages[i]); if (folio == prev_folio) continue; prev_folio = folio; if (folio_is_longterm_pinnable(folio)) continue; collected++; if (folio_is_device_coherent(folio)) continue; if (folio_test_hugetlb(folio)) { isolate_hugetlb(folio, movable_page_list); continue; } if (!folio_test_lru(folio) && drain_allow) { lru_add_drain_all(); drain_allow = false; } if (!folio_isolate_lru(folio)) continue; list_add_tail(&folio->lru, movable_page_list); node_stat_mod_folio(folio, NR_ISOLATED_ANON + folio_is_file_lru(folio), folio_nr_pages(folio)); } return collected; }
#ifdef CONFIG_ELF_CORE struct page *get_dump_page(unsigned long addr) { struct page *page; int locked = 0; int ret; ret = __get_user_pages_locked(current->mm, addr, 1, &page, &locked, FOLL_FORCE | FOLL_DUMP | FOLL_GET); return (ret == 1) ? page : NULL; } #endif /* CONFIG_ELF_CORE */
part of policy use code likely
static __always_inline long __get_user_pages_locked(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long start, unsigned long nr_pages, struct page **pages, int *locked, unsigned int flags) { long ret, pages_done; bool must_unlock = false; /* * The internal caller expects GUP to manage the lock internally and the * lock must be released when this returns. */ if (!*locked) { if (mmap_read_lock_killable(mm)) return -EAGAIN; must_unlock = true; *locked = 1; } else mmap_assert_locked(mm); if (flags & FOLL_PIN) mm_set_has_pinned_flag(&mm->flags); /* * FOLL_PIN and FOLL_GET are mutually exclusive. Traditional behavior * is to set FOLL_GET if the caller wants pages[] filled in (but has * carelessly failed to specify FOLL_GET), so keep doing that, but only * for FOLL_GET, not for the newer FOLL_PIN. * * FOLL_PIN always expects pages to be non-null, but no need to assert * that here, as any failures will be obvious enough. */ if (pages && !(flags & FOLL_PIN)) flags |= FOLL_GET; pages_done = 0; for (;;) { ret = __get_user_pages(mm, start, nr_pages, flags, pages, locked); if (!(flags & FOLL_UNLOCKABLE)) { /* VM_FAULT_RETRY couldn't trigger, bypass */ pages_done = ret; break; } /* VM_FAULT_RETRY or VM_FAULT_COMPLETED cannot return errors */ if (!*locked) { BUG_ON(ret < 0); BUG_ON(ret >= nr_pages); } if (ret > 0) { nr_pages -= ret; pages_done += ret; if (!nr_pages) break; } if (*locked) { /* * VM_FAULT_RETRY didn't trigger or it was a * FOLL_NOWAIT. */ if (!pages_done) pages_done = ret; break; } /* * VM_FAULT_RETRY triggered, so seek to the faulting offset. * For the prefault case (!pages) we only update counts. */ if (likely(pages)) pages += ret; start += ret << PAGE_SHIFT; /* The lock was temporarily dropped, so we must unlock later */ must_unlock = true; retry: /* * Repeat on the address that fired VM_FAULT_RETRY * with both FAULT_FLAG_ALLOW_RETRY and * FAULT_FLAG_TRIED. Note that GUP can be interrupted * by fatal signals of even common signals, depending on * the caller's request. So we need to check it before we * start trying again otherwise it can loop forever. */ if (gup_signal_pending(flags)) { if (!pages_done) pages_done = -EINTR; break; } ret = mmap_read_lock_killable(mm); if (ret) { BUG_ON(ret > 0); if (!pages_done) pages_done = ret; break; } *locked = 1; ret = __get_user_pages(mm, start, 1, flags | FOLL_TRIED, pages, locked); if (!*locked) { /* Continue to retry until we succeeded */ BUG_ON(ret != 0); goto retry; } if (ret != 1) { BUG_ON(ret > 1); if (!pages_done) pages_done = ret; break; } nr_pages--; pages_done++; if (!nr_pages) break; if (likely(pages)) pages++; start += PAGE_SIZE; } if (must_unlock && *locked) { /* * We either temporarily dropped the lock, or the caller * requested that we both acquire and drop the lock. Either way, * we must now unlock, and notify the caller of that state. */ mmap_read_unlock(mm); *locked = 0; } return pages_done; }
same as gup but sets/unsets mmap_lock
/* user gate pages are read-only */ if (gup_flags & FOLL_WRITE) return -EFAULT; if (address > TASK_SIZE) pgd = pgd_offset_k(address); else pgd = pgd_offset_gate(mm, address); if (pgd_none(*pgd)) return -EFAULT; p4d = p4d_offset(pgd, address); if (p4d_none(*p4d)) return -EFAULT; pud = pud_offset(p4d, address); if (pud_none(*pud)) return -EFAULT; pmd = pmd_offset(pud, address); if (!pmd_present(*pmd)) return -EFAULT; pte = pte_offset_map(pmd, address); if (!pte) return -EFAULT; entry = ptep_get(pte); if (pte_none(entry)) goto unmap; *vma = get_gate_vma(mm); if (!page) goto out; *page = vm_normal_page(*vma, address, entry); if (!*page) { if ((gup_flags & FOLL_DUMP) || !is_zero_pfn(pte_pfn(entry))) goto unmap; *page = pte_page(entry); } ret = try_grab_page(*page, gup_flags); if (unlikely(ret)) goto unmap;
Most of these seem like sanity checks right up until line 897 i.e, 'if(!page)'* after which we seem to unmap the page.
static struct page *follow_page_mask(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long address, unsigned int flags, struct follow_page_context *ctx) { pgd_t *pgd; struct mm_struct *mm = vma->vm_mm; ctx->page_mask = 0; /* * Call hugetlb_follow_page_mask for hugetlb vmas as it will use * special hugetlb page table walking code. This eliminates the * need to check for hugetlb entries in the general walking code. */ if (is_vm_hugetlb_page(vma)) return hugetlb_follow_page_mask(vma, address, flags, &ctx->page_mask); pgd = pgd_offset(mm, address); if (pgd_none(*pgd) || unlikely(pgd_bad(*pgd))) return no_page_table(vma, flags); return follow_p4d_mask(vma, address, pgd, flags, ctx); }
places mask after following page into pte
if (likely(!pmd_trans_huge(pmdval))) return follow_page_pte(vma, address, pmd, flags, &ctx->pgmap); if (pmd_protnone(pmdval) && !gup_can_follow_protnone(vma, flags)) return no_page_table(vma, flags); ptl = pmd_lock(mm, pmd); if (unlikely(!pmd_present(*pmd))) { spin_unlock(ptl); return no_page_table(vma, flags); } if (unlikely(!pmd_trans_huge(*pmd))) { spin_unlock(ptl); return follow_page_pte(vma, address, pmd, flags, &ctx->pgmap); }
branch prediction to check if pmd is there and if it's big
/* FOLL_GET and FOLL_PIN are mutually exclusive. */ if (WARN_ON_ONCE((flags & (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_GET)) == (FOLL_PIN | FOLL_GET))) return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); ptep = pte_offset_map_lock(mm, pmd, address, &ptl); if (!ptep) return no_page_table(vma, flags); pte = ptep_get(ptep); if (!pte_present(pte)) goto no_page; if (pte_protnone(pte) && !gup_can_follow_protnone(vma, flags)) goto no_page; page = vm_normal_page(vma, address, pte); /* * We only care about anon pages in can_follow_write_pte() and don't * have to worry about pte_devmap() because they are never anon. */ if ((flags & FOLL_WRITE) && !can_follow_write_pte(pte, page, vma, flags)) { page = NULL; goto out; } if (!page && pte_devmap(pte) && (flags & (FOLL_GET | FOLL_PIN))) { /* * Only return device mapping pages in the FOLL_GET or FOLL_PIN * case since they are only valid while holding the pgmap * reference. */ *pgmap = get_dev_pagemap(pte_pfn(pte), *pgmap); if (*pgmap) page = pte_page(pte); else goto no_page; } else if (unlikely(!page)) { if (flags & FOLL_DUMP) { /* Avoid special (like zero) pages in core dumps */ page = ERR_PTR(-EFAULT); goto out; } if (is_zero_pfn(pte_pfn(pte))) { page = pte_page(pte); } else { ret = follow_pfn_pte(vma, address, ptep, flags); page = ERR_PTR(ret); goto out; } } if (!pte_write(pte) && gup_must_unshare(vma, flags, page)) { page = ERR_PTR(-EMLINK); goto out; } VM_BUG_ON_PAGE((flags & FOLL_PIN) && PageAnon(page) && !PageAnonExclusive(page), page); /* try_grab_page() does nothing unless FOLL_GET or FOLL_PIN is set. */ ret = try_grab_page(page, flags); if (unlikely(ret)) { page = ERR_PTR(ret); goto out; } /* * We need to make the page accessible if and only if we are going * to access its content (the FOLL_PIN case). Please see * Documentation/core-api/pin_user_pages.rst for details. */ if (flags & FOLL_PIN) { ret = arch_make_page_accessible(page); if (ret) { unpin_user_page(page); page = ERR_PTR(ret); goto out; } } if (flags & FOLL_TOUCH) { if ((flags & FOLL_WRITE) && !pte_dirty(pte) && !PageDirty(page)) set_page_dirty(page); /* * pte_mkyoung() would be more correct here, but atomic care * is needed to avoid losing the dirty bit: it is easier to use * mark_page_accessed(). */ mark_page_accessed(page); }
finds page in pte. Judging by the complexity of the logic this is most likely policy code because we're literally getting user page
struct folio *folio = page_folio(page); if (WARN_ON_ONCE(folio_ref_count(folio) <= 0)) return -ENOMEM; if (unlikely(!(flags & FOLL_PCI_P2PDMA) && is_pci_p2pdma_page(page))) return -EREMOTEIO; if (flags & FOLL_GET) folio_ref_inc(folio);
checks for code that is involved in policy but is not the actual logic
if (unlikely((flags & FOLL_LONGTERM) && !folio_is_longterm_pinnable(folio))) { if (!put_devmap_managed_page_refs(&folio->page, refs)) folio_put_refs(folio, refs); return NULL;
checks for longterm folio pins.
if (WARN_ON_ONCE((flags & (FOLL_GET | FOLL_PIN)) == 0)) return NULL; if (unlikely(!(flags & FOLL_PCI_P2PDMA) && is_pci_p2pdma_page(page))) return NULL;
Time saving predictions(unlikely) and single time warning func(WARN_ON_ONCE) for flags. Not actual policy logic so low confidence.
if (unlikely(page_folio(page) != folio)) { if (!put_devmap_managed_page_refs(&folio->page, refs)) folio_put_refs(folio, refs); goto retry;
Uses prediction to check if a folio still points to the page. This is part of the function that tries to retrieve the folio to confirm that it is associated with a page.
folio = page_folio(page); if (WARN_ON_ONCE(folio_ref_count(folio) < 0)) return NULL; if (unlikely(!folio_ref_try_add(folio, refs))) return NULL;
These increment the reference count for the folio since you're returning a reference of the folio. Important function so important internal logic subsequently
freedom to study the program's “source code,” and change it, so the program does your computing as you wish
I don't expect everyone to read every single line of the code for a project they are trying to use, that isn't very reasonable. What I do see though, is that a lot developers have a mental barrier to actually opening up the source code for the project they are trying to use. They will read the documentation, run the tests, use the example code, but when they are faced with a problem that could be solved through a one or two line change in the source code, they shut down completely. The point is that you shouldn't be afraid to jump into the source code. Even if you don't fully understand the source code, in many cases you should be able to isolate your issue to a specific block. If you can reference this block ( or line numbers ) when opening up your support request, it will help the author better understand your problem.
Rails' observers were partly inspired by aspect-oriented programming -- they're about cross-cutting concerns. If you're putting business logic in observers that is tightly coupled to the models they're observing, you're doing it wrong IMO.
after_commit on: :create do OnboardingDripper.subscribe!(self) end
Résumé de la vidéo [00:00:02][^1^][1] - [00:48:41][^2^][2]:
Cette vidéo présente le framework Observable pour créer des tableaux de bord, des rapports et des applications web de manière efficace et gratuite. Elle explique comment utiliser Observable pour documenter des fonctionnalités, introduit le concept de Data loader pour rafraîchir les données, et montre comment intégrer des réalisations Observable dans un site web statique.
Points forts: + [00:00:08][^3^][3] Introduction à Observable * Présentation du framework Observable comme générateur de site statique gratuit et open source * Utilisation de Markdown et JavaScript pour la documentation * Hébergement gratuit sur des plateformes comme GitHub Pages + [00:01:36][^4^][4] Spécialisation pour les tableaux de bord * Observable est spécialisé pour les applications nécessitant un rafraîchissement régulier des données * Introduction du concept de Data loader pour une mise à jour périodique des données * Création de sites web statiques capables de rafraîchir leurs données efficacement + [00:03:00][^5^][5] Développement JavaScript avec Observable * Observable comme environnement de développement JavaScript unique avec réactivité entre déclarations * Explication de la réactivité et de la dépendance des variables dans Observable * Utilisation de Markdown, LaTeX et JavaScript pour créer des contenus interactifs + [00:10:13][^6^][6] Utilisation de bibliothèques et gestion de versions * Observable permet d'appeler des bibliothèques externes et contient un gestionnaire de versions simplifié * Partage et publication de classeurs pour la collaboration et la réutilisation * Exemples de tutoriels et de cours disponibles sur Observable + [00:24:26][^7^][7] Démarrage avec le framework * Processus de création, d'édition et de prévisualisation d'un site avec Observable * Utilisation de GitHub Actions pour le rafraîchissement automatique des données * Intégration d'animations et de visualisations dans un site web statique + [00:40:15][^8^][8] Exemples d'applications créées avec Observable * Présentation d'applications variées, telles que l'évolution des joueurs d'échecs et un tableau de bord d'hôtel * Conversion d'une application JavaScript existante en une version améliorée avec Observable
le dialogue social 00:26:44 n'occulte pas non plus les élèves les syndicats d'élèves sont plutôt des associations qui peuvent se constituer librement mais qui doivent être autorisés par le chef par le chef d'établissement et le conseil d'administration pour pouvoir exercer 00:26:57 leur activité au sein des lycées j'en revois à l'article R 511-9 du code d'éducation la liberté de réunion des élèves est prévue et encadrée aux articles 00:27:11 l511-2 et r51-10 du code d'éducation ainsi que leur liberté d'expression qui est consacrée elle à l'article R 511-8 si le chef d'établissement doit 00:27:24 permettre aux associations d'élèves de jouir de leurs droits et de leur donner quelques é là encore boîte au lettres panneau d'affichage il doit surtout savoir qu'il est garant du fait que l'objet comme l'activité de 00:27:36 l'association n'est ni politique ni religieux et doit être compatible avec les principes du service public de l'enseignement le tout dans le respect du code pénal il en va de l'ordre public 00:27:48 scolaire et par conséquent d'un dialogue social apaisé
le chef d'établissement est également garant d'un dialogue social constructif avec les usagers d'une part les associations de parents d'élèves participent aux différentes instances collégiales des établissements publics 00:26:06 des établissement scolair et le code deéducation leur consacre une sous-section spéciale à l'article D 111-6 et suivant le code précise que les associations parents d'élèves doivent 00:26:18 avoir pour objet la défense des intérêts moraux et matériel commun aux parents d'élèves dans le cadre de leur mission les associations bénéficient d'un certain nombre de faité matérielle elles aussi et logistique que le chef 00:26:31 d'établissement doit permettre une boîte aux lettres des tableaux d'affichage et puis l'autorisation le cas échéant de réunion ponctuell peut-être parfois de du matériel informatique
You can use inline R code (see Section 3.1) anywhere in an Rmd document, including the YAML metadata section. This means some YAML metadata can be dynamically generated with inline R code, such as the document title
Does this apply to .qmd documents?
2019
[[code yellow]] on search revenue [[2019-02]]
Moderate people, not code.
Les conditions permettant cette inscription et cette fréquentation sont fixées par convention entre les autorités académiques et l'établissement de santé ou médico-social.
l'Etat met en place les moyens financiers et humains nécessaires à la scolarisation en milieu ordinaire des enfants, adolescents ou adultes en situation de handicap.
le plus proche de son domicile
Une information sur les risques liés au harcèlement scolaire, notamment au cyberharcèlement, est délivrée chaque année aux élèves et parents d'élèves.
prennent les mesures appropriées visant à lutter contre le harcèlement dans le cadre scolaire
Aucun élève ou étudiant ne doit subir de faits de harcèlement
Les parents d'élèves participent, par leurs représentants aux conseils d'école, aux conseils d'administration des établissements scolaires et aux conseils de classe.
Leur participation à la vie scolaire et le dialogue avec les enseignants et les autres personnels sont assurés
Les parents d'élèves sont membres de la communauté éducative.
Dans chaque école, collège ou lycée, la communauté éducative rassemble les élèves et tous ceux qui, dans l'établissement scolaire ou en relation avec lui, participent à l'accomplissement de ses missions.Elle réunit les personnels des écoles et établissements, les parents d'élèves, les collectivités territoriales, les associations éducatives complémentaires de l'enseignement public ainsi que les acteurs institutionnels, économiques et sociaux, associés au service public de l'éducation.
Dans le cadre d'une école inclusive, elle fonde sa cohésion sur la complémentarité des expertises.
L'Etat garantit le respect de la personnalité de l'enfant et de l'action éducative des familles
La formation scolaire favorise l'épanouissement de l'enfant
Tout enfant a droit à une formation scolaire qui, complétant l'action de sa famille, concourt à son éducation
L'acquisition d'une culture générale et d'une qualification reconnue est assurée à tous les jeunes, quelle que soit leur origine sociale, culturelle ou géographique.
permettre de façon générale aux élèves en difficulté, quelle qu'en soit l'origine, en particulier de santé, de bénéficier d'actions de soutien individualisé.
Il veille également à la mixité sociale des publics scolarisés au sein des établissements d'enseignement
Il veille à la scolarisation inclusive de tous les enfants, sans aucune distinction
Article L111-1Modifié par LOI n°2021-1109 du 24 août 2021 - art. 58L'éducation est la première priorité nationale. Le service public de l'éducation est conçu et organisé en fonction des élèves et des étudiants. Il contribue à l'égalité des chances et à lutter contre les inégalités sociales et territoriales en matière de réussite scolaire et éducative. Il reconnaît que tous les enfants partagent la capacité d'apprendre et de progresser. Il veille à la scolarisation inclusive de tous les enfants, sans aucune distinction. Il veille également à la mixité sociale des publics scolarisés au sein des établissements d'enseignement. Pour garantir la réussite de tous, l'école se construit avec la participation des parents, quelle que soit leur origine sociale. Elle s'enrichit et se conforte par le dialogue et la coopération entre tous les acteurs de la communauté éducative.
Elle s'enrichit et se conforte par le dialogue et la coopération entre tous les acteurs de la communauté éducative.
Article L111-1Version en vigueur depuis le 26 août 2021Modifié par LOI n°2021-1109 du 24 août 2021 - art. 58L'éducation est la première priorité nationale. Le service public de l'éducation est conçu et organisé en fonction des élèves et des étudiants. Il contribue à l'égalité des chances et à lutter contre les inégalités sociales et territoriales en matière de réussite scolaire et éducative.
masker.fit_transform
AttributeError: 'Brain_Data' object has no attribute 'fit_transform'
What makes Gawain so chivalrous
Gawain is known as being chivalrous because he was the proper hero, who morals matched his fight. Sir Gawain’s shield represented "the five virtues of chivalry, which were friendship, generosity, chastity, courtesy, and piety. These where the virtues people strove to live by and those they demanded of kings and knights."
The occurrence of a do-while instead of a while should always raise a question: why isn't the loop termination condition being tested at the beginning
Thinking about how you will observe whether things are working correctly or not ahead of time can also have a big impact on the quality of the code you write.
YES. This feel similar to the way that TDD can also improve the code that you write, but with a broader/more comprehensive outlook.
dernière question de la part de Cécile qui dit pour un scénario complexe vaut-il mieux faire une seule 01:18:16 automatisation ou décomposer en plusieurs étapes
Gérald qui demande lorsque le collaborateur s'en va comment fait-on pour récupérer les flux d'automatisation problématique qui paraît doit se présenter régulièrement 01:16:23 en amont ce sujet là et donc aujourd'hui l'idée c'est que ces outils là soient utilisés et là tout à l'heure clairement Erwan a dit à me connecter j'ai pas mon 01:16:37 outil de mot de passe clairement nous chez nos codes forgots on utilise un outil qui nous permet de sauvegarder les mots de passe pour que l'ensemble des membres y est axé pour se connecter aux outils qu'on a décidé d'utiliser pour 01:16:48 pour le fonctionnement de la plateforme et du reste et donc en gros si moi je suis absent ou pour X raisons la Saône n'est pas bloquée parce que les mots de passe sont dans ce coffre-fort qui est 01:16:59 qui est protégé et commun à quelques-uns d'entre nous
Benjamin se demande si s'il cherche des logiciels qu'ils utilisent mais qu'aucun figure sur les outils ne codes est-ce que dans 01:13:05 ce cas-là c'est possible de créer la liaison
qu'est-ce que ce serait des exemples un peu pour mettre la main à la pâte en sortant de ce webinaire
je remets la slide où il y avait des 01:08:58 exemples qui sont une dizaine d'exemples parmi des centaines possible
par exemple chez solidatech on se sert à la fois de 01:07:42 RTBF et de et de zappyer pour interconnecter justement nos posts sur les réseaux sociaux mais en fait ça permet de centraliser aussi bien Twitter que LinkedIn que 01:07:57 Twitter etc et ça nous permet de conserver un historique centralisé au même endroit sans avoir justement besoin au cas par cas d'aller voir ce qu'on a publié sur Twitter et en même temps sur Facebook etc et en fait tout en se 01:08:09 mettant en forme à calendrier on a les choses très clairement notre historique et donc on sait que bah oui on a déjà publié il y a trois mois sur Twitter tel sujet on va plutôt varier les plaisirs ou au contraire en parler sur Facebook pour pas oublier
on a une question de Gabriel qui qui est en plein dans le sujet des 01:06:08 automatisations et qui me paraissait pertinente qui demande avant d'automatiser des tâches comment savoir si les outils les applis sur lesquels on travaille sont interconnectables
démo de 20 secondes
des questions sur les tarifs de de toutes ces solutions
les outils no code c'est il y a une version gratuite puis 10 euros par 00:48:24 mois ou 20 euros par mois
Résumé de la vidéo [00:00:00][^1^][1] - [01:22:34][^2^][2]:
Cette vidéo est un webinaire organisé par Solidatech et Contournement, deux programmes de solidarité numérique qui aident les associations à renforcer leur impact grâce au numérique. Le webinaire présente les concepts et les outils du no code, c'est-à-dire la possibilité de créer des sites web, des applications, des outils internes et des automatisations sans avoir besoin de coder. Le webinaire explique les avantages du no code pour les associations, les différents types d'outils disponibles, les bonnes pratiques à adopter, et propose des démonstrations concrètes de création de projets no code.
Points clés: + [00:00:00][^3^][3] Présentation de Solidatech * Programme de solidarité numérique créé en 2008 * Facilite l'accès au numérique financièrement et accompagne aux usages * Propose des logiciels à tarif réduit, du matériel reconditionné, des ressources, des webinaires et des formations + [00:04:53][^4^][4] Présentation de Contournement * Programme de solidarité numérique créé en 2017 * Aide les associations à créer des sites, des applis et des automatisations sans coder * Propose des vidéos, des podcasts, des formations en ligne et des offres solidaires + [00:08:10][^5^][5] Introduction au no code * No code = créer des projets numériques visuellement sans écrire de code * Avantages : gain de temps, d'argent, d'autonomie, de créativité * Inconvénients : dépendance aux éditeurs, limites techniques, besoin de se former + [00:14:29][^6^][6] Panorama des outils no code * Différents types d'outils selon les besoins : site web, appli mobile, outil interne, automatisation, etc. * Différents niveaux d'accessibilité selon les compétences : débutant, confirmé, avancé * Exemples d'outils : Dorik, Webflow, Bubble, Glide, Zapier, Airtable, Notion, etc. + [00:20:10][^7^][7] Démonstration de Zapier * Zapier = outil no code qui permet d'interconnecter des outils entre eux pour automatiser des tâches * Exemple : automatiser le traitement des candidatures à une formation * Explication pas à pas de la création d'un zap (automatisation) + [00:29:00][^8^][8] Démonstration de Softr * Softr = outil no code qui permet de créer des sites web et des applis à partir de bases de données Airtable * Exemple : créer un site de recrutement pour les métiers du no code * Explication pas à pas de la création d'un site avec Softr + [00:36:38][^9^][9] Bonnes pratiques du no code * Commencer par définir son besoin et son objectif * Choisir l'outil le plus adapté à son projet * Se former et se documenter sur l'outil choisi * Tester et itérer son projet * Se faire accompagner par des experts si besoin + [00:39:34][^10^][10] Questions-Réponses * Réponses aux questions des participants sur le no code, les outils, la sécurité, le rgpd, etc. * Présentation d'un bon d'achat de 80 euros valable un mois sur les formations de Contournement * Conclusion et remerciements
partage les coulisses de contournement là vous voyez un tableau dans le ça alors on va juste faire un truc c'est imaginons que je veux veiller à chaque 00:33:09 fois qu'il y a le mot clé #noode sur Twitter ou alors qu'il y a hâte solidatech
exemple maison c'est nos codes for good
trois dispositions nécessiteraient des modifications législatives (sur l’article L.312-16 du code de l’éducation)
Résumé de la vidéo [00:00:00][^1^][1] - [01:30:42][^2^][2] :
Cette vidéo est une présentation en français sur les outils numériques pour les associations, organisée par Solidatech et animée par Erwan Khezzar, cofondateur de Contournement. Elle aborde les sujets suivants :
Points forts : + [00:00:00][^3^][3] Présentation de Solidatech * Un programme de solidarité numérique créé en 2008 * Une filiale des Ateliers du Bocage, membre du mouvement Emmaüs * Plus de 32 000 associations bénéficiaires et plus de 500 000 outils numériques distribués + [00:04:12][^4^][4] Présentation de Contournement * Une entreprise qui forme à contourner les obstacles techniques du numérique * Une approche basée sur les outils no code, qui permettent de créer des sites, des applis, des outils sans écrire de code * Un exemple de projet réalisé avec Glide : H24 Urgence, une appli qui cartographie les maisons de santé + [00:15:32][^5^][5] Panorama des outils no code * Une typologie des outils selon leur fonctionnalité : création de sites, d'applis, d'outils, d'automatisation, etc. * Une présentation de plusieurs outils avec leurs avantages et leurs limites : Webflow, Bubble, Glide, Airtable, Zapier, Notion, etc. * Une démonstration de Airtable, un outil de gestion de bases de données visuelles et collaboratives + [01:11:22][^6^][6] Questions-réponses * Des réponses aux questions des participants sur les outils no code, leur utilisation, leur coût, leur sécurité, etc. * Des conseils et des ressources pour se former et se lancer dans le no code * Une offre de réduction pour la formation initiation au no code de Contournement
without any spooky action at a distance.
Confirmed. Einstein. Physics.
A system is a composition of objects thatare abstractions, which hide data andexpose behavior*
Composition Abstraction Hide data Expose behavior
Visual Studio Code has integrated source control management (SCM) and includes Git support out-of-the-box. Many other source control providers are available through extensions on the VS Code Marketplace
This is an excellent resource for learing about Git integration with VS Code
we should break down and MR into "Blocks"
看主体代码,主流程,折叠没有用的代码,忽略注释
except StopAsyncIteration if is_async else StopIteration:
Interesting: using ternary operator in except clause
we are certainly special I mean 00:02:57 no other animal rich the moon or know how to build atom bombs so we are definitely quite different from chimpanzees and elephants and and all the rest of the animals but we are still 00:03:09 animals you know many of our most basic emotions much of our society is still run on Stone Age code
for: stone age code, similar to - Ronald Wright - computer metaphor, evolutionary psychology - examples, evolutionary paradox of modernity, evolution - last mile link, major evolutionary transition - full spectrum in modern humans, example - MET - full spectrum embedded in modern humans
comment
insights
Examples: humans embody full spectrum of METs in our evolutionary past
Modern clients are produced by a modern code generator, combined with hand-crafted functionality for some services.
The libraries in this repo are simple REST clients. These clients connect to HTTP/JSON REST endpoints and are automatically generated from service discovery documents. They support most API functionality, but their class interfaces are sometimes awkward.
Moves the modules in lib/ to app/models and lib/integrations to app/integrations.
We decide on app/lib v. lib/ once and for all
It is also worth noting that lib/tasks typically has application-specific tasks, thus not fitting into the condition for lib. Which makes me question the criteria for lib
lib/ is intended to be for non-app specific library code that just happens to live in the app for now (usually pending extraction into open source or whatever).
Stuff like a generic PhoneNumberFormatter is exactly what lib/ is intended for.
If application code lives in app, then doesn't that imply that things in lib (such as PhoneNumberFormatter) are not application code? I think that's one of the reasons why your recommendation of app/lib felt right to me -- my classes feel like they belong in app somewhere.
@tmoschou You can find the source for Apple's pkill on opensource.apple.com/source. It's together with other utilities in the collection adv_cmds. Maybe you can spot the bug.
This snippet removes some of the empty a elements to make the headings anchors instead:
javascript
([ ...document.querySelectorAll("a[name] +h1, a[name] +h2, a[name] +h3, a[name] +h4, h1 +a[name], h2 +a[name], h3 +a[name], h4 +a[name]") ]).map((x) => {
if (x instanceof HTMLHeadingElement) {
var link = x.previousElementSibling;
var heading = x;
} else {
var link = x;
var heading = x.previousElementSibling;
}
link.parentElement.removeChild(link);
heading.setAttribute("id", link.name);
})
The HTML encoding of this document contains several errors, some of which substantially affect the way it's read. This fixes one of those problems in Appendix II:
javascript
([ ...document.querySelectorAll("op") ]).reverse().forEach((op) => {
let f = document.createDocumentFragment();
f.append(document.createTextNode("<OP>"), ...op.childNodes);
op.parentElement.replaceChild(f, op);
})
The problem show be apparent on what is, at the time of this writing, line 4437:
html
<code>IF ?w THEN ?x<OP>?y ELSE ?z<OP>?y</code>
(The angle brackets around the occurrences of "OP" should be encoded as HTML entities. Because they aren't they end up getting parsed as HTML op elements (which isn't a thing) and screwing up the document tree.)
ou, pour l'élection des représentants des parents d'élèves, exclusivement par correspondance sur décision du chef d'établissement, après consultation du conseil d'administration. Les votes sont personnels et secrets.
Les pubLications des Lycéenssont-eLLes Libres ?Elles sont libres, mais contrôlées. L’article R.511-8du code de l’éducation
article L. 212-15
https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/codes/article_lc/LEGIARTI000027682709
article L. 216-1
https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/codes/article_lc/LEGIARTI000027682737
Art. D 411-1 du code del’éducation
https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/codes/article_lc/LEGIARTI000044541942
Besides that ffscreencast can act as an ffmpeg command generator. Every available option can also just show the corresponding ffmpeg command instead of executing it. Non-ffmpeg commands, such as how the camera resolution is pulled and others can also be shown instead of being executed.
Fig. 5.1 An early bulletin board system. The entire interface was just plain text, and you had to type in commands to navigate to the different threads and read or reply with messages.
This would be a killer introduction to computing I wonder if there's a demo of this anywhere
Configuring PyCharm: Open PyCharm with ‘Pytest Web Framework’ Press Ctrl+Alt+S > Project Click ‘Project Interpreter’ Select Python 3.6 Click ‘OK’ Go to write over 100500 automated tests!!!
This section provides a step-by-step guide on setting up PyCharm for automated testing using the 'Pytest Web Framework'.
So now we have a file that you need to open in JMeter UI, configure number of threads that you want to execute and you are good to go.
After converting the Postman test into a JMeter format, users can easily adjust the concurrency settings by configuring the number of threads in the JMeter UI, offering flexibility in load testing scenarios.
Let’s add a test that will validate that number of results on a page is lower then total number of results.
This code snippet in Postman ensures that the number of displayed results on a single page is always less than the total count of results, ensuring pagination is functioning correctly.
Critical Code Studies
TypeTest(x, obj.type, FALSE) ; x.type := ORB.boolType
The explicit x.type assignment here is redundant, because TypeTest will have already done it (in this case because the third argument is false).
IF sym = ORS.ident THEN ORS.CopyId(modid); ORS.Get(sym); Texts.WriteString(W, modid); Texts.Append(Oberon.Log, W.buf) ELSE ORS.Mark("identifier expected") END ;
This "IF...ELSE Mark, END" region could be reduced by replacing the three lines corresponding to those control flow keywords with a single call to Check:
Check(ORS.ident, "identifier expected");
there's really shocking data that shows red zip codes are getting red or redder and blue ones Bluer and Bluer
walking bass, ching-a-ding, oom-pah
a saxophonist may decide to double orhalve the tempo
A pianist may use stride
the code of G of of a transformer the T in in a 00:25:17 GPT is 2000 lines long it's not very complex it's actually not a very intelligent machine it's simply predicting the next word
https://kimberlyhirsh.com/uploads/2023/5976538a38.jpg
Putting a list of one's core values in the front of their notebook can be a useful reminder within their journaling or bullet journal practice.
Micro.blog Micro Camp 2023 Handout and Worksheet: Getting the Right Things Done
the Carthusian monks decided in 2019 to limit Chartreuse production to 1.6 million bottles per year, citing the environmental impacts of production, and the monks' desire to focus on solitude and prayer.[10] The combination of fixed production and increased demand has resulted in shortages of Chartreuse across the world.
In 2019, Carthusian monks went back to their values and decided to scale back their production of Chartreuse.
Replace all NaN elements in column ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, and ‘D’, with 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively.
可以对部分列进行操作,不需要对所有列都进行操作(填补缺失值)
Incitement of violence towards any individual
Believing in "government" REQUIRES hypocrisy, schizophrenia and delusion. One illustration of this is the bizarre and contradictory way in which social media platforms PRETEND to be against people advocating violence.